First signs
It is advisable to recognize the onset of teething in a child in time in order to be able to provide him with the necessary help. As a rule, symptoms of the upcoming appearance of the first tooth in a baby appear within a few days - in most children this period lasts up to several days and ends with the eruption of the outer shell of the gums.
Parents can recognize that their baby is starting to teethe by the following signs:
- The appearance of sudden changes in the child’s behavior: sleep disturbance, irritability, crying, refusal to take the breast or pacifier;
- The formation of increased salivation, often accompanied by the appearance of rashes around the baby’s mouth, chin, and chest due to excessive saliva;
- At the site of tooth eruption, the gums swell and become swollen;
- The child bites everything that gets into his hands, trying to relieve the irritating itching that appears in the gums.
When teeth start cutting
There is no exact answer as to what time a child’s teeth are cut – the timing varies from person to person. However, you can focus on the average, standard periods of eruption approved by WHO:
- the lower incisors appear at 6–7 months;
- upper – at 7–8 months;
- upper lateral incisors – at 8–9 months;
- the lower ones are closer to a year.
According to the standard, a one-year-old child must have eight baby teeth.
From one year to one and a half years, the child acquires larger teeth - upper and lower molars, and from fifteen to twenty months - upper canines, which are also called “ocular.” The fact is that the optic nerve runs next to them, so these teeth are often more difficult for the child than others. Irritation of the nerve causes sharp pain and sometimes watery eyes.
It can be difficult even for a doctor to understand that the first teeth are being cut. After all, this process is often accompanied by an increase in temperature, changes in stool and mood, and refusal to eat.
What you need to know about deadlines
With the correct development of the newborn’s body, teething occurs at certain times according to the principle of pairing. Usually identical teeth erupt at the same time - this applies to pairs of central and lateral incisors and canines.
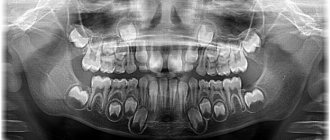
At birth, there are 20 follicles in both jaws of the baby - 10 for each jaw, which are the rudiments of temporary teeth. The newborn also has 16 permanent tooth buds. Another 16 primordia begin to form after birth.
The order of eruption of baby teeth:
Important:
Here are the average dates for teething in newborns. However, the development of each organism is strictly individual, so it is possible that these dates may shift in one direction or another in approximately 50% of cases. Therefore, do not panic if deviations from the given deadlines are insignificant.
There are cases when a baby was born with the first tooth. This makes breastfeeding much more difficult, so you need to get appropriate advice from your doctor.
With artificial feeding, there may be a delay in teething, while a breastfed baby's teeth erupt earlier in 10 cases out of a hundred. In addition, the delay in the eruption of baby teeth is influenced by the condition of the mother during pregnancy - for example, toxicosis, infectious diseases, stress, as well as diseases suffered by the baby.
Structure
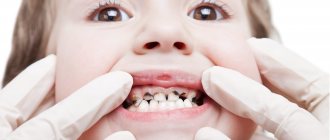
The structure of a baby tooth is significantly different from a molar tooth. Its enamel and dentin are thinner, their layers are 0.1-1 mm and 0.5-1.5 mm, respectively.
They are much smaller in size than molars, but the incisors are more convex in shape. Their root canals are wider, which increases the risk of bacteria entering and multiplying with subsequent inflammation.
The pulp of the front and chewing milk teeth in children occupies a larger volume than in the molar; on this topic, you can find many photos about the structure of a child’s jaw, what it consists of, and diagrams of the roots of the dentition in an adult and a child. In addition, children's teeth are characterized by a low degree of mineralization, and therefore are more vulnerable to caries. By the way, even adults sometimes have baby teeth, but usually no more than one.
What should you pay attention to when teething?
The above symptoms of the onset of teething are characteristic of almost all infants. However, some children have additional symptoms that need to be taken seriously:
- Temperature increase;
- Formation in the mouth of small watery blisters with cloudy or clear liquid;
- Increased redness and inflammation of the gums;
- Inflamed oral mucosa, accompanied by the formation of slight erosion.
In a healthy baby, when teething, contrary to popular belief and the advice of “experienced” relatives, the temperature does not rise. If this happens, it means that the child’s body is simultaneously exposed to some kind of inflammatory disease.
Most often, the listed signs indicate the development of a viral form of stomatitis or ARVI, which is not surprising given the child’s desire to put everything in his mouth. Therefore, you need to show the child to the doctor. If the pediatrician does not detect signs of an acute viral infection, take your baby to a dentist so that he can determine what form of stomatitis your child has caught and prescribe adequate treatment. Unfortunately, pediatricians are most often incompetent in this situation.
Treatment.
