May 15, 2020
If the lower or upper jaw becomes numb, this may be a natural reaction of the body, for example, to medical intervention, or it may indicate various problems that require immediate medical attention. In today's article by the editors of the UltraSmile.ru portal, we propose to analyze in detail the main reasons why numbness and discomfort occurs in the lower part of the face.
There can be several reasons for jaw numbness
Inflammatory process on the root of the tooth
If you are wondering why the lower jaw is numb, then the first thing you need to pay attention to is the condition of the oral cavity. An unpleasant symptom can be caused by dental diseases such as periodontitis and a cyst on the root of the tooth. Then, in addition to discomfort, a slight tingling sensation may be observed in the jaw and chin area, as well as pain when pressing or chewing food on the causative tooth.
The photo shows a cyst
Surgical intervention
Some patients report that their upper or lower jaw goes numb after undergoing the following dental procedures:
- tooth extraction: most often, an unpleasant symptom occurs after a complex removal of third molars, accompanied by drilling of the roots, peeling of the soft gum tissue and suturing,
- vestibuloplasty,
- trimming the frenulum of the tongue,
- bone tissue augmentation surgery: sinus lift and bone grafting,
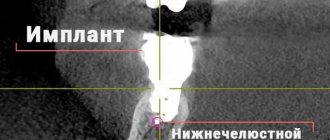
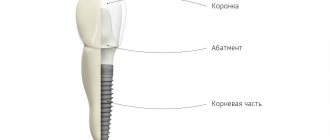
- implantation1: especially when a large number of teeth were restored at once,
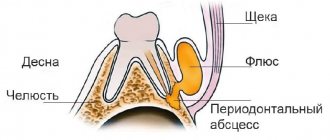
- opening and removal of cysts, granulomas, abscesses.
This condition can occur after surgery.
Why does the jaw go numb in the above cases? This may be a normal reaction of the body to nervous and physical stress, surgery, tissue injury and capillary damage. Most often, the symptom is associated with compression (squeezing) of nerve endings due to the formation of physiological edema that occurs after surgical procedures. Normally, the numbness should go away within a week after the intervention, but if it persists longer, it may indicate other problems. Read on!
When your head hurts and your face goes numb
There may be several reasons for feeling unwell. And it is not always clear which doctor to contact with a particular ailment. Our expert will help you navigate. In order to get a complete answer, in the comments to this article you need to:
- briefly outline the main symptoms;
- make the question as specific as possible;
- write a question in the comments under this article.
You will find answers to your questions in the next issue of the section “What kind of doctor do I need?”
Question: I have a terrible headache, and part of my head and face go numb. The hand goes numb, there is not enough air.
Headache is one of the most common symptoms and includes all types of pain and discomfort in the head area. There are four main types of headaches:
- vascular headache occurs as a result of a mismatch between the resistance of the vascular wall and the increase in pulse volume of blood;
- headache of muscle tension: with prolonged tension or compression of the soft tissues of the head;
- liquorodynamic is associated with tension in the membranes of blood vessels (with an increase and decrease in intracranial pressure);
- neuralgic pain occurs when pressure is applied to trigger zones.
There are also mixed headaches with a combination of the main types and psychalgia, or hypochondriacal headache, which occurs with mental disorders.
All types of headaches differ in location and connection with physical activity.
You should also differentiate between headaches and migraines. Migraine is an intense headache, usually unilateral, pulsating in nature, lasts up to 72 hours, may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, hypersensitivity to light, sounds, etc., intensifies with physical activity. Some patients may experience an aura in the form of a short-term visual disturbance preceding an attack of headache. Facial numbness may also occur both during the aura and at the peak of the headache.
The patient needs to consult a neurologist to identify the cause of the headache, determine treatment tactics and prevent possible serious consequences of the disease.
_____________________________________________________________________
Question: At night I have a cough, as if something is tickling or bothering me in my throat.
Coughing is a protective reflex. It helps clear the airways of excess mucus or foreign bodies. The moment a person coughs, air abruptly leaves the lungs, forcing out what is obstructing breathing.
