Can a baby cut teeth at such an early age?
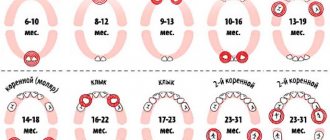
The average time for teeth to appear in infants is 6–8 months. The first to grow are the two lower central incisors, which usually erupt one after the other. But you should understand that the time frame is not limited. Sometimes the process may take some time. There are cases when the first incisors appear earlier. Therefore, when asked whether teeth can be cut at two months, experts answer in the affirmative. A deviation of the time frame by several months in both directions is considered normal. Only if a one-year-old child does not have a single tooth should you consult a doctor.
Each organism is individual, so some babies already have their first tooth at 2–3 months. The process is determined not only by genetics, but also by a number of other factors:
- climatic conditions;
- maternal nutrition;
- features of the course of pregnancy;
- disruptions of the endocrine system - sometimes the early appearance of teeth may indicate its abnormalities.
If during pregnancy the mother took multivitamins or additional mineral complexes containing vitamins D and C, then the timing of teething may accelerate. A woman’s consumption of fermented milk products in large quantities also contributes to this.
Features and anomalies during the eruption of baby teeth. Why and what to do?
The period of teething is one of the most difficult in infancy. Especially if the baby has problems. In this article we are not talking about fever, cough, runny nose and diarrhea during teething. We will focus on more serious troubles. And they, lately, are becoming more common and different. And the most harmless of them is that the child’s teeth grow crookedly. This happens often in children. Now we will only talk about baby teeth! Permanent teeth are a separate matter.
Milk teeth rarely grow crooked. More often, parents are concerned about the spaces and gaps between their baby teeth. In both cases, it’s okay. The fact is that the rudiments of baby teeth are formed in the first months of pregnancy. On a small jaw, the teeth are located close to each other. As the jaw grows, the teeth move away from each other and uniform gaps form between them. If the gaps are uneven - very large (three), this may indicate the absence of individual teeth or uneven growth of the jaws - contact your dentist.
If a child has a crooked tooth growing, or baby teeth are growing very crowded, there may be several reasons:
- poor nutrition of the mother during pregnancy, when tooth buds were forming;
- lack of calcium, microelements, vitamins in the child’s diet (with a monotonous diet);
- insufficient load on the baby's teeth - when feeding only liquid, ground food after 8-10 months. It is imperative to let your child chew apples, carrots, peels, and dried fruits on his own;
- chronic diseases of the nasopharynx: runny nose, tonsillitis, adenoids, which provokes constant mouth breathing;
- bad habits: pacifier, finger sucking, sleeping with a pacifier in the mouth, bottle feeding after a year. It is necessary to teach your baby to drink from a cup, eat with a spoon, and chew age-appropriate food sooner.
All these factors, as well as heredity, can cause improper growth of baby teeth. Crooked baby teeth can only be treated by a pediatric dentist, who can assess the complexity of the problem, because often the teeth straighten on their own as the baby grows. But there is no need to rely on this, because you may miss more serious problems. After all, crooked baby teeth in children - photo can cause improper growth of the rudiments of permanent teeth, and therefore their curvature, loss from the dentition, etc.
There are other features of the growth of baby teeth. The most common:
- increasing the spaces between teeth. The large gap between the upper frontal incisors is a consequence of the deep location of the maxillary frenulum. Consult an orthodontist at the Utkinzub clinic;
- the black edging of the cervical zone of the teeth is a violation of the absorption of iron, which provokes increased proliferation of leptotrichia bacteria. Treatment by a dentist and treatment of the cause by a pediatrician;
- yellow-brown teeth already when teething ( the child grows dark teeth ) is the result of the mother’s treatment with tetracycline antibiotics during pregnancy (tetracycline teeth);
- greenish staining of baby teeth – metabolic disorders, in particular bilirubin. Also observed in hemolytic diseases associated with the destruction of red blood cells. A complete medical examination is indicated;
- Red baby teeth occur with the disease “porphyria” and appear as a result of a violation of the metabolism of porphyrin - a red pigment. A complete medical examination is indicated.
- gray, soft teeth – lack of enamel coating, hypoplasia. Appears when the mother has a malnutrition during pregnancy or as a result of metabolic disorders in the child. Contact your dentist.
Other developmental anomalies of the dental system may be associated with genetic diseases, constitutional causes, congenital developmental anomalies, and tumors. (“Absence of milk teeth – adentia. Second row of teeth”) All the above-described cases of abnormal development, including crooked teeth in children , are a reason to contact a pediatrician and pediatric dentist as soon as possible. The sooner the cause of the anomaly is identified, the greater the chances of quickly and effectively correcting the situation and guaranteeing the child a full, healthy life.
What are the symptoms of teething
Only some parents do not encounter difficulties with their child’s teething and notice the incisor by chance, not understanding when it appeared. In most cases, the process is accompanied by unpleasant symptoms:
- Swelling, “looseness” of the gums. Redness and bumps may form. Sometimes the teeth show through the gums. In some cases, there are bluish hematomas.
- Increased salivation. This may cause rashes around the mouth. But salivation at 2 months of age does not always indicate teething. During this period, such a process is physiological. If the rashes appear in other places, this is not related to teething.
