The powerful lymph nodes located around the pharynx cannot cope with the attack of the pathogen, so the body begins to produce antibodies that can find pathogenic bacteria, paralyzing their activity.
As a result, streptococci are defeated, but the child’s body produces so many antibodies that, in addition to foreign cells, the body’s own tissues, primarily the heart and joints, begin to suffer. Therefore, it is always better to entrust the treatment of sore throat in a child to a qualified doctor.
In 10% of cases, sore throat in children can be caused by Staphylococcus aureus, rarely pneumococcus, Haemophilus influenzae, chlamydia and fungal flora. Viral pathogens (adenoviruses, herpes virus) more often attack the body of children under 3 years of age.
How and why does infection occur?
Infection occurs by airborne droplets, from a sick person, by using shared utensils and eating contaminated food, as well as by a number of other factors:
- weakened immunity;
- hypothermia or consumption of cold foods and drinks;
- mouth breathing (for chronic adenoiditis, deviated nasal septum);
- irritation of the nasopharyngeal mucosa with a runny nose;
- recent viral diseases;
- inflammatory diseases of the ENT organs (sinusitis, sinusitis, otitis);
- caries and other oral infections.
Secondary tonsillitis in children can occur against the background of scarlet fever, diphtheria, mononucleosis, as well as blood diseases.
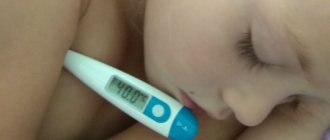
In any case, a sore throat develops rapidly, in a matter of hours, and is especially acute in children, accompanied by the main symptoms—a sore throat when swallowing and an increase in body temperature.
Causes of pathology
The infection is caused by group A streptococcus. A person can be either a carrier of the pathogen or an active source of infection. The greatest contagiousness is observed in the first 1-4 days of the acute period. 3 weeks after the onset of the disease, the likelihood of the infection spreading is reduced to zero. Up to 20% of the adult population are asymptomatic carriers of streptococcus. There is a seasonal dependence: the largest number of infections is recorded in the autumn-winter period against the background of acute respiratory viral infections, tonsillitis, and pneumonia.
Sore throat in children: forms and clinical manifestations
Depending on the nature of the change and the degree of damage to the tonsils, several forms of angina are distinguished.
Catarrhal sore throat
A mild form, characterized by enlargement and redness of the tonsils, as well as the absence of purulent lesions. The child feels dry mouth, a whitish coating appears on the tongue, and the cervical lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. In addition to a sore throat that gets worse when swallowing, the child feels a sore and burning sensation. The temperature rises to 38 degrees, children complain of weakness and headache.
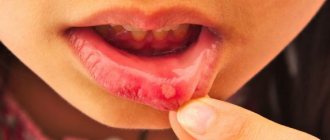
Follicular tonsillitis
A serious disease in which the tonsils become covered with purulent pinpoint follicles. On days 2-3, the ulcers open, leaving wounds that heal quickly. There is severe pain in the throat, radiating to the ear, making it difficult to swallow, children refuse to eat and drink. The lymph nodes are enlarged and painful when pressed lightly. Fever and chills are accompanied by a temperature of up to 40 degrees, vomiting, convulsions and fainting are possible.
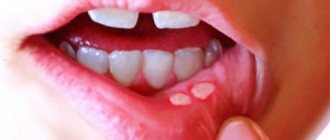
Lacunar tonsillitis
In the lacunae, between the lobes of the tonsils, islands of yellow purulent plaque appear, which tend to unite into wide purulent foci. The symptoms are similar to those of purulent follicular tonsillitis, but are more pronounced and are accompanied by severe intoxication of the body. It hurts the child to turn his head, his mouth opens with difficulty, which makes speech slurred.
Viral (herpetic) sore throat
Most often, the development of the disease is facilitated by vitamin deficiency and weakened immunity. The tonsils become covered with red blisters, which burst, leaving small ulcers in their place. In addition to a sore throat, symptoms are acute respiratory in nature: cough, runny nose, abdominal pain, indigestion, as well as stomatitis and conjunctivitis. Lack of timely treatment of herpetic sore throat in children can lead to serous meningitis.
Fungal tonsillitis
A relatively mild form of sore throat that occurs in children under 3 years of age. It is distinguished by a coating of white, curdled flakes on the tonsils and, with proper treatment, goes away within a week.
Description and symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
Chronic tonsillitis occupies a leading place among inflammatory diseases of the throat. Throat diseases reduce the quality of life and lead to complications. Chronic inflammation of the tonsils is often observed in children starting from 3 years of age and in young people.
