All articles
Teething
26.09.2017
How to determine that a child is teething, when to contact a doctor, and what you need to know about ways to cope with discomfort.
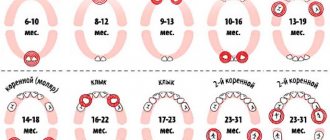
Most babies start teething between the sixth and tenth month, and everyone experiences it differently. The process may start a little earlier or later, there's nothing wrong with that. Typically, by the age of two and a half, a child has all 20 baby teeth.
Kamistad® Baby
Happiness starts with a smile
Go to website
Sometimes teeth cut unnoticeably, in other situations the following symptoms can be observed:
- The gums become inflamed and swollen, becoming sensitive to touch;
- More saliva is produced than usual;
- The child becomes capricious and irritable;
- There is a desire to gnaw and chew something hard;
- The child refuses food;
- There are problems with sleep.
During teething, a fever may occur, but usually the temperature does not exceed 38°C). In addition, diarrhea (loose stools) may occur. These symptoms should be discussed with your pediatrician to rule out infection and other serious causes.
Here are some tips to help cope with your child's discomfort:
- Gently wipe your face to remove saliva and avoid skin irritation and rashes;
- Let's chew some cool things. This could be a chilled (not frozen!) durable rubber teething ring or a cold apple (if baby is already eating solids). Avoid rings that are filled with liquid, and make sure your child doesn't chew on plastic items that may break;
- Wipe your gums with a clean, damp cloth. You can first put the napkin in the freezer;
- Give your child cool, age-appropriate foods. This could be applesauce or unsweetened yogurt.
Over-the-counter medications may also help. Use ibuprofen or paracetamol as a pain reliever (syrup and suppositories are better for children). Remember that if you have a fever, aspirin should not be taken until you are 19 years old. Symptoms can also be relieved by using teething gels. They may have anti-inflammatory, anesthetic, and antiseptic effects. Avoid products that contain belladonna extract or benzocaine.
The American Dental Association suggests starting to care for your teeth as soon as the first one appears. Use a soft toothbrush for children and fluoride toothpaste. The required amount of paste for a child under three years old is about the size of a grain of rice. If the child is from three to six years old, you should focus on the size of a pea.
Share:
Teething in children symptoms
Teething is most often preceded by changes in the baby's behavior.
Signs that may signal the beginning of the process and should alert mom and dad:
- copious secretion of saliva, leading to a cough, as well as rashes around the mouth and on the chin;
- swelling, discoloration of the gums, anxiety of the child when touching them;
- restless sleep;
- problems with appetite up to complete refusal of food;
- increased body temperature;
- irritation of the gums, which the baby tries to scratch, putting everything that is within reach into his mouth;
- obvious signs of nervousness.
In some cases, the process of teething is similar to the manifestations of infectious diseases: it is accompanied by nausea, changes in stool, runny nose, and vomiting. To avoid possible complications, it is better to show the child to a pediatrician.
Features and nature of diarrhea
This condition is characterized by increased intestinal motility with changes in stool color and consistency. The basis of the problem is the accelerated passage of food through the intestines, which is accompanied by insufficient absorption of fluid, as well as an increase in the formation of mucus. In healthy infants, sometimes after eating or during feeding, stool occurs due to the gastrocolytic reflex.
There are pathological defecation:
- with a large amount of stool (for diseases of the pancreas, stomach, dysfunction of the small intestine);
- with a small amount of stool (with peptic ulcers and colitis affecting the distal intestine).
Loose stools are normal for babies. Sometimes the stool takes on a greenish tint, which occurs mainly when feeding cow's milk - this is not dangerous. Diarrhea can also occur with a urinary tract infection.
Frequent soft stools (4-6 times per day) can be observed in healthy infants; This should not be a cause for concern unless there are signs of anorexia, vomiting, weight loss, weight gain, and bloody discharge. Increased peristalsis is common for breastfed babies. How many days can a child have diarrhea without consequences? The risk of developing complications of diarrhea in children at any age depends on the nature of the course - acute (up to 14 days) or chronic (from 2 weeks or more). In some situations, especially in children under one year of age, diarrhea can lead to serious complications within a few hours.
Temperature during teething in children
Hyperthermia syndrome is the baby’s body’s response to changes that occur in his body during teething. The fact is that during this period the immune system of the child’s oral cavity weakens, and the fight against bacteria occurs through fluctuations in body temperature.
Also, around this time, the interaction of the baby’s vital systems of the body is adjusted, including heat exchange.
The normal duration of hyperthermia is up to five days. Usually the fever subsides immediately after the edge of the tooth appears.
