Definition of disease. Causes of the disease
Stomatitis is an inflammation of the oral mucosa.
This disease is characterized by all the signs of an inflammatory process: redness, pain, swelling, dysfunction, increased local and general body temperature. Stomatitis can occur on the mucous membrane of any part of the oral cavity: on the gum, on the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the palate, in the vestibule of the oral cavity, in the retromolar fossa, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips. The disease can manifest itself in a variety of forms: it can be redness of the mucous membrane in a certain area or the appearance of ulcers in the mouth. Stomatitis manifests itself with decreased immunity and chronic diseases, and stomatitis can also develop as a protective reaction of the body to the action of various irritants (for example, mechanical trauma to the mucous membrane from the sharp edges of teeth).
Inflammation of the oral mucosa occurs in most cases in children [12]. But recently, stomatitis has also appeared in the adult population. This is mainly due to the weakening of a person’s immunity, for example, with acute respiratory viral infections, chronic diseases, and HIV infection.
Preventive measures
A very important part of prevention is timely treatment of dental and ENT diseases.
Stomatitis can occur in anyone, regardless of age and lifestyle, but compliance with the following preventive measures can reduce this risk:
- Maintaining oral hygiene and timely treatment of dental diseases.
- Providing a balanced diet to supply the body with the necessary amount of vitamins and nutrients.
- Taking vitamin complexes in spring and autumn.
- Timely treatment of diseases of the ENT organs and digestive system.
- Rejection of bad habits.
Symptoms of stomatitis
The manifestation of stomatitis can be different.
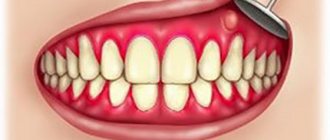
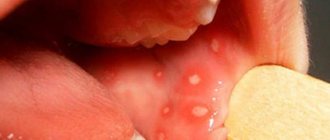
This depends on the form and stage of development of the disease. The first symptom is redness of the oral mucosa in a certain area. The spot does not rise above the level of the mucous membrane, has a round or oval shape and may be pinkish or whitish in color. Next, the area around the affected area becomes swollen, hyperemic, and pain appears. Aphtha appears at the site of the spot. Aphtha (from the Greek aphtha - ulcer) is a superficial defect of the mucous membrane, having a round shape and a grayish fibrinous coating. If you remove necrotic plaque from the surface of the aphthae, the ulcer will begin to bleed [5]. Most often, aphthae are located along the transitional fold, on the lateral surface of the tongue, on the mucous membrane of the cheeks and lips.
In severe forms, the amount of fibrinous plaque on the surface of the ulcer increases, and an infiltrate appears at the base of the aphthae (an accumulation of cellular elements of blood and lymph in the mucous layer). With such a clinical picture in the oral cavity, the patient experiences pain, burning, itching, bad breath, increased salivation, and eating becomes difficult. Body temperature rises to 38 ℃, weakness appears.
A feature of the disease is frequent relapses. Repeated rashes may appear after a few days or every few months. It depends on the ability of the immune system to fight infection.
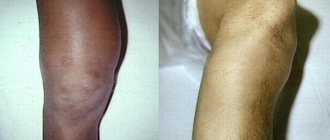
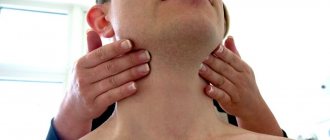
In the most severe cases, stomatitis manifests itself in the form of ulcers on the mucous membrane. An ulcer is a deep defect of the mucous membrane, in which the entire thickness of the mucous membrane is affected. The ulcer is surrounded by an inflammatory infiltrate, the edges of the ulcer are uneven, scalloped (jagged) [5]. When ulcers appear in the oral cavity, the general condition also worsens. The submandibular lymph nodes on the affected side may become inflamed. On palpation they will be enlarged and painful.
With candidal stomatitis, a white coating appears on the tongue and gums; when trying to remove the plaque, the affected areas begin to bleed. There is also an unpleasant taste in the mouth and a burning sensation. If candidal stomatitis develops against the background of diabetes mellitus or immunodeficiency conditions, it always has a chronic course.
With viral lesions of the oral mucosa, pain occurs, which intensifies during eating and when talking. The mucous membrane turns red and swells, then small blisters appear on it. The bubbles quickly open and aphthae form in their place. In moderate and severe forms, body temperature rises to 37-40 ° C, general malaise, weakness, and headache are noted.
