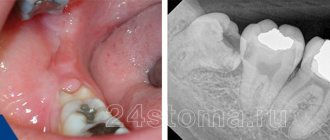
This condition can have a different nature of occurrence and is provoked by both objective reasons and factors of a psychogenic nature.
Unusual sensations
It happens that a person can feel phenomena in the face and head that are unusual for the usual state. They are called paresthesias and are manifested by the following symptoms:
- tingling;
- burning;
- "goosebumps"
- numbness;
- itching and rashes.
Often facial paresthesias have an organic basis and become a sign of the disease:
- neuritis, neuralgia of the cranial nerves;
- multiple sclerosis;
- stroke and other circulatory disorders in the brain;
- shingles;
- migraine;
- diabetes;
- epilepsy;
- hypertension.
In certain cases, unusual sensations are observed in certain parts of the face. For example, similar manifestations in the language may appear for the reasons listed above, but often have a different etiology. They are provoked by cancer of the tongue and larynx, as well as trauma by a splintered tooth or denture.
Dental procedures cause numbness and other unusual feelings, especially after tooth extraction. Another reason for their appearance may be an uncomfortable position during sleep or an unsuitable pillow. But the sensations caused by such phenomena usually pass soon.
Another group of provoking factors consists of psychogenic and neurogenic disorders.
Professional treatment for tongue numbness
Loss of tongue sensitivity is not an independent disease, but a symptom accompanying the underlying pathology. Only after identifying the reason why the tongue is numb will the specialist prescribe treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the underlying disease or irritating factor.
In cases where paresthesia is caused by osteochondrosis, the following are indicated:
- physiotherapy;
- massage manipulations;
- physiotherapy;
- taking painkillers and drugs that enhance bone tissue regeneration.
Injuries that cause the feeling that the tip of the tongue is numb are treated with antiseptic rinses and dental gels. Allergic reactions that reduce the sensitivity of the organ are eliminated with antihistamines.
VSD (vegetative-vascular dystonia) is treated with drugs that increase blood circulation and dilate blood vessels in the brain. It is recommended to change the diet, introduce a nutritious diet, follow the rules of rest and work: 8-hour sleep, active lifestyle.
Oncological diseases require surgical intervention coupled with drug therapy ; at the initial stage of the disease, endoscopy can be done. In case of laryngeal cancer, the affected tissue is removed; in case of pharyngeal cancer, partial removal is performed, followed by restoration using plastic surgery.
Trigeminal neuralgia can be treated surgically, but destruction of the nerve is often required. Radiosurgery, a minimally invasive (bloodless) operation, is sometimes used.
Numbness caused by diabetes mellitus is eliminated after a course of treatment of the underlying disease. Injections or tablets are prescribed to normalize insulin levels, which eliminates dry mouth, thirst and loss of sensitivity.
Disorders of facial innervation
A neurotic face may develop due to damage to the nerves that innervate it. Most often these are the trigeminal and facial nerves.
The trigeminal nerve is the 5th pair of cranial nerves. It is the largest of all 12 pairs of these nerve fibers.
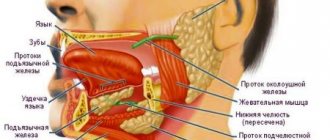
N. trigeminus arises symmetrically on both sides of the face and consists of 3 large branches: the ophthalmic, maxillary and mandibular nerves. These three large processes innervate a fairly large area:
- skin of the forehead and temples;
- mucous membrane of the oral and nasal cavities, sinuses;
- tongue, teeth, conjunctiva;
- muscles - chewing, floor of the mouth, palatine, tympanic membrane.
Accordingly, when it is damaged, pathological sensations arise in these elements.
Facial nerve – 7th pair of cranial nerves. Its branches surround the temporal and ocular region, the zygomatic arch, and descend to and behind the lower jaw. They innervate all facial muscles: auricular, orbicularis and zygomatic, chewing, upper lip and corners of the mouth, cheek. As well as the muscles of the lower lip and chin, around the mouth, the muscles of the nose and laughter, and the neck.
N. facialis is also paired, and is located on both sides of the face.
In 94% of cases, the damage to these nerve fibers is unilateral, and only 6% is a bilateral process.
Disruption of innervation can also be primary or secondary.
Primary is the lesion that initially involves the nerve. This could be hypothermia or strangulation.
Secondary damage develops as a consequence of other diseases.
Another reason for the development of facial neurosis is neurogenic and mental disorders. When unpleasant sensations in the face and head occur against the background of psycho-emotional arousal, shock, or as a result of stressful situations.
Possible complications
This disease does not threaten health, but significantly reduces the quality of life. If you ignore an unpleasant symptom, glossalgia can become chronic. Its symptoms will occur from time to time, exacerbating the unstable psycho-emotional state. Against the background of pain, anxiety, eating disorders, sleep disorders, nervousness, and phobias can develop. As the condition worsens, treatment should be carried out not only by the dentist, but also by other specialists - a neurologist, psychiatrist or psychotherapist.
A long-lasting symptom can cause forced dietary restrictions, which can affect the overall health and cause vitamin deficiencies, weight loss, and lack of minerals.
Possible complications include inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity. For example, a lack of saliva can lead to aphthous stomatitis, and when exposed to adverse factors or injuries, the likelihood of glossitis, gingivitis and other ailments increases.