Tickling and discomfort in the throat can be the body’s reaction to internal and external irritants. Here are the main reasons for the development of cough and throat discomfort:
- infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract, both acute and chronic: pharyngitis, laryngitis, tonsillitis, rhinitis, etc.;
- allergic reactions: this can be a seasonal exacerbation; allergens can also be pet hair, house dust, household chemicals, bed mites, low-quality bedding, feather or down pillows and blankets, house plants;
- industrial aerosols (dust and gas contamination of atmospheric air);
- smoking;
- endocrine diseases: dryness of the oral mucosa in diabetes mellitus, formations of the thyroid gland, which can cause pressure on the larynx;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract with reflux of gastric contents into the esophagus, worsening in a horizontal position of the body, which is accompanied by heartburn, belching, bitterness in the mouth and a sore throat;
- autonomic disorders and neuroses after prolonged stress.
To determine the cause of a night cough and discomfort in the throat, you need to consult a general practitioner who, when collecting an anamnesis and examining the patient, will be able to determine the examination tactics and refer him to the necessary specialized specialists (otolaryngologist, allergist, endocrinologist, gastroenterologist, etc.).
_____________________________________________________________________
Question: Good afternoon. Fingers often go numb - the little and ring fingers on the right hand, sometimes they even turn blue, sometimes the whole palm turns blue. This also happens on the left hand, but less often. During sleep, the hands also turn blue, but completely, from the elbow to the tips of the fingers.
Blue discoloration of the upper or lower extremities is called peripheral cyanosis. Peripheral cyanosis (acrocyanosis) is associated with insufficient blood supply to small capillaries in areas of the skin distant from the heart. This disorder occurs due to narrowing of small capillaries and slow local blood circulation.
Peripheral cyanosis may be accompanied by cold hands and feet, and a feeling of numbness in the extremities. The causes of peripheral cyanosis may be:
- neurohormonal changes associated with the menstrual cycle;
- Raynaud's syndrome (secondary manifestation of a number of causes);
- diseases of the cardiovascular system;
- diseases of the bronchopulmonary system;
- low blood pressure;
- a number of systemic diseases;
- hypothermia, etc.
The patient needs to see a general practitioner, who, after collecting an anamnesis and examination, will be able to determine the examination tactics and refer him to the necessary specialists. In this case, a visit to a cardiologist, neurologist, rheumatologist, pulmonologist, etc. may be required.
occupational therapist, head of the hospital “Clinics for the whole family 1 + 1”
answered your questions Photo depositphotos.com The author’s opinion may not coincide with the opinion of the editors
Medical errors made during dental treatment
Dental treatment, and especially procedures that require surgery, are best done by professional doctors. Then the risk of developing any complications will be minimal. If a patient turns to an insufficiently experienced specialist, then there is always the possibility that not everything will go smoothly. For example, numbness of the lower jaw and chin can occur if the dentist damaged the nerve during the administration of anesthesia through a syringe or injured it during the operation. The cause of the pathology can also be incorrect calculation of the dosage of the anesthetic.
The numbing effect also occurs after improper treatment
Read the article on the topic “TOP 30 dental clinics.” In it you will find information about the best clinics in their segment.
The problem may arise after poor-quality treatment and filling of tooth canals. For example, if the doctor moved the filling material beyond the root. Or, during the treatment of deep caries and pulpitis, he left microbes inside the canals, which subsequently provoked root inflammation and periodontitis.
Hemifacial spasm (facial hemispasm) - symptoms and treatment
The main goal of treatment for hemifacial spasm is to achieve stable remission without losing the patient’s ability to work and social activity [25].
medications are used to treat hemifacial spasm : clonazepam, levetirace, carbamazepine, baclofen, gabapentin [7]. They belong to anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants, affecting muscle tone and the ability to conduct nerve impulses. However, their effectiveness has not been reliably proven. In addition, patients are forced to take drugs for a long time in fairly high doses, which inevitably leads to side effects such as lethargy, drowsiness, lethargy, dizziness, muscle weakness, dyspeptic disorders, fluctuations in blood pressure, rhythm disturbances and cardiac conduction, and many others. which affects the quality of life.