If at a temperature of 38 degrees for three days the child is not capricious and shows sufficient activity, then there is no need to worry, the baby’s body itself copes with the threat.
Hyperthermic syndrome, expressed as a temperature above 38 degrees, is already a reason to consult a doctor. Based on the need and condition of the child, the doctor will prescribe antipyretics.
Causes of diarrhea in a child
The acute process is often infectious in nature, especially if it occurs suddenly or is combined with vomiting, blood, fever and anorexia. Maintenance treatment is prescribed based on clinical diagnosis and continues until improvement occurs.
Chronic diarrhea in a child without fever can develop due to the following reasons:
- Allergic gastroenteropathy. Cow's milk protein causes bloody diarrhea and vomiting. The condition is normalized when hydrolyzed protein is included in the diet instead of cow's milk. Most children improve spontaneously.
- Disaccharidase deficiency. It is characterized by the absence of lactase, which breaks down lactose into galactose and glucose. The disorder may be congenital or develop after a gastrointestinal infection, acting as a temporary disorder. An improvement in the condition after eliminating lactose or other carbohydrates from the diet confirms the diagnosis. In this case, the child has light diarrhea and there is severe irritation in the perineal area caused by liquid feces.
- Gluten enteropathy (celiac disease). In celiac disease, the wheat protein fraction damages the intestinal mucosa, which can impair fat absorption. This leads to malabsorption and anorexia, which is accompanied by the passage of copious amounts of stool. Changes in the body occur when consuming products made from wheat flour and dishes containing gluten.
- Cystic fibrosis. Cystic fibrosis is characterized by the development of pancreatic insufficiency, which is accompanied by a deficiency of trypsin and lipase. In this case, there is a large loss of fat and protein in the stool, which means that physical development is delayed. The stool is usually smelly. Children with cystic fibrosis often develop respiratory problems.
Inflammatory processes in the intestines and some infections can also cause diarrhea. The most common is gastroenteritis, an infection of the small intestine that is accompanied by vomiting. The main danger of this disease is dehydration and water-electrolyte imbalance. Dehydration develops especially often and quickly against the background of rotavirus infection.
The causes of secretory diarrhea in a child are usually due to infection:
- bacterial (staphylococcus, salmonella, E. coli, shigella);
- parasitic (giardiasis, amoebic dysentery).
Secretory diarrhea can also be caused by inflammatory bowel disease. In children it can occur with excessive consumption of carrots and peas. The reason is increased intestinal motility. This type of diarrhea goes away on its own over time. Diarrhea with blood in a child develops against the background of an acute intestinal infection - campylobacteriosis, necrotizing enterocolitis, intussusception (intestinal obstruction).
Black diarrhea
After taking activated carbon and some vitamin and mineral preparations, stool may turn black. This may also be due to internal bleeding - from the stomach, esophagus or intestines, which occurs against the background of serious pathologies (ulcers, cancer, polyps, etc.). Associated symptoms of internal bleeding may include pale complexion, dizziness and anemia.
If you have black diarrhea, you should consult a doctor immediately. For diagnosis, a specialist will prescribe fibroesophagogastroduodenoscopy (examination of the esophagus, stomach cavity and duodenum using a gastroscope, which is inserted into the stomach through the mouth and esophagus) or colonoscopy (probing of the colon).
Chronic diarrhea
Frequent diarrhea in a child can manifest itself as a mild illness or more serious disorders. At the same time, the intestinal walls become susceptible to various allergens and toxins, and the protective functions of the liver are reduced. The body absorbs vitamins and minerals worse, metabolic processes worsen, and liver and pancreas diseases occur.
The following factors can trigger the development of chronic diarrhea:
- long-term use of medications, especially antibacterial ones;
- long-term treatment with hormonal drugs and NSAIDs;
- unbalanced diet;
- immunodeficiency states;
- stress, emotional overstrain.
Chronic diarrhea causes nausea, loss of appetite, bad taste in the mouth, belching, pain and bloating, weakness and trouble sleeping. To make a diagnosis, a microbiological examination of the stool is performed, as well as an assessment of the digestive system. Therapy is aimed at eliminating the causes and restoring the general condition.
Diarrhea with mucus
Mucous diarrhea in a child develops against the background of a violation of the intestinal microflora, polyps and hemorrhoids. Mucus binds and removes pathogenic microorganisms. Clinical signs of hemorrhoids include itching and bleeding from the anus. Intestinal diverticulitis also causes mucus to be secreted in the feces. Associated symptoms are abdominal pain arising on the left side and flatulence.
