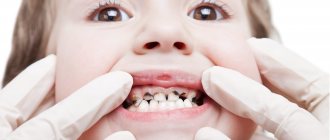
Pediatric dentistry can be considered a separate section of modern dental practice, because due to the structural features, the treatment of baby teeth is somewhat different from the treatment of permanent teeth. Unfortunately, many parents are still convinced that baby teeth do not need dental care - after all, they will soon break down and fall out anyway. Therefore, children are not taken to the dentist very often, and if they are taken to the doctor, it is with advanced diseases and multiple problems.
In fact, dental treatment should be carried out at any age, and the sooner you consult a doctor with a problem, the higher the likelihood of getting rid of it quickly and without any complications. If a child has bad baby teeth, this will inevitably affect the health of his permanent ones - this is what parents need to remember when they want to “pity” the baby and not take him to an appointment with the “evil dentist.”
Gum inflammation
The most common inflammatory gum diseases in children are stomatitis and gingivitis. Stomatitis, or, as it is usually called, thrush, is an infectious inflammatory process provoked by fungi of the genus Candida. Treatment is antifungal and anti-inflammatory therapy, always carried out under the supervision and recommendations of a dentist. Self-medication can be dangerous, as some children may have allergic reactions to certain medications or antiseptics.
Gingivitis most often occurs due to plaque on baby teeth and insufficient general hygiene, but the reasons for their development can also be trauma to the gums during teething or other injuries, untreated caries. With this problem, you also need to contact a doctor, who will select the optimal treatment regimen and prevent gingivitis from developing into childhood periodontitis.
The advantage of filling over silver plating
Silvering of teeth is the smearing of teeth with silver nitrate, which has an antiseptic effect. Its disinfecting properties should stop the spread of caries.
However, silvering is only a method of preserving destruction, permissible only in the very early stages, and not a treatment. In some cases, silvering does not help, and the carious process moves on imperceptibly underneath it.
Giving a child a filling is the most effective way to solve the problem of caries.
You can make an appointment at the Shifa pediatric dentistry by calling the contact number or using a special form. We try to provide our clients with the most favorable cost of treatment - check out the price list on the “Prices” page.
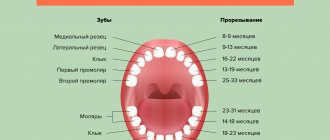
Caries, pulpitis and periodontitis of primary teeth in children
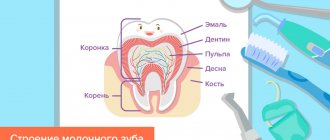
Milk teeth have thinner enamel and dentin layers than permanent teeth, they have a larger pulp chamber and, therefore, infection spreads faster to the pulp. They are more often susceptible to carious lesions - and not least because of night feeding or the habit of drinking drinks from a bottle at night (mostly sweet or sweetened - tea, juices).
In addition, caries is often provoked by plaque on baby teeth, which forms faster than in adults, and which not all parents are in a hurry to remove. Many people begin brushing their children’s teeth at a more or less conscious age, while a child should be taught hygiene and regularly remove plaque from the moment the first teeth erupt, that is, from about six months of age. Also, the cause of diseases of the dental system can be an insufficient amount of solid food in the baby’s diet, since chewing solid food helps to clean the dental surfaces themselves.
The child's nutritional habits, lack of hygiene, and too thin enamel layer provoke a phenomenon called circular caries of baby teeth - carious lesions spread over the entire tooth surface, as if encircling the crown.
Caries quickly turns into pulpitis - an inflammatory lesion of the dental pulp. Most often, a doctor is consulted precisely at this stage of the infectious process, ignoring the initial stages of damage to dental tissues. Pulpitis, in turn, provokes periodontitis of primary teeth in children - inflammation of the periodontal tissues near the tips of the tooth roots. This condition is usually accompanied by severe pain, severe swelling of the affected area, and often an increase in body temperature.
Restoration in children's practice - to be or not to be?