For primary hemifacial spasm, neurosurgical intervention (microvascular decompression of the facial nerve) is possible, which has shown its effectiveness in 86-93% of cases of surgical treatment. It was developed and first performed in February 1966 by the American neurosurgeon Peter Jannetta [7]. First, the doctor makes an incision in the area behind the ear on the affected side, then cuts out a small area of bone. Having displaced the cerebellar hemisphere, the doctor determines the compression zone and eliminates it: delicately separates the vessel from the nerve and places a special biologically inert material - Teflon wool - between them. The bone defect is replaced with a bone fragment or a special plate, which is firmly fixed.
For secondary hemifacial spasms, it will be effective to eliminate the cause (removal of the tumor, exclusion of the aneurysm from the bloodstream, treatment of the underlying disease, etc.).
In the presence of contraindications to surgical treatment, in case of secondary hemifacial spasm, when surgical treatment is not indicated (stroke, multiple sclerosis, etc.), refusal of surgery, and in elderly people, injections of botulinum toxin type A (BTA) [1 ][7]. According to the recommendation of the European Federation of Neurological Societies (EFNS, 2011), BTA drugs are recommended as the first line of treatment for hemifacial spasm (recommendation class C) [28].
BTA is a highly effective treatment method for hemifacial spasm with minimal risk of adverse events and can be considered as an alternative to surgical treatment. It has been verified by controlled studies and 35 years of clinical practice [26]. Moreover, it is known that in 20% of cases of surgical treatment of hemifacial spasm, a relapse develops; side effects are frequent (impaired functions of the cranial nerves, infections, liquorrhea, hemorrhages), which are more difficult for patients to tolerate than BTA [7].
Californian ophthalmologist Alan Scott first used BTA in 1977 to treat strabismus. In 1985, he was the first to use local injections of BTA in humans for the treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm [29]. In 1985, neurologist Mitchell Breen published results of successful treatment of blepharospasm and hemifacial spasm using BTA [30]. Since then, BTA has been used not only in ophthalmology, but also in the treatment of diseases of the nervous system. The use of BTA was officially approved by the FDA (Food and Drug Administration - USA) in 1989. One of the first indications for the use of BTA was hemifacial spasm [31].
Botulinum toxin is produced by the gram-positive bacterium Clostridium botulinum. It is a neurotoxin that blocks the release of acetylcholine (a neurotransmitter that mediates the transmission of signals between neurons) from the presynaptic nerve ending. Thus, peripheral cholinergic (excited by acetylcholine) transmission at the neuromuscular synapse is disrupted. This reduces muscle contraction and leads to a dose-dependent, reversible decrease in muscle strength [25][26].
In Russia, the following BTA preparations are approved for use: conditionally 100-unit - "Botox", "Lantox", "Xeomin", "Relatox", "Botulax" (some drugs are available in bottles of 50 and 200 units) and " Dysport" (in bottles of 300 and 500 units). The drugs have similar effectiveness; they differ in storage and dilution features. Only in the instructions for the drug "Relatox" (Russia) hemifacial spasm is not included in the indications for use. The dosage of the drug is calculated individually for each patient and in accordance with the instructions for medical use. The conversion factor for units of action between Dysport and 100-unit drugs has been scientifically calculated; it is 3:1 or less for neurological indications and 2.5:1 for aesthetic indications [32]. The final dose calculation remains with the doctor. In Wolfgang Jost's atlas of botulinum therapy, doses are already indicated taking into account this recalculation per point of administration [33]. When treating hemifacial spasm, the average dose for Dysport can be 120-170 units. [14], for Xeomin - 30-50 units. depending on the muscles involved. The dose of administration at one point for Xeomin is 1.25-5 units. [33][34].
BTA is able to eliminate hyperkinesis during hemifacial spasm while preserving muscle function; it must be prescribed as soon as the diagnosis is made. Before carrying out botulinum therapy, the doctor must obtain voluntary informed consent for BTA injections. Injection sessions are recommended every 3-4 months in the target muscles. It is permissible to carry out injections “at the patient’s request,” that is, earlier or later than the recommended dates. This depends on the resumption of hemifacial spasm symptoms. After injections, it is recommended to actively contract the injected muscles for 20 minutes, and the patient should be under medical supervision for 1 hour to monitor for immediate allergic reactions [26]. To reduce the risk of developing intradermal hematomas on the face, it is recommended to cool the injection sites for 10-20 minutes.