Is stomatitis contagious?
The disease can be recognized and treated in a short time.
At the appointment, the doctor must correctly determine the causes and type of stomatitis, because drawing up a treatment plan depends on this. Depending on the classification, appropriate drugs are selected. Is stomatitis contagious?
Inflammatory ulcers that arise as a result of:
- allergic reaction;
- mechanical damage to the mucosa;
- during intoxication.
The disease is contagious if it develops during an infection in the body.
This class includes: fungal, herpetic, infectious stomatitis. Stomatitis in children can be caused by the herpes virus, chickenpox, adenovirus, influenza or parainfluenza. Transfer methods:
- general toys;
- household items;
- dishes and cutlery;
- hygiene items;
- towels
It can also appear with a weakened immune system or while taking antibiotics.
Whether stomatitis is contagious can only be determined by a doctor upon examination of the oral cavity. You cannot self-medicate and wait until the inflammation goes away on its own.
Incubation period
When any virus enters the human body, there is an incubation period during which symptoms do not appear or do not indicate a specific type of virus. It is impossible to predict the incubation period of the virus before the onset of stomatitis, because:
- The type of virus itself is not known.
- It is not known whether stomatitis will occur at all or whether it can be avoided.
However, in cases of stomatitis, it is noticed that the virus is activated within a period of several days (herpes, measles, adenoviruses) to two weeks (chickenpox). And with proper treatment it goes away in about a week or two.
In cases of herpes, the virus most often remains dormant in the host’s body after treatment. At the same time, others can become infected, and the person himself, until the level of immunity sharply decreases against the background of other diseases, will feel completely healthy.
How to get rid of stomatitis?
Stomatitis is perhaps the most common and unpleasant disease of the oral cavity. When an infection enters the body, ulcers form in the mouth. They cause discomfort and can subsequently lead to serious complications. How to treat stomatitis ?
Treatment of any infectious diseases first of all involves going to the doctor. Antibacterial therapy should be carried out under medical supervision. Bacterial disease most often goes away in 1-2 weeks. If the stage is not advanced, it can be treated independently. How to treat stomatitis at home :
- Rinse your mouth with soda solution. Add 1 spoon of soda to a glass of warm water. You can also use boric acid (1 teaspoon per 150 ml of water) or hydrogen peroxide (1 teaspoon per half a glass of water).
- Chamomile decoction. Heals wounds quickly.
- Sea buckthorn oil has an antibacterial effect. You can use antiseptics: chlorhexidine or miramistin.
- Anesthetic dental gels will help relieve severe pain. They should contain lidocaine.
Soda solution can also be used to treat stomatitis in infants .
Wipe the mouth and tongue with moistened gauze. If signs of stomatitis (bacterial) do not disappear, you should consult a doctor.
In case of aphthous form of the disease, you should urgently go to the clinic. How to determine:
- multiple large and deep ulcers;
- grayish coating in the center;
- red rim around the wound.
This type of stomatitis should not be treated at home. It is forbidden to cauterize ulcers with alcohol, iodine, or brilliant green. An advanced disease can lead to suppuration and tissue death.
How to get rid of stomatitis in children?
Basic methods of local therapy:
- Treating the oral cavity with baking soda. For preparation you will need 1 tablespoon per glass of boiled water. Apply 3-6 times a day.
- Rinse with Blue solution. Or 2% boric acid.
- Use of antifungal agents. This includes medicated creams and ointments. For example, Clotrimazole, Pimafucin, Nystatin, Candide.
Symptoms of stomatitis in children and treatment can be determined by a doctor. Treatment is carried out in accordance with the doctor's prescriptions. If the dosage is not followed correctly or the course is interrupted, side effects may occur.
You should not self-medicate, as this can harm the baby.
Only a pediatric dentist will prescribe the correct therapy. He can also advise treating stomatitis in children at home .
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the depth of tissue damage and the cause of inflammation, experts distinguish the following types of stomatitis:
- catarrhal;
- aphthous;
- candida;
- ulcerative;
- herpetic;
- traumatic;
- allergic.
The catarrhal form of stomatitis is the mildest and rarely causes complications. But treatment is still required, mainly local. The most severe course is ulcerative necrotizing stomatitis, which often causes bacterial complications.
The candida type occurs more often in young children.
Each type of disease has its own characteristics, causes of development and symptoms. It is difficult to determine the shape yourself.