Facial nerve neurosis
Neuritis (neurosis N. Facialis) or Bell's palsy occurs due to inflammation of the nerve fiber. Reasons leading to this condition:
- pinched nerve as a result of narrowing of the channel through which it passes. This may be a congenital phenomenon or result from inflammation;
- hypothermia;
- other diseases and infections: herpes, mumps, otitis media, stroke, cancer, central nervous system infections;
- injury N. Facialis.
The onset of the disease is usually gradual. Manifested by pain in the behind-the-ear area. After a couple of days, neurological facial symptoms appear:
- smoothing of the nasolabial fold, drooping of the corner of the mouth;
- the face becomes asymmetrical with a skew towards the healthy side;
- eyelids do not droop. When you try to do this, your eye rolls;
- any attempt to show at least some emotion ends in failure, since the patient cannot move his lips, smile, or manipulate his eyebrows. Such manifestations can worsen to the point of paresis and paralysis of the facial muscles, that is, to partial or complete immobility of the affected part of the face;
- taste sensitivity decreases, salivation appears;
- the eyes are dry, but there is lacrimation when eating;
- hearing on the affected side worsens.
The severity of pathological symptoms depends on the degree and area of damage to the nerve fiber. If the disease is treated inadequately, complications may arise in the form of muscle contractures (immobility).
Since the disease is inflammatory in nature, its treatment is aimed at eliminating it. For this, the patient is prescribed hormonal anti-inflammatory drugs - glucocorticoids, as well as decongestants.
Other methods include:
- prescription of vasodilators and analgesics, B vitamins;
- anticholinesterase agents to increase nerve conduction;
- drugs that improve metabolism in nervous tissue;
- physiotherapy;
- massage, exercise therapy in the recovery stage.
And only in extreme cases, when conservative therapy is ineffective, neurosurgical intervention is resorted to.
Treatment of tongue numbness with folk remedies
Depending on the cause of numbness in the tip, root, or sides of the tongue, treatment may include alternative medicine methods. Rinses and compresses can significantly improve the condition and speed up the restoration of sensitivity.
Common traditional medicine recipes used for diseases of the oral cavity:
- A spoonful of soda and 4 drops of iodine are dissolved in a glass of warm water. Rinsing is done daily, morning and evening.
In addition to pronounced anti-inflammatory properties, plants have a calming effect. Two tablespoons of dry herb are brewed with a glass of boiling water, the decoction is infused for 15 minutes. The resulting infusion is used for daily rinsing of the mouth and for oral administration: take 1 tablespoon.
If the cause of numbness in the mouth is a disorder of the nervous system, the use of chamomile and sage in therapy is effective.- A tablespoon of St. John's wort and the same amount of celandine are poured into a glass of boiling water and infused for about 30 minutes. The resulting infusion should be used to rinse your mouth morning and evening.
- You can fight lost sensitivity of the tongue with the help of garlic. To do this, take a garlic clove and roll it in your mouth. The procedure should be done as often as possible. After using garlic, apply a compress with sea buckthorn oil to the tongue, which will prevent possible irritation of the mucous membrane.
- Dried femoral grass is poured with a glass of water, brought to a boil, and then boiled for about 5 minutes. The broth must be filtered and cooled. Rinsing is done twice a day, after which 1 tablespoon of infusion is taken orally.
Numbness of the tongue is a sign of a serious pathology, and not a separate disease. It is important to determine the root cause that caused the loss of organ sensitivity, and only a doctor can do this. Therefore, it is necessary to contact a therapist as soon as possible, who, after carrying out the necessary diagnostic measures, will redirect the patient to the right specialist. Timely identification of the cause of numbness and timely treatment will help prevent the development of the underlying disease and possible complications.
Trigeminal neuralgia
This is another lesion of the nerve fiber structure, which is often chronic and accompanied by periods of exacerbation and remission.
It has several causes, which are divided into idiopathic - when a nerve is pinched, and symptomatic.
The main symptom of neuralgia is paroxysmal sensations in the form of pain on the face and in the mouth.
Pain sensations have characteristic differences. They are “shooting” and resemble an electric shock; they arise in those parts that are innervated by the n.trigeminus. Having appeared once in one place, they do not change localization, but spread to other areas, each time following a clear, monotonous trajectory.
The nature of the pain is paroxysmal, lasting up to 2 minutes. At its height, a muscle tic is observed, that is, small twitching of the facial muscles. At this moment, the patient has a peculiar appearance: he seems to freeze, but does not cry, does not scream, and his face is not distorted from pain. He tries to make a minimum of movements, since any of them increases the pain. After the attack there is a period of calm.
Such a person performs the act of chewing only with the healthy side, at any time. Because of this, compaction or muscle atrophy develops in the affected area.
The symptoms of the disease are quite specific, and its diagnosis is not difficult.
Therapy for neuralgia begins with taking anticonvulsants, which form its basis. Their dose is subject to strict regulation and is prescribed according to a specific scheme. Representatives of this pharmacological group can reduce agitation and the degree of sensitivity to painful stimuli. And, therefore, reduce pain. Thanks to this, patients have the opportunity to freely eat and talk.
Physiotherapy is also used. If this treatment does not give the desired result, proceed to surgery.
Diagnostics
The cause of tongue numbness is determined by a dentist. Patients with neurological symptoms are referred for consultation to a neurologist. In the absence of manifestations of dental and neurological diseases, an extensive examination is carried out with the involvement of a gastroenterologist, psychiatrist, and other specialists. To make a diagnosis:
- Dental examination.