A decrease in hyperkinesis after the administration of botulinum toxin is usually observed quite quickly - already on days 2-5, sometimes reaching the maximum effect by the end of the week (less often by days 10-14). The effect lasts up to 3-6 months. With regular repeated administrations of BTA, in most cases the positive effect is consolidated. The severity of hyperkinesis when they resume is less than before botulinum therapy and tends to decrease [14]. For facial symmetry in the muscles contralateral (on the opposite side) to the hemifacial spasm, it is necessary to perform BTA injections at 50% of the dose administered into the ipsilateral (on the side of the disease) muscles. It is advisable to do this after 2-3 weeks to evaluate the effect of the injected BTA and identify the muscles requiring aesthetic correction [35]. There is usually no decrease in sensitivity to BTA. Against the background of the effect of therapy, there is the possibility of gradual withdrawal of previously received medications [14][34].
More often, injections are performed in the following muscles: the circular muscle of the eye (orbicularis oculi); zygomaticus minor (zygomaticus major et minor); circular muscle of the mouth (orbicularis oris); subcutaneous muscle of the neck (platysma); frontal muscle (frontalis); muscle that wrinkles the eyebrow (corrugator supercilii); muscle that lowers the nose (procerus); nasal muscle (nasalis); muscle that lifts the upper lip and wing of the nose (levator labii superioris alaeque nasi); muscle that lifts the upper lip (levator labii superioris); laughter muscle (risorius); muscle that lifts the angle of the mouth (levator anguli oris). The drug should not be injected into the middle zone of the upper eyelid - in the projection of the muscle that lifts the upper eyelid, as this can lead to drooping of the eyelid [26][28].
Treatment with the drug should be carried out by specialists (neurologists, neurosurgeons) who have experience in the diagnosis and treatment of such conditions and have been trained in the treatment.
Contraindications to the use of BTA include pregnancy, hypersensitivity to one of the components of the drug, and acute diseases [26]. In the treatment of hemifacial spasm, according to various authors, temporary adverse reactions . They are distributed according to frequency as follows: very often - ptosis (drooping); often - weakness of the facial muscles, diplopia (double vision), dry eyes, swelling of the eyelids, lacrimation; infrequently - paresis (weakening) of facial muscles; rarely - ophthalmoplegia (paralysis of the eye muscles), entropion of the eyelid [26]. They do not require additional interventions and regress on their own within a few weeks [14][26][34]. To reduce the risk of side effects, it is important to maintain the dose of BTA and begin treatment with the minimum effective doses. Drugs that affect neuromuscular transmission, such as aminoglycoside antibiotics, should be used with caution during the period of BTA action [26].
To assess the effectiveness of treatment, scientists have developed a special system using five- and six-point scales. For example, according to Vincent Marneffe (neurosurgeon) [36], the result is considered “excellent” with the complete disappearance of hyperkinesis, “good” - if the disappearance is more than 80%, “satisfactory” - if the disappearance is from 20 to 80%, “unsatisfactory” - if hyperkinesis disappeared by less than 20%. Tetsuo Iwakuma et al [37], Peter Giannetta [21], Robert Auger et al [38] suggested “excellent,” “good,” “satisfactory,” “unsatisfactory,” “poor,” and “recurrent” results for the treatment of hemifacial spasm. One should strive to achieve “excellent” and “good” treatment results [7].
Drug therapy for hemifacial spasm is a thing of the past. Only in the presence of comorbid disorders (depression) can a doctor prescribe antidepressants in addition to the main treatment [25][26].
Thus, the use of BTA requires visiting a doctor 3-4 times a year without the need to constantly take other medications and undergo other procedures. It is also necessary to conduct cognitive behavioral therapy with patients for better social adaptation [25][26].
Inflammation and neuralgia of the trigeminal nerve
The branches of the trigeminal nerve cover almost the entire face, so it is quite natural that even after damage or inflammation of a limited area, discomfort can spread to the entire head, but most often it is the lower jaw that becomes numb.