Types of tonsillitis
- Acute tonsillitis (tonsillitis) is an infectious disease with local manifestations of acute inflammation of the components of the lymphatic pharyngeal ring, most often the palatine tonsils, which is caused by streptococci or staphylococci, less often by other microorganisms.
- Chronic tonsillitis is a long-term inflammation of the pharyngeal and palatine tonsils. Develops after a sore throat and other infectious diseases accompanied by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the pharynx (scarlet fever, measles, diphtheria), or without a previous acute illness.
There are two stages. Compensated and decompensated stages:
- The compensated stage is a dormant focus of infection. There is no visible reaction from the whole body, no repeated sore throats. The barrier function of the tonsils and the reactivity of the body are not impaired. The edges of the palatine arches thicken, cicatricial adhesions appear between the tonsils, plugs form in the lacunae of the tonsils, liquid purulent discharge forms, and the submandibular and cervical lymph nodes enlarge. One of the problems of the compensated form of tonsillitis is bad breath, which occurs as a result of the formation of plugs in the lacunae.
- During decompensation, frequent sore throats are a concern; complications of tonsillitis in the form of abscesses, inflammatory diseases of the ear and sinuses, as well as damage to other organs (heart, kidneys) are often observed. Exacerbation of chronic tonsillitis is also called tonsillitis.
Symptoms of chronic tonsillitis
- discomfort and pain when swallowing, especially in the morning;
- dryness, sore throat; sensation of a foreign body in the throat
- cough;
- bad breath;
- increased fatigue, weakness and sweating;
- decreased performance;
- low-grade fever 37.2-37.5°C
- deterioration of sleep;
- decreased appetite;
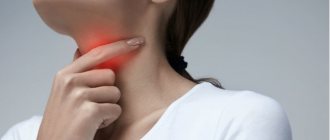
- pain in the cervical lymph nodes.
Causes that can lead to chronic tonsillitis
The following factors have a particularly strong influence on the chronicity of the process:
- Frequent sore throats, especially in the absence of adequate treatment;
- Impaired nasal breathing, which can be a consequence of both a deviated nasal septum and chronic rhinitis and sinusitis. If rhinitis is of an allergic nature, then it is advisable to do an allergen test and undergo appropriate treatment;
- Low body immunity.
Chronic tonsillitis develops due to a number of factors
- Intoxication - due to the absorption of bacterial toxins and products of chronic inflammation in the tonsils. Intoxication explains symptoms of chronic tonsillitis such as fatigue, weakness, headache, low-grade body temperature, etc.
- The formation of plugs in the tonsils irritates the nerve endings and causes moderate pain in the throat and heart area, cough, and bad breath. Nerve endings undergo degenerative changes, which can cause neurosis and other disorders of the nervous system.
- The body develops sensitivity to bacterial and tissue antigens - an allergy develops. Therefore, chronic tonsillitis is also of an autoimmune nature.
Chronic tonsillitis with complications can lead to functional disorders of cardiac activity, acquired heart defects. Chronic tonsillitis is associated with pathologies such as rheumatism, infectious arthritis, diseases of the urinary system, prostate gland, meninges, etc.
Features of the disease in children
Intensive development of the lymphoid ring begins in infancy - in the second year of life. Immediately after birth, the tonsils are underdeveloped and do not yet function fully. A feature of the tonsils in children 1-3 years old is deep lacunae, as well as narrow, densely branching orifices, which can extend to the capsule. Sometimes the lacunae turn sharply and extend under the integumentary epithelium instead of going deep into the tonsils. At the end of narrow passages there are characteristic expansions that contribute to the development of the inflammatory process.
A feature of younger age is hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue, which, along with an increase in the number of lymphoid follicles, leads to the growth of tonsils. The latter reach their largest size by 5-7 years. At this age, children are most susceptible to infectious diseases and most need protection from infections. Representatives of this age category are recommended to receive preventive vaccinations aimed at mobilizing lymphoid tissue to develop immunity.
The cause of hypertrophy of lymphoid tissue is the intensive formation of active immunity, which is accompanied by local production of antibodies in response to the penetration of an infectious agent. With age, by the age of 9-10, antibodies accumulate in the body, the immune system improves, which leads to age-related involution of lymphoid tissue. Part of it degenerates and is replaced by connective or fibrous.
