The palatine tonsils are an organ of our immune system. They are designed to protect against pathogens. In a healthy state, the tonsils cope with this function, but if the tonsils become inflamed, they themselves become a source of infection. Inflammation of the tonsils is called tonsillitis. The disease can occur in acute and chronic forms. Treatment of tonsils should be carried out under the supervision of an ENT doctor. What treatment should be carried out when your throat hurts and your tonsils hurt, read the new article.
The palatine tonsils (or tonsils) are an organ of the human immune system that protects the body from the effects of pathogens. They are located in the throat at the very entrance to the respiratory tract and, like guards, are the first to meet the enemy. How do the tonsils fight pathogenic flora? It’s very simple - the tonsils produce cells of the immune system - leukocytes, which, when an “invader” is detected, surround the enemy and destroy him.
The main function of the tonsils is protective. Their task is to pass bacteria and viruses further into the trachea and lungs. Healthy tonsils cope with this successfully. But if for some reason a person’s immunity is too weak, the tonsils’ own strength is not enough to cope with the enemy - inflammation of the tonsils occurs. This condition is accompanied by acute sore throat and other unpleasant symptoms, which we will discuss in detail below.
If high-quality treatment of the tonsils of the throat is not carried out during this period, the patient may face serious health complications: pathological changes will affect not only the throat and tonsils, but also other human organs and systems, for example, the heart and kidneys.
What to do if your tonsils hurt in your throat will be discussed in our new article.
Symptoms:
- red, swollen tonsils with white or yellowish coating or streaks;
- a sore throat;
- difficult and/or painful to swallow;
- fever (temperature above 38.0);
- cervical lymph nodes are enlarged;
- hoarse or hoarse voice;
- headache;
- stiff neck muscles;
- abdominal pain (especially in young children).
In infants:
- drooling due to pain in swallowing;
- anxiety;
- refusal to eat
- With chronic tonsillitis, your breath may smell bad.
Causes of blood appearing on the tonsils
Blood on the tonsils is an alarming symptom that should not be ignored. It may appear against the background of existing inflammatory diseases of the tonsils, or for no apparent reason. It is possible to determine exactly whether this symptom is dangerous only after examination by an otolaryngologist. At home, accompanying symptoms will help suggest a diagnosis.
Chemical burn as a cause of bleeding
You can burn your tonsils by accidentally overdosing the dosage of medications when rinsing
Blood on the tonsils can occur due to a chemical burn. You can get it at home if household chemicals and other irritating substances accidentally come into contact with your tonsils.
Chemical burns are most often work-related injuries, but can also occur as a result of self-medication for sore throat.
Quite often, damage to the mucous membrane occurs when gargling with iodine, vinegar or other potent substances when the recommended dosages are exceeded.
A chemical burn is a reason to immediately go to the hospital. Chemicals deeply affect the mucous membrane, causing deep erosions and non-healing ulcers to form at the burn site.
Thermal burn
If blood comes from one gland after a burn with hot food or boiling water, we are talking about a serious injury. Thermal burn of the tonsils can also be caused by inhalation of steam, for example, due to home inhalations according to folk recipes.
As a rule, after receiving a burn, a person strives to immediately cool the affected area. Use cold water or pieces of ice. This is effective for skin burns, but has a different effect on the mucous membrane of the tonsils, resulting in blisters and bleeding erosions.
Thermal burn itself is not dangerous, but only if treated in a timely manner. It is necessary to consult a doctor who will treat the tonsils with a wound-healing agent and prescribe adequate therapy for speedy tissue restoration.
Mechanical damage to the tonsils
Children constantly put everything in their mouths and can easily injure their mouth and throat.
If there is bleeding from the tonsils, the cause may be mechanical damage to the mucous membrane. This happens due to:
- eating hard foods that scratch the tonsils;
- getting a foreign object into the throat;
- attempts to independently rinse the lacunae of the tonsils;
- removing plaque from the tonsils using improvised objects.
No one is immune from damage to the tonsils by solid food. Usually the cause is snacking on the go and hastily eating crackers and other solid foods.
Note! Those with a sweet tooth can be injured by regular candy, whose sharp edges can scratch the throat and tonsils.