Numbness of the lower jaw and chin due to inflammation or damage to the trigeminal nerve is often accompanied by other unpleasant symptoms: it is difficult to open the mouth, talk, chew and even swallow food, the sensitivity of the lips and tongue disappears, and uncontrolled salivation appears.
Unpleasant sensations are caused by inflammation of the ternary nerve
The cause of trigeminal neuralgia can be not only dental treatment2 and surgical intervention in the maxillofacial area. There are many other factors. Read about the most common of them, as well as about methods of treating pathology here.
Numbness of the cheek as a symptom of the disease
Numb cheeks can be not only a harmless reaction to incorrect head position, but also a symptom of a serious illness. Most often, numbness and tingling (paresthesia) occurs due to neurological or vascular pathology.
Transient ischemic attack
Sudden numbness in the face may indicate poor circulation to the brain. This is a dangerous condition called transient ischemic attack (TIA). With this pathology, the brain suffers due to the fact that a sufficient amount of blood and oxygen is not delivered through the vessels.
Symptoms of a TIA include:
- dizziness, which is accompanied by nystagmus, nausea, vomiting;
- speech disorder;
- numbness of the face and limbs;
- impaired mobility of the limbs (paresis);
- lack of coordination;
- memory loss.
A transient ischemic attack is also called a microstroke. The difference from a stroke is that the changes in the brain are reversible.
Osteochondrosis
The cause of paresthesia may be osteochondrosis, a degenerative disease of the spine. If the cervical region is affected, then the unpleasant sensations are localized in the face - the cheeks, lips, chin, and tongue become numb.
The main symptoms of osteochondrosis include:
- tingling, burning, numbness in the face and neck;
- dizziness, noise in the head;
- pain in the cervical spine, arms.
Symptoms occur due to compression of blood vessels and nerves that are located near the spine.
Trigeminal neuralgia
Sensitive innervation of the cheeks is carried out by branches of the trigeminal nerve. Therefore, if the left or right cheek is numb, the cause may be nerve damage.
The cheek area is innervated by two branches of the trigeminal nerve:
- The maxillary nerve provides sensation to the upper cheeks as well as the upper lip.
- Mandibular nerve - innervates the lower part of the cheeks, as well as the lower lip and chin.
The trigeminal nerve is a pair, so the lesion can be unilateral - only on the left or right side.
How does trigeminal neuralgia manifest?
- pain in places of innervation - cheek, lips, eyes hurt;
- numbness, tingling in the affected area;
- burning.
The cause of neuralgia can be trauma, inflammation, or dental diseases.
Vitamin and mineral deficiency
If the upper or lower jaw, as well as the lips, tongue and chin, go numb, then the reasons for this phenomenon may lie in an acute lack of B vitamins. With their deficiency, the conduction of nerve impulses is disrupted. To replenish the body’s “pantry” with B vitamins, you need to include foods such as nuts, beans, chicken, cheeses and cereals in your diet.
“My lower jaw constantly went numb during pregnancy. I complained to the doctor, but she said that this happens often. Pregnant women have metabolic disorders and slow blood flow, and they are always lacking vitamins and minerals. To correct the situation, I took all sorts of vitamins as prescribed by the doctor, had a massage, and tried to eat right. BUT nothing helped. I already began to suspect some serious abnormalities in my health, I donated blood, but the tests were normal. Everything went away a few weeks after giving birth!”
Alina I., review from babyblog.ru
Lack of vitamins also contributes to jaw numbness
What to do
To get rid of unpleasant sensations, you need to identify their cause.
In most cases, it is enough to adjust the regime - take breaks from work, exercises to strengthen the neck muscles, choose a comfortable pillow.
If numbness is a symptom of the disease, treatment is selected depending on the etiology.
Changing mode
The following recommendations will help you get rid of this unpleasant symptom:
- normalization of the work and rest regime (take short breaks every 45 minutes of work);
- physiotherapy;
- massage of the collar area;
- properly selected pillow and mattress.
Following these recommendations will relieve sensitivity disorders if there is no organic cause.
