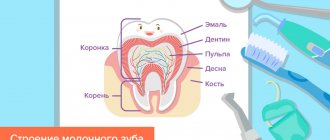
Milk teeth are bone formations that are designed for mechanical processing of food in order to prepare it for subsequent digestion. They also influence diction and make the child’s speech correct and clear. In terms of their anatomical structure, they are in many ways similar to permanent ones, but they all have some differences. Among them:
- the coronal part is smaller;
- the thickness of enamel and dentin is less (from 0.6 to 1 mm);
- reduced degree of mineralization;
- no immune zones;
- the pulp volume is large;
- dental canals are shorter;
- poorly developed tubercles in the closure zone.
As for the number of root canals, their number remains unchanged.
The roots of baby teeth are slightly inclined. This is explained by the fact that the rudiments of permanent units are located above them.
It is a mistake to believe that children's teeth do not have roots. But this is what many adults think when they look at their children’s fallen teeth. In fact, by the time of prolapse, the formations located in the alveoli are almost completely resolved.
What are the dangers of premature removal of baby teeth?
Speech disturbances, inhibited bone growth and unnecessary pain are just some of the unpleasant consequences of not properly caring for baby teeth. Some parents mistakenly believe that there is no need to worry about baby teeth if they fall out anyway. Premature loss of primary teeth, that is, 3-4 years before the date of their physiological loss, in adulthood leads to unpleasant consequences - crowding or various types of malocclusion.
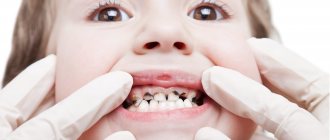
Baby teeth have a specific structure and are very susceptible to caries. Their premature loss is most often caused by advanced caries or mechanical injuries. If primary teeth begin to deteriorate, inflammation of the pulp quickly occurs, and then inflammation easily occurs with complications around the periapical tissues or abscesses. In such cases, it is often impossible to perform root canal treatment. All that remains is to remove the baby tooth. The whole process of pain and treatment exposes the baby to many troubles, and it is worth protecting him from this.
What to do in the first minutes if a child has a broken tooth?
First, calm down yourself and calm your child. If you have something cold on hand, it is good to immediately apply a compress to the injury site to relieve pain and prevent severe swelling (if the injury is not open).
For an open wound, clean it of large contaminants and cover it with a sterile gauze pad. Time is very important! The most important thing is to get to the dentist as quickly as possible! The doctor will conduct an examination, take an x-ray to see all damage to the hard and soft tissues surrounding the tooth and rule out a fracture of the jaw bones, as well as carry out the necessary treatment.
In the future, such teeth require dynamic observation at a time determined by the dentist. With timely treatment and regular monitoring, the prognosis is favorable.
Why do baby teeth deteriorate?
Damage to a baby tooth most often occurs due to caries in early childhood. This disease can take different forms. The wrong way to feed a baby can lead to bottle tooth decay. If the baby falls asleep with a bottle in his mouth or is given formula or sweet tea after waking up at night, then streptococcal bacteria develop in the mouth during sleep. They are the ones who contribute to the occurrence of this variant of the disease.
In older children, two and three years of age, circular caries is observed. This is the name of the early stage of caries with an acute course. It first begins to attack the front teeth, most often in the upper jaw and symmetrically on both sides, and then leads to pulp complications. A tooth with a damaged crown is not suitable for root canal treatment and must be removed. Leaving a baby tooth damaged by caries is dangerous because it is an inflammatory source in the child’s mouth.
Another very common cause of loss of baby teeth is childhood trauma. It is not uncommon for a child to lose teeth due to a fall. One of the main reasons is that the design of primary incisors is completely different from permanent incisors. They are smaller, have shorter roots, and the jaw bones are more spongy. Children of certain ages are at greater risk of injury:
- the first and second years of life are when they are just learning to walk, but the older the child, the greater the risk;
- later, at the age of four to six, other activities appear: playing with a ball, running, climbing.
So it is not difficult to lose a tooth. Often, the premature loss of baby teeth in children is not given much attention. However, the roots of an extracted baby tooth are usually not completely resorbed, and the root of a permanent tooth is still in the early stages of development. This has quite serious consequences, so the indications and contraindications for removal should not be ignored.
Do you need pain relief?
Anesthesia when removing temporary units is necessary when they are pulled out before the roots are reabsorbed. Without anesthesia, the procedure will cause pain to the child, since there are many nerve endings in the oral cavity. When removing, the following anesthesia methods are used:
- General anesthesia. They are used only if the child has mental illness or other remedies do not work on him.
- Local anesthesia with spray or gel. The method is suitable if the unit begins to wobble and does not cause severe discomfort.
- Anesthetic injection. The injection is given in the gum. Anesthesia lasts longer than when using gels and sprays, and has a more pronounced analgesic effect.
Removal of baby teeth in children
It all depends on the number of lost baby teeth, their location in the jaw and how much time is left before the permanent tooth erupts. If it is three or four years, the more likely it is that the permanent tooth will be delayed or will not grow. The hard and compact bone tissue formed above the tooth germ will be difficult for him. The opposite is true when the time to a supposedly permanent dentition is quite short. Then the eruption of the permanent tooth usually occurs earlier than it would have happened naturally.
