Symptoms of a tooth bruise
Immediately after an injury, an appointment with pediatric dentistry is required. Often parents bring their children after a week or a week and a half. This makes examination and treatment of lesions difficult. In the first hours after damage to the masticatory organ:
- Children feel pain.
- Pain increases when biting on a pathological unit.
- The gums swell, redden, and become dense.
- If, as a result of a bruise, a vascular bundle ruptures, blood appears, and pulpal hemorrhage may develop.
- The baby's condition worsens, he becomes restless and whiny.
- The temperature may rise. The child loses his appetite.
Only a doctor can help in such a situation. If a child’s baby tooth darkens after an impact, the blood vessels and pulp tissues could be damaged. In most cases, such processes are reversible. You should take your child to the doctor if there are signs of a bruise. Without treatment, the structure of the abnormal units will suffer, which will negatively impact dental health. The symptoms of severe damage are easy to recognize. In addition to painful sensations, pinkish enamel is clearly visible due to rupture of blood vessels. Brown spots appear after trauma to the periodontal tissues that hold the unit.
Symptoms and diagnosis of injuries
If the blow was quite strong, it can cause damage to some periodontal tissues, including tearing of blood vessels and fibers. However, the tooth looks absolutely healthy and has no visible damage. Quite often, the tooth maintains its position, its mobility does not increase. However, after an injury, the gums around the tooth may swell slightly.
In addition, for the first time after a strong blow, the patient may experience discomfort and pain when biting food, when contacting the opposite jaw, or when drinking cold or hot drinks. Sometimes there is slight bleeding that cannot be stopped on your own. Strong impacts can damage the pulp chamber and the vessels in it, so the tooth may immediately turn pink. You can also detect chips and small cracks in the enamel, but most often only a doctor notices them.
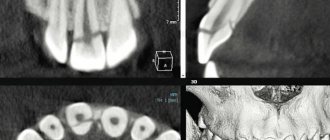
Patients with such symptoms are necessarily referred for X-ray examination and computed tomography. As a result, the specialist receives a three-dimensional image of the jaw tissue and can make a final diagnosis. The condition of the pulp can be assessed using electroodontodiagnosis technology. Additionally, transillumination may be prescribed, thanks to which existing cracks in the tooth are clearly visible.
Possible consequences
Moms and dads must remember that the rudiments of the molars suffer from injuries to temporary rudiments. In such permanent teeth, enamel develops poorly and hypoplasia develops. The germ may even die. Therefore, treatment of baby teeth in children should be carried out on time. If the pulp area is severely damaged, the tissues will gradually begin to die and become necrotic. Necrosis causes inflammation and discoloration of the crowns in a dark color. It happens quickly. After some time, cysts form on the damaged areas. To establish a diagnosis, doctors refer for an X-ray examination.
If a child's baby tooth has been displaced by an impact, it may become loose for several weeks. Even slight staggering may occur due to damage to the alveolar process. When mammary rudiments are not treated after injury, it causes irreversible consequences. Swelling and redness usually appear in the area where the main impact occurred. The hematoma can be pronounced, and can also be determined only during palpation. When you press it, the baby experiences discomfort and pain. A fracture of the alveolar process is expressed by pain when moving the jaws. If the ligaments are torn, pain is observed on the entire surface of the dental system.
Luxation of a baby tooth
Luxation of a baby tooth is a fairly common dental problem among pediatric patients. In this situation, the upper and lower incisors are most often injured, less often the premolars and molars. In the absence of professional medical assistance, such a condition can cause inflammation of the bone and surrounding soft tissues and lead to deformation of the dentition.
What is a luxated baby tooth?
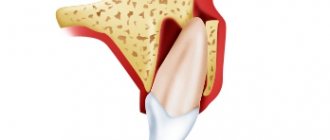
In clinical terminology, luxation of a baby tooth is its persistent pathological displacement in relation to the tooth socket. Depending on the nature of the displacement, the dislocation can be incomplete or complete.