The doctor assesses the condition of the tongue, identifies areas of epithelial desquamation, cracks, and signs of inflammation. Examines the oral cavity for other changes, specifies the type of fillings and dentures. - Neurological examination
. For isolated pathologies, curtain and pharyngeal reflexes and the excitability of the muscle fibers of the tongue are examined. For neurological diseases, reflexes, muscle strength, and sensitivity in various parts of the body are examined. - Saliva studies
. The water indicator is determined using special strips. Potential differences are measured to detect galvanic currents. The subjects are prescribed sialography and ultrasound of the salivary glands. - Other instrumental techniques
. For glossodynia and glossalgia, electromyography is performed. If diseases of the digestive system are suspected, an ultrasound of the abdominal cavity and gastroscopy are performed. - Lab tests
. As part of a laboratory examination, microscopic and microbiological examination of saliva, general and biochemical blood tests, and determination of the acidity of gastric juice can be performed.
Examination of the tongue
Real life examples
Some famous people, whose fame sometimes trumpets all over the world, were also hostage to the pathology of the facial nerve.
Sylvester Stallone, who is known for his enchanting roles, was injured at birth. The actor's mother had a difficult birth and he had to be pulled with forceps. The result is damage to the vocal cords and paresis of the left side of the face. Because of this, Stallone had problems with speech, which became a reason for ridicule from his peers.
The actor grew up as a difficult child. But, in spite of everything, he managed to overcome his defect and achieve considerable success, although partial immobility of his face remained.
Domestic showman Dmitry Nagiyev received facial asymmetry, which was nicknamed “Nagiyev’s squint”, due to paresis of the facial nerve. The illness happened unexpectedly. As a theater student, one day he felt that his face was not moving.
He spent 1.5 months in the hospital to no avail. But one day in his room a window broke due to a draft. Fright provoked a partial return of mobility and sensitivity of the facial part, but the left part retained its immobility.
What is dystonia?
Dystonia of the tongue muscles causes involuntary movements of the tongue and uncontrolled mobility of structures adjacent to the tongue, which can lead to problems with chewing food and articulating sounds. As experts note, this may result in weight loss and loss of the ability to speak. In particularly severe cases, for example, when a patient may suddenly choke on food, tongue dystonia can provoke the development of more serious health problems.
According to observations, musicians who play wind instruments are more susceptible to spasms of the mouth muscles.
Migraine
This condition is accompanied by attacks of unbearable headache. It is also associated with disruption of the trigeminal nerve, or more precisely, with its irritation in one part of the head. This is where the pain is subsequently localized.
The onset of migraine includes several stages:
- initial;
- aura;
- painful;
- final one.
Paresthesia of the head and face appears with the development of the aura stage. In this case, the patient is bothered by a feeling of tingling and crawling, which occurs in the arm and gradually moves to the neck and head. The person’s face becomes numb and it becomes difficult for him to speak. I am concerned about dizziness and visual disturbances in the form of light flashes, floaters and a decrease in the field of vision.
Facial paresthesia is a precursor to migraine, but often the attack occurs without the aura stage.
Diagnostic features
It is important to distinguish glossalgia from organic diseases of the tongue that develop as a result of injuries, neuralgia and neuritis. The doctor will also make sure that there are no bite defects. The main diagnostic criterion for glossalgia is the discrepancy between the sensations of the intensity of the impact. In addition, visible changes in the tongue and mucous membranes are almost completely absent.
In case of injuries, the pain has a clear localization and does not spread beyond the boundaries of the lesion. With neuralgia, sensations occur briefly in the area of innervation of the nerve. With neuritis, pain most often appears only on one side, and is also accompanied by sensory disturbances.
Psychogenic causes of facial neurosis
Undoubtedly, disturbances in facial sensations quite often become a consequence of pathology of internal organs and blood vessels.
But often they are caused by psychological disorders and pathological thoughts that arise in our heads.
Facial paresthesias can be situational in nature and develop during episodic nervous excitement: as a result of quarrels, prolonged and intense screams. Such phenomena cause overstrain of the muscles, especially the cheeks and those located around the mouth. As a result, we experience facial numbness and even mild soreness.
The feeling of fear causes us to breathe quickly and shallowly, or to hold our breath. Disturbances in the respiratory rhythm can also provoke impressions that are atypical for us. A feeling arises that is characterized as a “chill running through.” Moreover, it is more concentrated at the roots of the hair. In this case they say: “chills to the marrow of the bones.” The face also becomes cold, a slight tingling appears in its area.
Such phenomena are disturbing when we are overwhelmed by strong emotions. But they accompany people suffering from mental disorders systematically.
A special type of neurotic facial manifestations is a nervous tic. It is characterized as an uncontrolled and systematic contraction of the facial muscles.
The disorder more often accompanies men. And it manifests itself with the following symptoms:
1.Motor:
- frequent blinking, winking;
- setting the lips with a tube;
- nodding head;
- constant spitting or sniffing;
- opening or upturning of the corner of the mouth;
- wrinkling of the nose.
2. Vocal:
- screaming;
- grunt;
- coughing;
- repetition of words.
There are also signs – precursors – that signal the appearance of a tic.
These include itching, facial heat and other paresthesias. Naturally, these signs are considered pathological if they occur in an inappropriate situation. It happens that only the patient himself feels them, but they are not visible to others.
But often twitching and other nervous symptoms become noticeable by other people, and they cause a lot of discomfort to the patient.
Tics can be simple, when there is only one symptom, or complex, which combines several manifestations.