The causes of childhood respiratory diseases are fungi, bacteria and viruses. If a child gets sick too often, the tonsils are regularly attacked, so the body does not have time to fully defend itself. This becomes the main reason for the development of chronic tonsillitis, along with incorrectly prescribed antibiotic treatment.
Chronic tonsillitis in a child turns into a constant source of infection, depleting the immune system. Quite often, the disease leads to serious complications, especially if timely help is not sought.
Symptoms
Unlike adults, in children the disease develops quickly, occurs in an acute form and is quite obvious. An obvious indication of chronic tonsillitis may be the following local reactions:
- redness of the tonsils;
- their increase, looseness;
- purulent discharge;
- enlarged cervical lymph nodes.
Frequent sore throats, bad breath, and discomfort during swallowing may also indicate the chronic nature of tonsillitis. Some patients experience sleep problems, headaches, and a subfertile temperature (37-37.5 °C).
Chronic tonsillitis in a pregnant woman
Symptoms of the disease in a pregnant woman are fever, general weakness, dry cough, sore throat, which is accompanied by a sensation of a foreign body. This is due to the fact that the tonsils withstand the attack of tonsillitis and respond to it with pain.
Not everyone knows that even a mild sore throat can harm the unborn child, as well as the woman herself. Sometimes the disease causes early miscarriage, and sometimes causes the development of late toxicosis, which negatively affects the development of the fetus. Since the presence of a chronic infection in the body weakens the immune system, a pregnant woman is at risk of developing other diseases.
Clinical studies have confirmed that chronic tonsillitis has repeatedly caused poor labor and premature birth, so women with this diagnosis are often recommended to have a cesarean section. Sometimes a disease that is not treated during pregnancy leads to the development of a heart defect in the child.
Causes of chronic tonsillitis in pregnant women
- sore throat, which has become a latent chronic form;
- hypothermia;
- deficiency of vitamins and nutrients;
- weakened immunity;
- problems with nasal breathing caused, for example, by a deviated nasal septum, polyps or adenoids;
- untreated caries;
- sinusitis.
To avoid undesirable developments, pregnant women are advised to eat well, avoid hypothermia, visit the dentist and generally monitor their health.
Why is chronic tonsillitis dangerous?
Regardless of the form of its occurrence, chronic tonsillitis can cause allergization and infection of the body. In the absence of medical control, the disease can lead to serious complications - frequent exacerbations in the form of a sore throat, recurring up to 6 times a year.
Another serious complication is phlegmon of the neck, which occurs against the background of severe forms of peritonsillar abscess. In addition, weakening of the tonsils leads to the penetration of infection into the underlying respiratory tract and the development of pharyngitis and bronchitis. In general, chronic tonsillitis either itself becomes a source of concomitant diseases or complicates their course.
An infection that has entered the body finds “weak” spots and can cause diseases of any of the systems - bronchopulmonary, urinary, cardiovascular. A chronic focus of infection has a negative effect on the blood coagulation system, metabolic and endocrine processes, the adrenal cortex, and the course of allergic conditions. Inflammation of the palatine tonsils causes epileptic attacks and aggravates the course of encephalitis and cerebral rheumatic vasculitis. The most dangerous is the decompensated form, which provokes changes in internal organs.
Consequences of chronic tonsillitis
- The disease in a certain way affects the course of collagen diseases - rheumatism, systemic lupus erythematosus, scleroderma, polyarthritis, dermatomyositis, periarthritis nodosa.
- The cause of frequent sore throats is heart disease - arrhythmias, endocarditis, myocarditis, acquired defects. Since there is a close connection between the lymphatic system of the heart and the ducts of the tonsils, even people under the age of 30 are diagnosed with cardialgia.
- Chronic intoxication has an adverse effect on blood vessels, especially capillaries. Patients complain of increased fatigue, weather sensitivity, headaches including migraines, and dizziness (Meniere's syndrome).
- The consequence of the chronic form of tonsillitis can also be diseases of the gastrointestinal tract - gastritis, colitis, duodenitis, stomach and duodenal ulcers.
- Against the background of chronic tonsillitis, skin pathologies and diseases of the subcutaneous fatty tissue often develop - psoriasis, neurodermatitis, acne, microbial eczema, atopic dermatitis, polymorphic exudative erythema. It makes no sense to treat them until the source of infection is eliminated.
- Chronic tonsillitis often causes lung diseases - bronchial asthma and chronic bronchitis, and also contributes to the exacerbation of chronic pneumonia. According to pulmonologists, the number of complications with such diagnoses can be reduced by 2-3 times if the source of infection is carried out in a timely manner.
- The disease also has a negative effect on the accommodative apparatus of the eye. Early sanitation can, according to ophthalmologists, prevent the development of myopia, as well as prevent relapses of conjunctivitis and blepharitis.
- The liver and the biliary system are also targeted by infection: cholecystitis, cholangitis and cholangiocholecystitis develop against the background of tonsillitis.
- Weakening of the functions of the pancreas due to focal infection in the tonsils contributes to the formation of diabetes mellitus. The thyroid gland also suffers, and its hormone-forming function is disrupted (thyrotoxicosis).
- Against the background of tonsillitis, there are disorders in the reproductive sphere: potency in men decreases, and in women of childbearing age, uterine bleeding, endometriosis, uterine fibroids, hypomenstrual syndrome and infertility are observed. Cases of pathological pregnancy - threats of miscarriage and premature birth - are not uncommon.
- Another serious consequence is kidney damage (pyelonephritis, glomerulonephritis, nephritis, etc.).
Why is a sore throat dangerous?
As practice shows, only in half of the cases are enlarged tonsils and sore throat caused by purulent sore throat. Many diseases, such as diphtheria or Epstein-Barr virus, have symptoms similar to sore throat. Therefore, only a qualified doctor with modern diagnostic equipment and a well-equipped laboratory can accurately determine the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment.
Each causative agent of sore throat is sensitive to a certain type of antibiotics prescribed by a doctor depending on the diagnosis.
Remember!
Incorrect or untimely treatment of sore throat in children, as well as relying on folk remedies for “red throat” can lead to serious complications and irreversible consequences.
Delay in diagnosis and prolonged treatment provoke the development of rheumatoid arthritis, vascular diseases, heart diseases (including rheumatic endocarditis), renal failure and many chronic diseases leading to disability.
Diagnosis of chronic tonsillitis
Diagnostic measures begin with an examination of the patient by a doctor who is interested in the appearance of the tonsils, as well as the presence of purulent or other contents in the lacunae. If this is detected, then it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological analysis of the discharge, followed by testing for sensitivity to antibiotics. A similar procedure is performed even if surgical removal of the tonsils is indicated to prevent postoperative infectious complications.
Often diagnostic measures include consultation with a cardiologist, nephrologist and so-called rheumatic tests. This allows you to determine how far the process has gone and whether there is systemic autoimmune damage to the target organs, such as the heart, kidneys and joints.
If there are indications for surgical removal of the tonsils, the patient must undergo additional examination, which includes:
- Blood test for hepatitis and HIV infection;
- Blood sugar test, since diabetes mellitus is a contraindication to such an operation;
- Cardiogram;
- Consultation with a therapist.
Scarlet fever: symptoms and signs
The disease begins acutely, with a sharp rise in temperature. Headache, muscle and joint pain, body aches, rapid heartbeat, and general weakness increase. Intoxication can cause vomiting.
The tonsils, arches, pharynx and palate are excessively red, sometimes a coating appears like a sore throat (whitish, gray, purulent). The jaw and parotid lymph nodes become inflamed and enlarged, swallowing becomes painful and difficult. On days 4-5, the tongue becomes bright crimson with hypertrophied papillae.
Atypical forms of scarlet fever:
- extrabuccal - the pathogen penetrates through damaged skin, a purulent-necrotic focus is formed at the site of penetration with a most concentrated rash around, the pharynx is not affected;
- erased (in adults) - with symptoms of mild to moderate respiratory infection;
- scarlet fever with toxic-septic shock - develops more often in adulthood with severe cardiovascular and renal complications.
What type of rash occurs with scarlet fever depends on the nature of the infection and the age of the patient. In typical cases, the first elements of the rash appear on the 1-2 day in the face, upper torso, then on the elbows, groin folds. The nature of the rash is multiple dark dots turning into dark red stripes. Sometimes the elements merge into a large erythema (redness of a large area). On the face, rashes are observed on the forehead, temples, and cheeks.
Principles of treatment
The disease does not require hospitalization. All events are held at home.
Scarlet fever in children: how to treat a contagious disease:
- antibiotics (penicillin group) for a course of 10 days;
- antitoxic serum;
- gargling with a solution of furatsilin, a decoction of chamomile, calendula, eucalyptus;
- in case of dehydration - intravenous infusion of saline preparations;
- symptomatic therapy – antipyretics, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- gentle diet, bed rest.
The modern approach to the treatment of streptococcal infections guarantees a favorable outcome without serious consequences. Re-infection is diagnosed in 1-3% of patients.