Drug treatment
Treatment consists of eliminating the cause, that is, the underlying disease. Symptomatic therapy is not provided.
| Disease | Treatment methods |
| Transient ischemic attack | The main goal of treating TIA is to restore normal blood flow. The following drugs can be used for this: · antiplatelet agents (Aspirin, Clopidogrel); · indirect anticoagulants; · infusion therapy. It is also important to treat concomitant diseases that increase the risk of stroke - arterial hypertension, atherosclerosis and diabetes. |
| Trigeminal neuralgia | For treatment, antiepileptic drugs are used - Carbamazepine, Oxcarbazepine. Additionally: · anti-inflammatory drugs; · painkillers; · sanitation of the oral cavity. |
| Osteochondrosis | Treatment of osteochondrosis is complex: · drug therapy, which includes anti-inflammatory drugs, muscle relaxants, B vitamins; · physiotherapy; · fixation of the cervical spine (Schanz collar). |
| Migraine | Drug treatment includes the following drugs: · analgesics (Solpadeine, Ibuprofen); · serotonin inhibitors (Naratriptan, Sumatriptan); · beta blockers (Metoprolol, Propranolol); · antidepressants (Amitriptyline). |
Serious diseases of the body
If the lower jaw is numb and the symptom either goes away or systematically appears again and again, then this may indicate cervical osteochondrosis. The problem arises due to poor circulation, compression of nerves and blood vessels in the cervical spine. In this case, the jaw, chin, lips become numb, and dizziness becomes a constant companion of the sick person.
Often, facial paresthesia (a sensitivity disorder characterized by tingling and numbness) occurs due to serious illnesses that require immediate medical attention. Let's list them:
- neuritis and neuroses,
- diabetes mellitus: an unpleasant symptom appears due to a decrease in blood glucose levels,
- hypertension,
- epilepsy,
- sinusitis and sinusitis: the upper jaw goes numb,
- meningitis,
- stroke and cerebrovascular accident,
- vegetative-vascular dystonia and anemia,
- oncology: the problem occurs due to compression of the spinal cord or brain by a tumor.
This symptom may be a consequence of a serious illness in the body.
Numbness of the face
Stroke
Diabetes
35609 March 16
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. Numbness of the face: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
Numbness of the face occurs when the sensitivity of skin and muscle receptors to various impulses is impaired. This symptom may develop gradually or appear suddenly. Loss of facial sensitivity is described as burning, tingling, sometimes pain, and in some cases as a complete absence of sensation. When the face is numb, the color of the skin over the affected area may change in the form of pallor or redness.
In severe cases, sensory impairment is accompanied by a decrease in the motor function of the facial muscles.
Types of facial numbness
Any external influence, be it heat or cold, light touch or strong pressure, leads to activation of skin receptors and muscle structures. Each receptor is associated with a specific type of nerve fiber that transmits a specific type of sensitivity (sensation of pressure on the skin, vibration, stretching of the skin, and temperature sensitivity). An impulse is generated in the receptor, which is sent through nerve fibers at high speed to the nerve ganglia, which are a collection of sensory neurons. This is where primary information processing occurs to activate vital reflexes. Subsequently, the impulse goes to the brain, where it is processed in special nerve centers, and the person feels pain, pressure, vibration, etc. Thus, we can talk about the following types of sensitivity disorders:
- Violation of surface sensitivity
occurs when receptors (temperature, tactile, pain, etc.) and nerve fibers of the facial skin are damaged. - Violation of deep sensitivity
occurs when the receptors and nerve fibers of the facial muscles are damaged. - Violation of complex types of sensitivity
. A similar type of disorder occurs when the cerebral cortex is damaged. There is no recognition of two different stimuli that simultaneously affect the skin, or the person cannot determine the location of the touch.
Possible causes of facial numbness
In many cases, numbness in different parts of the face is short-term, passing within a few minutes.
Such episodes can occur when the head is positioned in an awkward position, for example during sleep.
This occurs due to compression of the nerve fibers and a temporary disruption of impulse conduction. There is a burning and tingling sensation in the affected area. Partial loss of sensitivity is observed with prolonged exposure to the cold due to vasospasm. After gradual warming of the skin, sensitivity is restored.