The most common, main cause of tics is mental stress. It can be caused by a strong stress factor of one-stage action. Perhaps you were very scared of something, or broke up with your loved one. That is, the shock was so strong for you that your nervous system lost control.
Or, on the contrary, disorders develop as a result of prolonged monotonous exposure. Symptoms often appear due to lack of sleep and overwork.
Their duration varies. A situational nervous tic disappears a few hours or days after the cause is eliminated. In another case, it persists for years or haunts the patient throughout his life. In such a situation, in addition to eliminating the provoking factor, subsequent psychological work with the patient is required. This type of disorder is called chronic.
A nervous tic can be one of the signs of mental disorders such as neurosis, obsessive thoughts and phobias, depression.
Another group of provoking factors include:
- diseases - stroke, brain injury, infections or poisons;
- neurodegenerative diseases - Huntington's chorea. Characterized by destruction of brain tissue. Accompanied by uncoordinated, sudden movements, as well as neurological disorders of the face. Of these, the first sign is slow eye movements. Then a muscle spasm of the face occurs, which manifests itself in grotesque facial expressions - grimacing. Speech, chewing and swallowing are impaired;
- burdened heredity;
- parasitic infestations;
- eye fatigue due to prolonged eye strain;
- unbalanced diet, when the body receives little magnesium, calcium, glycine. These elements participate in the normal conduction of nerve impulses and are responsible for the coordinated functioning of the nervous system.
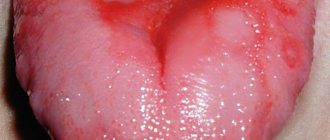
Manifestations of glossalgia
With this disease, patients note a burning sensation, tingling, itching, and rawness in the tongue area. An unpleasant symptom may appear from time to time or bother you constantly. Some patients associate these symptoms with eating spicy foods.
Indirect symptoms include dry mouth and fatigue when speaking. It is worth noting that with overwork and nervous excitement, the symptoms become more pronounced. Sometimes the symptoms of glossalgia appear only in certain situations, for example, before an important event. During meals, manifestations of the disease may become less pronounced or even completely absent.
The feeling of burning and tingling most often spreads to the sides and tip of the tongue. They occur much less frequently on the back and root of the tongue. The pain is widespread, there is no obvious focus, and the location can change quickly. The symptom may disappear and appear in another area.
It is important to note that there are no visible changes in the mucous membrane of the tongue and oral cavity. Only some people suffering from this disease may experience swelling or plaque on the tongue, hypertrophy of the lingual papillae. Varicose veins of the tongue are typical for elderly patients.
Many people with glossalgia experience symptoms of depression. Sometimes there is excitability, increased anxiety, and suspiciousness. Many people suffer from fear of developing cancer and other serious diseases, and the disease is accompanied by sleep disturbances, pain in the chest area, etc.
Nervous tics in children
There are several types of such disorders in childhood.
Transient tic disorder begins to manifest itself during early school age. Its duration ranges from 1 month to 1 year. Motor types of tics occur more often. Mainly typical for children with developmental delays and autism.
Chronic disorder occurs before age 18. And lasts from 1 year and above. In this case, either motor or vocal tics develop. The earlier the pathological symptoms appear, the easier and faster they pass.
Tourette syndrome is a multiple tic disorder characterized by both motor and movement types. A serious disease, which, however, softens with age.
A special type of disease, which is also characterized by signs of the nervous type, is minor chorea. It develops against the background of infections caused by streptococcus: sore throat, tonsillitis, rheumatism. Accompanied by pathological changes in nervous tissue.
Along with hyperkinesis, emotional instability, irritation, restlessness and anxiety, this condition corresponds to neurotic changes in the face. They are expressed in tension and spasms of the facial muscles, which is often mistaken for grimacing. There is also a spasm of the larynx, manifested in inappropriate screams.
At school, such children, not knowing the true cause of facial hyperkinesis, and even in combination with increased activity, are reprimanded and kicked out of class. Such an attitude towards the child forces him to miss school classes and avoid going to school. Treatment for chorea minor, along with sedatives, includes antibiotics to fight infection and anti-inflammatory drugs.
A nervous tic leaves a heavier imprint on a child’s psyche than on an adult. It often causes anxiety and detachment, withdrawal, and even provokes depressive disorders. Causes sleep disturbances, speech difficulties, and learning difficulties.
Tic disorders lead to distorted self-perception and decreased self-esteem.
Parents of such children are advised not to focus the child’s attention on the problem. On the contrary, they recommend finding ways to shift attention and increase self-esteem. A special place is given to support groups for such people and communication in general.
Causes of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes
The following factors can provoke the development of neuralgia of the submandibular and sublingual nodes:
- physical impact - prolonged or regular hypothermia of the ganglia;
- chronic inflammatory processes in the oral cavity - stomatitis, multiple caries, gingivitis, periodontitis;
- infectious pathologies - viral diseases, sepsis, syphilis, tuberculosis;
- chronic diseases of the digestive system and pelvic organs;
- negative consequences of surgical interventions - removal or prosthetics of teeth;
- foci of infection in nearby organs - sore throat, otitis media, sinusitis.
Often neuralgia can appear due to intoxication of the body with poisons, salts of heavy metals, and low-quality alcohol. It can also develop against the background of allergic and endocrine diseases, and be one of the manifestations of hypovitaminosis.
How to get rid of nervous tics
In order to free yourself from unpleasant sensations, you must first eliminate their problem. Sometimes all it takes is a good night's sleep. In another case, you need to change the situation for a while, get out of the destructive environment.