The particular relevance of the use of composite materials in pediatric dentistry is due to the following factors: in childhood, the percentage of traumatic lesions of the frontal group of teeth is very high, because they are one of the first to erupt and protrude from the occlusal plane of the primary teeth that have not yet been replaced. In addition, some dental pathologies can be observed mainly in children. For example, with destructive forms of hypoplasia or fluorosis, teeth are destroyed so quickly that, due to the desire of doctors to follow the old treatment method (namely, wait until the root tips are closed), the only method of treating such teeth is often orthopedic restoration of the crown part.
For a long time, pediatric dentists were afraid to use composite materials in their practice, citing the following reasons:
* inappropriateness of restoring a tooth that may still be erupting;
* the inability to bring teeth into bite after various types of injuries, because microfractures appear at the root, which, if the load is not applied in a timely manner, can increase and lead to the death of the pulp and resorption of the tooth root.
* unsafe use of composite materials, because they are highly toxic and in teeth with uncovered apices and still wide dentinal tubules can lead to pulp death.
* inappropriateness of using composite materials in the treatment of destructive forms of hypoplasia and fluorosis at an early age, because their abrasion coefficient is lower than that of natural enamel. And in this regard, restorations made from composites require repair or complete replacement after some time.
In addition, often doctors and relatives of patients do not consider aesthetic restoration of teeth at a young age important and limit themselves to temporary structures, forgetting about the psychological aspects. But the trend of today is such that it is fashionable to be healthy and beautiful.
The achievements of modern dentistry dispel fears of using composites in pediatric practice. For example, with regard to toxicity, it is now known that the bonding system has a direct effect on the tooth. The latest generation adhesive systems are not only non-toxic, but may also contain fluorine compounds. The toxic monomer contained in chemically cured composites has practically sunk into oblivion along with the use of chemical composites themselves.
Of course, before starting restoration, it is necessary to carry out all examination methods (x-ray, EDI). However, we must not forget that the protective forces of the child’s body are very great, and in each case we try to individualize the algorithm of actions.
Despite the fact that the evolution of composite materials is advancing by leaps and bounds, pediatric dentistry places increased demands on restorative materials:
— Low toxicity.
— High degree of adhesion of the material to tooth tissues.
— Abrasion coefficient as close as possible to natural tooth tissues.
— Possibility of immediate and final restoration of teeth (both frontal and chewing group).
— Preparation that does not require intervention in healthy tooth tissue.
— Excellent aesthetic characteristics.
From an esthetic point of view, restoring the teeth of young patients is often very difficult. This is due to the fact that the shape and color of children's teeth have a number of features. For example, the macrorelief is characterized by the presence of a scalloped cutting edge that has not yet been subjected to physiological abrasion. The surface layer of enamel in children is formed by the protruding tops of prisms, which gives it the appearance of a “cobblestone street.” In addition, micropores are found in the enamel of children's teeth under a microscope. We must not forget that the Recius lines (enamel growth zones), which form perikemata on the surface, are more pronounced in childhood. All this affects the surface gloss of the enamel and visually makes it brighter. Children are characterized by pronounced mamelons. The most typical for the incisal edge of young patients is the presence of three large mamelons or three mamelons with a split middle one. (Fig. 1)
Fig.1
Tooth color is dictated by the optical characteristics of dentin and enamel. The enamel is responsible for the brightness of the tooth. Enamel is characterized by such a property as opalescence, this is the ability to reflect predominantly short waves (blue) and transmit long ones (orange-red). Dentin is responsible for the richness of tooth color. Dentin of natural teeth has the property of fluorescence. Currently, the identity of the fluorescence of the material and the tooth is becoming an integral requirement for a modern composite. Another optical medium of the tooth is the dentin-enamel junction, which plays a large role in the formation of color.