However, facial numbness can be a symptom of a serious medical condition.
Acute cerebrovascular accident, or stroke
– a common cause of sudden numbness of the face in combination with a violation of facial activity. Hemorrhage or blockage of brain vessels by a thrombus (blood clot) occurs, acute oxygen deficiency and damage to neurons with disruption of their functions develops. Symptoms develop unexpectedly, sometimes accompanied by headache.
The main signs of a stroke are: numbness of the face and limbs on one or both sides, sudden weakness, speech impairment (inability to clearly pronounce words), drooping of the corner / corners of the mouth, uncoordination of movements.
If these symptoms appear, you should immediately seek medical help. A cerebral aneurysm
can cause numbness in the face due to compression of nerve fibers and sensitive centers of the brain. It usually develops gradually; at the onset of the disease, symptoms may be completely absent. Numbness first affects one area of the face (for example, perioral), and with further growth of the aneurysm, the affected area gradually expands. Sensations may also change: from tingling, burning at first - to a complete absence of sensations later.
There is a danger of rupture of a cerebral aneurysm; in this case, the symptoms are similar to those of a stroke and appear quickly.
Trigeminal neuritis
often accompanies inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity (caries, periodontitis), ear (otitis), paranasal sinuses (sinusitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis), parotid glands (mumps). The branches of the trigeminal nerve are irritated, which can lead to numbness in the corresponding areas of the face.
Impaired sensitivity with increased tone of the masticatory muscles
occurs due to compression of the branches of the trigeminal nerve by muscle fibers. Hypertonicity of the masticatory muscles is characteristic of damage to the temporomandibular joint due to arthritis and arthrosis, incorrectly selected braces, and certain diseases of the pharynx, for example, peritonsillar abscess.
Diabetes
– with this disease, the process of utilization of glucose from the blood is disrupted, which leads to damage to the vascular wall and disruption of the nutrition of nerve bundles. In the absence of maintenance therapy, tingling and partial loss of sensitivity in areas where the blood supply is impaired may occur.
Numbness of the face in multiple sclerosis
occurs due to demyelination (disappearance of the outer sheath) of the nerve fibers of the trigeminal nerve. Numbness is often preceded by severe pain not only in the face, but also in the limbs.
Tumors of the brain and its membranes
lead to impaired sensitivity in the facial area due to compression of the neurovascular bundles or tumor growth in them.
Which doctors should I contact if I have facial numbness?
If your face becomes numb, you should consult a neurologist or therapist. In some cases, consultation with an otolaryngologist, endocrinologist, or dentist may be required.
Diagnosis and examinations for facial numbness
Depending on the suspected cause of facial numbness, the following laboratory and instrumental studies may be required:
- clinical blood test;
Keeping the head and neck in an unnatural position for a long time
Impaired blood circulation and circulation, compression of nerve endings and, as a result, numbness of the jaws and other areas of the face, can be caused by spending a long time at the computer. Especially when a person props his cheek or chin with his hand. The problem often occurs in people who have an uncomfortable pillow or mattress, sleep in one position for a long time or stay in one position.
After being in an uncomfortable position for a long time, this symptom may occur.
Usually, an unpleasant symptom goes away almost immediately after eliminating the irritating factor or doing a little warm-up.
As you can see, there are many reasons why the upper and lower jaw become numb. Some of them are very dangerous. Therefore, if an unpleasant symptom accompanies you for a long time and appears frequently, then you should consult a doctor. It is best to start the examination with a dentist, but in the future you may need the help of a cardiologist, neurologist, endocrinologist, oncologist, psychotherapist and other specialists.
Notice
: Undefined variable: post_id in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content/themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
45 Notice
: Undefined variable: full in
/home/c/ch75405/public_html/wp-content /themes/UltraSmile/single-item.php
on line
46
Rate this article:
( 4 ratings, average: 4.25 out of 5)
prevention
- Osmanova Z.Kh., Salikhova A.A. Possible postoperative complications when using dental implants // Bulletin of medical Internet conferences. – 2021.