Among the auxiliary methods used are herbal soothing teas, baths with the addition of aromatic oils, swimming, walks in the fresh air or sports: running, yoga.
Add ingredients with a high content of calcium and magnesium to your menu. These include fermented milk products, buckwheat, bran bread, red fish, eggs, and meat. Vegetables and fruits include beets, currants, dried fruits, nuts and parsley.
If these foods do not fit into your diet, consider taking appropriate vitamin supplements. Do not overuse strong tea and coffee.
And most importantly: remain optimistic and calm in any situation!
In cases where the condition worsens, psychotherapy is sought. Cognitive behavioral therapy is especially effective in helping to stop tic disorders at the stage of their precursors.
Habit reversal therapy teaches patients movements that help prevent the development of neurological facial symptoms.
Medications include anticonvulsants and muscle relaxants, Botox injections, and antidepressants.
If the above methods are ineffective in combating nervous tics, they turn to deep brain stimulation. A device is installed in the GM that controls electrical impulses.
Treatment methods
Treatment of glossalgia begins with sanitation of the oral cavity: the doctor will prescribe treatment for caries, replacement of incorrectly installed dentures, as well as replacement of fillings that have expired. Making new dentures allows you to create the correct bite height. Also, at the same time, it is necessary to visit other specialists of a narrow profile - a neurologist, endocrinologist, psychotherapist, etc.
The main treatment tactic is to influence the links of the pain symptom. So, the doctor may prescribe bromine, iron, tranquilizers, and sedatives. B vitamins and lingual nerve blocks may be recommended to help restore normal function.
If the mucous membranes are dry and there is insufficient salivation, the doctor will prescribe a vitamin A solution or another product to moisturize and stimulate saliva production.
Reflexology and physiotherapeutic methods can be used as an addition to the main course of treatment. If suspiciousness, increased anxiety, or depression are present, then working with a psychotherapist is indicated.
General recommendations include the following:
- A gentle diet - eating soft foods, avoiding sour, salty, fatty foods, spices and seasonings.
- Normalization of neurological status if necessary. As prescribed by a neurologist or psychiatrist, you can take antidepressants, anti-anxiety medications, nootropics, and drugs to improve sleep.
- Psychotherapy according to indications. In some cases, good results can be achieved with the help of short-term or long-term psychotherapy.
It is important to be attentive to your psycho-emotional state. Relaxation methods, development of stress resistance, and breathing exercises may be recommended to bring the psychological state into balance.
How to remove teak yourself
If a nervous facial tic is situational and is not too intense, but at the same time obsessive, you can try to get rid of it using physical methods.
One way is to try to disrupt the pathological muscle rhythm by overexerting it. For example, if your eye twitches, try to close your eyes tightly.
It is possible to calm an overexcited muscle through a light massage. Or apply cold to it. The temperature difference will also help. Wash your face alternately with cold and warm water.
Numbness of the tip of the tongue and lips
Numbness often affects the tip of the tongue and lips, causing discomfort; the reasons for this are:
- A side effect from certain medications, in particular antibiotics. By damaging nerve endings, they can cause numbness of the entire tongue, as well as its tip and lips.
- Some diseases of the oral cavity and speech. Often such a disease is glossalgia. It often occurs in women after 40 years of age, causing problems with the digestive system, endocrine disorders, etc.
- Age characteristics. For the most part, this applies to women during menopause. This period in the fairer sex is associated with various disruptions and changes in the body, the mucous membrane is disrupted and this often affects the sensitivity of the tip of the tongue, and sometimes the lips.
- Various allergic reactions. It is known that allergies are characterized by swelling, impaired sensitivity, difficulty breathing, and numbness of the lips and tongue is often observed.
- Often, numbness of the lips is associated with various mental disorders. At the same time, rapid heartbeat, shortness of breath, redness of the face, and a feeling of anxiety develop.
- High blood pressure can also lead to severe numbness of the lips, and loss of sensation in the lower extremities can also occur. In this case, you need to take medications that lower blood pressure or, in more complex cases, call a medical team.
- Side effects during pregnancy associated with increased blood pressure and swelling.
- Poisoning, alcohol and tobacco abuse, radiation.
In addition, numbness of the tip of the tongue and lips can also be observed in certain diseases:
- Stroke
- Diabetes
- Hyperthyroidism
- Neuritis
- Syphilis
- Multiple sclerosis
- Brain tumors
- Malignant tumors of the spinal cord
- Bell's palsy
- Certain types of migraine.
In addition to the listed diseases, this phenomenon is diagnosed with tumors of the nasopharynx, multiple sclerosis, herpes zoster on the face, with some viral infections, etc.
Diagnosis of these pathologies is possible only in medical centers; in no case can such diseases be treated independently.
Particular attention should be paid to vascular problems, since they are becoming the leading cause of death in the world. In addition to impaired coordination and speech, a patient with a stroke attack is almost always diagnosed with numbness of the lips and tongue, and sometimes paralysis of one part of the face. If the listed signs are observed, you should immediately call an ambulance. Before her arrival, place the patient on a high pillow, provide access to air, and do not use any medications yourself.
Dermatillomania
Neurosis of the face and scalp can manifest itself in a behavioral disorder such as dermatillomania.
Its main manifestation is scratching the skin of the face and head, not because of itching, but because of dissatisfaction with its appearance. This also includes an obsessive zeal to squeeze out pimples, scratch off scabs, and pull out hair. Self-injurious actions cause a short-term feeling of pleasure, followed by feelings of shame, frustration, and dissatisfaction.