According to various studies, the majority of teeth belong to shade – A on the Vita scale (Yamomoto 1992, Vanini 1994, Tuati 2000). Due to the fact that the enamel of children is brighter than that of adult patients, the color of their teeth most often corresponds to shades A1, A2 (according to Vita, since the most common lesions in childhood are injuries to the frontal group of teeth, accompanied by a violation of the integrity of the crown angle or the entire cutting edge, pediatric dentists need a material that reproduces all the optical characteristics of the cutting edge of the tooth.
At the moment, the restoration material that best meets all the requirements of pediatric dentistry is Enamel plus.
Enamel plus is a radiopaque, microhybrid, light-curing composite that allows you to achieve excellent results in aesthetic restorations of anterior and posterior teeth, using direct and indirect methods. Еnamel plus is a unique restoration system that makes it possible to reproduce all the optical effects of the cutting edge.
Its creator is Dr. Lorenzo Vanini (Italy). When developing this material, L. Vanini took into account all the components of tooth color. His main task was to create a material, using which it would be possible to obtain a predictable result, which is so important in the daily practice of a dentist. The Enamel plus set includes three basic enamels, seven universal fluorescent dentins, two intensive enamels (for personalizing the enamel on the surface) and opalescent enamels, which can be used to highlight internal incisal opalescences and mamelons. (Fig. 2) In addition, the set includes a Glass Connector . It is a flowable composite that mimics the protein layer of natural teeth and six colors to replicate the characteristics. To determine the color, it is proposed to use the Enamel plus scale, made entirely of composite. (Fig. 3) The set also includes a special color card. This card remains in the medical history, and you can use it in further work. (Fig. 4, 4a)
Rice. 2.
Rice. 3.
Rice. 4.
Rice. 4a.
To obtain maximum results when using the Enamel plus HFO system, it is proposed to use the anatomical layering technique developed by L. Vanini. The anatomical stratification technique involves the construction of lingual enamel, internal dentinal body and vestibular enamel.
Before moving on to consideration of the stratification technique, I would like to note some features of cavity preparation under Enamel Plus. The fact is that preparation for this material is distinguished by the possibility of maximizing the preservation of healthy tooth tissue and does not require modeling a fold on the enamel. It is by increasing the width of the rebate and covering a larger surface of the enamel with a composite material that doctors often try to improve the aesthetics of their restoration (make the transitions of the material to the tooth tissue less noticeable and avoid the appearance of a gray stripe at the border of the filling with the tooth). At the same time, sometimes restorations of large cavities of classes III and IV turn into the production of veneers using the direct method, which is absolutely incorrect in pediatric dentistry, especially in cases where the tooth has not yet fully erupted. When preparing under Enamel plus HFO, a groove is formed on the vestibular enamel and proximal surfaces, along the edge of the cavity being prepared, with a spherical bur, the palatal side is processed at 90 degrees. This preparation technique is very gentle. (Fig. 5, 5a)
Rice. 5.
Rice. 5a.
Rice. Defect in the cutting edge of the 21st tooth.
Rice. Temporary restoration with composite without adhesive preparation.
Rice. Taking a silicone impression.
Rice. Example of a silicone key.
Restoration of dental injuries without opening the pulp.
The most common defect requiring restoration in children is trauma to the frontal group of teeth without opening the pulp. The break line is located parallel or diagonally to the cutting edge. In this case, the medial angle is most often affected.
After completing the color card, preparation and adhesive surface treatment, we begin to restore the lingual enamel. Because enamel in children has a high brightness; most often, we take the shade of enamel GE3. (Fig. 6, 6a)
Rice. 6
Rice. 6a
To simplify the task in case of extensive defects, a silicone block is made, which allows a thin layer to distribute the material and avoid inaccuracies in the formation of the macrorelief. (Fig. 7) When modeling, to create a more regular surface, in addition to conventional trowels, silicone trowels (micerium) are used, which give “finger effect” (Fig. 8).
