What are the features of the eruption of “temporary” teeth?
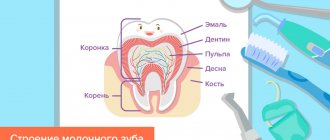
Baby teething normally occurs at six months of age. The first sign of this process is the formation of a dental tubercle on the edge of the gum. This occurs as a result of pressure on the mucous membrane - it gradually stretches, becomes thinner and a breakthrough occurs. Then you can see the edge of the crown of the new tooth above the gum. As soon as the entire crown appears above the gum cavity, this is the eruption of the tooth.
In various sources you can find exact dates for teething, but they are arbitrary. Any discrepancies with them depend on the individual developmental characteristics of the baby. There is no need to worry if your child's first tooth appears later or earlier than his peers. Teething is a natural process that occurs on an individual schedule.
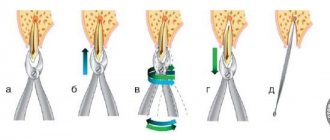
Did you know that baby teeth have roots? It’s just that by the time they begin to fall out, they resolve on their own. If sometimes a tooth has to be removed before its natural loss occurs, its root can be seen.
In erupted baby teeth, the formation of roots occurs according to the following scheme:
- The formation of the roots of the incisors occurs by the age of two.
- The roots of the molars will be fully formed by the age of 4 years.
- The formation of the roots of the fangs occurs by the age of 5 years.
“Why do other children already walk at 9 months, but mine is not yet?”
The development skills mentioned are indicative only. If a baby at nine months does not speak, crawls little or only crawls on its belly and does not try to get up, there is no need to worry. Every child is different and while we can help them develop, they learn new skills at their own pace and in their own time. In addition, already at 9 months of age, the difference in development between boys and girls becomes noticeable.
But if there is something that worries you, even the smallest thing, share your concerns with your baby’s pediatrician. Only the doctor will determine what is the norm for proper development for your baby, and what you need to pay attention to. Whether it is necessary to take a massage course to prepare for walking, sign up for a swimming pool to support immunity and sound sleep, introduce new educational games and work on hearing and speech, or on the fact that the child does not sit independently - the answers to these questions are individual and depend on many factors. A child never needs everything at once: listen to the recommendations of specialists.
*The ideal food for an infant is mother's milk. WHO recommends exclusive breastfeeding for the first 6 months. MAMAKO® supports this recommendation. Before introducing new foods into your baby’s diet, consult a specialist.
What is the approximate timing of teething in children?
The timing of teething is influenced by the child’s intrauterine development, because the process of their mineralization occurs even before the baby is born. The health of baby teeth, as well as permanent teeth, and the timing of their eruption depend on the course of pregnancy.
As teeth grow, mineral accumulation and root growth continue in their crowns. Their growth stops after they are fully formed. The duration of this dormant period lasts until approximately three years of age.
Important: If a baby tooth has been treated, very often slower resorption of its root occurs. Therefore, as soon as the time has come for it to fall out, it will continue to be in its original place. In such cases, it needs to be removed to make room for further growth of the permanent tooth.
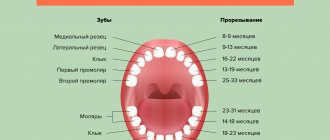
Based on their numerous observations, the approximate timing of teething in children has been established:
- At 6-8 months of age, the child begins to erupt the lower and upper central incisors.
- From 8 to 14 months, the baby develops lateral incisors (2 upper and 2 lower).
- The eruption of the first molars occurs at 12-16 months. At the same time, gaps remain between them and the incisors for future fangs.
- The appearance of fangs occurs between 16 and 24 months.
- Eruption of the second molars occurs from 20 to 30 months.
At 2-2.5 years of age, a baby should have 20 teeth:
- 8 incisors;
- 8 molars;
- 4 fangs.
Sometimes teething may occur in the wrong direction. By the age of three, when the dentition is fully formed, the baby is actively chewing food, and they return to their normal position.
Important: The timing of teething is different for each child. There is no need to panic if by the age of three your child does not yet have a full set of teeth. But if the baby has no teeth at all by the age of one year, be sure to consult a pediatrician who will help you find out the possible reasons for the delay in teething.
Similar problems are possible due to some diseases:
- Disruption of metabolic processes in the body.
- Rickets.
- Endocrine diseases.
With such diseases, the following symptoms may occur:
- Late closure of fontanelles.
- Child growth retardation.
- Curvature of the legs.
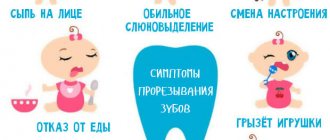
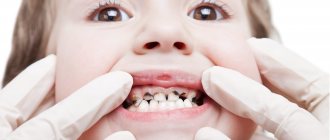
Carefully examine your baby's gums: they should be red and swollen. To help your baby speed up the teething process and relieve pain, you can buy special teething toys. They cool easily, and the coolness perfectly relieves pain and itching from the gums. Children chew such rings with great pleasure, thereby speeding up the eruption of their first teeth.
