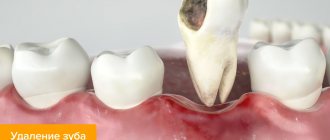
The inflammatory process in the subgingival and subperiosteal jaw area with purulent formation (abscess) is called gumboil or periostitis. Its main cause is inflammation of the tooth root. A visual sign of the disease is a swollen cheek (a “bump” forms in the problem area).
Most of us prefer to treat flux on the gums at home, but periostitis is a fairly serious disease, the absence or untimely treatment of which poses a threat to the health of the entire body. In the article we will talk about the symptoms, causes of periostitis, and how to cure gumboil.
Content:
- Why does it occur
- Signs
- How it proceeds
- Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
- What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
- How to remove flux
- How to speed up recovery
- Preventive actions
An inflammatory dental disease that affects the periosteum tissue is called periostitis by dentists.
It is popularly known as flux. It is easy to recognize on your own - a painful abscess forms on the gum, which does not go away for a long time. It is unwise to fight this disease without medical help. When it appears, you should definitely make an appointment at a dental clinic and, during an in-person examination, find out from the doctor how to remove the flux without negative consequences for health.
It is simply impossible to ignore periostitis. It is usually accompanied by acute throbbing pain. Sometimes it can even lead to fever and a sharp decrease in performance. When there is a lot of pus in the “bag”, it bursts. Then the purulent masses flow out, and the symptoms cease to be so bright.
Flux - treatment in a dental clinic
The choice of treatment method for flux depends on the type of periostitis, its severity, and the individual characteristics of the body. In the acute form, the nerve is removed, the wound is opened and cleaned, treated with antiseptics, and antibiotics are prescribed.
To defeat purulent flux in an adult, they resort to a more comprehensive treatment program. In this case, additional procedures may be prescribed, as well as complex antibiotic therapy.
Regardless of the type of periostitis (excluding the chronic form of flux), a mandatory step is a course of antibiotics, which is selected individually. As a rule, with the right course of treatment, the flux goes away within 7-10 days (stable positive dynamics of recovery are recorded on days 3-5). In the chronic course of the disease, the tooth after gumboil is usually removed.
Let us remind you once again that by refusing professional help, you risk your health. Without the participation of a doctor, there is a high probability of the formation of a gingival fistula, the penetration of pus into nearby tissues, which causes the development of phlegmon.
Why does it occur
In order to understand how to remove flux, it is necessary to establish what led to its appearance. If the provoking factor is not eliminated, the disease may return. Among the main reasons for the violation:
- untreated deep caries;
- a large amount of hard plaque extending far under the gum;
- dental root cyst;
- inflammatory lesion of the gingival pocket;
- receiving mechanical injuries;
- general hypothermia of the body (especially against the background of reduced immunity);
- poor oral hygiene.
According to statistics, most often the disease occurs precisely because of advanced caries and pulpitis. If there is a large “hole,” the infection easily penetrates deep into the dental tissues, affects the surrounding structures and causes nerve destruction. Then pulpitis develops.
If left untreated, it will become chronic. The pain will become mild, but this does not mean that the disease has gone away. It’s just that now it’s happening secretly. The infection will continue to destroy the internal structures of the diseased unit. As they die, narcotic masses will begin to be released. To remove them, an abscess forms on the gum. This is flux.
If it is localized on the periosteum of the upper jaw, then the upper lip and the area under the eye swell. If inflammation progresses in the lower jaw, the chin and cheek swell, and the lymph nodes become painful.
Compresses and lotions for periostitis
Compresses and lotions have a local anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect, they destroy pathogenic microbes and will help get rid of swelling on the mucous membrane. You can use the drug Dimexide, which is diluted with water until a concentration of 20-30% is reached. The compress is applied to the area of inflammation and left for about an hour.
Soda lotions also help a lot. Baking soda is diluted in a volume of two teaspoons in 200 ml of water. You can moisten a cotton pad or several layers of gauze with the solution and then apply the lotion to the affected area of the gum.
Good therapeutic effectiveness is also observed when using salt compresses. It is enough to dissolve a couple of teaspoons in 100 ml of warm water. A gauze swab soaked in the solution should be applied to the inflamed area and held between the gum and cheek for at least half an hour.
Signs
You can understand that periostitis has developed by the following symptoms:
- tooth pain;
- swelling of the gums;
- an abscess at the base of the diseased unit;
- increased pain when pressing on the affected area;
- swelling of the cheek;
- increased body temperature;
- swelling of the lymph nodes.