Rice. 7
Rice. 8
Using a special brush, a thin layer of Glass Connector is applied to the inner surface of the enamel sheet, and it should be located strictly at the enamel-dentin border. (Fig.9)
Rice. 9
After applying the Glass Connector, we begin modeling the dentinal body. To achieve optimal saturation of the restoration, 3 base dentin colors are used. For example, if we want to end up with color A2 (according to Vita), we should start with UD4, then layer UD3 and UD2 - lighter ones.
At the stage of applying the last dentin, mamelons are modeled (Fig. 10, 10a, 11, 11a, 12,12a)
Rice. 10
Rice. 10a
Rice. eleven
Rice. 11a
Rice. 12
Rice. 12a
The finished dentin body is covered with a thin layer of Glass Connector.
To recreate the opalescence of the enamel, opalescent enamel (OBN) is applied between the mamelons and in the incisal area. After this, if necessary, intense white enamels (IM, IW), opalescent enamels (AO, OW) and paints for characterization are applied (Fig. 13, 13a, b)
Rice. 13
Rice. 13a
Rice. 13b
The final stage is the application of the main enamel (GE3) - vestibular enamel sheet. (Fig. 14, 14a, 14b, 15, 15a)
Rice. 14
Rice. 14a
Rice. 14b
Rice. 14c
Rice. 15
Rice. 15a
Thus, with strict adherence to the anatomical stratification technique, the use of Enamel plus material allows one to achieve a natural appearance of teeth in the restoration.
Surface treatment
Includes final modeling of the tooth shape (macro- and microrelief) and surface polishing. To simplify the task, when creating a vestibular convexity, transition lines, and Recius lines, guidelines can be drawn on the surface of the tooth with a slate pencil. Modeling of macro- and microrelief is recommended to be done with diamond burs. After which we begin polishing the surface. To do this, use the polishing system included in the Enamel plus HFO set, which includes three pastes and polishers with a silicone head, goat bristles and a felt disc. (Fig. 16)
Rice. 16
Recommendations for doctors
The requirements for restorations made from Enamel plus are no different from those for any other composite.
We must remember that before starting work, it is necessary to establish individual oral hygiene. After all, good hygiene will prolong the life of any restoration.
The key to the success of your work is high-quality insulation of the working area. From the age of 7-8 years, children can easily tolerate the rubber dam. It is important not to forget that what frightens patients most of all (and, it should be noted, not only children) is the unknown. Therefore, before starting treatment, we show and tell you what it is and why. Let's compare the rubber dam to an umbrella or a cloak for a tooth. Rubber dam is used both for direct restorations and for fixation of indirect restorations.
High-quality finishing and polishing of the surface will not only improve the appearance of your restoration, but will also make it more durable. Despite the fact that we recommend polishing fillings once a year, our foreign colleagues have excellent results 9-10 years ago. Moreover, during this time the patient never came for polishing or simply for a medical examination. It was a completely different tooth that brought him to the clinic. Neither the esthetics nor the marginal fit of the Enamel plus restoration performed for trauma was compromised (Dr. F. Mangani, Italy).
Conclusion
Using Enamel plus HFO, the pediatric dentist will receive the final result of the restoration immediately after a dental injury, detection of caries or any other destructive process.
Due to the high adhesion force of the material (30 mPa), excellent strength characteristics, and the degree of abrasion as close as possible to natural enamel (Fig. 17 diagram). Enamel Plus HFO makes it possible to restore teeth even with partial eruption. Moreover, after complete eruption, after a year, five or even ten years, the restored tooth will look natural.
Rice. 17 diagram
Author:
Timoshenko O.A., dentist, Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Sechenov Moscow Medical Academy
Treatment of baby teeth
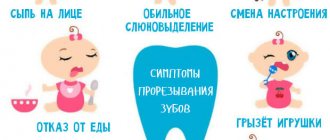
At the initial stages, caries is treated without tissue preparation - remineralization of the enamel, as well as modern Icon technology, which allows filling without drilling, easily cope with carious lesions of the enamel layer. In later stages, when the dentinal layer is affected, as well as in the case of pulpitis and periodontitis, treatment of baby teeth with tissue preparation will be required. You should not be afraid of such procedures - modern methods of anesthesia allow them to be carried out completely painlessly and comfortably for a small patient. In addition, the anesthetics used are harmless, with a minimum concentration of the active substance. And the site of the upcoming injection itself is numbed by applying a special gel or spray (application anesthesia).
