Periostitis is an inflammation of the periosteum, which most often develops as a result of other diseases. Typically, the inflammatory process begins in one layer of the periosteum, and as the disease progresses, it spreads to the rest. The bone and periosteum are closely connected to each other, so there is a possibility of developing a complication in the form of osteoperiostitis - the spread of inflammation, including to bone tissue.
Uncomplicated forms of periostitis are treated by dentists. In addition to treating this disease, it is important to pay attention to the treatment of the underlying pathology that caused the inflammation.
Causes of pathology
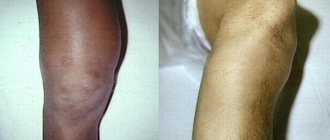
If the lymph node in the neck under the jaw is inflamed, then the possible causes are:
- diseases of infectious origin that affect the ENT organs and the upper parts of the respiratory system (tonsillitis, sinusitis, tonsillitis, laryngitis, pharyngitis, otitis media);
- diseases developing in the oral cavity (caries, periodontal disease, periodontitis, periostitis, or gumboil, pulpitis, gingivitis, alveolitis, stomatitis);
- systemic infections (measles, whooping cough, mumps, popularly called mumps, chicken pox);
- pathologies affecting the immune system (lymphomas, leukemia, lupus, HIV);
- neoplasms (benign or malignant) of various origins (atheromas, granulomas, lipomas, cysts);
- infections caused by parasitic microflora (lymphoreticulosis, toxoplasmosis);
- disruptions in the functioning of the immune system.
You should know that the above ailments are not always accompanied by inflammation of the lymph nodes. Quite often, the nodes remain in a normal state even if the disease is acute.
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, then in 60% of cases the pathology is caused by dental problems, in 30% by diseases of the respiratory system. In 20% of cases, the reason why the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed and hurts is advanced caries, leading to the development of a purulent abscess. After tooth extraction or conservative treatment of caries, pathological processes in the lymph nodes stop.
But sometimes it is tooth extraction that can become a provoking factor and cause an enlarged lymph node. A similar situation is possible if an infection enters the hole.
Diagnostics
Therapists are involved in determining the cause of neck swelling. According to indications, patients are referred to otolaryngologists, endocrinologists, maxillofacial surgeons, and other specialists. The examination includes objective, instrumental, and laboratory techniques. The following diagnostic procedures are carried out:
- Questioning, general examination
. A basic study that allows you to establish a preliminary diagnosis and draw up a plan for further examination. Involves studying symptoms, medical history, and assessing external changes. - Sonography
. Ultrasound of the neck is informative when studying the condition of organs and soft tissues, it allows you to identify tumors, areas of inflammation, determine the localization and boundaries of pathological processes. An ultrasound of the thyroid gland is prescribed if an endocrine cause of neck swelling is suspected. Ultrasound of the lymph nodes is recommended for lymphadenitis and cancerous tumors. - Radiography
. To exclude subluxations and vertebral fractures, X-rays of C1 or the cervical spine are prescribed. If there are symptoms of damage to the ENT organs, an x-ray of the larynx is performed. - Other visualization techniques
. CT and MRI of the neck are performed to detail the information obtained during sonography or radiography and make it possible to clarify the location, volume, and nature of the pathological process. - Radioisotope scintigraphy.
Effective in studying the thyroid gland, visualizes nodes, confirms the presence of diffuse changes. - Endoscopic examination of the throat.
Direct and indirect laryngoscopy, microlaryngoscopy, fibrolaryngoscopy are prescribed for lesions of the larynx. According to indications, a biopsy is performed during the study. - Lab tests
. Depending on the existing symptoms, general and biochemical blood tests, examination of the level of thyroid hormones and antibodies to them, microbiological analysis of swabs, punctures, blood samples, cytological or histological examination of a biopsy specimen can be performed.
Neck palpation
Stages of disease development and symptoms
Lymphadenitis in its development goes through 3 stages:
- stage
– the lymph nodes take on the appearance of mobile, compacted tubercles, when pressure is applied to them, pain appears, the temperature rises, sleep is disturbed, and general weakness is detected;
- stage (purulent abscess)
– the lymph node enlarges more and hurts even if you don’t touch it, which limits the motor activity of the jaw, pus accumulates in the lymph node, the skin around it becomes red, and the temperature is constantly elevated;
- stage (purulent phlegmon)
– the tumor spreads to the lymph nodes located in the armpits, the pain intensifies significantly, the skin turns blue, the temperature rises to 40⁰.
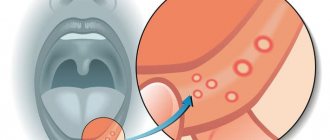
Periostitis of the jaw - symptoms and treatment
Treatment of periostitis is always surgical; if you deviate from this rule, there is a serious danger of a limited focus of inflammation flowing into a more dangerous - diffuse form, which will require different treatment tactics and often hospitalization of the patient.
Treatment of periostitis is standard and consists of eliminating the source of primary inflammation and evacuation of pus, i.e., removing the causative tooth (in cases of unfavorable treatment prognosis) and surgically opening the site to its entire width, followed by drainage.
The procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia; in some cases, drug sedation is indicated; anesthesia is also possible. You need to understand that the introduction of an anesthetic into tissues strained by exudate (fluid accumulation) is an extremely painful procedure, therefore, the method of pain relief before periostotomy (opening an abscess) has its own specifics: conduction anesthesia is preferable (a type of anesthesia when the nerve is blocked to the operation site) followed by local anesthesia performed superficially with a thin needle, without immersing the needle into the abscess.
