Root resorption is one of perhaps the most mysterious phenomena in dentistry, which occurs in people regardless of age, gender and state of oral health. No matter how well you fill the root canals or perform prosthetics, all this is meaningless if root resorption occurs. It occurs even when at first glance the patient is dentally healthy. The questions are why does it arise? and how to eliminate it? dentists have been fighting for over a century. This article discusses the types, diagnosis and treatment of root resorption.
Etiology of the disease
The most common reasons for the development of resorption are:
- Injuries to dental tissues;
- Death of pulp tissue;
- Periodontal diseases and treatment;
- Whitening teeth that have undergone endodontic treatment.
There are also a number of reasons that are less common. These include compression created by:
- ectopically erupted teeth;
- neoplasms of benign and malignant nature;
- cysts.
The pressure created by them leads to damage to the periodontal ligament and cement, which protect the tooth root from resorption.
In our clinic you can get a free dental consultation!
The main reasons for the development of pathology
Root resorption of temporary and permanent teeth most often occurs due to trauma and mechanical damage, as well as due to untreated or poorly treated periodontal diseases. Tissue resorption can begin in units with a long course of chronic inflammation of the nerve, infected or dead pulp.
Less commonly, the anomaly develops due to benign and malignant neoplasms, due to cysts. In this case, the overgrown tumors exert constant pressure on the surrounding tissues, damage the periodontal ligaments, and the process of root resorption begins.
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2021, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
8 years of experience
Arzumanov
Andranik Arkadievich
Dentist-orthodontist
Graduated from Moscow State Medical University. Internship - Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics.
Residency at Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics. Member of the Professional Society of Orthodontists of Russia since 2010.
More about the doctor...
Complications
After any operation, complications of varying severity may occur. Patients experience unpleasant symptoms: swelling of the mucous membrane, hyperemia, even increased body temperature. In some cases, persistent pain syndrome is noted. Minor bleeding from the wound (as if a small amount of blood is leaking) and hematoma are a common postoperative phenomenon during the first three days. However, if the swelling does not subside and the bleeding does not stop, you need to tell your dentist about it.
Some patients survive the postoperative period without any consequences. Some patients complain of malaise, increased body temperature and loss of strength. This is the body's individual reaction to surgery. During the first few days you may feel unwell to varying degrees of severity, but it will go away later.
Types of complications:
- numbness of part of the face due to damage to the facial nerve;
- perforation of the maxillary sinus;
- transition of the inflammatory process to the adjacent healthy molar.
Damage to the nerve makes itself felt by pain and numbness of the cheek, neck, and neighboring areas of the body. You should immediately inform your doctor about this; the pinched nerve will not go away on its own. To relieve pain, take painkillers.
Perforation of the maxillary sinus may occur during treatment of the roots of the upper teeth. This pathology requires long-term and thorough therapy.
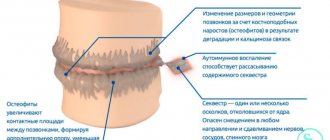
Classification of tooth root resorption
Depending on the reasons that led to the development of the disease, the following types of this pathological condition are distinguished:
| Type of resorption | Causes | Features of the course |
| Physiological | Occurs in children during the change of primary teeth to permanent ones due to the selective activity of osteoclasts. | More often it develops in healthy teeth, as well as teeth affected by caries, which has or has not been treated. X-rays can reveal the preservation of bone tissue. |
| Pathological | It develops as a complication of trauma, reimplantation, pressure from other teeth, cysts and other neoplasms, pulpal or periodontal infection. | The disease occurs against the background of chronic inflammatory processes in periodontal tissues resulting from tumors and cysts. X-rays reveal destruction and absence of bone tissue. |
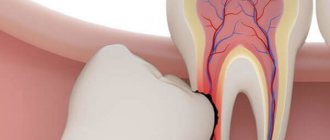
Depending on the localization of pathological processes, external and internal tooth root resorption are distinguished.