If these symptoms occur, you should make an appointment with the dentist as soon as possible. In the early stages, the problem can be eliminated quite easily and quickly. Delay is fraught with health-threatening complications.
Therapy and rehabilitation
Treatment of the disease is carried out by two methods - conservative and surgical. The choice of method depends on the form of the disease, its severity, and the course of the disease. In the early stages of development of the pathological process, conservative treatment is possible by prescribing a complex of drugs:
- broad spectrum antibiotics
- anti-inflammatory;
- painkillers;
- antipyretic.
IMPORTANT! Conservative treatment requires careful compliance with all doctor’s instructions until the process is completely eliminated. Otherwise, there is a risk of the disease becoming chronic.
Purulent periostitis is treated by wide opening of the purulent sac with dissection of the periosteum to the bone. At the same time, the issue of treating the tooth that caused the inflammatory process is being resolved. Most often, such a tooth is removed. After removing the pus, medications are prescribed, including antibiotics, anti-inflammatory and painkillers. Additionally, physical therapy may be prescribed: UHF, microwaves. The patient is recommended to frequently rinse the mouth with a solution of baking soda or sage tincture.
Simple periostitis requires complete rest of the injured area and treatment with physiotherapeutic procedures. All other types are reduced to treating the underlying disease or eliminating the focus of fibrous tissue growth.
IMPORTANT! Under no circumstances should you treat flux yourself. It is especially not recommended to pierce a purulent sac: there is a high risk of infection in neighboring tissues.
To speed up the treatment and recovery processes, you can resort to traditional medicine methods.
How it proceeds
The disease progresses through several successive stages:
- Acute serous. Spreads quickly. In just two or three days, a large, painful “bump” forms, with pus inside. The cheek tissues swell.
- Acute purulent. The pain becomes more pronounced, the person feels an unpleasant pulsation. The mucous membrane in the area of the affected unit turns red and swells. Body temperature rises.
- Acute diffuse. The swelling becomes voluminous. It can go under the eye or onto the nose. The patient's appearance changes significantly for the worse.
- Chronic. The painful process fades away and is replaced by a chronic one. The patient may mistakenly think that the problem has disappeared without a trace. In fact, it only calmed down for a while. Periodically, the disease will recur.
The sooner a sick person consults a doctor, the higher his chances of a speedy recovery.
Let's talk in more detail about the main types of fluxes.
Acute serous periostitis. As we wrote above, the inflammatory process occurs quickly and passes within a few days. It is characterized by severe swelling of the soft tissues. It is localized directly on the area with the diseased tooth, which is the main reason for the development of gumboil. The degree of inflammation depends on the structure of the vessels in the periosteum. The cause of the development of an acute form of serous flux can also be bruises and fractures. In this case, periostitis is called traumatic or post-traumatic. Most often it goes away on its own, but in some cases it can cause severe inflammation and the development of another type of flux - ossifying (fibrous growth).
Acute purulent periostitis. This type of gumboil is characterized by severe pain, which is often pulsating and spreads to the organs of vision and hearing, causing migraines. Pain is managed with medications and cold compresses. You should not heat the swelling site - this can lead to increased pain.
Purulent flux occurs with an increase in temperature to 37.5-38 degrees, the patient develops weakness and general malaise. It should be noted that the course of the disease depends on the location of the inflammation: in the lower jaw the process is more complicated.
The localization of inflammation depends on the location of the lesion:
- 1
Maxillary incisors - an inflammatory process on the upper lip and can spread to the nose. - 2
Maxillary canines and premolars - an inflammatory process in the periosteum.
- 3
Molars - an inflammatory process in the upper part of the cheeks.
- 4
Premolars - inflammation is localized in the lower part of the cheeks.
Chronic periostitis. The rarest form, which is usually localized in the periosteum of the lower jaw. In the chronic course of the disease, local inflammation is present, which does not change facial features. Characteristic symptoms are swelling in the mouth, enlargement of the periosteum, and lymph nodes. The development of this type of periostitis is a long process that takes from 4 to 8 months.
Features of the development of periostitis in children and adults
In adults, the disease usually has vivid symptoms. Most often it is caused by bad habits and ignoring the rules of oral hygiene. The tissues surrounding the root become inflamed. Persistent pain forces a person to seek dental care.
In children, flux usually progresses with mild symptoms. This is due to the fact that in children the immune system reacts less actively to abnormal processes in the oral cavity. Even if the purulent “bump” does not hurt the child, a consultation with a dentist is still required.
