Quite often in their practice, ENT doctors are faced with such a problem as paranasal sinus cyst. Despite the fact that the disease occurs frequently, in almost every tenth person, it is mainly discovered by chance, for example, during an X-ray examination for a completely different reason. This is explained by the fact that a cyst in the nose may not bother the patient for a long time and may not manifest any symptoms. Therefore, it is important to understand that timely treatment of cysts is necessary to avoid possible complications and to improve the patient’s quality of life.
What is a paranasal sinus cyst?
A paranasal sinus cyst is a formation with an elastic, elastic wall filled with fluid. Its size and location can be very different, which is reflected in clinical manifestations (patient complaints).
According to the classification, there are several types of cysts:
- Retention (true): occur due to blockage of the ducts of the glands of the mucous membrane;
- Pseudocysts (false): appear under the influence of an allergen, due to an infectious disease or due to an inflammatory process in the roots of the teeth of the upper jaw.
In addition, cysts are classified depending on what contents they are filled with, i.e. mucous, purulent and serous.
List of sources
- Zakharova, G.P. Clinic, pathogenesis and surgical rehabilitation of patients with cyst-like formations of the maxillary sinuses / G.P. Zakharova // Sat. scientific tr. XV Congress of Otorhinolaryngologists of Russia. - St. Petersburg, 1995.-T. 1.-S. 96-102.
- Daynyak, L.B. Nose and paranasal sinuses / L.B. Daynyak // Guide to otorhinolaryngology. M.: Medicine, 1994. - P. 222.
- Guryev I.S., Dolzhikov A.A. Features of patho- and morphogenesis of cysts of the paranasal sinuses. Russian rhinology. 2002; 2:53-54.
- Allahverdiev S.A., Lopatin A.S. Choosing the optimal surgical approach for maxillary sinus cysts. Russian rhinology. 2010;(1):34-35.
- Kulakov A. A. Surgical dentistry and maxillofacial surgery. National leadership / ed. A. A. Kulakova, T. G. Robustova, A.I. Nerobeeva. - M.: GEOTAR-Media, 2010. - 928 p.
How does a sinus cyst appear?
The mechanism of development of paranasal sinus cysts is quite simple.
Let's start with the fact that in the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses there are glands that produce mucus. Each such gland has its own excretory duct for secreting secretions, which opens on the surface of the mucous membrane of the sinus.
Under the influence of various unfavorable factors, the mucous membrane thickens and the excretory ducts become clogged. At the same time, the gland continues its work with the same force, mucus is formed, but the exit for it is blocked. Due to wall pressure, the glands begin to fill with mucus, stretch and form a cystic neoplasm. Approximately the same effect is obtained if you put an inflatable balloon in a water tap and open the tap - water will flow and inflate the balloon.
There are several UNFAVORABLE FACTORS that will contribute to the development of this process, namely changes in the thickness of the mucosa and blockage of the ducts:
- exposure to an allergen and the occurrence of allergic reactions,
- polyps,
- infectious diseases,
- chronic diseases developing in the nasal cavity (rhinitis) or in its paranasal sinuses (sinusitis: sinusitis, sinusitis, etc.),
- diseases of the teeth of the upper jaw, anatomical features of the structure of the nose.
Possible risks
A cyst in the maxillary sinus and sinus lifting can be complicated in different ways and seriously interfere with any dental interventions by the doctor. When a cystic formation is removed, the risk of perforation of the mucous membrane of the maxillary sinus only increases, as do subsequent associated problems. It is also possible for the cyst to accidentally open and spill its contents into the sinus. This threatens further infection and the development of acute or chronic sinusitis.
When performing a sinus lift for a maxillary sinus cyst, the doctor must remember that the formation promotes the resorption of bone tissue. The thinner the alveolar bone, the less load it can bear. Therefore, any careless movement can lead to a fracture of the bone crest.
During the sinus lifting process, a barrier membrane is necessarily installed that will protect the operated area from unfavorable external factors and the additional impact of osteoclasts (cells that destroy bone).
In addition, only the safest and highest quality grafts are used in the bone grafting process with minimal risk of rejection. This precaution is due to the fact that a significant deficiency of bone tissue will not suffer additional problems in the form of poor engraftment. The doctor will not be able to perform a second operation, and he will have to look for alternative solutions.
Symptoms of a maxillary sinus cyst
So, what symptoms should you pay attention to? In what cases is it necessary to consult a doctor?
Of course, first of all, it should be said that a maxillary sinus cyst (both right and left) can develop asymptomatically (that is, its appearance and constant presence in the maxillary sinus does not cause discomfort for a person) with a diameter of less than 1 cm.
In this case, usually, the detection of a cyst occurs either accidentally (for example, an x-ray examination to confirm the diagnosis of sinusitis), or with further significant growth of the tumor (more than 1 cm in girth).
If a cyst in one of the sinuses causes discomfort (it is larger than 1 cm), then the following symptoms are observed:
- difficulty breathing (especially after exercise),
- constant nasal congestion (a common symptom for children),
- local pain over the affected sinus (usually the maxillary, right or left),
- false symptoms of increased intraocular pressure (caused by a cyst with a volume of more than 1 cm, hence the unpleasant sensations),
- purulent discharge (if concomitant diseases are headed by sinusitis),
- symptoms of innervation damage (hypo- or anosmia - loss of smell),
- excruciating headaches that quickly recover even after strong analgesics (compression of the trigeminal nerve branch).