Sometimes even specialists do not have enough clinical picture to make an accurate diagnosis. Additional laboratory tests are often required to determine why stomatitis occurs in the mouth and whether it is associated with other diseases.
Diagnostic features
At the initial appointment, the dentist examines the oral cavity and analyzes complaints. To make an accurate diagnosis, you need to distinguish this form of the disease from others, as well as differentiate it from other pathologies that have similar symptoms. For extensive lesions, different diagnostic methods may be used:
- clinical blood tests;
- microflora smear;
- blood for PCR to determine the causative agent of the disease;
- biopsy (if indicated).
They are also necessary for recurrent forms of the disease. In simple cases, laboratory diagnostics are not required; aphthae are determined visually by an experienced specialist.
With the help of a comprehensive examination, the doctor will determine which microorganism caused inflammation with subsequent ulceration of the mucous membrane. He also differentiates the disease from herpetic stomatitis and oncological pathology.
Causes of stomatitis
Many factors contribute to the development of stomatitis. One of the common causes of the disease is the action of an irritant . The mucous membrane can be affected by constant mechanical trauma (biting the cheeks and tongue, trauma from tartar, incorrectly made prosthesis or crown) [5]. Injury can be caused by exposure to a thermal or chemical agent, for example, when a mucous membrane is burned by hot food or when an allergy occurs to certain foods (for example, citrus fruits) or medications. The risk group includes smokers, since nicotine also acts as an irritant to the mucous membranes.
Oral hygiene plays a major role in the development of stomatitis. With improper oral care, plaque and tartar accumulate; the microorganisms present in them (staphylococci, streptococci) can cause irritation and inflammation of the oral mucosa. As a result, stomatitis occurs as a protective reaction of the body.
Sometimes inflammation of the mucous membrane occurs in various chronic diseases and pathologies with an unclear etiology (cause). Stomatitis can manifest itself in the oral cavity against the background of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (with helminthic infection), cardiovascular system, blood diseases (anemia), endocrine disorders (diabetes mellitus). Very often, stomatitis develops during HIV infections and can be one of the diagnostic signs when identifying HIV.
Reason/Example
| Fungal infections | ⠀•⠀Candidiasis |
| Bacterial infections | ⠀•⠀Acute necrotic ulcerative gingivitis ⠀•⠀Syphilis ⠀•⠀Tuberculosis |
| Viral infections | ⠀•⠀Chicken pox ⠀•⠀Herpes simplex virus |
| Physical factors | ⠀•⠀Poorly fitting denture ⠀•⠀Improperly made crown ⠀•⠀Improper bite ⠀•⠀Biting cheeks and lips ⠀•⠀Tartar |
| Medicines | ⠀•⠀Antibiotics ⠀•⠀Barbiturates ⠀•⠀Chemotherapy drugs |
| Allergens | ⠀•⠀Occupational exposure to dyes, acid fumes, heavy metals ⠀•⠀Allergic reaction to food |
| Chronic diseases | ⠀•⠀Diabetes mellitus ⠀•⠀Anemia ⠀•⠀HIV infection |
If you notice similar symptoms, consult your doctor. Do not self-medicate - it is dangerous for your health!
Causes of acute stomatitis
Acute stomatitis occurs most often after damage to the mucous membrane or against the background of a viral disease. Injuries create favorable conditions for the proliferation of pathogenic microorganisms, including the herpes virus. Stomatitis in adults usually has a herpetic form.
Relapses of the inflammatory process usually occur in the cold season, when acute respiratory viral infections, in particular influenza, progress. This coincidence is not accidental. Viral diseases contribute to the appearance of stomatitis in adults and children.
Causes of chronic stomatitis
Chronic stomatitis in the oral cavity regularly worsens. In the summer, a temporary remission is observed. Chronic inflammation is caused by concomitant pathologies of the endocrine system, digestive tract, and diseases of an autoimmune nature. Dental diseases, including caries, periodontal disease, and gingivitis, also contribute to the protracted course of the inflammatory process.
Treatment of stomatitis with folk remedies
Treatment of diseases, especially in the early stages, is possible at home. How is stomatitis in the mouth treated in adults ? Anti-inflammatory and healing folk remedies:
- chamomile with honey;
- burdock root and chicory herb;
- grated raw potatoes (keep in mouth for 5-7 minutes);
- yarrow decoction;
- crushed burdock seeds;
- garlic mixed with curdled milk (or sour cream).