The face of such patients is covered with scars and scars due to constant trauma to the skin. This process is uncontrollable and can occur at any time of the day. But most often traumatic actions are carried out in front of a mirror.
Symptoms of the disorder also include the habit of biting the lips and mucous membranes of the cheeks. Patients are not deterred by the prospect of redness, bleeding, and scarring of the skin. They repeat the ritual day after day. It lasts from a few minutes to an hour.
Such actions can be provoked by feelings of fear, anxiety, and close examination of one’s skin because there is nothing to do.
Dermatillomania has been described as a state of addiction. It begins with concentrating on what the patient thinks is a skin defect. Gradually, attention is increasingly focused on this detail. A person begins to think that he is sick with something serious. This provokes irritability and nervousness in him, leading to obsessive actions.
The root cause of the disease is rooted in the psychological state of a person and lies in self-dissatisfaction, anger, feelings of shame and malice. Traumatic rituals are a way of punishment, self-flagellation.
Treatment of this pathology requires the intervention of a psychotherapist and a dermatologist.
The main method of treating addiction is psychotherapy, in particular cognitive behavioral therapy.
Yoga, physical exercise, relaxation procedures, as well as any hobby that absorbs a person and helps redirect attention will help reduce anxiety, distract and relax.
The help of a dermatologist is necessary to eliminate skin lesions in order to prevent infection and reduce the degree of dermatological defect.
Treatment of tongue spasms
But how can all this help people suffering from tongue spasms? Since dystonia greatly affects the lives of patients, many researchers are busy developing various methods of treating it. The most conservative approach is offered by speech therapy. Repeated exercises strengthen the tongue muscles, and the patient learns to properly tense and relax them when speaking and swallowing food, experts explain.
A more radical method is Botox injections. Botulinum toxin temporarily paralyzes the facial muscles, preventing spasms, but such injections must be done every two to three months when the effect of the drug wears off. Despite a number of disadvantages, this method of treating dystonia is the most effective today, clinicians note.
Treatment of dystonia involves the participation of a whole group of doctors from various specialties. The approach to treatment will depend on the nature of the symptoms that bother you, as well as on your desire to use the treatment method suggested by your doctor. Tongue spasms can cause a lot of trouble, but once the correct diagnosis is made and the appropriate treatment is chosen, patients can expect to return to normal life.
Neuroses
This is a large group of diseases, manifested primarily in psycho-emotional disorders, as well as malfunctions of the autonomic nervous system. They do not cause pathological disorders of the nervous tissue, but have a significant impact on the human psyche.
There are several types of disorders in which the symptoms are visible.
Muscular neurosis is manifested by muscle tension, spasm and convulsive twitching. Neurosis of the facial muscles makes itself felt with the following manifestations:
- nervous tic;
- lip tension, clenching;
- convulsive contraction, the face seemed to move;
- tingling, burning sensation;
- muscle pain;
- Tension of the neck muscles is manifested by a feeling of lack of air, a lump in the throat.
When we find ourselves in a stressful situation, our body produces stress hormones. They, among many other reactions, cause muscle tension. Now imagine, if we are exposed to chronic stress, what happens to our muscles, and specifically to the muscles of the face. Being systematically in hypertonicity, they overexert themselves. This is what causes their nervous twitching, spasms, and convulsions.
Another type of neurosis is skin. It causes paresthesias in the facial skin of the following type:
- severe itching, burning in the facial and scalp without clear localization;
- sensation as if something were touching the face. And it's terribly annoying;
- the appearance of red spots on the face and neck. Possible rash.
The causes of such phenomena are nervous and mental overstrain, chronic stress, sleep disturbances, as well as disruptions in hormonal regulation.
With neuroses associated with disruption of the autonomic nervous system, various manifestations may also occur. Malfunctions in the functioning of the vascular network occur, and a vascular neurotic disorder develops.
Vascular neurosis of the face is manifested by flaking and dryness, a feeling of tightness of the skin. She becomes pale, sometimes cyanotic, and her sensitivity worsens. In addition, sneezing appears, the nose is stuffy, the eyes become red and watery, the skin itches and itches. This indicates the development of vegetative-allergic reactions.
Features of the course of neurosis in women
Neurosis is diagnosed in a third of the world's urban population. Neurology is one of the most common ailments of the nervous system—the disease occurs in every fourth person with mental illness. A study of the incidence of neurosis has shown that neurotic disorders are common in men and women over 30 years of age. However, neurotic disorders in women usually occur in a more severe form than in men.
The reason for such conclusions is the emotionality of women. Doctors note that neurosis most often appears in expressive and emotional people. According to statistics, women are more sensitive than men.
Experts also say that, unlike men, women suffer from neurosis almost twice as much. Menopause is considered one of the causes of neurosis in women. Any hormonal changes affect our nervous system and can bring unpleasant consequences.
Perhaps, in this case, a social factor also plays a role - men are less likely to go to doctors, especially to a psychotherapist. However, today experts say that the flow of men to psychotherapists has increased, but women are still more willing to go to a doctor for help.
Also, by the will of fate and centuries-old traditions, not only a career and daily work falls on a woman’s shoulders, but also cleaning the house and raising children. The modern woman has more tasks, the principle “you need to be strong and hold on” is firmly stuck in your head. However, this unknown force will not protect you from overload and fatigue. Then for help you need to contact a psychotherapist who will prescribe treatment. Psychotherapy sessions help to influence the cause of neurosis, change the attitude towards a traumatic situation and facilitate the release of emotions, accelerating recovery.