- Restless state. The child cries a lot, is capricious, and the quality of his sleep deteriorates. Often the baby cannot be calmed down. Conventional methods (swinging, pacifiers, etc.) do not help.
- Increased body temperature. More often these are indicators up to 37.5 ˚C. This can happen due to local inflammation (of the gums). A higher temperature indicates viral activity.
- Loss of appetite. During the period of teething, children eat poorly or refuse to eat at all. Sometimes the baby cannot be put to the breast. Some babies kick their legs and arch when feeding.
- Runny nose and cough. Due to increased salivation, mucus flows down the back of the throat. It gets into the nasal passages, since the baby at the age of two months is more in a lying position. When mucus enters the throat, it provokes a cough. More often it appears during sleep.
Such symptoms do not occur all at once and can be combined in different ways. They often become a serious cause for concern for parents. Even the fact that a child is teething at such an early age is already shocking to them.
It is important not to confuse the signs of infectious or neurological diseases that have similar symptoms with the process of teething. Therefore, it is better to show the baby to the doctor. The following symptoms are also reasons to seek help: the child is very lethargic, has a high temperature (above +38 C), vomiting or mouth ulcers. A child may also vomit due to excessive salivation when mucus enters the stomach. Loose and frequent stools also indicate an infection. Diarrhea can cause dehydration.
How to help your baby teething
There are several ways that can help your baby teething:
- Swollen gums can be massaged with a cold teaspoon or a clean finger - as a result of light pressure on the sore spot, the process will speed up.
- It is worth purchasing two tooth rings, boiling them and putting them in the refrigerator, then giving them to the baby one at a time, changing them as they warm up. Do not buy rings that are filled with liquid: if they happen to burst, water may get into the child's mouth, and there is no guarantee that it is clean.
- Use special pain-relieving dental gels that can be used to treat your gums.
- Until the tooth appears, the child needs a special diet. If he is breastfed and feeds by the hour, try transitioning him to free-feeding. Older children receiving complementary foods should be given light foods - milk soups and liquid porridges. During this period, increase the volume of herbal teas, and, on the contrary, limit the amount of juices and vegetables.
It is recommended, even before the first teeth erupt, after each feeding, to wipe the baby’s gums with gauze soaked in boiled water, attached to a finger. This can prevent the accumulation of microbes that multiply and can eventually cause tooth decay. As soon as the first tooth appears, brush it with a silicone finger brush. There are special children's toothpastes that are allowed almost from birth. But the question of whether they should be used must be decided by the pediatrician, taking into account the thickness of the plaque and the type of feeding.
Pastes that are marked 0–3, 3–6 are gel with natural antiseptics and lactic enzymes. After the baby turns one year old, they can be replaced with ones that contain xylitol, a sweetener and at the same time an anti-caries component.
How to help your baby
If a baby starts teething at 2 months, in addition to fatigue due to sleepless nights, parents feel worried about their baby. Since he suffers from pain, discomfort, eats little and sleeps poorly, it is necessary to help relieve unpleasant symptoms. To do this, use the following methods:
- Massage the gums. You must first wash your hands thoroughly. The massage is done with the tip of your finger. It is worth trimming your nails to avoid damaging your gums. Massaging helps relieve pain. The degree of effectiveness of the method can be determined by the child’s reaction.
- Cold is applied. Regular teethers, which are sold in pharmacies and offered to older children, will not be chewed by a baby at the age of two months. In this case, he can cool the pacifier or apply a gauze pad to the problem area. It is pre-moistened with cold water or chamomile infusion, which helps relieve inflammation.
- Lubricate the gums with anesthetic gels. For example, “Kamistad” or “Kalgel” are products that can be used even at an early age.
- They give antipyretic and painkillers based on ibuprofen and paracetamol. Candles are given to 2-month-old babies. This could be, for example, “Efferalgan”.
During the teething period, it is important to provide the baby with proper care. It is necessary to keep the pacifier clean. Saliva should be wiped off only with clean napkins. The skin around the mouth should be lubricated with a special baby cream. You also need to walk more - fresh air will only do you good. But it is better to avoid places with large crowds of people so that the baby does not catch an additional virus.
If a child’s teeth appear early, if he is breastfed, it is worth visiting a dentist. The fact is that the risk of developing bottle caries in this case is quite high.
How do baby teeth erupt?
At first, the child begins to be bothered by swollen gums on the lower jaw, then a thin strip of two incisors appears, which becomes higher every day and the tooth takes on a normal shape.
The rate of teething depends on the formation of the tooth germ in the intrauterine development of the fetus. The buds of teeth begin to form as early as the 7th week of pregnancy, so future dental health depends entirely on the health of the pregnant woman, who should not smoke and eat properly.
What can cause a child's anxiety:
- Swollen, inflamed gums.
- Increased secretion of saliva.
- Due to the constant flow of saliva, a rash may appear on the skin of the baby's cheeks.
- A runny nose and mild diarrhea may occur.
- Appetite decreases, the child sleeps poorly and becomes increasingly restless.
- The child puts various objects into his mouth to scratch his swollen gums.
- Teething may be accompanied by fever. It usually grows if two teeth erupt at once.
- The child becomes lethargic and inactive.