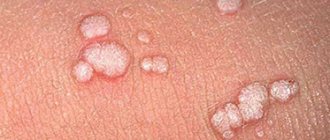
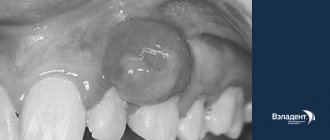
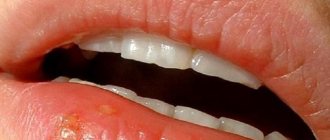
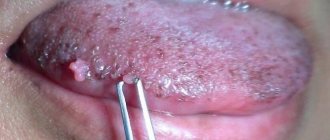
Oral papillomas are benign neoplasms in the oral cavity that grow from epithelial cells. Papillomas are discovered during a dental examination and look like separate growing seals on a small stalk, they are painless and have a white or pale pink color.
This type of neoplasm in the oral cavity is diagnosed most often. About 60% of patients are women aged forty years, about 20% are teenagers of any gender. Often, adults experience the appearance of individual papillomas, while children may experience so-called papillomatosis (multiple papillomas). In half of the cases, papillomas are localized on the mucous membrane of the tongue.
Papilloma in the mouth: causes of appearance
The most common cause of this type of tumor is the human papillomavirus (HPV).
Factors that provoke the appearance of papillomas in the oral cavity are, for example, constant microdamage to the cheeks and tongue. A relatively small damage is enough for viral particles to penetrate inside and trigger the formation of papilloma. In children, the provoking factor is a too short frenulum of the tongue - the lower incisors injure it, creating a gateway for infection.
When analyzing papilloma under a microscope, it can be noted that this neoplasm is a tumor, which consists of many layers of epithelial tissue, which in some places has become significantly keratinized. In some areas, traces of the appearance of a focus of inflammatory infection can be noted.
Types of fibroids
There are six main types of oral fibromas, they differ in nature, cause of appearance and clinical manifestations:
- Dense fibroma of the oral cavity has a rather dense consistency. It is due to the fact that the “framework” of the tumor includes coarse connective fibers with a small number of nuclei, which are located close to each other. Localization: hard palate and gums.
- Soft fibroma has a soft consistency due to thin, loose connective tissue fibers and a large number of nuclei. The typical location of soft oral fibroma is the mucous membrane of the tongue and cheeks. There are also tumors of related types: fibrohemangiomas, fibrolipomas, etc.
- Fibroma caused by irritation is, by and large, not a full-fledged neoplasm, but a consequence of hyperplasia that developed after chronic irritation and mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. This type of oral fibroma is the most common. Fibroids from irritation appear on the oral mucosa in the form of pink papules.
- Symmetrical fibroids appear near the third molars on the surface of the palate and on the gums. They have a dense consistency and shape reminiscent of legumes. This type of neoplasm is not a true tumor, but the result of an increase in gum volume; this pathological process occurs with the formation of scars.
- Lobed fibroma of the oral cavity has a characteristic lumpy surface and grows due to reactive hyperplasia of the gum tissue when they are chronically injured due to removable dentures.
- Fibrous epulis is a benign neoplasm of the oral cavity located on the gums. Epulis of the fibrous type is usually quite dense in consistency and grows slowly.
Classification of oral papillomas
Based on the number and concentration of neoplasms, oral papilloma is differentiated from papillomatosis – a massive accumulation of neoplasms in one place.
According to their origin, papillomas are divided into the following types:
- Traumatic (reactive) papilloma. May appear after traumatic effects of a mechanical, chemical or temperature nature. A distinctive and characteristic feature of reactive type oral papilloma is that their growth stops immediately after the irritant that caused them is eliminated.
- True (neoplastic) papilloma. This type of papilloma begins to develop after the mechanism of cell division, growth, and differentiation is disrupted. In most cases, this type of papillomas appears in the distal part of the cheek, in the area located behind the molars and in the area of the pterygomandibular fold.