If your body lacks vitamins, you can prepare a vitamin salad.
Burdock leaves, horseradish roots, green onions, sour cream and salt are added to it. Effective treatment of stomatitis at home is possible. The patient must also:
- perform daily oral hygiene;
- follow a diet;
- limit alcohol consumption;
- give up sweets, chips, crackers.
There is a high probability of this disease appearing again. But if you carry out the right treatment, this will not happen.
How to treat stomatitis in children?
Parents who discover ulcers in their child’s mouth are required to contact a pediatric dentist. The following will help prevent the spread of infection:
- limiting contact with other children;
- allocation of separate dishes;
- own personal hygiene items.
The course of therapy consists of taking medications:
- painkillers;
- antiseptic;
- antiviral;
- healing.
How to treat stomatitis in children ? Allowed to process places:
- Oxolinic ointment. Apply 2-3 times daily.
- Acyclovir. The interval between applications is 8 hours.
- Tebrofen gel. No more than 4 times a day.
Pain-relieving ointments can be used. For example, Lidochlor and Kamistad (allowed for 3 months).
Ointments and gels
1. Acyclovir An antiviral drug that has a highly selective effect on herpes viruses. In case of herpes, it prevents the formation of new rash elements, reduces the likelihood of complications, accelerates the formation of crusts, and reduces pain in the acute phase of herpes zoster. The ointment is applied to the affected areas of the skin 4-6 times a day (as early as possible after the onset of infection). Cost: up to 220 rub.
2. Metrogyl denta
A combined antimicrobial drug, the effectiveness of which is due to the presence of two antibacterial components in its composition.
For aphthous stomatitis, the gel is applied to the affected area of the oral mucosa 2 times a day for 7-10 days. The drug is contraindicated in people under 18 years of age. Cost: up to 300 rub.
3. Oxolinic ointment Demonstrates antiviral activity against herpes simplex viruses, herpes zoster, and influenza viruses (mainly type A2). For external use. Non-toxic, non-irritating if the required amount and concentration have been applied and the skin at the application site has not been damaged. Cost: up to 100 rub.
4. Vinilin is a drug that has an antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, enveloping effect, promotes the cleansing and healing of wounds and ulcers. The antimicrobial effect of the drug inhibits the growth and development of microorganisms. Envelops and regenerates. Vinilin acts as a local anesthetic. Vinylin is usually prescribed by dentists for the treatment of stomatitis, because it has not only antimicrobial, antiviral and antifungal effects, but also healing. A protective film is formed, which protects the wound from irritation upon contact with products, thereby reducing pain. Vinilin does an excellent job of treating stomatitis, but it should be used as prescribed by a dentist. Suitable for any type of stomatitis. Cost: up to 200 rub.
1. Anaferon Lozenges. Immunomodulatory agent. When used prophylactically and therapeutically, it has an antiviral effect. It is used for complex treatment of infections caused by herpes viruses, as well as acute and chronic viral infections. Allergic reactions and increased individual sensitivity to the components of the drug are possible. Contraindications include individual sensitivity to the components of the drug. It is not recommended for use by people with congenital lactose deficiency syndrome. Cost: up to 240 rub.
2. Immunal The drug is in the form of drops for oral administration. Used in cases of decreased immunity, stimulates the immune system in uncomplicated acute infectious diseases. Contraindicated during breastfeeding without prior consultation with a doctor. Cost: up to 340 rub.
3. Givalex Antibacterial and antifungal agent. It has a bacteriostatic and weak bactericidal effect. The drug is in the form of a spray and solution in bottles. It is used as a means for the local treatment of infectious and inflammatory lesions of the oral cavity and pharynx, which are caused by microflora that are sensitive to the action of the drug. It is used to prevent the development of infectious and inflammatory lesions after dental surgery. During pregnancy, use according to strict medical indications. If breastfeeding, use of Givalex should be discontinued. Cost: up to 150 rub.
4. Clotrimazole
Clotrimazole is an antifungal medicine.
Has a wide range of antifungal effects. The active ingredient of the drug is an imidazole antimycotic agent. . This medicine is effective against dermatophytes and yeast fungi. In addition, the drug has an antimicrobial effect. Clotrimazole should not be used if you are hypersensitive (allergic) to clotrimazole, its auxiliary ingredients, or in the first trimester of pregnancy. Cost: up to 360 rub.