Blood on a child's tonsils may be due to the fact that young children like to put small objects into their mouths. Careless movement can cause injury to the tonsils. Caution must be exercised with children - before diagnosing mechanical damage to the throat by a foreign object, symptoms of tonsil disease and other causes should be excluded.
Perhaps the most common cause of bleeding from the tonsils is an attempt to independently clean the lacunae professionally. A person purchases a special syringe with a curved tip, inserts the tip into the lacuna to remove the plug, and as a result scratches the delicate mucous membrane. Bleeding from the tonsils is often observed when trying to remove plaque, characteristic of chronic tonsillitis, with improvised objects, such as a cotton swab.
Blood due to tonsillitis
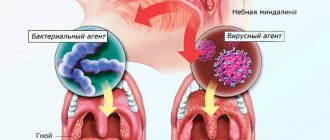
Acute tonsillitis can cause bleeding from the tonsil. This occurs due to swelling of the tissue of the tonsils and an acute inflammatory process, during which small capillaries are damaged. If there is bleeding from the tonsil, you must first rule out acute tonsillitis. Symptoms of the disease:
- severe pain in the throat when swallowing;
- hyperemia and swelling of the throat;
- high body temperature;
- symptoms of intoxication.
In chronic tonsillitis, drops of blood may also be found on the tonsils. This is due to plugs in the gaps. The deposits in the recesses of the tonsils harden over time. During meals, they can move due to the pressure of hard food, as a result of which dense deposits scratch the mucous membrane of the lacunae, causing bleeding.
Necrotizing tonsillitis is especially dangerous. This is an acute infectious process caused by pyogenic bacteria, which lead to necrosis of the affected tissues. As a result, blood appears on the tonsils, a gray-green coating is observed, under which large ulcers are identified. The disease occurs in an acute form and is accompanied by high body temperature.
Peritonsillar abscess
The disease is accompanied by a bright fiery throat color
The disease is an advanced acute bacterial tonsillitis and is manifested by the formation of a large cavity filled with pus. The abscess occurs in a severe form - cutting and tearing pain, body temperature above 39 degrees, severe symptoms of intoxication. If the disease is not treated, after 5-6 days the abscess will open on its own. As a result, a wound is formed from which pus and blood ooze.
Opening an abscess is very dangerous, as it can lead to blood poisoning (sepsis) if purulent masses enter the bloodstream. If you suspect an abscess, you should consult a doctor. Urgent hospitalization is indicated when an abscess is opened.
Blood after tonsillectomy
Bleeding after removal of tonsils or tonsillectomy is quite common. Moreover, if on the first day after the operation the appearance of droplets of blood is considered normal, then blood a few days after tonsillectomy is a reason to immediately consult a doctor.
Important! The risk of bleeding continues for 14 days after surgery.
Bleeding from the tonsils after a patient has had their tonsils partially removed may indicate an infection. Since the tonsils are very sore in the first days after surgery, a person may not notice a deterioration in well-being. Infection of a postoperative wound is very dangerous and requires urgent medical attention.
Malignant neoplasms
Another reason why blood bleeds from the tonsils may be malignant neoplasms of the tonsils and larynx. This disease does not have any associated symptoms and can only be diagnosed by a doctor.
If blood appears, and other causes have been excluded, you should undergo a comprehensive examination by an otolaryngologist in order to exclude benign and malignant neoplasms.
Candidiasis of the tonsils
A rare cause of blood on the tonsils is candidiasis or thrush. This is a disease of a fungal nature, manifested by the formation of a thick yellow plaque on the tonsils. Under the plaque, which is a waste product of yeast, ulcers form that can bleed. Candidiasis can only be diagnosed by performing a smear.
Complications of tonsillitis
- Labored breathing.
- Sleep apnea (holding your breath during sleep).
- Spread of infection to the tissue near the tonsils (peritonsillitis), peritonsillar abscess - accumulation of pus behind the tonsil.
- Acute cervical lymphadenitis is inflammation of the cervical lymph nodes.
Streptococcal tonsillitis can cause complications such as:
- acute rheumatic fever, affecting the joints, heart and other organs;
- glomerulonephritis (inflammation of the kidneys, which can lead to serious consequences, including kidney failure).
Treatment with antibiotics significantly reduces the likelihood of complications after streptococcal sore throat.