- Viral papilloma of the oral cavity. May appear after the patient has been infected with the human papillomavirus. This type of infection occurs through direct contact with a carrier of the virus. When the integrity of the oral mucosa is compromised (for example, due to microtrauma), a path for infection appears.
What is the best way to treat?
A large number of papillomas certainly causes inconvenience and does not look aesthetically pleasing. However, this is not a reason to use old-fashioned methods for removal with thread, pliers or a blowtorch.
For single small (1x1 mm) formations, celandine juice
- a proven folk remedy.
When there are many papillomas or they are large, this method is not suitable
, as it can last for months and lead to severe inflammation.
Removal using radio wave surgery is much more convenient and effective
The operation does not require special preparation, is practically painless, and after it you can drive a car.
Once I had the opportunity to remove about 70 papillomas from one patient at once. It is difficult to convey all the joy of a person who got rid of them, whom they tormented for several years.
Treatment of oral papillomas
Diagnosis of this disease includes a collection of the patient’s medical history, as well as a thorough histological examination of removed papillomas.
Treatment of papillomas is only surgical. The neoplasm is excised down to the borders of healthy tissue. Techniques such as electrocoagulation, cryosurgery, sclerotherapy and others are rarely used, since as a result of their implementation it is impossible to conduct a histological analysis of the papilloma removed to the base.
If a large accumulation of papillomatous neoplasms is detected, a combined technique is used: a scalpel is used to dissect the largest number of papillomas accumulated in one place, and single papillomas are removed using electrocoagulation.
If oral papillomas have a viral etiology, antiviral and immunomodulatory therapy is prescribed along with surgical intervention to prevent relapses.
Depending on the etiology of the disease, relapses may occur with greater or lesser probability. So, if there is a human papillomavirus in the body, the risk of papillomas returning after surgery is quite high.
Papillomas in the throat - treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis
Let's take a closer look at how complete treatment of laryngeal papillomatosis in children and adults occurs, its full cycle, in the Yesong center, in Korea.
Data from the study:
1 OPERATION
“The intratrochlear excision method is the surgical removal of masses of papillomas with the capture of a 2 mm layer of the mucous membrane, including submucosal glands, using minimal cold instruments for children and some adults, with complete removal of the papilloma, especially if the papilloma has re-formed at the site of the scar from a previous operation and CO2 laser applications. Papillomas are excised to a healthy mucous membrane, all infected parts of the mucous membrane are removed.
IMPORTANT: Since papillomas cells can grow deep into the tissue, destroying the membrane barrier, complete removal of the submucosal gland in the affected area is necessary to reduce the risk of relapse.
Next, the surface of the larynx is treated with a 585 nm pulsed color dye laser ( PDL laser) or KTP laser to prevent scarring and stenosis formation. In the study, the use of cold instrumentation followed by treatment with a PDL laser instead of a CO2 laser resulted in a significant reduction in laryngeal scarring. Minimizing the formation of scars and scarring of the vocal folds after surgery is the basis for effective voice restoration in the subsequent recovery period.
After laser treatment, Cidofovir into the affected area to prevent future relapses.
The operation is completed with the “microflap” technique - suturing the vocal cords in order to minimize the adhesive process and possible stenosis of the larynx.”
Laryngoscope 126: June 2021 Kim and Baizhumanova: Recurrent Respiratory Papillomatosis and Its Treatments. Page 1360-1361
2 OPERATION
On the 4th day after the first operation, a second throat operation is performed . After the first operation, fibrin is formed on the operated surface, in simple words - a film. If it is not removed, it becomes a denser tissue, and adhesions appear, which lead to laryngeal stenosis, that is, fusion. Fibrin is removed during a second microsurgery under general anesthesia. This procedure helps prevent the formation of adhesions and stenosis on the vocal cords.
3 OPERATION
Next, on days 8-9 after the first operation, the final operation is performed under general anesthesia to remove fibrin. During the third surgical intervention, additional tissue treatment is performed with drugs that prevent tissue fusion. Laryngeal microsurgery is repeated using the “microflap” technique: suturing the vocal cords to prevent vocal cord adhesions and stenosis.