Diarrhea with mucus in children occurs as a result of insufficient bowel function. As a rule, this is associated with poor nutrition. This condition is accompanied by malaise, nausea and rumbling in the stomach. Liquid feces with mucus also occur with IBS (irritable bowel syndrome). To identify the disease and the purpose of therapy, you need to contact a specialist and conduct a diagnosis.
Diarrhea and fever
Diarrhea, vomiting and fever are the main signs of an intestinal infection, which can be caused by bacteria or viruses. An accurate diagnosis can only be made by a doctor after examination.
In the first hours after the onset of alarming symptoms, frequent small drinks are necessary. Dark colored urine may indicate a lack of fluid in the body. Normalizing the water-salt balance during intestinal infections is extremely important. Refusal of food and heavy drinks in case of diarrhea, vomiting and fever is a necessary condition. Drug treatment of intestinal infections is carried out under the strict supervision of a doctor.
Severe diarrhea
If the small intestine is affected, severe diarrhea may occur. This can happen during food poisoning and intestinal infections. Often such stools are watery, may contain food debris and do not cause abdominal pain. Bile acids and peptide molecules can promote the release of water and ions. The severe condition can occur when the absorption of bile and fatty acids is impaired, such as in Crohn's disease.
What should I give my baby when teething?
Medicines specially designed for this difficult period of a child’s growing up help reduce the level of anxiety of both the baby and the parents. Soothing, antiseptic, and painkillers are available in the form of gels, suppositories and ointments. Let's look at the most popular of them:
● Viburkol suppositories for teething children
Homeopathic suppositories Viburkol are a working and very popular remedy that has antipyretic, soothing and anti-inflammatory effects. Rectal suppositories effectively relieve mild pain, thereby helping the child feel better.
The herbal composition of the drug (chamomile, plantain, sleep-grass) allows you to avoid complications that are frequent companions of chemical drugs in traditional medicine.
● Cholisal gel for teething children
Lowering temperature, reducing inflammation, relieving pain, resisting microbes and fungi, Cholisal gel has become a salvation for millions of mothers. Relieving almost all symptoms of teething in babies, this drug effectively and quickly calms them down, which means it gives parents the opportunity to enjoy peace of mind.
The gel contains neither lidocaine nor sugar, and it works due to the antiseptic cetalkonium chloride and the anesthetic choline salicylate.
The instructions for the gel indicate an age limit of one year. However, the process often begins earlier, so Cholisal is also applied to children under one year of age when teething.
Gels for teething in children
In addition to the Kholisal discussed above, there are a number of gels that effectively reduce the negative signs of the appearance of the first teeth:
- Kalgel.
Lidocaine, which predominates in the gel, cools the child’s gums, but has a short-term effect, which means the product must be applied frequently.
- Kamistad baby.
Operating through a pair of lidocaine hydrochloride plus chamomile, Kamistad baby quickly relieves pain and calms the baby.
- Baby doctor.
Homeopathic medicine of natural origin is in demand precisely because of its natural composition: plantain, chamomile, echinacea and calendula work well for children who reject chemical medicines.
- Pansoral – first teeth.
Another gel with a “green” composition (saffron, marshmallow, chamomile) is used to relieve pain in children from 4 months. It has no side effects, which means it is safe for babies.
- Dentol baby.
A cheap anesthetic based on benzocaine effectively relieves the pain that accompanies the appearance of children's first teeth.
- Dentinox.
The already proven combination of chamomile and lidocaine hydrochloride, present in Dentinox, is used not only by children, but also by adults (the appearance of wisdom teeth can also be very painful). The gel contains fructose, so it should not be used by people who have problems digesting sugar.
Impurities in stool
Norm
A few white lumps in the stool of a breastfed baby are not a pathology. In children receiving dense foods, there are undigested pieces of vegetables and fruits, the skin is also normal.
- White lumps in the stool. Of course, even a breastfed baby's stool is not uniform. Most often, mothers are worried about white lumps - these are traces of breast milk; their presence in small quantities is considered normal. If your child's weight is constantly growing, there is no reason to worry. Many white lumps in an infant's stool are a reason for a nursing mother to think about a proper diet with fewer fatty foods in the diet. Such lumps also occur in bottle-fed children - these are the remains of undigested milk formula. With age, as the digestive systems and functions develop, such lumps in the stool are no longer observed.
- Small pieces and fibers in the stool. With age, we accustom the child to denser foods - pieces of boiled, and then fresh vegetables and fruits. But your baby will not be able to learn to chew correctly and thoroughly (mechanically process food) right away. And even the intestinal microbiota cannot “finish” large pieces of vegetables and fruits (dietary fiber) - the bacteria of the digestive tract normally process dietary fiber; our body does not have enzymes to digest it.