You should definitely show your baby to an endocrinologist in the following cases:
- The baby was born with teeth.
- The eruption of the first teeth occurred before the age of 3 months.
The order in which primary teeth appear is extremely important because it influences the formation of the bite. Heredity plays a primary role in this case. If mom or dad's teeth grew incorrectly, then there is a high probability that their child will experience the same thing.
Permanent teeth
The change in the primary bite begins in children aged 5-6 years. By this time, the roots of baby teeth begin to dissolve and tooth mobility appears.
- At this age (5-6 years), the lower front incisors are the first to be replaced. In parallel with them, at about 6 years of age, the first permanent chewing teeth appear. Often their appearance is not even noticed, since they erupt behind the milk teeth.
- At 6-7 years old, the upper front incisors are replaced
- At 7-9 years of age, the baby teeth will fall out and be replaced by permanent lateral incisors.
- At the age of 9-11 years , the fourth and fifth milk teeth (molars) will be replaced by the 1st and 2nd premolars.
- The last ones, at the age of 11-13 years, will be replaced by permanent teeth - fangs.
- By the age of 12-13, all baby teeth will be replaced by permanent ones and the child’s mouth now has 24 teeth. Oral hygiene often suffers at this age. This is due to adolescence. Carise especially often affects the fissures (grooves) of the sixth teeth - molars. The process happens very quickly and often develops into pulpitis! Therefore, it is important to pay attention to caries prevention. A good way to protect the fragile enamel of permanent teeth is by sealing fissures and maintaining some professional hygiene. and, of course, following some rules.
- At 13-14 years of age, the second molars (seventh teeth) will erupt.
- And already at the age of 18, and sometimes later, wisdom teeth appear.
In order to keep your teeth healthy and straight, we recommend that you come for a preventive examination to the dentist every 6 months and visit the orthodontist at the ages of 6, 12 and 18 years.
Problems that arise during teething in children
During the teething process you may encounter the following problems:
- Late or early appearance.
Most often, early teething can occur with the lower central incisors. Sometimes a child may already be born with them.
Late teething is possible due to poor nutrition of the child, as well as past illnesses and concomitant chronic pathologies.
- Violation of the order and pairing of teeth eruption.
It is also possible that one or more teeth are missing from the dentition. This situation is possible due to the death of the embryos during the prenatal period of the baby’s development.
- Increase in temperature during teething.
Permissible deviations from the norm
Most pediatricians and dentists are of the opinion that the normal deviation from the periods given in the table is 6 months. A delay within these limits is a physiological phenomenon and should not be alarming.
That is, until the age of one year, adults do not need to sound the alarm. When there are no signs of gum swelling before eruption by 12 months, it is recommended to consult with specialists and undergo an examination.
READ ALSO: What are the signs of teething in a 4 month old baby?
Possible causes of irregular teething schedule
The deadline is considered violated when it deviates from the norm by more than 6 months. If there are still no teeth at 8 months, this cannot be considered a pathology. There are two forms of such deviation - early eruption (acceleration) or later. The reasons for such violations of the norm are different; most often they are associated not with pathology, but with the genetic characteristics of the body.
READ ALSO: How many months do the first teeth appear: approximate appearance diagram
Teeth erupt prematurely
There are cases when a child is born with teeth; they are called neonatal. In the old days, people were afraid of such children and attributed supernatural abilities to them. In fact, there is nothing special about this, because the baby’s teeth are formed in the womb (we recommend reading: what to do when the baby is teething?). He is born with the germs of teeth hidden in the soft tissue of the gums. In some children they erupt prematurely. Neonatal teeth are soft and mobile and do not need to be removed. If it is removed in infancy, another milk “brother” will grow in its place, and dental replacement will still take place on time. Early teething indicates the child’s acceleration, accelerated physical development, and does not threaten him in any way.
What should parents do?
Parents need to take into account the standards given above. If the baby is only eight months old, there is no need to sound the alarm. There is no need to worry if a one-year-old child has only 7 teeth instead of eight or only 2. If they have not appeared at all by the age of one year, you should proceed as follows:
- Visit a pediatrician and draw his attention to the current situation. The doctor will most likely order an examination of the baby.
- The results of blood, urine, and other samples taken will help the doctor determine the cause of the delay, which may indirectly indicate some pathologies in the child’s body.
- If the doctor suspects anomalies of intrauterine development, it is recommended to take an x-ray from a pediatric dentist. It will show whether the child has the beginnings of baby teeth.
- If no abnormalities are detected in the baby, then these are his personal physiological characteristics.
- To speed up the maturation of bone tissue, your pediatrician may prescribe vitamin D.
- Parents can promote teething themselves if they gradually give the child solid food (a slice of carrot or apple). The baby's body will receive a signal that it already needs an organ to chew food.
The appearance of the very first teeth can be painful for the baby. He is worried, does not sleep, cries all the time, his gums are swollen, and his temperature may rise. What should parents do about this? Adults should take this calmly and help the child with the following actions: