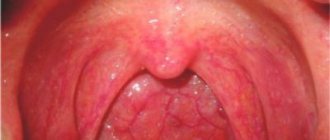
Enlarged tonsils in a child may indicate that the body is fighting some kind of infectious carrier, or some other pathologies. With this symptom, it is necessary to treat the underlying pathology in the body.
Author:
- Oganesyan Tigran Sergeevich
ENT pathology expert
4.10 (Votes: 10)
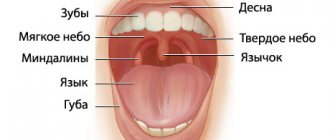
Tonsils (tonsils) are a collection of lymphoepithelial tissue, which is the point of contact of the immune system with the external environment. Thanks to this, the body produces protective immunoglobulin proteins in response to bacteria, viruses, fungi and other foreign microorganisms. Thus, the formation and maturation of immunity occurs. Located at the border of the respiratory and digestive tracts, the tonsils promptly intercept viruses and bacteria that enter the body with inhaled air, water and food.
Enlarged tonsils in a child are not a separate disease. They say:
- that the body is fighting some kind of infectious carrier;
- about genetically determined proliferation of lymphoepithelial tissue without an infectious agent;
- about possible blood diseases (oncohematological diseases), autoimmune diseases and diseases of the endocrine system.
The problem is that tonsil hypertrophy progresses quickly, and it is important not to miss the moment when the painful condition begins to cause severe discomfort to the child, but to treat the underlying pathology in a timely manner. Only an experienced doctor, whose specialization is children's ENT diseases, can correctly determine the true factor in the appearance of the symptom and choose competent therapy to eliminate it.
When should you see a doctor?
Even slightly enlarged tonsils in a child are a signal to contact a pediatric otolaryngologist. However, mild hypertrophy of the glands often does not manifest itself in any way, so it cannot be noticed visually. A visit to the doctor is required if the child, in addition to enlarged tonsils, has:
- classic signs of a cold: pain when swallowing, redness of the throat, cough, nasal congestion, fever, uncharacteristic weakness, headache;
- white plaque on the tonsils;
- swollen lymph nodes;
- pustules, ulcers in the larynx;
- swelling of the neck.
What are the indications for adenoid removal (adenotomy)?
Adenotomy
- Cost: 50,000 - 80,000 rubles.
More details
- Poor nasal breathing during the period when the child is healthy. This is dangerous because the child’s body experiences hypoxia (oxygen starvation). Insufficient oxygen supply to the body can lead to a delay in the psychomotor development of the child; the child may be adynamic, or, conversely, hyperactive. Due to the fact that the child constantly breathes through his mouth, the facial skeleton (adenoid face) is formed incorrectly. The quality of life of such children certainly suffers.
- Hearing loss or frequent inflammation in the ears are also direct indications for adenotomy. The mechanism of occurrence of this pathology occurs as follows. Where the adenoids are located, there is the mouth of the auditory tube (Eustachian tube) - an organ that connects the middle ear (what is located behind the membrane) and the nasopharynx itself. If, with your mouth closed, you pinch the tip of your nose and exhale into your nose, then air will enter your ears due to this very organ. Due to the close anatomical location of the adenoids and the auditory tubes, the inflammatory process from the adenoids can move to the mouth of the auditory tubes, causing in turn inflammation and, as a consequence, dysfunction of the auditory tube. In addition to the chronic inflammatory process in the auditory tubes, when adenoids grow, they can cover the mouths of the auditory tubes, leading to the development of adhesive otitis media or the formation of exudative otitis media (fluid in the middle ear). Frequent purulent-inflammatory phenomena in the cavity of the middle ear (sound transmitting apparatus) lead to the formation of adhesions and scars between the auditory ossicles, which subsequently leads to hearing loss in adulthood. In these cases, between the organ of hearing and the natural filter in the form of adenoids, we choose the organ of hearing.
- It is also necessary to part with adenoids if the child often suffers from adenoiditis, which, with local treatment, does not produce significant positive dynamics, but only leads to recovery for a short period of time. This is a consequence of the fact that the adenoids do not carry out their immune function, they have worn out themselves as a natural filter, are a source of chronic infection and need to be sanitized (removed). Adenoiditis can also often be associated with herpes viral infection (Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, type 6 virus), which live in the lymphoid tissue, leading to a decrease in immunity, including local immunity. If your child suffers from ARVI more than 6 times a year, there is cervical lymphadenitis (enlarged lymph nodes), conservative treatment of adenoiditis helps for a short time, in this case you need to contact a pediatrician for further examination for a herpes viral infection. When this group of viruses is detected, adequate treatment is prescribed, and if positive dynamics are observed in the adenoids during therapy, the child should be observed and there is no need to rush into surgery.
But if, together with treatment from a pediatrician, no effect is observed, then, according to the law of surgery, the tissue that prevents a person from living is removed.
Causes of enlarged tonsils in children
The increase is caused by the following infectious agents: pneumococci, staphylococci, herpes, streptococci, chlamydia, Haemophilus influenzae, adenovirus, influenza virus. They can be located in the lacunae of the tonsils without manifesting themselves in any way (for example, remain after treatment for a disease), but at a favorable moment they begin to actively multiply and cause an enlargement of the organ. Such triggers can be:
- decreased immunity;
- allergies;
- bad ecology;
- hormonal disorders;
- severe hypothermia;
- lack of vitamins;
- infections.
Causes and routes of infection
The very name of the disease already makes it clear that the source of infection is a variety of viruses. These can be herpes viruses, influenza, Coxsackie viruses, ECHO viruses, adenoviruses, enteroviruses and others. Therefore, the disease is conventionally divided into adenoviral, influenza and herpetic.
The disease is highly contagious: you can become infected during a conversation, by sneezing, through dishes, toys, and food. Viruses that enter the body reach the surface of the tonsils and settle there. From the moment of infection, the patient remains a source of infection for another 30 days. Many factors increase the likelihood of developing the disease:
- cold season;
- improper and unbalanced diet;
- lack of personal hygiene;
- hypothermia (for example, caught in the rain, eaten cold ice cream);
- smoking in front of a child;
- bad ecology;
- climate change;
- weak immunity;
- the presence of a chronic source of infection in the body (for example, chronic tonsillitis);
- carious teeth;
- allergic reactions;
- tuberculosis, diabetes and other diseases;
- stressful situations.
Sore throats caused by influenza viruses or adenoviruses usually occur during the cold season, especially during outbreaks of epidemics, when the body's defenses weaken. Herpetic sore throats are more common in the summer. In order to understand in time that we are dealing with viral tonsillitis, it is necessary to be able to distinguish the main symptoms of the disease in a child.
The degree of enlargement of the tonsils in a child
There are 4 stages of hypertrophy of the glands:
- At the first stage, the inflamed tissue of the tonsils covers no more than 30% of the lumen between the pharynx and the sky. In this state, it causes almost no discomfort, so it is difficult to detect at this stage.
- At the second stage, hypertrophied tissue covers half of the lumen. The child begins to have difficulty swallowing and breathing freely, and a sensation of a foreign body in the throat.
- At the third stage, there is severe difficulty in breathing and swallowing.
- On the fourth, the pharynx is almost completely blocked by inflamed tonsil tissue. It is difficult to bring the condition to this stage, since already at the third stage the child’s well-being requires immediate medical attention.
Adenoids treated or removed
The most common pathology in children is enlargement of the nasopharyngeal tonsil (adenoid vegetations, adenoids). According to various authors, the presence of adenoids is noted in children under 14 years of age from 5 to 45% of cases .
adenoids
Adenoids are located in the vault of the nasopharynx, where the nasal cavity ends, serving as a natural filter that prevents viral and bacterial agents from entering the lower parts of the respiratory system - the trachea and bronchi. In children, during the inflammatory process in the adenoids (local fight against viral or microbial agents in the tissue of the nasopharyngeal tonsil), difficulty in nasal breathing may be observed due to the fact that the tissue closes the lumen of the nasal cavity at the back, thereby interfering with the normal passage of air, the presence of mucous discharge in the anterior parts of the nasal cavity, snoring. Children experience a “choking” type cough due to secretions getting from the nasopharynx onto the vocal cords.
Cough is not always associated with adenoiditis (inflammation of the adenoids). Often, a cough is associated with one or another problem in the lower parts of the respiratory system (tracheitis, bronchitis, pneumonia, childhood infections). To exclude this pathology, the child must be consulted with a pediatrician, who will perform auscultation (listen to organ sounds), giving a conclusion about the presence or absence of pathology.
Due to the specific location of the adenoids, it is impossible to apply ointment, apply sprays, or use rinses; because of this, adenoids take a relatively long time to be treated.
How is inflammation treated?
The tactics for treating enlarged tonsils in a child consists of treating the underlying disease that caused this symptom (taking antibiotics, antiviral or antifungal drugs), and influencing them directly to regenerate the affected tissues. The latter includes:
- washing the tonsils from pathogenic microorganisms and mucus with antiseptic solutions;
- reducing swelling - taking antihistamines and ultraviolet irradiation;
- UHF therapy, which improves blood microcirculation;
- exposure to ultrasound to free the lacunae of the tonsils from pus, which can accumulate in them;
- laser exposure to destroy infection and its pathogens.
Treatment of hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils
To delete or not to delete - that is the question. The answer to this depends on how much the overgrown tissue burdens the child’s life. If the tonsils are too large, they are trimmed down to normal size, making room for air and food. This operation is called partial tonsillotomy. The remaining tissue is quickly restored and fully copes with its tasks. But if the reasons that prompted it to increase so much remain in force, there is a risk of the situation repeating itself.
How to treat hypertrophy of the palatine tonsils in a way that is not so radical? Reduce the load on the lymphoid tissue of the pharynx. To do this, firstly, treat diseases of both the upper respiratory tract and other organs. Secondly, not only “fight the enemy,” but also help the body become capable of self-defense. In addition to the immortal healing “triad” - sun, air and water, an individual diet is also suitable. This is not a dietary restriction, but an integrated approach to choosing food products that are healthy for a given child, physical exercise, a hardening system, a daily routine, the psychological atmosphere in the home, etc. After all, the Greek word “diet” originally meant a way of life in general.
Holistic methods of influencing the body - homeopathy, herbal medicine and acupuncture - can provide good help to the child’s body.
Make an appointment
Complications of tonsillitis
With proper treatment, recovery occurs in 7-10 days. If medications are ineffective, life-threatening complications may develop:
- paratonsillitis - acute inflammation of the tissues near the tonsils;
- peritonsillar abscess - the formation of a cavity with pus inside the same area;
When the process spreads into deeper tissues, phlegmon may develop. All types of complications are observed and treated exclusively in the hospital, with further use of surgical treatment methods .
Clinical recommendations for disease prevention
The main methods of preventing tonsillitis in children are compliance with sanitary and hygienic measures (avoiding contact with patients and their things, washing hands, using a scarf and hand sanitizers) and strengthening the immune system (hardening, playing sports, etc.).
Tonsillitis is a common disease in children and adults, which without proper treatment can become chronic. If you notice symptoms of illness in your child, immediately contact the children's medical department.
Sources:
- HELL. Vetrova. Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, vol. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64.
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan. Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2021 Sep; 10(9): e3343.
- T.V. Spichak. Diagnosis and treatment of tonsillitis in children from the standpoint of evidence-based medicine // Issues of modern pediatrics, 2010, vol. 9, no. 2, pp. 130-135.
The information in this article is provided for reference purposes and does not replace advice from a qualified professional. Don't self-medicate! At the first signs of illness, you should consult a doctor.
Types of disease
- Spicy. Most often, the acute form develops after suffering from acute respiratory viral infection, due to reduced immunity. Source: A.D. Vetrova Acute tonsillitis in children: a pediatrician’s point of view // Pediatric pharmacology, 2014, v. 11, no. 2, pp. 61-64
- Chronic. Occurs after relapses if the patient has not fully recovered. Diseases in the mouth, nose, and structural features of the tonsils contribute to the development of chronic tonsillitis. Source: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6248716/ Raja Kalaiarasi, Kalaivani S Subramanian, Chellappa Vijayakumar and Ramakrishnan Venkataramanan Microbiological Profile of Chronic Tonsillitis in the Pediatric Age Group // Cureus. 2021 Sep; 10(9): e3343
Surgery to remove tonsils
The importance of the tonsils cannot be underestimated. We found this out at the very beginning of the article. The main goal of any therapy is to try to reduce the tonsils without surgery and preserve them as an organ of the immune system. Many adult patients mistakenly believe that they will have less pain after surgery. It is a myth! Yes, the tonsils will stop bothering you. But now the infection from the outside will enter the pharynx and further into the respiratory tract without encountering any obstacle, which will not have the best effect on the incidence of respiratory tract diseases.
The operation to remove the tonsils is called tonsillectomy.
Certain indications are required for the operation. The patient's fatigue due to frequent exacerbations and unpleasant symptoms is not such an indication.
Surgical intervention is prescribed in the following cases:
- recurrence of sore throats more than four times throughout the year;
- a peritonsillar abscess that has occurred;
- poor performance of rheumatic tests;
- complications on other organs and systems of the patient.
Before deciding to undergo surgery, it is necessary to try to treat a child or adult patient conservatively, that is, to reduce the tonsils without surgery.