Experienced dentists try to carry out treatment quickly so that the child does not have time to get tired and capricious. If a child has bad baby teeth and a large amount of work is required, it is divided into several stages. It also happens that the child does not want to contact the doctor, is too afraid of treatment, or the volume of manipulation is too large and serious - in such a situation, it is possible to carry out therapy under anesthesia or with intravenous sedation (with a preliminary examination).
In case of pulpitis, the root canals are filled with special pastes that dissolve simultaneously with the “milky” root, so there is no chance that the medicinal material will remain in the tooth socket and will prevent the new tooth from growing properly.
How fillings are done in Shifa dentistry
Dental treatment is possible only with the child’s consent, willingness to open his mouth and permission to put a filling. In case of a high level of anxiety, psychological preparation for treatment is indicated; it consists of preparatory teeth cleaning and demonstration of the stages of treatment on a model of artificial teeth. Give the pediatric dentist the opportunity to provide your child with details about the upcoming procedure at the first visit. Having experience communicating with children of different ages, the doctor can predict the child’s reaction.
For young children (up to 3 years old), as well as in the case of a child’s categorical refusal of treatment, sedation may be used, i.e. dental treatment in a dream.
The installation of children's fillings takes place in the following sequence:
- topical anesthesia - treatment of the gums with painkillers to reduce sensitivity at the site of the upcoming injection;
- local anesthesia - injection into the gums in the area of the upcoming treatment;
- cleaning the affected tooth structures using a bur under the control of a caries detector;
- direct filling;
- grinding and polishing the filling surface.
The installation of fillings in our clinic complies with international standards of pediatric dentistry.
Restoration of baby teeth
If a child’s baby tooth breaks off or if the dental crown is severely damaged by caries, restoration is carried out. However, if for adult patients one of the most important aspects during restoration is aesthetics, then for children functionality is much more important. Therefore, restorative filling materials are always selected taking into account the patient’s age - for children, durability and impeccable aesthetics are not so important, a good marginal fit of the fillings and the preservation of dental tissues are much more important. Filling materials that are too strong can put pressure on dental tissues and contribute to their destruction, and therefore dentists choose materials that will recreate and maintain the integrity of the dental crown until the moment of natural tooth loss.
How is restoration carried out?
The method involves restoring part of the apex-crown directly at a doctor’s appointment, right in the little patient’s mouth. Using a composite material, various chips and cracks in the enamel are eliminated, color and shape are corrected. The doctor applies a composite material to the damaged areas in layers, which hardens using an ultraviolet lamp. In essence, this is a regular filling, but it is what allows a baby to create a new tooth.
This method is not very durable, since restorations require careful handling - minimal chewing load, protection from impacts. You need to try to explain to your child that you should not bite off too hard foods with your restored teeth. Nevertheless, restoration is quite useful as a temporary option, especially when it comes to a quick change from a primary bite to a permanent one.
Removal of baby teeth in children
Removal of baby teeth in children is carried out only for specific indications or in the case when the tooth is ready to fall out on its own and just needs a little “help”. If there is a choice - to remove or treat, a competent dentist will always advise treatment, since the early loss of baby teeth leads to a number of serious disorders of the dental system, including the appearance of permanent bite defects.
Extraction operations should be carried out exclusively in the dentist’s office - attempts to remove teeth at home can lead to injury to soft tissues, infection of the socket, injury to the rudiment of a permanent dental unit, etc. The doctor will perform the extraction under local anesthesia quickly, competently and completely painlessly.