Tips and tricks
To ensure that going to the steam room is as safe as possible and does not aggravate your well-being, you should follow several rules when you have a cold:
- When visiting the steam room, you should not get your hair wet. It is advisable to wear a felt cap, which will protect your head from overheating.
- You should not immediately sit on the highest shelf upon arriving at the bathhouse - the body must be slowly prepared for the rise in temperature.
- The time spent in the steam room should be limited. After the end of the event, you need to rest in the dressing room until your body cools down.
- In between runs in the steam room, it is necessary to compensate for the supply of lost fluid. For these purposes, herbal tea with raspberries or currants is ideal.
What happens if you don't undergo therapy?
It is unacceptable to treat purulent gum lesions as a minor dental disorder. It is very insidious and rarely disappears without a trace on its own. Often, if treatment is refused, the following occurs:
- Abscess. It is a consequence of a long-term presence of a pus-filled sac in the area of the tooth root. The abscess grows and then ruptures.
- Phlegmon. Represents an extended lesion. It usually occurs after a rupture of a purulent sac, if the patient does not comply with the dentist’s instructions, does not rinse the mouth with a special antiseptic solution, or apply anti-inflammatory gels.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw. It occurs if the gums are not treated for a very long time. The pathological process spreads to the jaw bone, which is very dangerous.
- Inflammation of individual sinuses of the skull. It is also diagnosed with advanced periostitis. The maxillary, frontal and sphenoid sinuses are affected.
It is extremely rare that the disease affects brain tissue. Then the person may even die.
Treatment of periostitis with physical factors
The complex approach to the treatment of periostitis is complemented by the use of therapeutic physical factors:
- ultra-high-frequency therapy (an electromagnetic field, or UHF, acts as a therapeutic factor in inflammatory processes);
- magnetic applicators (magnetotherapeutic treatment of inflammatory processes);
- medicinal electrophoresis (using an electric current of low voltage and low strength, a medicinal substance is introduced into the body as an additional therapeutic factor);
- helium-neon laser rays (have anti-inflammatory, bactericidal, regenerative effects).
How to remove flux
To avoid purulent damage to the pulp zone and periosteum, you need to receive qualified dental care in a timely manner. In the early stages of the disease, in order to prevent further progression of the inflammatory process, the patient is prescribed anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics. It is mandatory to open the abscess. The wound is then cleaned and washed with an antiseptic.
In some cases, to prevent re-accumulation of pus, drainage is installed for several days. All surgical procedures are always performed under general anesthesia so that the patient does not experience pain.
To support the patient’s body, he is additionally prescribed a vitamin and mineral complex. If necessary, physiotherapy is included in the treatment course. Good results can be obtained using UHF and electrophoresis.
It is important to strictly follow all medical recommendations and under no circumstances interrupt antibiotic therapy. Treatment is considered successfully completed if pus is no longer released, pain does not occur, and the entire wound has healed. In some cases, after healing, a small bluish scar remains on the gum. You shouldn't worry about it. This means that the defeat was very deep. Over time, the gums will return to their normal appearance.
Flux: symptoms, causes of appearance
Characteristic symptoms of flux:
- swelling of the gums and face;
- pain in the area of the tooth that caused inflammation;
- enlargement and hardening of lymph nodes in the neck and head;
- general malaise: weakness, fever up to 38 degrees, headache.
Three stages of development of periostitis can be distinguished:
- at the first stage, pain occurs that bothers you when eating (due to contact with the site of inflammation);
- the gums swell, a “bump” appears, in which pus subsequently accumulates;
- swelling of various parts of the face (lips, cheeks, chin) occurs, the temperature may rise to 38 degrees, the pain radiates to the ear and visual organs.
The main reasons for the development of flux:
- advanced caries;
- complications after poorly performed treatment of pulpitis;
- gum injuries;
- hypothermia;
- jaw injuries;
- flux after tooth extraction;
- complications after flu or sore throat;
- inflammation of the gum pocket.
The following types of fluxes are distinguished:
- Ordinary. Pathogenic bacteria do not take part in the inflammatory process, but infiltration of the periosteum occurs.
- Fibrous. A chronic form of gumboil that develops as a result of exposure to irritants on the gum tissue. Thickening of the periosteum occurs.
- Purulent. It develops as a result of damage to the gums through which pathogenic bacteria penetrate. Often combined with purulent osteomyelitis.
- Ossifying. Develops as a result of prolonged irritating effects on the periosteum. Chronic illness.
- Serous. Periostitis with less pronounced symptoms develops quickly, but goes away within 2-3 days.
