Teething is a process characterized by the axial movement of teeth from a non-functional position (from the bone jaw tissue) to a functional position (on the surface of the alveolar process and gums). Most often, the formation of a temporary bite causes a lot of inconvenience, not only to the baby, but also to his worried parents. In this article from the “Pediatric Dentistry” section, we will try to figure out in what order baby teeth erupt, and what symptoms accompany the development of this process.
Teething: sequence and timing
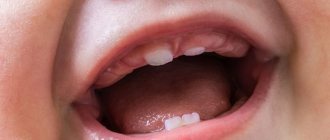
Normally, teething in babies occurs according to the scheme below:
- central incisors: at 6 months. – in the lower dentition, at 8 months. – on the upper jaw;
- lateral incisors: at 10 months. – in the top row, at 11-13 months. – on the lower jaw;
- first molars (at one year of age);
- canines in the upper row (1 year 4 months);
- canines in the bottom row (1 year 6 months);
- second molars on both jaws (2 years).
The timing of the appearance of the first teeth can vary under the influence of many factors, including:
- toxicosis during pregnancy;
- the presence of Rh conflict;
- prematurity;
- receiving intracranial injury during childbirth;
- infectious diseases;
- congenital hypothyroidism;
- rickets;
- pathology of the pituitary gland;
- neonatal sepsis;
- refusal to breastfeed the baby;
- noticeable weakening of the immune system.
It has been proven that in first-born children, teething occurs much earlier than in infants born at a later time. Boys' first teeth appear later than in girls, while in children of old-time mothers - significantly earlier than in babies born to young parents.
Galvanic syndrome
This is the case when physics interferes with physiology. Painful sensations are caused by microscopic current discharges, which have an extremely unpleasant effect on the vulnerable mucous membrane of the mouth. The syndrome occurs due to the fact that in your mouth there are fillings and other dental structures that contain many metals and alloys that are widely used in modern dentistry. An artificial tooth contains a lot of conductive materials and as a natural result: the current irritates the delicate mucous membrane, which leads to the development of inflammation, and this process can spread further to the throat. Eliminating this problem is quite simple, although it is associated with material and aesthetic losses. It is necessary to remove the current conductor - the dental structure. Experience shows that the pain disappears almost instantly, although the inflamed tissues will need time to recover. Well, there is a need to replace the removed structures. Usually, in this case, the doctor prescribes you a course of restorative immunotherapy to minimize all the negative effects of irritants. And problems with missing teeth will be solved by ceramic materials. They are beautiful, natural and have no problems with conductivity.
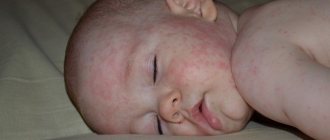
Teething symptoms
There is an opinion that the appearance of the first teeth is accompanied by the development of a whole complex of pathological processes (fever, the appearance of a rash, abnormal stool, vomiting, convulsions, etc.). In fact, the formation of a temporary bite is a natural process that is not characterized by the symptoms described above. Pathologies detected during the teething period are most often manifestations of infectious diseases or a consequence of changes in diet.
In particular, factors that can lead to the appearance of unpleasant symptoms include:
- introduction of artificial complementary foods;
- hypovitaminosis;
- acute viral infections;
- stomatitis;
- tonsillitis;
- runny nose;
- otitis;
- vaccination, etc.
The true symptoms of teething are:
- hyperemia and gradual swelling of the gums;
- the appearance of a small bluish hematoma on the gum tissue;
- slight bleeding from the gums;
- wet cough;
- mild itching caused by mechanical irritation of sensitive nerve fibers in the gum tissue;
- increased salivation;
- various somnological disorders;
- sharp deterioration in appetite;
- tearfulness, capriciousness.
The danger of redness of the throat during this period
During teething, the baby's body weakens and becomes vulnerable to pathogenic bacteria or colds.
When a baby is teething, the child endlessly puts various objects into his mouth, which are not always sterilely clean. It introduces an infection and hyperemia of the tonsils occurs (tonsillitis, pharyngitis, sore throat occur), this is a very dangerous disease for such young children.
If some symptoms intensify and last more than 2-3 days (fever, red sore throat, runny nose with yellow or green discharge, cough or wheezing in the chest), you should consult a pediatrician.
