Why did gumboil appear after dental treatment?
Swelling of the gums indicates the occurrence of an inflammatory process, which caused the complication. If painful sensations are observed against the background of the tumor, the main reasons for this may be:
- Periodontal inflammation. The tumor is observed on both cheeks, but pronounced swelling occurs only on the infected side.
- Neglected teeth, improper placement of fillings. Before swelling occurs, pain occurs. After 2-3 days, a flux with pus may form.
- Incorrect development of wisdom teeth. A hood forms from the mucous membrane, in which food particles accumulate and become inflamed.
- Removal of a tooth. Due to mechanical damage to the tissue, swelling can be considered normal.
- Cyst. The inflammatory process lasts for 1.5-2 years and injures the periosteum. The pathology occurs against a background of severe pain.
Attention! Swelling of the cheek after dental treatment can develop due to infection in the socket, which not only causes discomfort and swelling, but can also lead to more serious consequences.
If there is no pain during swelling, the reasons for this are as follows:
- allergic reaction to anesthesia, dental materials (swelling sometimes affects the entire face);
- removal of the nerve: part of the nerve may remain in the canals; after installation of the filling, flux appears;
- dissection of the gums, extracted tooth (in these cases, swelling is normal);
- infectious inflammation of the lymph in children, accompanied by aches and fever;
- neurological diseases accompanied by swelling, congestion in the ears, sore throat, weakness.
Important! In the case of severe pathologies of internal organs, the drainage of fluid is often disrupted; as a result, it accumulates in the nose, cheeks, neck, cheekbones and near the eyes.
What types of pathology are there?
Doctors distinguish two types of disease - acute and chronic. After extraction, an acute form usually occurs, accompanied by severe symptoms, sudden appearance and rapid development. The chronic type of the disease is sluggish; the patient may not be aware of its existence for six months or even several years, until the pathology worsens due to decreased immunity or other provoking factors (hypothermia, stress, physical and emotional overload).
What does flux look like?
It is of infectious origin, the process occurs against the background of inflammation of the body of the jaw or in the periosteum. Flux is formed not only after dental surgery, but also after furunculosis or tonsillitis. If the cheek and gums are swollen, there is throbbing or mild pain, in advanced stages pus may appear and the temperature may rise. On the upper jaw, the flux covers the lip, cheek, gum and nasolabial area. In addition to the face, the infection often spreads to the neck.
Anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment. After using topical medications, you should not eat or drink liquids for 2 hours.
Swelling on the inside of the cheek
Anesthesia makes tooth extraction easier. But, if after treatment of a tooth your cheek is swollen, you should find out the origin of the pathology. You may need treatment for your gums. Discomfort appears in many patients after depulpation. Pain and swelling on the inside of the cheek can be observed from 2 hours to 7 days. If discomfort intensifies or occurs 2 days after surgery, you should immediately consult a dentist.
If, after removing the nerve, in addition to painful sensations, the gums become inflamed, purulent discharge appears, and the temperature rises, you should visit a dentist. He will find out why the cheek is swollen and how to remove the gumboil.
Attention! You cannot take painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs before consulting a doctor; this will complicate the diagnosis, which will not allow you to prescribe adequate treatment.
What to do if swelling appears after treatment at the dentist
If after tooth extraction your cheek is swollen from the tooth, there is no need to worry - this is a normal reaction. You can take a pain reliever that your dentist recommends. When a pathological condition is accompanied by pain and weakness, the temperature should be measured.
Edema does not always indicate a complication; it is worth distinguishing a simple reaction of the body from a pathological condition. Don't worry if:
- the flux disappears 3 days after surgery;
- the swelling is not pronounced and does not increase in size;
- no temperature or it does not exceed 37.5 degrees;
- the pain is aching, slight, gradually goes away, eliminated with analgesics;
- in the hole there is a bloody dense clot, which is covered with fibrous tissue within 2-3 days.
On a note! Do not apply hot lotions to the injured area, release pus yourself, or massage the gums. This will provoke further development of the infection, which will lead to serious consequences.
The following symptoms indicate complications:
- the flux grows;
- there is severe pain that cannot be relieved with analgesics;
- tension together with surgery;
- temperature over 37.5-37.6 degrees;
- it hurts to swallow, speak, open your mouth;
- there is no blood clot in the hole or it is covered with a green, gray or yellow coating;
- unpleasant odor from the mouth;
- itching, hyperemia, shortness of breath - indicate an allergic reaction.
Attention! If you have any of the symptoms, you should consult your doctor. Such signs indicate infection. If an operation was performed, the treatment is carried out by a dental surgeon or an endodontist if the root canals were cleaned.