Symptoms of neurosis in women
The signs of neurosis in women differ from the opposite sex due to our physiological characteristics of the body. For example, among women the list of symptoms of neurosis includes insomnia, frequent nightmares and sleep paralysis, but this is not observed in men. Also, in women with neurosis, there is a deviation in the menstrual cycle.
Doctors identify the following most common symptoms of neurosis in women:
- anxiety;
- irritability;
- expressiveness of behavior;
- refusal to eat;
- impairment of physical qualities: loss of strength, feeling tired, loss of endurance;
- heart and headaches;
- vestibular disorders, balance disorders
- excessive tearfulness;
- sudden mood swings.
There are several types of neurosis, one of them is hysterical, most often called hysteria. According to doctors, signs of this type of disease are most often observed in women. Experts interpret hysterical disorder as an ardent desire to attract attention to the sick person. The disease is characterized by demonstrative behavior. A person suffering from such a disease often screams loudly, makes scandals, and sobs bitterly.
Medical psychotherapists have extensive experience and all the necessary resources for the successful treatment of neuroses.
Features of the course of neurosis in children
Neurasthenia is also common in children of primary and preschool age. Symptoms of the disorder are similar to those in adults. The difficulty in determining pathology lies only in the fact that young children often cannot explain what is happening to them and how they feel.
The child's appetite decreases, sleep problems appear, and nightmares often occur, as a result of which the baby may even cry out in his sleep and wake up without understanding what is happening. Increased sweating occurs and the temperature of the extremities decreases.
In addition to all the above signs of pathology, the child may have a headache, he is sensitive to bright light and loud sounds. There is also often a sharp change from positive emotions to negative ones: crying, aggression and depression.
Experts recommend immediately seeking help from a doctor, since neurosis in childhood is much more difficult to treat than in adults.
What types of neurosis exist and how do they differ?
- Depressive.
This type of neurosis is characterized by such symptoms in a person as tearfulness, sudden changes in mood, feelings of despair and helplessness. The person suffering from the disorder loses interest in life and becomes melancholy. During depressive neurosis, a person experiences low self-esteem, guilt, and frustration. - Anxious.
Often has manifestations at the physical level: dry mouth, increased sweating, rapid heartbeat. Anxiety neurosis can result in panic attacks and phobias. A person constantly experiences a feeling of fear. - Hysterical (“conversion disorder”)
- most often manifests itself if a person has experienced a strong emotional shock or a traumatic event. There is a change or loss of motor/sensory function indicating a physical disorder that is not detected. For example, after an accident, a person may experience loss of speech, although there is no physical reason for this. - Obsessive-compulsive.
Intrusive thoughts and images appear. Often such thoughts have no rational grain and are catastrophic in nature. To counter the overwhelming anxiety, a person performs compulsive, repetitive actions. - Rehearsal.
It manifests itself as attempts to resolve an issue that in the past remained unfinished. A person suffering from rehearsal neurosis transfers conflicting relationships from the past to the present and believes that this reality still exists today. - Hypochondriacal.
The patient becomes too suspicious and overly concerned about his health; he finds symptoms of various diseases where they actually do not exist. A person invents a terrible disease, torments himself, and stress or anxiety appears. Despite negative tests and consultations with doctors, the patient remains convinced of this. - Depersonalization.
Fear, panic and anxiety appear. It’s as if a person lives in a dream, “disconnecting” from his own body and thoughts. - Military or post-traumatic stress disorder.
It manifests itself under very shocking circumstances, when a person saw death or was captured or suffered serious injuries (physical and psychological). This type of neurasthenia is manifested by very strong stress, panic attacks, and an aggressive state. Such stress is dangerous because it can lead to disability, including functional disability that negatively affects daily life.
For example, a person believes that everyone treats him badly or no one likes him. As a result, he begins to behave in accordance with his ideas about others.
Neurosis and memory problems
Excessive anxiety leads to decreased concentration, which means that the patient often has problems with memory and attention. In order to influence the problem, you can take vitamin complexes of natural origin, as well as conduct useful memory training.
Experts recommend engaging in light physical activity and daily exercise to relieve anxiety and excessive worry.
Try not to multitask, this will only make the problem worse. It is better to remove all distractions while working or doing what you love. Such distractions include a mobile phone or any other mobile device. Turn them off when doing important things.
To reduce the strain on your eyes and brain, take breaks from work and study. Don't overwork yourself. You can take a walk in the fresh air or do some exercise.
Neurosis and psychosis: what is the difference?
Often these concepts are confused or interchanged. But diseases are different in their manifestations and the internal feeling of a person. For example, during the development of obsessive-compulsive neurosis, a person maintains a sense of reality and looks for new ways to adapt to it. He recognizes that he is suffering from a disorder and that this suffering is a product of mental instability.
During psychosis, a person perceives the world around him differently. He adapts reality according to his personal perception (often delusional), experiences hallucinations and delusions. And the main thing is how psychosis differs from neurosis: the patient is not aware of his problem.
Neurosis and vegetative-vascular dystonia
As we mentioned above, during neurosis signs appear on the physical level, such as rapid heartbeat, fluctuations in blood pressure, chest pain, difficulty breathing, etc. All these symptoms are similar to the signs of a disease such as vegetative-vascular dystonia.