5. Ketotifen Ketotifen is produced in tablets and syrup. The main ingredient of the product is ketotifena fumarate. The drug is intended for long-term use. The maximum effect can be achieved only after several weeks of treatment. The average course of therapy can last from 2 to 3 months. Discontinuation of the drug is carried out gradually - from 2 to 4 weeks. Ketotifen is not prescribed to those whose profession involves driving vehicles or potentially dangerous machinery. Cost: up to 100 rub.
6. Tavegil Tavegil in solution for injection is used in the prevention and treatment of pseudoallergic and allergic reactions. Tavegil is not prescribed to patients undergoing treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. In addition, the drug is not prescribed to patients with damage to the lower respiratory system. Cost: up to 200 rub.
Drugs that accelerate the healing of the mucous membrane
1. Vitamin A Has a general strengthening effect, normalizes tissue metabolism, and participates in redox processes. Increases the body's resistance to infection. The drug is taken orally early in the morning or late in the evening, 10-15 minutes after meals, 1 capsule 1 time per day. Long-term daily use can cause intoxication, hypervitaminosis A (headache, nausea, vomiting). Contraindicated during pregnancy and breastfeeding. Cost: up to 100 rub.
2. Sea buckthorn oil Oil preparations always act more gently than aqueous or alcoholic medicinal solutions. This oil can be used if there is no allergy to natural oils. Treatment is carried out by lubricating the areas of erosion a maximum of three times a day. A cotton swab or disk should be dipped in oil and then applied to the mucous membrane. Cost: up to 150 rub.
Anti-inflammatory drugs, antiseptics
Anesthetic (painkiller) drugs dull pain in the mouth for a short time. 1. Hexoral Antiseptic for topical use in ENT practice and dentistry. The drug has a wide spectrum of antibacterial and antifungal effects, in particular against gram-positive bacteria and fungi of the genus Candida. It is prescribed as a symptomatic remedy. The drug is sprayed into the mouth or pharynx, and the affected areas are treated while holding your breath. One injection for 1-2 seconds 2 times a day. The duration of treatment is determined by the doctor. Cost: up to 310 rub.
2. Lidocaine Asept Available in aerosol form. The drug can be used for local anesthesia in dentistry. Apply topically, externally. The dosage varies depending on the doctor's indications. You can also apply it using a cotton swab soaked in it. Contraindications include hypersensitivity to lidocaine. Cost: up to 280 rub.
3. Decathylene Has antibacterial and antifungal effects. Affects microorganisms that cause mixed infections of the mouth and throat. Decathylene does not contain sugar, so it is suitable for people with diabetes. Recommended for aphthous stomatitis. Contraindications – hypersensitivity to any of the substances that are part of the drug. Cost: up to 1300 rub.
Prevention
Prevention helps avoid relapses of stomatitis. First of all, it is worth protecting the mucous membrane from the action of aggressive factors: poor-quality hygiene products, cold or, conversely, scalding food, traumatic dentures and uneven edges of teeth, cigarette smoke, and alcoholic beverages.
Strengthening local immunity plays an important role in preventive measures. The oral mucosa is a protective barrier. If the normal microflora is disrupted, the number of potentially dangerous infectious pathogens increases, they actively multiply and cause a response - an inflammatory process.
To strengthen the immune system, you can use natural factors (hardening with water, sun, air) or natural and artificial immunostimulants.
It is recommended to consume honey in courses, which has antimicrobial activity and functions as a biostimulator. Among medications to strengthen local immunity, it is useful to chew Echinacea tablets and use the drug Imudon.
The presence of bad habits, especially frequent smoking, disrupts the local microflora, irritates the mucous membrane and causes inflammation. Try to gradually reduce the number of cigarettes to give up them painlessly.
Several times a year it is necessary to take courses of multivitamin preparations. Prophylactic treatment usually takes 1-2 months. Pay attention to the quality of your diet. Your daily diet must include vegetables and fruits. Avoid foods that irritate or damage the mucous membrane. Be sure to promptly treat tooth decay and remove tartar at the dentist's office. Carefully choose a specialist who selects the prosthesis and installs it. During the period of adaptation to prosthetics, use the dental gel Cholisal with antimicrobial activity or Metrogyl denta.
Sources:
- https://ProBolezny.ru/stomatit/
- https://stom-info.ru/stomatit/
- https://stomatita.ru/
- https://atvmedia.ru/materials/stomatit-vo-rtu-u-vzroslyh