When is it necessary to remove tonsils?
If bleeding is not observed for the first time and is caused by regular damage to the tonsils due to pronounced proliferation of the organ’s lymphoid tissue, a decision is made on complete or partial resection of the tonsils. In this case, the operation poses less of a threat to health than regular damage and the constant risk of infection of the organ.
Removal is indicated if a malignant process is suspected. Lymphoma of the pharyngeal ring (cancer of the tonsils) is a fairly rare, but very dangerous cancer pathology with a high mortality rate.
Diagnosis of tonsillitis
- For tonsillitis, the doctor will examine the child's throat, as well as his ears and nose, where there may also be inflammation.
- The doctor will examine the child's skin, since streptococcal sore throat sometimes causes a specific rash. This is what is called “scarlet fever” - it is not some kind of separate disease, but a sign of damage to the body by streptococcus.
- The doctor will feel the cervical lymph nodes - as a rule, with tonsillitis they swell.
- The doctor will feel the spleen to distinguish a sore throat from mononucleosis, which also causes swollen lymph nodes.
- The streptococcal test is a simple and accurate way to distinguish streptococcal tonsillitis from viral tonsillitis. The doctor takes a scraping from the child’s throat and within 24-48 hours the result is ready.
- In some cases, a general blood test may be needed, the results of which can also indicate the viral or bacterial nature of the disease. It is usually taken if the streptococcal test is negative, but the course of the disease leaves the doctor in doubt.
About the clinic
Euromed Clinic is a multidisciplinary family clinic in the center of St. Petersburg.
- Calling a doctor to your home
- 24/7 therapist appointment
- Tests, ultrasound, x-ray
- Whole body diagnostics
- Hospital and surgery
- Vaccination
Find out more about the clinic
Diagnostics
The first thing to do if you find blood from the tonsil is to consult a doctor. Even minor mechanical damage to the tonsil is fraught with dangerous complications.
The otolaryngologist will perform a pharyngoscopy and interview the patient. You may also need ultrasound diagnostics, a throat smear, a general and biochemical blood test. To establish the cause, it is important to take into account the medical history, as well as recent surgery or other manipulations of the tonsils, for example, washing the lacunae. Based on the results of the examination and examination, the doctor will select the optimal treatment regimen.
Treatment of tonsillitis
The child should be provided with:
- peace and the opportunity to sleep as much as he wants;
- Drink plenty of fluids to relieve sore throats and prevent dehydration;
- air humidification;
- a sore throat can be relieved by both warm drinks and cold ice cream, especially popsicles;
- for a sore throat, it helps to gargle with a solution of table salt and soda - a teaspoon of salt and a small pinch of soda per 250 ml of warm water;
- Children over 4 years old can be offered lozenges for sore throats. Do not give candy to small children - they may choke;
- do not smoke when your child is sick, avoid strong odors that irritate the throat;
- A sore throat and fever can be relieved by medications containing paracetamol and ibuprofen. Don't give children aspirin; in rare cases, it can cause deadly Reye's syndrome.
Confirmed bacterial tonsillitis (usually streptococcal tonsillitis) is treated with antibiotics. It is dangerous to interrupt or stop the course because it increases the likelihood of infection spreading to the joints, heart, kidneys and other organs. Continue taking antibiotics even if your symptoms are completely gone.
Treatment methods
Therapy is prescribed by a doctor only after determining the root cause
What to do if there is bleeding from the tonsil - it depends on the cause of the bleeding. In case of acute infectious process (sore throat):
- rinse your throat with antiseptics;
- take antibiotics prescribed by your doctor;
- use antiseptic sprays and lozenges to reduce pain.
In this case, the blood is caused by inflammation and is only a symptom. Treatment is aimed at suppressing the bacterial infection.
In case of peritonsillar abscess:
- hospitalization is required;
- surgical opening of the abscess;
- taking antibiotics;
- gargling with antiseptic solutions.
Peritonsillar abscess is very dangerous and can be treated in a hospital setting. It must be removed surgically. The operation consists of cutting the abscess and draining the cavity to remove pus. Antibacterial therapy and symptomatic treatment are required. It is important to prevent pus from entering the general bloodstream and infecting the entire body.