How to speed up recovery
To make healing go faster, it is important not only to follow the dentist’s instructions, but also to remember the rules:
- do not heat the area where the pus was located;
- do not take antibiotics or any other medications unless prescribed by a doctor;
- do not use any folk recipes without consulting your doctor;
- Until the wound is completely healed, do not use aspirin or any medications that contain acetylsalicylic acid.
If the “bump” appears again, it is recommended to immediately contact a dental clinic.
what to do with flux?
Treat. Not at home, when it is possible to develop additional complications. And in dentistry - from a competent specialist who will prescribe you individual treatment and save you from suffering. Don't tolerate flux formation, know what to do with it, and stay healthy.
It is important to consider one more aspect: the diagnosis of flux. You should not try to diagnose yourself. “Wise” articles, both in electronic and print media, in addition to advice on the topic:
Preventive actions
To reduce the likelihood of periostitis, you need to take care of your teeth and visit the dentist at least once a year. You can't start caries. As soon as a dark spot appears on the surface of the dental crown, it needs to be treated.
After eating, it is advisable to rinse your mouth with warm water. To make hygiene as high as possible, it makes sense to use not only a brush and toothpaste, but also dental floss and irrigators. It is very important to remove tartar every year at the dentist's office.
An important place in the issue of prevention is given to diet. You should eat as much fresh fruits, vegetables, and plant foods as possible. They require more thorough chewing and thus have a positive effect on the ligamentous apparatus that holds the tooth. They also provide natural cleansing of crowns from soft plaque.
If you have any questions about how to remove flux, please contact the doctors at the Line of Smile dental clinic for help. We specialize in the treatment of this disease and know how to quickly rid our patients of it.
Rinse with flux
Rinse solutions have a regenerating and anti-inflammatory effect on the pathological focus. You can use a soda solution, which reduces pain and inflammation. Rinsing should be done every two hours. Two teaspoons of soda are dissolved in 200 ml of warm water and used throughout the day.
Manganese solution has good therapeutic efficacy. It will reduce swelling by eliminating pathogenic microorganisms. You can use the drug Rotokan, which includes chamomile, yarrow and calendula. To prepare the solution, just add one spoon of Rotokan to warm water. You should rinse your mouth at least 4-5 times a day.
Antiseptics such as Chlorhexedine and Miramistin are also used. They do not need to be dissolved in water. It is enough to irrigate the affected cavity in order to reduce swelling, pain and inflammation. Rinse products similar in their therapeutic effects to Miramistin and Chlorhexidine also include Furacilin, which is sold in tablets. A couple of tablets are enough to prepare 200 ml of solution for treating the oral cavity.
Diagnosis of tooth flux
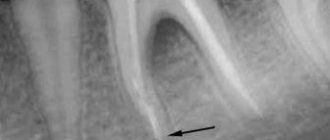
At the dentist's appointment, a thorough examination of the oral cavity and an X-ray examination - a targeted or panoramic image - is carried out. In some cases, two studies will be required to make an objective diagnosis.
As soon as the diagnosis is made - exacerbation of chronic periodontitis and the diseased tooth is identified, the doctor begins treatment.
Sage
Sage essential oils have pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effects. At the first signs of periostitis, you need to brew 60 g of sage leaves and 2 tablespoons of oak bark with boiling water, let it brew for 20-30 minutes in a warm place or in a water bath. Rinse your mouth with the prepared solution at least 8-10 times a day.
No less effective is an infusion of sage and iris roots, for the preparation of which you need to mix 50 g of each component. Pour 2 tablespoons of the mixture with boiling water and leave for half an hour to infuse. Rinse your mouth with the resulting product every hour until the pain decreases.
Tooth gumboil: what medications to take?
This is the most common question in Internet search engines when people try to deal with the problem on their own. Our answer: “Do not take anything before consulting a doctor!” Only the attending physician, taking into account the stage of the disease and your individual characteristics, can prescribe an antibiotic for tooth flux, which stops the inflammation process. The dentist will also advise which drug is best to use as an anesthetic.
Broom as a cold treatment
Most often we go to the bathhouse to steam with a broom. And this is certainly very useful. Its use increases blood circulation and promotes active sweating, and along with it, harmful toxins are removed from the body. A heated broom is used for massage, as well as for inhalations. The main thing is to take the right “model” with you, because everyone has their own healing effect.
For example, a birch broom is good for soothing muscles and joints, while a linden broom has a healing effect on the respiratory and nervous system. Made from fir and pine - plays the role of a disinfectant. And a eucalyptus broom has an excellent effect on the upper respiratory tract. This will support your body and help cleanse it, as well as increase sweating.