Redness in the throat of a baby may be a sign of diseases:
- mechanical, thermal damage;
- tonsillitis;
- pharyngitis;
- laryngitis;
- tonsillitis;
- allergic reaction;
- ARVI;
- acute respiratory infections;
- diseases of the stomach, esophagus;
- problems with the nasopharynx.
First aid for teething
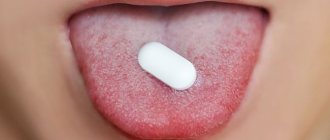
When baby teeth appear, the baby may require not only parental care, but also medical attention. The dentist may recommend that parents use anesthetic dental gels and treat the affected areas of the gums with decoctions of sage, oak bark or soda solution. If the pain is severe, the baby may be prescribed paracetamol, ibuprofen and other systemic painkillers.
To ease the discomfort that a child experiences when teething, it is necessary to use teethers - specialized devices made of rubber or plastic that the baby can bite and gnaw on without risking damage to the soft gum tissue. In addition, it is advisable to regularly massage the child’s gums with a finger wrapped in a clean, damp bandage.
Wisdom tooth is cutting and gums are swollen
Pain and slight swelling can be physiological and caused by the impact of sharp bumps on the soft gum tissue. They can also be a symptom of a pathological process that develops due to lack of space for the normal eruption of the eighth tooth. As a result, the G8's growth is going in the wrong direction. A hood is formed over the crown, under which microparticles of food that cannot be removed by traditional hygiene methods fall, and an inflammatory process develops.
What to do if your wisdom tooth is cutting out and your gums are swollen? If your gums or cheeks are swollen, you need to go to the clinic.
Intense pain and tumor growth on the gums can signal various pathological processes:
- pericoronitis;
- purulent inflammation, abscess, phlegmon;
- periodontitis;
- granuloma, cyst.
If you have a problem similar to that described in this article, be sure to contact our specialists. Don't diagnose yourself!
Why you should call us now:
- We will answer all your questions in 3 minutes
- Free consultation
- The average work experience of doctors is 12 years
- Convenient location of clinics
Single contact phone number: +7
Make an appointment
There are often situations when a wisdom tooth is cut and the cheek is swollen. This usually happens if the inflammatory process begins to spread to soft tissue. A swollen cheek is a sign of the progress of purulent inflammation, and it is dangerous to further delay contacting a periodontist. In most such cases, the “eight” will have to be removed.
Caring for emerging teeth
Teething is an absolute reason for making the first visit to the pediatric dentist. During the consultation, the doctor identifies all deviations in the structure of the child’s dental apparatus, assesses the condition of the frenulum of his lips and tongue, draws up a dental care plan and a plan for preventive visits to the dental clinic.
It is advisable to brush emerging teeth twice a day. Initially, you should use a baby silicone brush or a small piece of gauze without toothpaste for cleaning. A regular toothbrush can be used when the child is one year old, and toothpaste when he reaches two years of age. In addition, it is important to pay attention to the process of enamel mineralization. In particular, it is necessary to limit the consumption of sweets and include foods enriched with calcium, phosphorus and ascorbic acid in the baby’s diet.
Treating periodontitis correctly
Periodontitis is an inflammatory process in the gum surrounding the tooth. It can lead to weakening of the ligamentous apparatus of the tooth and its loss. We will lose a perfectly healthy tooth due to gum problems. Moreover, such inflammation is extremely painful and dangerous. The reason for its occurrence is due to changes in our diet. The food has become softer, there is no need to put stress on the teeth when chewing it - and this is the result. The teeth have weakened. Urgent assistance from a periodontist is needed, who will thoroughly clean the subgingival pockets of stone, plaque and infection, and place medications in the cavities affected by the infection. Usually this is quite enough to quickly improve the situation. To completely eliminate relapses of the disease, it is extremely important to regularly remove tartar and plaque from the surface of your teeth. Advanced cases also require taking antibacterial drugs.
Common symptoms of a seizure
What should parents pay attention to in order to contact a specialist in time and avoid dangerous complications? Convulsions in children under 1 year of age manifest themselves as follows:
- trembling of the chin, movements of the jaw, as if the baby was chewing something;
- twitching of eyelids, facial muscles;
- frequent eye rolling;
- rhythmic movements of arms and legs;
- constant twitching of the limbs during sleep;
- disturbance of the rhythm of heart contractions and respiratory movements (up to respiratory arrest);
- hiccups and constant yawning due to oxygen deprivation.