The diseased tooth must be removed in the case of an unfavorable therapeutic prognosis: the presence of large foci of bone destruction, incorrect previously carried out treatment of the canals, resulting in their perforation or blockage by a fragment of an instrument, etc. In cases of a favorable prognosis, endodontic treatment is carried out, which involves the removal of pulp decay from the canals, appropriate mechanical and medicinal treatment of the canals with a special instrument and powerful antiseptics to eliminate infection in them, followed by temporary filling with calcium preparations and temporary filling of the tooth. Subsequent X-ray monitoring is very important in order to confirm the effect of the canal therapy: the focus of destruction in the bone should decrease and subsequently disappear.
To evacuate pus, periostotomy is performed (dissection of the mucosa and periosteum) along the entire length of the infiltrate along the transitional fold.
As a rule, the surgeon detects a characteristic symptom - detachment of the periosteum from the bone, whereas in a healthy state the periosteum is firmly attached to the cortex. At this stage, the abscess is emptied, or the absence of pus is detected along with the periosteal reaction. The surgeon uses a blunt instrument to probe the entire abscess cavity to identify isolated lesions. In the case of the presence of pus, irrigation (washing) of the subperiosteal space with antiseptics is usually carried out, followed by the introduction of drainage (usually a strip of glove rubber) into the wound to prevent its edges from sticking together. The wound is not sutured; the patient is given a dressing after a day or two to remove the drainage [8].
In the absence of contraindications, antibacterial therapy (in most cases, semisynthetic penicillins) and NSAIDs (nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs) are prescribed. In case of severe edema, desensitizing drugs are prescribed. It is also necessary to prescribe analgesics or their direct intramuscular administration after surgery, since in the first hours after treatment, when the effect of the anesthetic wears off, severe pain symptoms appear. It also makes sense to locally cool the infiltrated area with ice for several hours to reduce bleeding and swelling. The cooling time must be assigned based on the patient’s subjective feelings, and not on specific time periods.
Almost always, this treatment leads to a positive result: within a few hours the patient experiences relief, decreased pain and swelling. Although the infiltrate in the form of a moderately painful compaction will persist for several days.
A follow-up visit the next day is necessary to confirm the results of the treatment and possible removal of the drain if there is no discharge from the wound. Subsequently, the patient is observed by a doctor for 3-5 days; it is quite legal to issue a certificate of incapacity for work for this period. After the pronounced symptoms of inflammation disappear, they begin to continue treatment of the causative tooth.
In rare cases, for example, when the incision is of insufficient length or when the drainage falls out and the edges of the wound stick together, treatment may be complicated due to a delay in the evacuation of residual pus from the lesion. In these cases, the incision should be widened and drainage should be ensured by introducing drainage.
Treatment methods
If the lymph node under the jaw is inflamed, how to treat it? The choice of treatment method is influenced by the cause of the pathology and its neglect. In mild cases, if the cause is eliminated, the inflammation will stop and the lymph node will return to its previous size. If complications are detected, the doctor will prescribe antibiotics or antiviral medications, painkillers, antipyretics and antihistamines. It is also necessary to take vitamins to strengthen the body's defenses. Traditional medicine will help speed up the healing process and eliminate unpleasant symptoms. The course of therapy takes a week and a half.
If a purulent infection occurs, then there will be a need for surgical intervention, during which the surgeon will open the inflamed lymph node and pump out the pus. Fortunately, this situation is extremely rare.
This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Elimination of pain in the muscles of the neck in front
Since this condition is classified as pathological, it requires the most prompt treatment possible. The best option is to consult a doctor, since this specialist has all the necessary knowledge regarding the fight against inflammatory and other diseases that occur in the cervical region. If you have neck pain in the front under your chin, call and make an appointment with the highly qualified, experienced doctors at the Energo Clinic. The telephone number for contact is indicated on the website in the “Contacts” section; registration is carried out on any day and time of day convenient for you.
Drug treatment
After collecting anamnesis, conducting an examination and finding out why your neck hurts in front under the chin, our neurologist
will write out the most detailed treatment plan for the disease and instruct what needs to be done to prevent the disease from worsening again. The most important point will be taking medications - painkillers and anti-inflammatory drugs, drugs whose action is aimed at maintaining the optimal condition of the muscular frame and skeletal system.
Massage and physical therapy
Conducted strictly in the presence of a chiropractor
,
massage therapist
or doctor at a physical therapy room. The neck is a rather delicate organ; it should not be pressed, and often not heated intensely, as this can cause a deterioration in the condition. At the same time, a soft, relaxing massage will help relieve muscle tension and normalize blood flow.
Surgery
It is necessary in situations where the condition threatens the normal course of a person’s life. For example, if the thyroid gland is enlarged and there is no effect from medications, the affected organ is removed in a surgical hospital. After the operation, it is necessary to follow the recommendations of the attending physician, undergo regular examinations by an endocrinologist, and take hormones.
ethnoscience
Effective for inflammatory diseases, but should only be used as an additional treatment measure. A proven folk remedy is a decoction of chamomile or calendula - it is used for colds and to relieve throat spasms. In situations where a person has pain in the neck under the chin as a result of thyroid pathologies, herbal medicine brings good results: certain medicinal plants contain components that have a positive effect on the state of the hormonal system.