Premature loss of primary teeth can also interfere with alveolar bone growth. A child who does not have teeth cannot bite properly, and the forces generated during this activity are not transmitted to the bones and muscles, which does not contribute to their proper development.
Losing two baby teeth on one side, such as the fourth and fifth, can lead to other consequences. With such extensive missing teeth, the occlusal forces between teeth that shape and guide the growth of the alveolar bone are compromised. Thus, growth is uneven and is expressed in the vertical layering of bone where there are no teeth.
Premature loss of a molar, that is, the primary five, always leads to an internal (i.e. forward) displacement of the fixed six. This is a common problem that causes the dental arch to shrink. As a result of this phenomenon, there may not be enough space for other molars. Consequently, crowding of teeth occurs, this feature looks unsightly when there is no room for the canine tooth and it grows outside the dental arch or does not grow at all because due to lack of space, it gets stuck in the bone.
Premature loss of incisors and primary canines, that is, the upper front teeth, contributes to poor jaw bone development, which can lead to malocclusion. For example, if the jaw is underdeveloped compared to the lower jaw, an anterior transverse bite will form (the lower front teeth will overlap the upper ones).
Speech problems may occur in children with severely defective primary teeth, especially the front incisors. Such deficiencies do not contribute to the correct position of the tongue on the palate, so there is a possibility of interdental lisp. As a rule, after the removal of a baby tooth, a child needs 1-2 years of visiting a speech therapist or dentist.
Missing teeth and speech defects not only affect health, but also have a psychological aspect: the child may have low self-esteem, be secretive or shy because of his appearance. Children's baby teeth are truly worth caring for. Oral hygiene is equally important at every stage of life.
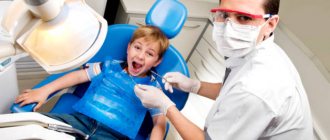
How to remove a tooth without damaging the child’s psyche?
How to extract a baby tooth from a struggling and crying baby is a very pressing problem. Much depends on the professionalism of the doctor and the attitude of the parents. A good specialist will remove the tooth quickly and painlessly. The task of parents is not to be afraid themselves and not to groom their child with oohs and aahs. The child, seeing your fuss, will instantly decide that something terrible is about to happen. Try to give him examples of other, more flexible children, or play on the desire to be bolder than the rest of his peers. And, of course, your presence in the dental office with your child is simply necessary.
Baby teeth play an important role in the formation of permanent occlusion; the health of molars depends on them. Therefore, removing them prematurely can only be done as a last resort. Only parents are able to protect their child from such troubles by regularly attending preventive examinations and monitoring the child’s compliance with the rules of oral hygiene.
Treatment of baby teeth by a doctor
Just like adults, children's baby teeth are susceptible to caries. The treatment in the clinic is similar to the treatment of permanent teeth, with the difference that you can use special plastic fillings for baby teeth in white or many other colors. In addition to the temperature, premature removal of a baby tooth can distort the growth of the upper or lower jaw, cause insufficient space in the arch for permanent teeth, or damage their buds. This is why it is so important that the baby tooth remains in the mouth until natural tooth replacement occurs.
As permanent teeth erupt, baby teeth tend to move around a lot. This may be accompanied by purulent inflammatory processes. Then it is better to remove the baby tooth. When the first permanent molars appear, it is worth considering dental fillings. The procedure consists of fixing them with a special varnish that protects them from rotting. The treatment is completely non-invasive and painless. The optimal time for placing fillings is about 6 years.
What if there is a root left in the gum?
If a tooth falls out after loosening on its own, then the absence of a root on the fallen unit is normal. By the time it falls out, it should no longer be there. However, if removed prematurely, it may remain in the gums.
In this case, most dentists do not recommend resorting to extraction of the remaining process. You need to wait until it resolves on its own. You should contact your dentist in the following situations:
- the remaining piece interferes with the child,
- the prolapsed unit is severely affected by caries,
- after the loss, the inflammatory process began.
Some sources contain information that if the remaining spine is loose, you can remove it yourself. However, experts do not recommend resorting to removal at home, since there is a risk of damage to nearby units and infection of the wound.
Content:
- Why is it necessary to replace baby teeth with permanent ones?
- When do the first baby teeth fall out?
- Which baby teeth fall out first?
- Drop order
- At what age do radical units appear?
- Possible abnormalities in the child
- Why do empty spaces remain unoccupied for a long time?
As the child grows, the baby teeth are replaced by permanent ones. This is a natural process, without which the full functioning of the dentofacial apparatus is impossible. But parents should treat it with the utmost responsibility, since very often violations in the sequence of loss of temporary units cause serious malocclusions that have to be treated in the future.
At what age do radical units appear?
We can talk about adult occlusion only a few years after the start of the change in time units. Typically, a stronger replacement will erupt several weeks or months (or, if pulled out prematurely, years) after the baby teeth fall out.
Central incisors grow from 6 to 8 years of age, lateral incisors from 7 to 9, premolars and canines from 9 to 12. Molars begin to grow at approximately six years of age. They immediately grow permanently, replacing the empty space.