Indications and contraindications
Dental restoration of teeth is necessary in the following cases:
- incorrect position of the tooth in the dentition (protrudes forward, depressed, shifted to the side);
- natural or acquired defects in the shape, color and size of teeth;
- disturbance in appearance, color differences after dental treatment;
- pigmentation, darkening of tooth enamel.
When using any method of treatment in dentistry, you need to remember about contraindications.
In our situation, the list of contraindications includes the following cases:
- Bruxism - involuntary knocking and grinding of teeth during sleep;
- straight bite combined with a high degree of abrasion of tooth enamel;
- allergic manifestations to materials used during treatment;
- strong closing of the upper incisors by the lower ones when closing the jaws (malocclusion);
- impossibility of providing systematic prevention and quality oral care.
What to do if baby teeth grow crookedly?
If parents notice that their child’s baby teeth are growing crookedly - for example, there is crowding or improper occlusion - this is a reason for a mandatory consultation with a pediatric orthodontist. It happens that due to anomalies of the facial skeleton (in particular, improper development of the jaws), defects are noticeable even with a primary bite, and with a permanent bite they will persist and worsen.
Therefore, it is recommended to show the child to an orthodontist from the age of three to determine whether there is pathology and find methods for its correction. There are malocclusions that are easily corrected at an early age and extremely difficult to correct in adults.
Reviews
Your feedback is to help potential patients make the right choice. Leave your suggestions or comments so we can work even better.
LEAVE FEEDBACK
How to protect baby teeth from caries?
Prevention is the best way to cope with any disease. Therefore, those parents who care about the health of their children should definitely think about caries prevention. How to protect baby teeth from caries? The recommendations of experts in this matter are as follows:
- The correct diet for the mother during pregnancy is with a sufficient amount of foods containing calcium, fluorine and phosphorus: cottage cheese, beef and beef liver, sea fish, nuts, fruits and vegetables, cereal porridges.
- Compliance with hygiene standards: daily brushing from the moment the first teeth appear, first with a cotton or gauze swab with boiled water, then with special baby brushes and pastes. Plaque on baby teeth should be removed promptly and thoroughly.
- A healthy diet for a child: as little fast carbohydrates, carbonated drinks, sweets as possible, more fruits and vegetables, cereals, and dairy products.
- Timely visits to the dentist for preventive examinations (at least once every six months).
It is important that parents develop a conscious attitude towards the health of their children's teeth and oral cavity in general. A timely visit to the dentist in case of any identified problems, as well as for regular medical examinations, will help maintain the health of the child’s dental system – and therefore the digestive system too.
Life time
It is impossible to determine the exact period during which the results of restoration will be effective. The duration is set individually.
It all depends on a whole range of factors:
- quality of subsequent oral care;
- types of materials used;
- applied technologies;
- specialist qualification;
- characteristics of the patient's body.
The service life of composite materials used in light fillings is at least 5 years.
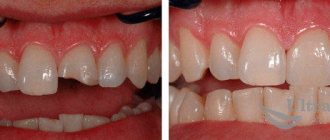
Installation of veneers: before and after photos
The service life of veneers depends on the material:
- composite - up to 5 years;
- porcelain - up to 15 years;
- zirconium - up to 20 years.
Prevention of tooth decay
We must try to avoid serious dental problems and prevent situations where a child could be injured or break a tooth. Parents should try to minimize all risks. To do this, it is enough to apply a few simple rules in practice.
For proper growth and development of bones and teeth, it is necessary to provide the child with complete, high-quality nutrition. Then the body will receive the entire complex of necessary micronutrients, vitamins, and substances.
When the baby has all his milk teeth, around the age of three, it would be good to give him more solid food. Various vegetables, fruits, and crackers are suitable for this. This way the child will become accustomed to more adult food, which will strengthen his teeth.
To maintain healthy teeth, you need to pay attention to the development of the child’s chewing muscles; for this, you should control the consistency of food.
It is important to teach your child to brush his teeth and instill the good habit of visiting the dentist periodically.
View prices
Making an appointment with a dentist