Clinical picture of osteomyelitis of the tooth socket
The clinical picture of osteomyelitis of the tooth socket is characterized by complaints of acute throbbing pain both in the area of the socket and in the area of neighboring teeth. General symptoms such as weakness, hyperthermia, headache, chills, impaired performance and sleep are also observed. Swelling of the perimandibular soft tissues develops, the submandibular lymph nodes are enlarged, dense, painful on palpation.
With osteomyelitis of the socket of only one molar of the lower jaw, the inflammatory process can spread to the area of the masseter or medial pterygoid muscle, which, in turn, can cause difficulty opening the mouth. When examining the oral cavity, the doctor may detect a dirty gray coating on the bottom and walls of the socket. You can also smell a specific smell. Percussion of adjacent teeth is painful.
The mucous membrane in the area of the transitional fold is hyperemic and swollen. Palpation of the alveolar process from the buccal and oral sides is sharply painful both in the area of the socket and adjacent teeth.
The acute phase of inflammation lasts about 6–8 days, sometimes 10 days. Then the inflammatory phenomena decrease, the process becomes chronic. The general condition improves, body temperature decreases. Swelling and hyperemia of the mucous membranes also decrease, and then pain on palpation of the alveolar process, swelling of facial tissues and submandibular lymphadenitis disappear. After 12–15 days, the tooth socket is filled with loose, pathological granulation tissue, sometimes bulges out of the socket, and pus can be released when pressure is applied.
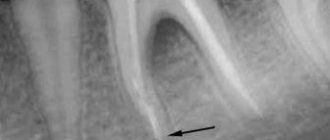
On the x-ray we see fuzzy blurred contours of the compact lamina of the alveoli; osteoporosis and bone destruction in the alveolar region are pronounced. In rare cases, after 20–25 days from the beginning of the acute period, it is possible to identify small sequesters.
Causes of limited osteomyelitis of the socket
1. as a complication of alveolitis. 2. as a result of decreased immunity
When does swelling of the cheek go away?
How long the swelling lasts after tooth treatment depends on the degree of damage. Swelling causes injury to tissues, ligaments, and blood vessels during surgery or root removal. After such an intervention, swelling is normal. It can last from 2 hours and last for 7 days or the first day after surgery. There are no painful sensations.
Swelling after surgery on a wisdom tooth can last 4 days longer and persists for 11 days. If the surgery was serious, a bruise may form on the cheek. Pronounced swelling, increasing every day, pain is a reason to urgently consult a dentist.
What is prohibited: actions that lead to worsening symptoms
- warming up the inflamed area: you should also not wrap your cheek with a scarf or warm bandage, rinse your mouth with hot decoctions and solutions,
- self-medication, especially with the help of folk recipes,
- taking blood thinning pills (Aspirin),
- hypothermia or overheating of the body, physical activity,
- drinking alcoholic beverages, smoking, drinking too much strong coffee: this leads to increased blood pressure, increased blood supply to inflamed tissues and the likelihood of bleeding,
- You should not sleep on the side where the swelling is located.
How to treat gumboil on the cheek
Once a tumor develops, antibiotics are often indispensable. The dentist selects them taking into account the stage of the pathology and the characteristics of the body. Antibiotic therapy should be completed to the end, otherwise further treatment will be greatly complicated.
If surgery is required, all activities are carried out in a dental clinic. For any complication, the patient is given local or general anesthesia. The gum is incised and the accumulated pus is completely pumped out. A drainage is placed to quickly remove fluid. The patient is prescribed antibiotics to allow the soft tissues to recover faster. In case of severe damage, the gum is sutured. In the absence of complications, this is not required.
How to remove swelling from the gums through surgery:
- In case of complicated flux, urgent hospitalization in a dental clinic and an operation performed by a dental surgeon are necessary.
- If an inflammatory process is diagnosed due to dental problems, endodontic therapy (cleaning and filling the canals) or root removal will be required.
- Broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed to treat infection in many situations. In case of serious complications, combination drugs are used to treat severe swelling, selected taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogens.
- Surgical treatment - incision of the abscess (on the face and oral cavity - the incision is made in both areas), removal of purulent discharge, treatment with disinfectants, installation of drainage. In severe cases, general anesthesia is used.
- Additional therapy - analgesics to eliminate discomfort, antipyretic drugs, large amounts of fluid (if necessary, fluid is introduced into the body by infusion during hospitalization).
Chronic pathology often occurs without pronounced symptoms, pus appears gradually. In this situation, the dentist uses a therapeutic approach, both surgical and conservative. Surgery can be replaced with herbs or antibiotics, or used as an additional treatment after consultation with a specialist.
Swelling of the cheek does not always indicate the presence of a serious pathology.
A tumor after depulpation is normal and does not require serious treatment. When the gumboil gradually grows, pain is observed against this background, and the help of a dentist is required. In case of serious complications, surgical intervention while taking antibiotics is indicated. The doctor's consultation