- Marine M.T. [and others] Neuropathy of the trigeminal nerve after surgical interventions in the maxillofacial region // Nervous diseases. – 2021.
Consulting specialist
Orlova Elena Vladimirovna
Doctor rating: 9.5 out of 10 (2) Specialization: Dentist-therapist Experience: 32 years
Left or right cheek goes numb: reasons not related to illness
Numbness of the face is not always associated with any pathology. Especially if episodes of sensory impairment are short-term and rare.
Parts of the face may become numb due to incorrect head position, prolonged sitting in an uncomfortable position, general hypothermia, or during periods of severe emotional shock. In these cases, there is no need to worry; numbness does not pose a danger to the human body.
Common causes of numbness that are not associated with illness:
- Incorrect work and rest schedule. Parts of the face may become numb if the head is in one position for a long time. For example, when working at a computer, reading, if breaks are not taken during work.
- Uncomfortable pillow. Uncomfortable head position during sleep can lead to compression of nerves and blood vessels. In the morning this will manifest itself in the form of numbness in different parts of the face.
- Panic attacks. The cheeks may become numb during panic attacks, during periods of severe shock. Numbness goes away along with other symptoms of nervous tension.
Comments
And if not the whole jaw is numb, but only its left half, and everything that is there: part of the lip, part of the cheek, teeth. Sensitivity disappeared completely. What could it be?
Svetlana (05/19/2020 at 15:14) Reply to comment
- Dear Svetlana, there can be a lot of reasons, ranging from a pinched nerve, ending with a mini-stroke, multiple sclerosis. If you experience similar symptoms, you need to call an ambulance.
Editorial staff of the portal UltraSmile.ru (05.24.2020 at 09:18) Reply to comment
Write your comment Cancel reply
Facial nerve paralysis
With facial paralysis, movement in the right or left side of the face is usually impaired. Main causes of the disease:
- Infections: chickenpox, herpes, cytomegalovirus infection, rubella, influenza and other acute respiratory viral infections;
- Meningitis and meningoencephalitis - inflammation of the brain and its membranes;
- Traumatic brain injuries. Most often, facial nerve paralysis develops after a brain contusion or a fracture of the base of the skull;
- Brain tumors;
- Otitis media is an inflammation of the middle ear (tympanic cavity).
If the cause of the disease cannot be determined, the doctor will diagnose idiopathic facial paralysis, which is also called Bell's palsy. It occurs in approximately 50%-80% of cases. Typically, Bell's palsy begins suddenly, and disturbances worsen over 2 days (48 hours). May cause headaches, weakness, pain behind the ear, decreased taste sensitivity and increased sensitivity to sounds.
With facial nerve paralysis, facial expressions are weakened, usually on one half of the face. When the patient tries to smile, bare his teeth, open his mouth or close his eyes, the face becomes asymmetrical and distorted. The eye on the affected side is constantly open.
At the appointment, the neurologist interviews and examines the patient. It is important for the doctor to understand when and how the disorders appeared, what preceded them, and what other diseases the patient has. During the examination, the neurologist identifies dysfunctions of the facial and masticatory muscles.
After this, the doctor prescribes an examination. This may include:
- Electromyography. A study during which a special device records electrical impulses from facial muscles;
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). This study helps identify the pathological changes that led to paralysis.
Treatment
- Exercises for facial muscles;
- Face massage;
- Physiotherapy;
- Anti-inflammatory therapy: glucocorticosteroids are used - hormonal agents that suppress immune and inflammatory reactions;
- Antiviral and antibacterial agents, if paralysis occurs due to infection;
- Eye protection on the affected side. With facial paralysis, the patient cannot close his eyes. To protect it, moisturizing drops (“artificial tears”), eye ointments with antibiotics, and a special “glass” bandage are used.
What is the risk of the disease?
If you immediately consult a doctor and begin treatment, the function of the nerve can be restored completely or at least partially. If treatment is not carried out on time, then paralysis can last a lifetime. The eye on the affected side will suffer the most. Due to the fact that the patient cannot close his eyelids and blink, the conjunctiva and cornea are not moistened with tears, they dry out. Vision decreases to the point of complete blindness.