REPEATING THE CYCLE
In a number of serious cases of recurrent laryngeal papillomatosis, it is necessary to resort to repeating the entire cycle. It must be remembered that this disease is a manifestation of a virus that is in the human body. When the immune system is weakened, even after a full cycle of treatment, the body may malfunction and a relapse occurs again. Therefore, it is important after treatment to take seriously the restoration of immunity and leading a healthy lifestyle.
Contact the clinic
Diagnosis of HPV
The main clinical sign of papillomatous infection is formation on the skin. Therefore, in most cases, an examination by a doctor is sufficient to make a correct diagnosis. Additional examination methods are:
- biopsy or scraping - taking biological material for further research;
- PCR (polymerase chain reaction);
- General and biochemical blood test.
These laboratory diagnostic methods help:
- detect the presence of papilloma virus in the child’s body (if there are no growths on the skin);
- accurately determine the HPV strain;
- understand the form of the infection (acute or chronic).
These data are necessary for assessing oncogenic risk and timely further examination.
Methods for treating papilloma on the inside of the cheek
A papilloma that appears on the cheek in the mouth should alert a person, although it is usually benign. Immediately after its detection, you need to contact an ENT specialist, dentist or therapist for diagnosis and effective treatment. A timely response to this growth will help to avoid malignant processes and prevent you from putting your life in danger.
Treatment of papilloma on the inside of the cheek with medications
In the photo there are preparations for papillomas on the inside of the cheek
First of all, you need to strengthen your immune system by drinking special immunostimulants . Among them, Immunal, which costs about 250 rubles, best copes with its tasks. (120 UAH). It is sold in liquid form, making it easy to use. It can be replaced by Lymphomyosot, also available in the form of drops. You can also recommend taking Echinacea purpurea, which is the most economical option. Treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa should be carried out for at least 2-3 weeks.
In parallel with taking immunostimulants, it is recommended to take antiviral drugs - Likopid, Kagocel or Tsitovir-3. On average, they need to be taken for 5-10 days; taking it longer is not recommended in order to avoid suppression of the intestinal microflora.
Among external agents, it is recommended to use Miramistin , which perfectly reduces the activity of bacteria, viruses and infections. They need to rinse their mouth 2-3 times a day for 2-3 minutes. It costs about 200 rubles. (90 UAH).
It has a good analogue - Chlorhexidine . Both are antiseptics, but the latter is recommended to be used 2-3 times a day. Successful treatment of papilloma on the buccal mucosa will take at least a week.
Traditional medicine for papilloma on the inside of the cheek
The most famous remedy is calendula tincture , which should be used to wipe the papilloma 3-5 times a day. To do this, you can use an ear stick or a piece of cotton wool, moistening them in the composition.
Instead, sea buckthorn oil ; it needs to be lubricated with the formation twice a day for 7-10 days.
You can also rub the cone with peeled garlic, treat it with the juice of celandine and aloe, potato and lemon.
, tincture of walnuts , prepared with the addition of 50 g of this component along with crushed green shells and the use of vodka, which is taken twice as much, is also very helpful All this is mixed and left in a jar for 2 weeks, kept in a dark place. After this time, the composition must be filtered, soak a cotton swab in it and wipe the growth. This must be repeated 3 times a day, treatment is carried out for about 2 weeks.
To combat papilloma on the oral mucosa, castor oil , which is recommended to be heated beforehand. They treat formations with an ear stick 2-3 times a day. For this to help, treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.
It is useful to rinse your mouth with a soda solution , for the preparation of which you should add this component (2 tsp) to 200 ml of warm water and stir well. This procedure must be carried out 5 times a day for 2-3 minutes.
No less useful will be lubricating the growth with propolis , which has strong cleansing and anti-inflammatory properties.
Also, when treating papilloma on the buccal mucosa, you should pay attention to an infusion of wormwood and chamomile , of which you need to take 2 tsp per 250 ml of water. The composition must be kept covered for 2-3 hours, filtered and used to rinse the mouth 3-4 times a day. This treatment should be carried out for at least 10 days.