Convulsions may be accompanied by nausea and vomiting, and in premature babies - sharp loud cries. The appearance of seizures is provoked by excessive motor activity in children.
Other manifestations of convulsive syndrome include bluish skin, fever, and loss of consciousness.
Clinical manifestations of different types of seizures
Different pathologies are characterized by a variety of muscle contractions. Seizures are classified into the following types:
- Small ones. They manifest themselves in the form of weak twitching of the limbs, blinking, trembling of the eyelids, and facial movements. Minor seizures are often not noticed by parents.
- Tonic. Characteristic of premature babies. They are manifested by pronounced tension in the muscles of the body, throwing back the head. Respiratory cessation may occur due to spasm of the airways.
- Clonic. They may affect one or more muscle groups, depending on this they are divided into:
- focal, or focal (occur in one area of the body);
multifocal, or multifocal (spread to several parts of the body);
- generalized (muscles of the whole body are involved).
- Myoclonic. Manifested by convulsive twitching of the muscles of one or more limbs.
- Febrile. Triggered by hyperthermia (high temperature).
With clonic convulsions, the child loses consciousness, and blueness (cyanosis) of the skin is observed.
Young children may experience convulsive twitching when falling asleep or during sleep. If they are not accompanied by specific symptoms and elevated body temperature, then they are considered safe and are regarded as the body’s reaction to the formation of the nervous system and the development of its activity.
If a convulsive attack develops, when breathing stops and consciousness is impaired, the child needs emergency medical care.
When does a child start teething - table
From 4 to 7 months is the age when most children develop their first teeth. The sequence of their eruption is visible from the table.
| Name of teeth | Period of eruption, months. | |
| 1. | Incisors (central and lateral) | 4-12 |
| 2. | First molars | 12-19 |
| 3. | Fangs | 18-24 |
| 4. | Second molars | 24-32 |
The appearance of all 20 baby teeth occurs by the age of 3. But this process is individual, so small deviations in one direction or another should not cause anxiety in parents. If you are still concerned about early or late teething, then check this point with your pediatrician.
Factors influencing the timing of eruption:
- the nutritional pattern of the expectant mother;
- water quality;
- baby food ration;
- climatic living conditions;
- heredity.
There is usually nothing wrong with teething. But still, most children at this time experience discomfort and become restless.
Principles of seizure therapy
Convulsive conditions in children require close monitoring by neurologists. Treatment of seizures is carried out in an inpatient department. It is aimed at normalizing metabolic processes in the child’s body and eliminating pathological processes in the brain. Drug therapy is selected for each child individually and depends on the type of seizures and the cause of their occurrence.
If a generalized (full-blown) seizure occurs, it is necessary to call an ambulance, since the child must be given sedatives and anticonvulsants. Before the doctors arrive, the baby should be undressed and freed from diapers. If the attack drags on, the baby is hospitalized in the intensive care unit for further emergency measures.
Unfortunately, even complex therapy does not always guarantee complete recovery, but timely contact with specialists can prevent complications and reduce the duration of the rehabilitation period.
How to avoid developing seizures: preventive measures
Recommendations for preventing seizures in your baby include the following:
- Even before the birth of the heir, the mother must take care of his well-being. To reduce the risk of developing convulsive disorders in the unborn child, the gynecologist prescribes folic acid supplements to the woman (2-3 months before the expected day of conception).
- A pregnant woman should protect herself from exposure to infectious and other negative external factors.
- During pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is contraindicated to take medications without a doctor's prescription.
Convulsive syndrome is a dangerous condition for the health and life of children that requires the help of competent specialists. To detect pathology and avoid irreversible complications in your baby, contact the Edkarik clinic in Kaliningrad. A pediatric neurologist will carefully examine the child, prescribe a full range of necessary examinations and, based on their results, select adequate treatment.
Diagnosis of seizure disorders in children
If convulsive twitching is not accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the child’s well-being, they can go unnoticed by his parents for a long time. In addition, newborns experience twitching of the limbs during sleep, various movements of the arms and legs. Alarming symptoms require consultation with a neurologist and a thorough examination of the body.
Electroencephalography is used to study brain activity, but minor seizures are not detected on the EEG.
For the purpose of additional diagnostics to identify the cause of convulsive syndrome, the following is indicated:
- CT scan of the brain;
- examination of cerebral vessels (angiography);
- carrying out blood tests for sugar, the content of trace elements in it, etc.