Incomplete dislocation, or traumatic dystopia, is a shift that occurs as a result of rupture or stretching of the structural components of the supporting apparatus of the tooth (periodontal ligaments). In this condition, there is a change in the position of the baby tooth vertically, in the anteroposterior or lateral direction.
Complete dislocation of a baby tooth in a child (extraction) occurs due to a total rupture of the periodontal and circular ligaments and the neurovascular bundle. In this case, the tooth completely loses connection with the socket and falls out of the soft tissues.
Causes of complete and incomplete dislocation of a baby tooth
- Mechanical injury (fall, blow).
- Biting into very hard food.
- Foreign body ingestion.
- Incorrect removal of a nearby tooth.
- Opening bottles with teeth, etc.
Clinical signs of luxation of a baby tooth
With incomplete displacement, the baby tooth changes its position and becomes mobile. If it emerges from the socket, its cutting edge protrudes above the edges of other teeth. During a traumatic rotation, the dystopic tooth may be located at an angle to the longitudinal axis, leading to malocclusion. In this condition, children complain of pain when biting, and minor bleeding from the periodontal gap may also develop.
Intrusion, or impacted dislocation of a baby tooth (immersion of the crown into the bone tissue of the alveolar process), is accompanied by bleeding, swelling of the lips and gums (a consequence of stretching of the neurovascular bundle). With a large impact force, the injured tooth can be found in the jawbone or soft tissues.
With complete dislocation (traumatic extraction) of a baby tooth, moderate bleeding from the socket, swelling of the gums and lips, and damage to the soft tissue of the alveolar process are observed.
Treatment
Partially avulsed baby teeth are secured with a metal splint or a plastic tray, and those that cannot be repositioned are usually removed. In case of impacted dislocation, the tooth is left in the socket (within a certain time its growth can be restored). It is secured with a metal splint or a plastic mouthguard. If post-traumatic inflammation develops, removal is performed.
If a baby tooth is completely dislocated and falls out of its socket, treatment is prescribed purely individually, taking into account the condition of the bone tissue at the tooth root and the viability of the pulp. In this situation, with unchanged periodontal tissues, tooth replantation is possible with subsequent anti-inflammatory and restorative drug treatment.
Treatment of tooth trauma
After a thorough examination and questioning of complaints, a diagnosis is prescribed. Treatment of dental injuries in children depends on the age and condition of the child. The dentist's actions are aimed at preserving the rudiments of permanent units. Therapy of temporary organs requires rest. Solid foods are excluded from the diet. If the cutting edge protrudes, it is ground off. Wearing a mouthguard is recommended; a release plate may be needed. Sometimes the pulp dies and periodontitis or pulpitis develops, which requires trephination of the dead pulp and filling.
If a child hits his teeth, but the color of the temporary units does not change, the molars will grow correctly. In case of darkening of the crowns, bone resorption is observed. These baby teeth are most often removed. Therapy can last from several days to 1-2 weeks. The treatment period is divided into several stages.
- Initial treatment and diagnosis of pathology.
- Emergency care: the sooner it is provided, the lower the risk of complications.
- Specialized treatment with specific clinical methods.
- Restoration of injured organs and tissues, clinical observation.
For preventive purposes, you need to show your child to the dentist at least once every 3 months for 12 months. If your baby complains, you need to visit the doctor more often.
What actions should be taken if a child suffers an injury to a baby tooth?
Let's start with the fact that injury is always pain. It would seem that baby teeth will change anyway... Why pay attention to them? Believe me, it is necessary and necessary to pay attention. If you do not contact pediatric dentistry for treatment of baby teeth, then in the future there is a risk that the infection that has affected the baby tooth will damage the germ of the permanent tooth. If you do not pay attention to the injury of a baby tooth, you may not see the damage in the bud of a permanent one.