All of these listed symptoms are a reason to contact an ENT doctor in order to avoid complications that such a process can cause!
Rehabilitation period
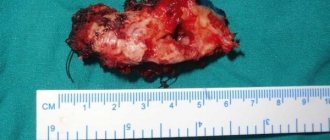
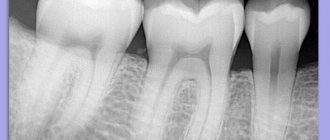
Figure 4. A cyst removed from the maxillary sinus with a tooth in it.
Source: Indian journal of ophthalmology / Open-i (Attribution 2.0 Generic) After surgery to remove a sinus cyst, no special recovery or treatment is usually required. Full recovery takes only a few days. With a small amount of intervention, patients feel well within a few hours after the intervention.
For the first time after surgery, it is advisable to avoid physical activity. You cannot visit the pool and sauna, you must not allow injuries. To avoid inflammation and other complications, you need to ensure high-quality oral hygiene and follow your doctor’s prescriptions.
Diagnosis of sinus cysts
In addition to the standard questioning and examination of the patient, all doctors at the Lor-Plus clinic are proficient in endoscopic examination techniques. Using an endoscope - a long thin tube with a miniature video camera, the doctor can conduct the most complete examination of the ENT organs, determine the presence of additional structural features of the nasal cavity, changes in the nasal mucosa in the deep sections that may interfere with normal breathing.
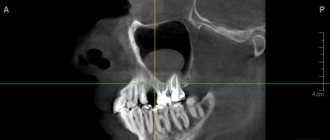
Currently, the gold standard for diagnosing sinus cysts is computed tomography . This method allows you to determine the size of the cyst and its location in the sinus with millimeter accuracy, which is very important for choosing a method for removing the cyst.
Treatment of maxillary cysts
There are no conservative methods for treating cystic formations in the maxillary sinus. The doctor chooses one of the options for surgical intervention, which depends on the type of cyst, its location, the professional qualities of the specialist and the individual characteristics of the patient.
In modern medicine, the following operations are widely used to treat cysts:
- Open surgery. A manipulation that involves general anesthesia and has many complications and risks. The anterior wall of the maxillary sinus is opened, and the cyst is removed through the resulting hole. The main problem is the overgrowing of the access with scar tissue. This completely contradicts the physiology of the body and does not allow sinus lifting and dental implantation in this area in the future.
- Endoscopic treatment. One of the most advanced and successful in modern medicine. Using a special instrument, the doctor enters the maxillary sinus through its natural opening without damaging the bone tissue. The cyst is then sucked out or desquamated.
- Classic removal. A typical open sinus lift approach is performed, through which the cyst is removed. The operation is performed in cases where the cause of the development of the formation is a diseased tooth.
Since cystic formations are most often discovered during the preliminary examination for sinus lift, the doctor must choose a treatment method that will not interfere with further bone grafting. The final decision always belongs to the patient, so he needs to be told the advantages and disadvantages of each therapeutic technique.
Consequences of deletion
For successful recovery after removal of the cyst, the patient is hospitalized. It lasts no more than 2 weeks:
- Every day the nose and sutures are treated and washed with an antiseptic.
- The patient takes antibiotics (broad-spectrum), antihistamines and, if necessary, painkillers.
- The patient will be offered to undergo a course of physical treatment aimed at resolving the swelling.
If the incision heals at a normal pace, the stitches will be removed after 7 days. But in general, rehabilitation will take up to 4 weeks.
During this period, the patient must follow a number of rules :
- Maintain oral and nasal hygiene.
- Rinse your mouth with plain water every time after eating.
- Do not pick your nose or put your fingers in your mouth.
- Reduce physical and thermal stress on the body. Therefore, stop playing sports for a while, do not bathe in hot water, and do not eat hot and spicy foods.
Important! At first, swelling of the lips and cheeks, numbness, and poor sensitivity in this area may persist. It happens that the sense of smell deteriorates for a while, breathing through the nose becomes difficult, and discharge appears. This is a temporary post-operative effect that will go away within a week.
Preventive measures
During the postoperative period, it is better to eat non-solid food at room temperature, so as not to irritate the nervous system and not fully restored tissues.
After and before the course of treatment, it is allowed to use traditional medicine.
Here are a few of them:
- The leaf of any plant must be washed and placed in the refrigerator, keeping it there for at least 3 days. Then the juice is squeezed out of it, mixing the resulting substance with water and instilling 3-5 drops of the resulting mixture into the nostrils several times a day.
- 2 gr. mumiyo and 5 ml. glycerol dissolves in warm water. Place this solution in the nostrils 3-5 times a day.
- Make an infusion of eucalyptus, tea and honey (in equal parts). The nasal passages are instilled in the morning, afternoon and evening.
Their individual use will not give great results, but together with other methods they provide a significant effect, reducing the size of the tumor and clearing the ducts. Plus, they must be agreed upon with the attending physician.
Possible complications
Since this formation is not malignant and does not form metastases, it does not lead to disruption of the functions of other organs. Only a large tumor can lead to complications.
If the cyst has been damaged, then there is a chance of contracting ENT diseases, infections, purulent infection of oral tissues, bones, and also the loss of several teeth. Otherwise, with proper treatment and recovery process, the risk of relapse is minimal.
Could she burst?
If the size is significant and there is overload in this area, the tumor may burst. The liquid will begin to flow out and cause inconvenience.