VSD is a complex of symptoms of different localization that occur when there is a malfunction in the autonomic nervous system. And neurosis is a disorder of the central nervous system caused by the psyche (stress, depression, etc.). Since the nervous system is connected, disturbances in one department provoke disruptions in the functioning of another.
How is neurasthenia diagnosed?
To diagnose and identify the disease, you need to consult a neurologist, and sometimes a psychologist and psychiatrist. At the city clinic, you can contact your primary care physician, who will write a referral to a neurologist. However, this takes time. You often have to wait 2 weeks for an appointment with a doctor. In some cases, this is simply impossible, since it is necessary to quickly conduct an examination and prescribe treatment before the situation becomes critical.
Therefore, we recommend contacting the Medunion medical clinic. We employ practicing neurologists, and you don’t have to wait several weeks for appointments. Sign up today for a time convenient for you, not for the remaining time, and get tested tomorrow.
Patients choose us because we provide the service of a specialist coming to your home if you cannot come to the clinic on your own. You can also take samples directly at home.
Diagnosis includes interviewing the patient or his immediate family (guardians), collecting anamnesis and studying the medical history. To make a diagnosis, the doctor needs to know the symptoms that bother the patient.
To exclude other pathologies, the neurologist prescribes laboratory tests:
- Blood analysis;
- Analysis of urine;
- Ultrasonography;
- CT scan;
- Magnetic resonance imaging.
The specialist will also conduct psychological tests. For example, color technique. It consists in the fact that the patient is offered a palette of colors from which he must choose the color he likes. Colors such as purple, gray, red, brown, black indicate a high probability of developing neurosis.
Discomfort in the lateral areas of the tongue
When the tongue hurts on the side of any side, the causes of the discomfort may be a discrepancy in the size of the dentures, inflammation of the mucous membranes, heavy smoking, or characteristic neuralgic manifestations.
Pain on the tip of the tongue
The tip of the tongue is constantly in contact with the teeth and is actively involved in the process of creating sounds, therefore it causes special discomfort to people. The most common reasons for this condition are:
- Minor injuries at the end of the tongue
occur most often, since it is this area that first encounters food, dentures and teeth.
- Glossalgia
accompanied by a burning sensation, as well as the possibility of pain spreading to other parts of the oral cavity.
- Glossitis
– inflammatory disease of the oral cavity.
- Stomatitis
causes small painful wounds at the end of the organ.
- Allergic manifestations
occur as a result of immediate contact with certain medications or foods.
Physiological causes of numbness
Numbness occurs with prolonged immobility. Whatever position we are in, some vessels become pinched, and we risk that the nerve endings, which do not receive proper nutrition, will lose sensitivity. Our body must move, changing the areas that have been subjected to compression, and then we will not be in danger of numbness. This usually happens during the day. But during deep sleep, we can lie in the same position for quite a long time without changing posture. And then, when we wake up, we notice that we have rested some part of our body, for example, a hand placed under our head.
Numbness is caused by exposure to cold. When in contact with cold air, the skin loses sensitivity. Local blood circulation is disrupted, and we cease to feel the nerve endings. If this situation lasts longer, frostbite is possible, but in most cases it is enough to rub the area of skin that has lost sensitivity or return to warmth, blood circulation will be restored and the numbness will go away.
If numbness occurs without an obvious connection with a specific situation, then it probably has a pathological cause.
Why does my tongue hurt at the tip, bottom or side?
Among the causes of pain in various areas of the tongue, mechanical damage or thermal burns are most often noted. To find out exactly why the tongue hurts, in each specific case it is worth dealing with the support of an experienced doctor. As a result of examination, surveys and thorough diagnosis, it is possible to determine one of the following causes of pain:
- Accidental cuts, bruises, burns or bites while eating, getting cosmetic punctures or talking;
- Inflammatory processes of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity of fungal or viral origin;
- Allergic reactions when taking specific foods or medications;
- Neuralgic reactions as a result of stressful situations or severe mental trauma;
- Improper functioning of the salivary glands;
- The presence of undiagnosed diseases of organs and body systems (digestive, cardiovascular, endocrine systems);
- Development of oncological diseases of the oral cavity.
What to do if your tongue hurts?
If you experience pain in any area of the tongue, you should make an appointment with a dentist or otolaryngologist. Before going to the clinic, it is necessary to exclude the presence of minor injuries or accidental burns, for which it is important to leave time to heal. If the cause of the pain was a cosmetic puncture, you must strictly adhere to all recommendations and carefully monitor oral hygiene. If your tongue hurts without punctures or wounds, you should consider one of the following options:
- Carrying out dental procedures
with surgery: anesthesia and medical procedures cause swelling of the gums and a small area of the tongue. The discomfort usually goes away as the swelling decreases.
- Inflammatory and fungal diseases of the oral cavity
eliminated by taking antifungal agents and maintaining constant cleanliness in the mouth.
- Inflammatory and infectious diseases of the upper respiratory tract
: sore throat, sore tongue - signs of inflammation of the tonsils or submandibular lymph nodes. The otolaryngologist will draw up a treatment regimen with the prescription of antiviral, painkillers and antihistamines.
Are you worried about short-term or constant pain in different areas of the tongue?
Try to find out the causes of discomfort, remember cases of injury or accidental burns. If pain continues to bother you, you should immediately consult a therapist, dentist or otolaryngologist. An experienced doctor will conduct all the necessary studies and take tests to accurately determine the diagnosis and create an effective treatment regimen. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details! Ask your doctor about contraindications and side effects.