In case of mechanical damage:
- eliminating the cause of bleeding in case of foreign object penetration;
- gargling;
- treatment of tonsils with a wound healing agent.
For severe injuries, it is recommended to use antibacterial agents, as there is a high risk of infection and the development of an abscess. Wound healing drugs are selected by a doctor, since they are not always necessary, because the mucous membranes are restored quite quickly.
For candidiasis of the tonsils:
- gargling with antiseptics;
- taking antimycotics;
- strengthening the immune system.
In case of fungal infection of the tonsils, it is necessary to take special medications, otherwise it will not be possible to defeat the causative agent of the disease and the disease will become chronic. Throat candidiasis can be diagnosed by analyzing a throat smear.
Blood in chronic tonsillitis: treatment methods
Bleeding from the tonsils in chronic tonsillitis is caused by hard deposits in the lacunae. First of all, professional cleaning of the gaps is carried out. The manipulation involves removing the plugs with a vacuum apparatus, followed by irrigating the gaps with an antiseptic or antibacterial agent that prevents the re-formation of plaque. To effectively get rid of traffic jams, a course of procedures is required.
Then a comprehensive treatment is prescribed - taking antibiotics, regular gargling, strengthening the immune system.
If conservative treatment is ineffective, complete or partial removal of the tonsils is indicated. To preserve the tonsils, cryodestruction is used. The method allows you to remove the source of infection and hypertrophied tissue, but does not affect the entire organ. The cryodestruction procedure involves applying liquid nitrogen to the tonsils.
Antiseptic treatment of tonsils
Before use, you should read the instructions for any individual contraindications and allergic reactions.
In case of bleeding caused by inflammation or mechanical damage to the mucous membrane, it is necessary to provide antiseptic treatment of the tonsils, otherwise there is a high risk of secondary infection. For this purpose, gargling and the use of special means are indicated.
For rinsing use:
- Furacilin solution;
- Chlorhexidine or Miramistin;
- salt and soda;
- iodine solution.
At home, it is preferable to use Furacilin, since this drug is an antibiotic. To prepare the solution, grind one tablet into powder and dissolve in a glass of water.
Gargling is done 4 times a day. Additionally, you can apply Lugol's solution to the tonsils - this will provide a long-term antiseptic effect.
What to do if there is bleeding after tonsil removal?
Bleeding after tonsillectomy is quite rare. This complication is typical only for an operation during which the tonsils were removed with a scalpel.
In the first week after removal of the tonsils, isolated drops of blood may appear, which is explained by mechanical damage to the tissue during chewing and swallowing food. This is explained by the fact that a wound remains at the site of the removed organ, which heals within several weeks. To avoid bleeding, in the first week you need to eat soft foods, giving preference to various purees.
If heavy bleeding occurs 7 or more days after surgery, a person should urgently seek medical help. The patient is hospitalized, the bleeding is stopped surgically. The patient must remain in the hospital for 3-5 days after the incident.
Why do tonsils become inflamed?
The tonsils themselves are not smooth, as they may seem externally. They have a porous structure and consist of winding channels (crypts) and depressions (lacunae). This is where the pathogenic microorganisms that the tonsils fight come from. In a healthy state, tonsils can cleanse themselves, removing dead bacteria and leukocytes from their thickness. But if a person’s immunity is weak, frequent inflammations lose their self-cleansing function - all this accumulates in the tonsil, forming purulent plugs.
Some patients mistake these white plugs on the surface of the tonsils for food debris, and do not receive quality treatment for the tonsils. But this is nothing more than a compressed infection that continues to maintain inflammation. That is why the patient has a sore throat during an exacerbation, the temperature rises, and bad breath appears due to traffic jams. Treatment of tonsils should be carried out efficiently and under the supervision of an otolaryngologist!
Inflammation of the tonsils is called acute tonsillitis, or tonsillitis. Prolonged inflammation, alternating with stages of exacerbation and remission, is called chronic tonsillitis.
Streptococci, staphylococci, pneumococci, anaerobic bacteria, and fungi can provoke an inflammatory process in the tonsils. In order to diagnose and begin to treat the disease in a timely manner, you need to be able to recognize the symptoms (and treatment should be carried out by a competent ENT doctor).