Providing QUALITY dental care to children from the moment the first tooth appears and up to 3 years of age is LIMITED to physiological reasons: mild excitability, restlessness, fear of unknown manipulations in the oral cavity. An attempt to cure teeth by talking to a child or holding him by force in his arms ends with POOR-QUALITY treatment, as a result of which various local complications can develop.
REMEMBER: FORCED TREATMENT WITH CHILDREN RESTRAINT CAUSES IRREPAIRABLE PSYCHOLOGICAL TRAUMA TO THE CHILD!
Like
Possible complications
"Surprises"
The problems that nature presents when infants have their first teeth do not end with the listed troubles. Sometimes other complications are possible:
- Formation of hematomas.
A bluish-colored bubble swells on the gum. Most often it resolves over time, but sometimes if the blister is too large, surgery is required. The doctor makes a small incision on the gum to remove the bloody fluid.
- The appearance of vomiting.
This may be caused by excessive salivation. However, if vomiting is accompanied by diarrhea and fever, these may be signs of rotavirus, so it is necessary to urgently show the child to the pediatrician.
- Cough reflex.
With normal teething it does not happen. The cause of the cough may be excessive saliva secretion, which causes the baby to choke.
If a runny nose appears, take your child to the doctor
- teething probably coincided with a cold.
Important:
If your baby is experiencing fever, diarrhea and vomiting during teething, take this seriously. The cause of their appearance cannot be teething. It is urgent to call a pediatrician, since the baby’s body is at risk of intoxication due to a developing infection.
How to relieve painful sensations
During this period, the baby's growing body undergoes important changes, and the support of adults and their care can significantly alleviate this condition. Firstly, take your child in your arms more often so that he feels supported; tactile contact will further calm and distract him. Secondly, make sure that he drinks the required amount of water - usually the baby begins to refuse the bottle, just feed him from a spoon.
You can put the baby to your chest to calm him down, do not forget about massaging the gums, which is best done using a special attachment on your finger.
What to use
If basic techniques do not save the situation, you should resort to auxiliary options. If the pain is very intense, try local anesthesia. For this purpose, special gels containing benzocaine/lidocaine are suitable, which are applied directly to the gums several times a day. They have a short-term effect and are safe for a small organism, but it is still recommended to consult a specialist first.
Preparations based on ibuprofen or paracetamol are good for relieving fever. You can take it several times a day, the drugs fight high fever and partially relieve pain.
But you shouldn’t ignore folk recipes either; it will be useful to make infusions of mint, chamomile, lavender, and sage. The resulting substance is impregnated with a cotton pad, which must be used to wipe soft tissues. You can also replace the infusion with a soda solution; this will require a glass of boiled water and 1 teaspoon of baking soda.
Additional Methods
At an early stage of life, it is especially important to support the child, since any load on the small body is felt very acutely. A special reaction to teething requires a special drug, for example, Dentokind copes well with all symptoms - it provides analgesia, an anti-inflammatory, calming effect, and sleep stabilization.
To satisfy your child’s craving to put various objects in his mouth and at the same time alleviate his condition, buy a special rubber ring, which is placed in the freezer for a short time for cooling and given to the child.
Perhaps the baby will not like such a ring, then watch what he likes. The main thing is that the objects do not have sharp corners and cannot damage the gums, for example, it could be a bagel or a bread crust.
Try to distract your child as much as possible, switch his attention to a game or an interesting cartoon. Daily walks will also help if you don’t have a fever and your condition allows it.
Category Children Published by Mister stomatolog
How to relieve your baby's condition with medications
If your baby is bothered by sore gums and begins to behave restlessly, you can give him a mild pain reliever that is appropriate for his age.
For the youngest, it is better to use candles, and older children can be given a special suspension. These drugs, in addition to a sedative effect, have mild antipyretic properties. In addition, pharmacies sell a special anesthetic gel, a small amount of which should be applied to the surface of the inflamed gum. However, you should not get carried away with such gels, since most of them promote increased salivation and also cause numbness, which makes the baby feel uncomfortable.
Important:
Before purchasing one or another medication to alleviate a child’s teething condition, you should definitely consult a pediatrician to rule out side effects.
How many teeth should a child have?
By the age of three, a child usually already has a full set of twenty primary teeth, and until about 6 years old, their number remains unchanged. Adolescents aged 13 to 18 years should normally have from 28 to 32 molars (depending on the presence of eights, which may erupt after 21 years or not appear at all).
Factors affecting tooth growth
The speed of formation of a mixed bite depends on several circumstances:
- baby's genotype;
- performance of the thyroid gland;
- gender;
- severe infectious and viral diseases suffered in the past;
- duration of natural feeding;
- the presence of congenital diseases.
You also need to monitor the period of eruption of molars. They should come out to the surface of the gums only after the milk unit falls out. Otherwise, a mandatory visit to the dentist will be required. Early loss of milk elements is also undesirable, as this negatively affects the proportions of the baby’s jaw and his bite in the future.