Tonsils - what are they and why are they needed?
The tonsils are represented by lymphoid tissue, which provides human protection, that is, it belongs to the organs of the immune system. The tonsils prevent harmful flora from entering the respiratory tract.
Lymphoid tissue contains lymphocytes. These cells actively fight microbes, viruses and fungi, preventing them from multiplying. The tissue of the tonsils is loose, so representatives of pathogenic flora are retained in it. If protection is provided at the proper level, then they will simply be destroyed by lymphocytes.
The tonsils (or palatine tonsils, which are located between the palatine arches) are a collection of lymphoid tissue that is designed to protect the respiratory system. The tubal tonsils are paired and are located in the pharynx. If you just look into your mouth, you won't be able to see them. They are rarely subject to inflammation.
Single tonsils include the pharyngeal and lingual tonsils. The pharyngeal tonsil is located at the arch of the pharyngeal wall. It is called adenoids, and when it becomes inflamed, it indicates adenoiditis. It most often affects young children. In adults it undergoes reverse development. The lingual tonsil is located under the tongue at the back of it. It gets inflamed less often than others.
Causes of inflammation of the tonsils
Inflammation of the tonsils most often results from infections caused by viral or bacterial flora.
Its representatives reach the tonsils through the nose and mouth, since most of them are transmitted by airborne droplets. They linger on the mucous membrane and provoke its inflammation.
Infectious agents that most often lead to disease:
- Staphylococci.
- Streptococci.
- Adenoviruses.
- Herpes virus.
- Haemophilus influenzae.
- Mycoplasmas.
People encounter pathogens every day. However, people don't get sick that often.
The infection develops when the body is simultaneously affected by several factors:
- Hypothermia.
- Weakened immunity due to a previous illness.
- Acute stage of chronic disease.
- Unbalanced diet, vitamin deficiency.
- Injury to the mucous membranes of the oral cavity.
- Emotional shock.
The final diagnosis will differ depending on the location of the inflammatory process:
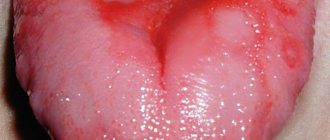
- Acute sore throat. Inflammation is concentrated in the tonsils, the degree of its intensity varies. Catarrhal tonsillitis is characterized by swelling of the mucous membranes, an increase in body temperature up to 38 °C, and mild pain. With follicular angina, all symptoms intensify. If you examine the surface of the tonsils, you can see a white coating on them. The third type of sore throat is lacunar inflammation. In this case, purulent masses accumulate in the folds of the tonsils. This leads not only to severe pain, but also to the appearance of bad breath.
- Chronic sore throat. This form of the disease develops in people who have not received adequate therapy for acute inflammation. From time to time, a sore throat will remind itself. If you examine the tonsils of a person with chronic tonsillitis, you can see white plugs on them, which are concentrated in the lacunae. At the same time, a person may not complain about a sore throat.
- Adenoiditis. With this disease, the inflammatory process will be concentrated in the pharyngeal tonsil. A person’s nasal breathing worsens, discomfort appears in the throat, and the mucous membranes swell. The disease tends to become chronic.
Forecast
Unilateral inflammation or swelling of the tonsils is a fairly common symptom. In most cases, discomfort in the throat goes away within a few days after starting regular gargling or using antiseptic sprays. However, for successful treatment it is important to identify the cause of unilateral damage to the tonsils and eliminate it.
It is recommended to trust your doctor in matters of diagnosis and therapy, and not try to cope with the pain on your own. The fact is that some diseases quickly become chronic, which is difficult to treat. In severe cases, chronic tonsillitis can only be eliminated through surgical methods.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils
Symptoms characterizing the inflammatory process in the tonsils may vary, although slightly.
Common signs of the disease include:
- Increase in body temperature to high levels.
- Swelling of the mucous membrane of the oropharynx, hyperemia of the mucous membranes.
- Cough.
- Runny nose. With angina, this symptom is most often absent.
- General physical weakness.
If a person is infected with herpetic sore throat, then in addition to a sore throat and high body temperature, he experiences discomfort in the abdomen, and a small rash that looks like blisters is noticeable on the tonsils and back wall of the throat. They contain liquid. In the future, it can become purulent. After opening the blisters, the affected areas become covered with crusts.
If a person has an inflamed lingual tonsil, this is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The tongue swells and it hurts for a person to move it.
- When chewing and swallowing food, severe discomfort occurs.
- Pain forces a person to change his speech, as intense movements of the tongue become impossible.
Sometimes the patient notices that his tonsils are inflamed, but does not experience pain. This symptom may indicate chronic tonsillitis.
The temperature remains within normal limits, as the immune system stops making efforts to fight the source of infection.
Inflammation of the tonsils
More often than other tonsils, it is the tonsils that suffer in people. The most common pathology is acute or chronic tonsillitis. This disease becomes dangerous for humans if there is no treatment. The therapy must be selected by a doctor; this is the only way to make it effective.
The success of treatment is determined by its focus. To do this, you need to know which microorganism caused the inflammatory reaction. For this purpose, the doctor prescribes a bacteriological examination of a throat smear. When the analysis is ready, the doctor will be able to select the optimal therapy.
Unilateral inflammation of the tonsil
If the infection affects the tonsil on one side, this indicates activation of local immunity. He dealt with the pathogenic flora on one of the tonsils on his own and is able to maintain its health.
Sometimes unilateral inflammation is a sign of facial neuritis, lymphadenitis or other disorders that are not associated with otolaryngological diseases.
Unilateral inflammation requires treatment, which is selected in accordance with the causes of the disease.
Preventive measures
To keep your tonsils healthy, you need to:
- avoid hypothermia, stress and anything that potentially threatens a decrease in immunity,
- promptly treat any infectious diseases,
- visit the dentist regularly, avoid caries and treat your teeth in a timely manner,
- avoid injury to the tonsils.
If a person is prone to throat diseases, you can consult a doctor about taking prophylactic medications to boost immunity. Quitting smoking will help reduce the risk of developing tonsillitis and pharyngitis.
Inflamed tonsils in a child
In children, the tonsils become inflamed very often. The causes in most cases come down to a viral infection or a sore throat.
If cold viruses have entered a child’s body, then most often his condition is not significantly affected. After 3 days there is a significant improvement that can be compared to recovery.
When a child has a sore throat, the symptoms will be as follows:
- Increase in body temperature to high levels.
- The appearance of a severe sore throat, which makes the child refuse not only food, but also water.
- Children become whiny and lose their usual activity.
- Breathing becomes heavier.
- A white coating appears on the tonsils.
If you can cope with a common cold on your own, then a sore throat requires medical help. Most often, this disease is treated with antibiotics.
Inflammation of the adenoids is no less common a problem than tonsillitis. With adenoiditis, the pharyngeal tonsil increases in size.
Symptoms that will indicate an inflammatory reaction:
- Snore.
- The appearance of mucus from the nose, which will have a green or yellow color.
- Headache.
- Deterioration in sleep quality.
- Cough.
- Voice change. He becomes nasal.
To cope with adenoiditis and prevent further growth of tonsil tissue, you need to consult a doctor.
Which doctor should you consult if you have inflammation of the tonsils?
The diagnosis and treatment of diseases of the tonsils is carried out by an ENT doctor, that is, an otolaryngologist. You should contact a specialist when the first symptoms of inflammation appear. However, few people rush to consult a doctor if their throat starts to hurt a little. It is possible that you will be able to cope with the disease on your own.
However, there are some conditions that require immediate medical attention:
- Body temperature reaches 38 °C and above. It lasts longer than 3 days.
- The person’s well-being deteriorates sharply.
- First there is an improvement, and then a deterioration in the condition.
- The child's tonsils become inflamed.
- Purulent foci of infection are visible in the throat.
Treatment of sore tonsils in adults
Most often, inflammation can be dealt with at home. However, if the lingual tonsil is affected, hospitalization is always required.
Self-therapy can only be carried out if a person is firmly convinced that the inflammation has a viral basis. A bacterial infection requires contacting a doctor, as it poses a danger to the patient’s health. Treatment boils down to taking medications that are aimed at eliminating the causative agent of inflammation. In addition, efforts need to be directed towards making a person feel better. This treatment is called symptomatic.
If a person decides to cope with inflammation on his own, but after 3 days there is no improvement, then he should consult a doctor.
Recommendations to speed up recovery:
- You need to drink as much fluid as possible. In addition to water, it is good to drink tea, compotes, broths, and fruit drinks.
- During the acute phase of the disease, a person must adhere to bed rest.
- There is no need to force yourself to eat. Food is consumed as appetite appears.
If the disease is complicated by suppuration, which cannot be relieved at home, the person is recommended to wash the tonsils in the ENT office.
Removal of tonsils is rarely done. Surgery is required only when all conservative methods have proven ineffective. Patients with chronic tonsillitis and adenoiditis may also need the help of a surgeon.
Medication correction
If the inflammation of the tonsils is of a viral nature, then it will be possible to limit oneself to symptomatic therapy; it is recommended to take antiviral drugs that have a local immunomodulatory effect. The body must cope with the infection on its own. You just need to help him a little.
For this purpose, drugs such as:
- Sore throat sprays and cough drops. Effective drugs are: Strepsils, Septolete, Ingalipt, Chlorophyllipt, Givalex, Tantum Verde, Lizak, Lizobakt, Faringosept, Throat spasm, etc. These drugs have not only an analgesic, but also an antiseptic effect.
- Gargles: Angilex, Chlorophyllipt, Furacilin, Streptocide, Rotocan, Givalex, etc. The more often a person performs this procedure, the faster the recovery will occur. Gargling allows you to remove not only viral flora from the tonsils, but also pus, as well as dead tissue.
- Drugs to reduce body temperature: Panadol, Nurofen, Nimesil, Efferalgan, Nise, etc.
If the inflammation was caused by microbial flora, then it can only be dealt with using antibiotics for a sore throat. Taking them helps prevent the development of complications. The drug must be recommended by a doctor. The dose is selected depending on the severity of the infection. For local therapy, agents with an antibacterial component are used, such as: Polydexa, Isofra, Rinil. If they do not achieve the desired effect, then the patient is advised to take systemic antibacterial drugs. These may be drugs such as: Augmentin, Flemoxin, Amoxiclav, Amoxicillin, Vilprafen, etc.
In order to avoid relapses, antibacterial drugs are taken in full course. The patient needs to complete treatment, even if he feels better after a couple of days of taking medications.
If more than 3 days have passed since the start of antibacterial therapy and there is no effect, then it is necessary to change the drug. This means that the pathogenic flora has resistance to it. In the future, tetracyclines (Tetracycline, Doxycycline, Unidox Solutab, etc.) or macrolides (Sumamed, Hemomycin, Azithromycin) can be used.
Taking a smear from the throat allows you to identify the representative of the pathogenic flora that caused the inflammation and determine which drugs it responds to. However, the results of the LHC culture will be known no earlier than in 5-7 days. Delaying treatment for such a long period of time can be dangerous. Bacterial inflammation, as well as a viral infection, requires symptomatic therapy with mandatory gargling.
Treatment of inflamed tonsils in children
Treatment of inflamed tonsils in children should be pathognomic, that is, aimed at eliminating the cause of the disease.
- If a child has an acute respiratory viral infection, then he needs to treat his throat, lower his body temperature, and give painkillers.
- A bacterial infection requires consultation with a pediatrician. The doctor must select the antibiotic.
- Adenoiditis takes longer to cure than other diseases. To carry out therapy, they resort to corticosteroid drugs (Flicosnase, Nasonex). Vasoconstrictor nasal drops (Nazivin, Xylometazoline, Rinazoline) are also used. To combat pathogenic flora, agents such as Protargol, Collargol, etc. can be used.
For the disease to lead to serious complications, parents should consult a doctor in the following situations:
- Body temperature remains high, even after taking antipyretic medications.
- White plugs or white plaque are visible on the tonsils.
- The child coughs a lot.
- Nasal discharge is yellow-green in color.
Inflammation of the tonsils: symptoms and treatment in adults
Varieties of the disease
Often in our lives we experience discomfort in our throat, as if a fish bone is stuck and it hurts to swallow.
This is the beginning of inflammation of the tonsils and tonsils. This is how a throat disease begins, which is called sore throat or acute tonsillitis. This is usually associated with a streptococcal infection, which resides in the loose tissues of the larynx and may not appear immediately. It camouflages itself and lies dormant in the body for a long time, waiting for the right moment that can provoke its activation. After all, the tonsils are an organ of the human immune system and their first task is to protect against pathogenic bacteria.
Therefore, they take the first blow and often become inflamed. Sore throat is manifested by a very high temperature, pain in the throat and lymph nodes, and white plugs in the tonsils.
Children and adults under 40 years of age are most often affected by this disease. Afterwards, the tonsils lose their function of protecting against microbes and can then completely atrophy.
Sore throat has two types:
- Compensated. Here the body turns on its defenses to fight the infection, and the disease proceeds quite easily, and only the symptoms of a sore throat appear, but there are no consequences.
- Decompensated. If the patient has a weakened immune system, then there are often complications in the heart, kidneys and musculoskeletal system. This happens with untreated tonsillitis, when general health improves, but the infection does not disappear. And with stress and hypothermia, the disease returns with renewed vigor and exhausts the body.
Causes of inflammation of the tonsils
Sore throat is an infectious disease, and a child or adult can become infected through contact with a sick person. And not only by airborne droplets, but also when using its hygiene items and utensils. Less commonly, infection is possible from a patient who has had a sore throat.
There are also other causes of sore throat:
- In adults, tonsillitis is caused by pathogenic bacteria such as pneumococci, staphylococci and streptococci. And children become infected with intracellular microbes (mycoplasma and chlamydia). This type of sore throat is called monocytic. At the same time, not only the lymph nodes, but also the liver and spleen enlarge.
- Mushrooms (Candida). They affect the tonsils and lead to their inflammation with reduced immunity. In a healthy human body, spores are present in small quantities, but with long-term use of antibiotics, our natural defense mechanism (immunity) weakens, and bacteria spread incredibly quickly. The tonsils can no longer stop them. A cheesy coating appears. It is necessary to treat with antifungal agents.
- Hypothermia. When there is a sharp change in temperature, we inhale cold air through the mouth, and preferably through the nose.
- Improper diet, which leads to a decrease in overall immunity.
- Mechanical damage to the tonsils.
- Long stay in water during the swimming season. In hot weather, drinking cold drinks leads to severe inflammation.
- Untreated diseases. These include: sinusitis, sinusitis, dental caries and gum disease.
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse.
- Sore throat can be a concomitant disease with diphtheria, scarlet fever and measles.
- Hereditary predisposition and genetic disorders.
Symptoms of inflammation of the tonsils and treatment in adults
In medicine, sore throat is divided into several forms:
- Catarrhal.
This disease is caused by a bacterial or viral infection of the upper respiratory tract affecting the lymphoid ring of the pharynx, and is quite simple. It is transmitted by airborne droplets from a sick person to a healthy person. In terms of symptoms and treatment, this type of acute tonsillitis is considered the mildest. The tonsils are not very enlarged, the body temperature is low-grade, and the pain in the larynx is not very pronounced. Dryness and soreness in the throat predominate. Redness of the tonsils and absence of pus are detected. When palpated with fingers, the lymph nodes are enlarged and painful. Recovery occurs within 5-7 days. A dangerous complication is the development of laryngitis.
- Follicular.
This is an acute purulent disease of the follicles of the palatine tonsils. And it appears after prolonged catarrhal inflammation of the tonsils or as an exacerbation of the inflammatory process. The appearance of sharp pain when swallowing saliva or food, painful sensations often radiate to the ears (stuffing, noise). Yellow-white pustules appear on the tonsils - follicles that are visible on the mucous membrane of the tonsils. The symptoms of the disease are identical to the flu: body and joint aches, severe fever, headache. The temperature remains at high levels and reaches 38 - 39 degrees, it is very difficult to bring it down during the first day. Regional (submandibular and cervical) lymph nodes are slightly enlarged and painful on palpation. Recently, follicular tonsillitis occurs without body heat, and doctors do not issue sick leave. The patient has to be at the workplace, which leads to various consequences. It is important to know how to cure inflammation of the tonsils so that the following complications do not occur: meningitis, sepsis, rheumatism of the heart, arthritis, peritonsillar abscess (ulcers on the follicles break out).
- Lacunarnaya.
The symptoms are identical to follicular tonsillitis, but the purulent plaque is gray or yellowish in color and occurs in the area of the glandular lacunae. It can be easily removed with a medical spatula. The tonsils become red and swollen. Regional lymph nodes are slightly enlarged. Aching pain appears in the lower back and calf muscles. Patients experience chills, headache, nausea and vomiting. The duration of treatment is about 14 days. The main complication in adults is conjunctivitis, acute otitis media of the ears, suffocation (false croup) and indigestion.
- Phlegmonous.
Or acute paratonsillitis. This is an inflammation with purulent discharge of the tonsils. This disease can occur after diphtheria sore throat. Less common are follicular or lacunar complications. Symptoms appear within 3 hours. Acute pain is observed in one of the tonsils (abscess). If the tonsils are inflamed, you must immediately contact a medical facility and begin treatment as soon as possible. The patient feels a little better when he lies down on the half where the inflammation occurs. There are also a number of distinctive features from other sore throats:
- Complete loss of appetite. The patient refuses to eat and drink due to severe pain.
- Significant change in voice when speaking (nasalness, hoarseness, and even temporary loss of speech).
- Impaired functioning of the upper and lower jaws. The patient cannot open and close his mouth or swallow saliva.
- Unpleasant purulent odor from the throat.
- Heat.
- Weakness, impaired performance, chills. Enlarged and painful lymph nodes.
- Formation of a purulent focus that must be opened in a medical facility.
The main complications are general blood poisoning, meningitis, and brain abscess.
- Herpetic.
This sore throat is a type of viral infection and is transmitted through the oral-fecal route or through discharge from the nasopharynx. The causative agent is the Coxsackie virus, which spreads in the summer season. The incubation period is 14 days. The symptoms of the disease are similar to the flu, and patients making a big mistake when taking anti-flu drugs. After three days, signs appear:
- A sore throat and a lump in the throat, and then an unbearable pain that prevents you from eating.
- Insomnia, leading to nervousness and irritability.
- Aches all over the body.
- A sharp increase in temperature to a critical level.
- The appearance of small red dots on the back wall of the throat, which after two days turn into white bubbles.
- Headache.
- Intestinal tract disorder.
- Salivation and unpleasant odor from the throat.
If these signs of inflammation of the tonsils appear in adults, you should not self-medicate, but should immediately consult a doctor to avoid complications such as meningitis, encephalitis and myocarditis. The medical institution will prescribe tests for serological and virological studies.
Treatment methods
If you suspect a sore throat, you should call a doctor at home, and before his arrival, gargle every half hour. A warm solution of soda with a pinch of salt and a few drops of iodine is suitable for this. The doctor will later prescribe a solution of Furacilin, Eludril or Rivanol to rinse the larynx.
In order for the product to properly help remove and wash away pus, germs and bacteria from the tonsils, it is necessary to throw your head back as high as possible and hold your breath while rinsing.
To reduce pain, you can take absorbable lozenges: Strepsils, Faringosept, Falimint and other drugs with menthol, honey or lemon.