Children, by nature, have very mobile and active behavior and lifestyle. This is wonderful! But sometimes they do not hear or perceive the warnings of adults aimed at ensuring safety. This leads to various injuries, often associated with teeth. When the question concerns the injury of a baby tooth, you can often treat the moment negligently with the expectation that it is still temporary and would have fallen out anyway.
Don't leave the situation to chance! Even if the injury affected a baby tooth, which was about to fall out anyway. The fact is that the force of a blow is sometimes impossible to estimate. Under the milk tooth is the germ of a permanent one. It is often impossible to conduct even a visual inspection on your own, not to mention what kind of trauma was caused to the gum and, possibly, the germ of a permanent tooth.
In a situation where there is an injury to a child’s tooth(s):
- Stay calm (although this is sometimes difficult in practice). If you are nervous, children will absolutely sense the mood, especially of loved ones.
- Do not scold your child under any circumstances (“I told you, I warned you!”) Do not forget that he is already in pain and scared. All educational moments and lessons from the situation can be raised later, after the pain has calmed down.
- Show maximum care and tenderness, reassure as much as possible.
- It is imperative to visit a dentist for an examination and consultation and conduct a diagnosis of dental treatment. When you call your clinic or the nearest one (at your discretion), DO NOT ask if a pediatrician is working today, DO NOT say that you need a pediatric dentist. It must be said directly that the child has suffered a tooth injury and needs an urgent examination by a doctor. In every decent clinic they should offer you to come right away, regardless of the doctor’s appointment, and they may warn you that you will have to wait. Or, at a minimum, they are obliged to offer: “wait, I’ll clarify what we can do for you, leave your contact phone number and we will call you back in the next 5-20 minutes.” In this case, they will offer to drive to the clinic or direct you where you can go directly at this moment. If they immediately answer you: “We’re all busy, we can’t help you,” don’t ever go to this clinic.
What the doctor will do at the appointment:
- Visually examine how serious or minor the injury is.
- Be sure to take a photo in the area of the injured tooth(s) to understand whether the permanent tooth(s) are damaged or not.
- He will remove the injured tooth so that it does not cause pain and inconvenience. If the blow was not severe and the tooth was only chipped, if recovery is possible, the pediatric dentist will cure it.
- If necessary, provide recommendations for care in the area of injury.
- As planned, he will make an appointment for the child to be examined by a pediatric dentist if it was not possible to get to him on the day of the injury.
Any experienced dentist will be able to visually and with the help of X-ray diagnostics assess how serious the injury is or whether everything was just a minor fright. Don't leave injuries unattended!
Causes
There are many reasons for a tooth bruise. The most common is a strong direct blow to the jaw. Athletes often receive such injuries; they are almost always the consequences of accidents. It is impossible not to notice it, since after a blow the front tooth hurts, and the pain is usually sharp.
There is another reason - the so-called chronic jaw injury. The peculiarity of such injuries is that they are insignificant in their impact, but a person is constantly exposed to them. Examples include some human habits: biting nails, holding a pen or pencil in the mouth, cracking nuts, etc. Under the influence of such seemingly insignificant factors, the enamel becomes thinner and microchips form on it. The result of these innocent habits is tooth loss.
Injury can also occur during dental procedures performed by an inexperienced dentist or using old equipment. Any violation of the treatment or removal technique can lead to damage to healthy tissue. That is why our clinic employs experienced, highly qualified specialists. We are responsible for the health of our patients.
What to do if your child has a tooth injury
An injury to a child's front tooth requires immediate attention to a dentist. The sooner you go to the doctor, the sooner your baby will receive adequate treatment. Speed of circulation is very important when it comes to preserving dental pulp. To do this, you need to see a doctor no later than two hours after the injury.
When visiting a French dental clinic, our doctors will provide first aid to the child, assess the degree and type of injury and advise you on further actions. Experienced European dentists use all their knowledge and experience to preserve a damaged tooth, restore its health and aesthetic appeal, and also provide acceptable conditions for the development of its root and the formation of a correct bite.