| Type of resorption | Internal root resorption | External root resorption |
| Localization | Pathology develops on the inner surface of the tooth root in the area where it borders the pulp cavity. | The disease develops on the outer surface, in the area where ligaments connect the tooth root to the jaw. |
| Causes | Inflammatory processes of the dental nerve or trauma to dental tissues. | Penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the root canal of the tooth, tooth dislocation, death of the nerve, completed process of root formation. |
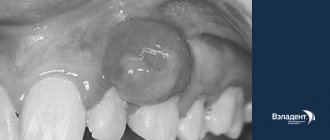
| Clinical manifestations | the presence of a “pink spot”, which appears due to the transformation of pulp tissue into granulomatous. It is visible because it shines through the tooth tissue, and after dying it changes its color to gray. As the disease progresses, the patient may experience pain, and the teeth become mobile. | It has virtually no symptoms and occurs against the background of penetration of blood vessels from surrounding tissues into the tooth root and connective tissue in different areas below the gum line. Due to pathological processes, the tooth may change color, but as a rule, the disease is detected by X-ray examination. |
| Features of the pathological process | Resorption occurs without clinical manifestations, so it is difficult to identify. As a rule, it is detected during a preventive dental examination. | It is considered the most aggressive and rapidly developing type of disease, characterized by extensive destructive processes of root tissue. |
Depending on the characteristics of the disease, three subtypes of external resorption are distinguished:
- Superficial is a physiological process, the development of which occurs as a reaction to orthodontic treatment or injury. The development of pathological processes rarely extends beyond the cement, so the defects are small in size and difficult to notice. The disease does not lead to impairment of the functionality of the affected tooth. After the trigger for its development is eliminated, the formation of new structures begins, which eliminates the need to treat root resorption;
- Inflammatory - characterized by very rapid development, since it occurs due to the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the tooth canals or the death of the tooth nerve. In the absence of adequate treatment, the pathological condition causes extensive destruction of dental root tissue, which ultimately leads to disruption of its function and loss of the enamel-cementum junction.
- Replacement - develops as a result of injuries (especially when a tooth is dislocated) or there may be a complication of inflammatory resorption, even if it was treated. The disease is chronic, requires professional dental treatment and in the vast majority of cases ends in tooth loss. It is characterized by damage to the periodontal ligament and the formation of bone in its place, which leads to tooth immobility.
A little about baby teeth
These are bone formations of the oral cavity. They are needed so that a person can eat normally, so that his diction is clear, and there are no problems when pronouncing sounds.
In their structure, temporary units are very similar to radical ones, but there are certain differences. Among them:
- smaller crown size;
- small dentin thickness (no more than one millimeter);
- absence of immune zones;
- high percentage of pulp tissues;
- low degree of mineralization;
- short channels;
- slightly pronounced tubercles along the line of contact of the upper and lower jaws.
An interesting fact is that the number of dental canals does not change throughout a person’s life. This is due to the fact that the rudiments of permanent teeth are localized exactly above the roots of the milk units.
Treatment of tooth root resorption
The treatment method for this pathological condition directly depends on its type, size of the defect, involvement of the nerve in the process and ease of access. Thus, the treatment of internal resorption, which appeared as a result of infection from the pulp, involves cleaning the dentinal tubules. If the process has spread beyond the channel, use calcium hydroxide. It is applied in the form of an intracanal inlay, which the patient must wear from six months to two years, depending on clinical indicators. The drug has an antibacterial effect and is able to eliminate the provoking factor from the main channel.
If the disease was caused by periodontal infection, the resorption cavity is opened in order to remove granulation tissue from it. After this, the dentist creates a cavity and fills it. Treatment of the nerve canal is resorted to only if there is a perforation. In this case, treatment is carried out before opening access to the resorption cavity. If access to it is difficult, obturation can be performed, which avoids surgical intervention. In this case, the patient must be observed to ensure that the treatment has given the desired result.
If resorption occurs due to compression by a neoplasm or an improperly growing tooth, the cause is eliminated. To do this, an operation is performed to eliminate the compression.
With replacement resorption, the factor that caused the disease is absent, so treatment tactics are selected individually. If the root cause was trauma, then efforts are directed toward eliminating periodontal damage. To do this, the tooth is replanted.
Diagnostics
It is not always possible to detect the presence of pathology in a timely manner due to the lack of patient complaints of discomfort in the oral cavity. As a result, the pathology develops over years until it is detected on an x-ray. This happens most often by accident and is surprising. Pathology often accompanies wearing braces. As soon as the orthodontic patient removes the braces, an X-ray or CT scan should be taken.
Sometimes it is recommended to take several pictures to get a complete picture of the problem area. Dentists recommend cone beam tomography: it provides a three-dimensional image.
The presence of external root resorption can be visually determined by a red (pink) spot on the gum next to the defective tooth. Sometimes inflammation is accompanied by a fistula. Accordingly, the diagnosis must be confirmed by an x-ray, which will show the lesion and its features.
Physiological resorption as a normal phenomenon in childhood
Physiological resorption of roots occurs in all children during the period of change in primary occlusion. On healthy units, root resorption occurs when the time for permanent eruption approaches. Resorption of teeth affected by caries (both treated and untreated) or pulpless may begin somewhat earlier than normal periods of eruption, but this situation, as a rule, is not critical, because the structure of the bone tissue is still preserved, and the process of resorption of temporary roots and formation of permanent ones is balanced.