Throat irrigators are also useful, such as: “Hexoral”, “Ingalipt”, “Miramistin”, “Aqualor”, “Proposol”, “Bioparox”, “Lugol-spray”.
Next, only a medical professional will competently tell you what to do if your tonsils are inflamed.
Diagnostics
The therapist conducts an examination at home or in the hospital:
- Measures temperature.
- Visually examines the throat for redness and enlargement of the tonsils.
- Palpates the lymph nodes.
- Listens to the patient's complaints.
- Takes a swab from the tonsils to determine the type of infection (bacteriological culture).
- Writes a referral for urine and blood tests.
- If necessary, refer the patient for an MRI.
Expert recommendations
The doctor will prescribe treatment and give instructions:
- Bed rest.
- Drink plenty of warm tea with herbs, lingonberry or cranberry juice, if there are no contraindications (renal failure or hypertension).
- Rinse or irrigate the larynx.
- Taking analgesics and antipyretics, such as Ibuprofen, Aspirin, Paracetamol, Analgin. They not only cope with high fever, but also provide relief for eating and drinking.
- It is necessary to eat warm porridge, puree soup, steamed cutlets, broths, and jelly. Forget about salty, coarse and smoked foods. The consumption of citrus fruits is also prohibited.
- How to relieve inflammation of the tonsils with the help of antibiotics is determined only by the therapist after receiving the test results. Viral forms of sore throat cannot be treated with them, but will only cause harm to the body. They are prescribed for illnesses caused by bacteria and fungi. Self-administration of antibiotics is strictly prohibited. The doctor prescribes penicillin drugs: Sumamed, Suprax, Amoxicillin in tablets or injections.
- After these procedures, improvement occurs on the third day, but in no case should treatment be stopped, since the body’s immune system is weakened by the fight against microbes, and the disease may return with renewed vigor. Therefore, the doctor must prescribe immunomodulators, such as Cytovir-3.
This drug must be used from the first day of illness. Especially if the sore throat is extremely severe, and the patient’s immune status is significantly below normal, and the body is tired of fighting various infections. We figured out how and with what to treat the tonsils when they are inflamed, but without an immunostimulant such as Cytovir-3, the disease will drag on for a long time.
Advantages of "Tsitovir-3":
- Increases the patient's cellular immunity.
- Produces antibodies that fight antigens.
- Helps the body fight sore throat.
- Copes with viral infections of the respiratory system.
It contains three components: bendazole, thymogen and ascorbic acid. Medicinal substances do not enter into a chemical reaction with each other, but in the body they have an effect by complementing each other.
"Tsitovir-3" promotes five-fold resistance to angina pathogens. A patient who initially takes this drug feels much better on the second day, he does not experience protracted forms of the disease, and the likelihood of complications is reduced by 7 to 12 times.
Now it has become clear what to do if the tonsils are severely inflamed. The first step is to boost your immunity to fight and quickly recover. The recovery process is quite long and difficult, and in order not to get sick you need to lead a healthy lifestyle.
Preventive measures
We all know very well that it is better to prevent a disease than to treat it for a long time. Therefore, it is worth paying special attention to the prevention of sore throat so that there are no complications in the future:
- It is necessary to maintain oral hygiene. Brushing twice a day, gargling, and flossing after every meal keeps germs from growing. You should also visit the dentist once every six months.
- Exercising will greatly strengthen the immune system, especially in the fresh air. You can run in the morning or walk to work and back, without using the elevator.
- Hardening has saved people from viral infections more than once. It is necessary to douse yourself with lukewarm water in the morning and lower its temperature every day. Or just dry yourself with a wet towel.
- Eat properly and balanced. Eat more vegetables and fruits, do not eat unhealthy foods (chips, soda, etc.). In autumn and spring, take vitamin complexes and immunomodulators.
- Maintaining order in the house (daily wet cleaning, ventilation of the room) is the key to your health.
- A trip to the seaside will help restore and strengthen your immune system.
In our article, we described in detail how to treat inflammation of the tonsils. Use our recommendations and stay healthy.