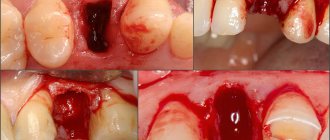
What to do if your cheek is swollen after tooth extraction?
Often after a tooth extraction procedure, many people experience swelling that may persist for some time.
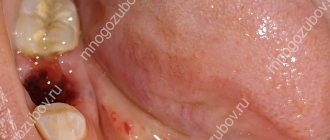
Its appearance is natural, since tooth extraction is essentially a surgical operation, after which the wound remaining in the oral cavity remains open. It recovers fairly quickly, but damaged gum tissue will remain swollen for some time. The size of the tumor may depend on several factors, such as the complexity of the removal procedure, the individual characteristics of the person, and the professionalism of the dentist.
What can lead to severe swelling
Some diseases and complications lead to similar non-standard reactions of the body to tooth extraction. Let's look at them in more detail:
- Systemic chronic diseases. These include diabetes, hypertension, cardiovascular diseases, and low immunity. All these diseases impair the body’s ability to recover after surgical procedures.
- Alveolitis is an inflammation of the alveolus (socket) that remains after tooth extraction. The cause of inflammation can be general diseases, smoking, mechanical damage, or non-compliance with doctor’s recommendations. As a result, a blood clot does not form in the socket, severe pain, a gray coating and an unpleasant odor occur. If alveolitis is not cured in time, dangerous purulent diseases such as phlegmon and osteomyelitis may develop.
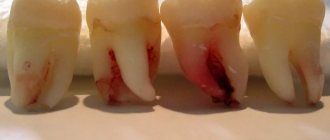
- Difficult tooth extraction. The presence of dental anomalies associated with incorrect tooth position (dystopia, retention) almost always complicates the extraction process. Often these deviations lead to greater trauma and, as a result, more pronounced swelling. The same can be said for third molar extractions. If the operation was performed professionally and the patient followed the dentist’s instructions, then there is no reason to worry.
- Incorrect tooth extraction. Doctor's mistakes include: incomplete root removal, removal of the interradicular septum, leaving fragments in the alveolus, infection. A more rare cause of inflammation is the presence of a cyst that was not detected during surgery: its growth is accompanied by an increase in edema.
To speed up healing and eliminate any unpleasant symptoms that may arise, do not delay your visit to the dentist. It is advisable to contact the surgeon who performed the tooth extraction procedure.
Signs of a tumor that is not dangerous to health
- swelling of the gums and cheeks does not increase and does not have a pronounced form;
- after removing a tooth that caused severe pain, or a wisdom tooth, discomfort and pain should gradually subside;
- even if during the removal procedure you had a slight fever, it should no longer be present, and in no case should it rise;
- there is no unpleasant odor from the hole, which may occur in case of complications.
The cheek tumor can reach its maximum size the day after tooth extraction. Then the swelling should subside.
Normal sensations after surgery
Any implantation operation is a great stress for the body. At first, the body tries to reject the foreign element, so the following symptoms are normal:
- pain in the place where the new tooth is installed;
- redness of the gums around the implant;
- swelling of the gums or even the cheeks;
- temperature.
As we already said, in a week all that will remain is unpleasant memories. But a healthy process is very important:
- contact an experienced specialist for the operation;
- choose a good implant system with which the risk of complications will be minimal;
- Take proper care of your gums and teeth after surgery and follow your doctor’s instructions.
On a note. The first few years after implantation, you should visit the dentist more often - at least once every six months. Remember that complications can appear after 3-4 years - due to poor quality care, infections, mechanical damage. The doctor will help you prevent them, adjust your dental care, and carry out cleaning, if necessary.
How to remove swelling of the cheeks and gums
If the tumor does not cause particular concern, then it is a natural phenomenon after tooth extraction.
There are ways to relieve pain and reduce swelling, as long as it is not harmful to health.
- It is necessary to apply cooling compresses to the inflamed cheek several times during the day, this can be a bottle of cold water, ice in a cloth, a damp towel, which should be kept for twenty minutes, periodically cooling it in cold water. You will immediately feel relief and notice how the tumor decreases in size.
- People with high blood pressure are more susceptible to post-operative swelling. They are recommended to take sedatives and blood pressure-normalizing medications after tooth extraction.
- Conventional anti-edema products can relieve swelling well - gels, creams, ointments that can be applied to the outside of the cheek.
- To relieve pain, which is inevitable after complex removals, you can take a painkiller (except aspirin) or an anti-inflammatory drug and lie down to rest.
Indications for surgery
- Cyst due to periodontitis. As a rule, if it is small in size, it is treated with medications. Surgery is resorted to when the tumor has reached more than 1 cm in diameter.
- Poor filling of the canals, which can cause inflammation.
- If treatment is required on a tooth that has a crown.
Thus, root resection helps not only to save the diseased tooth, but also to prevent the spread of infection to healthy tissue.
Contraindicated actions for swelling:
- Under no circumstances should you heat the swollen area, or touch the wound with your hands and tongue;
- rinsing on the first day after tooth extraction is not recommended, as it can wash away the blood clot that protects the socket from infections. In the future, you can rinse your mouth with antiseptic solutions - miramistin, furatsilin, or decoctions of chamomile, sage;
- the first two to three hours after the removal operation, you should refrain from smoking, drinking and eating;
- Until the wound is completely healed, you should not consume solid food, hot and carbonated drinks, or alcohol.
If you follow these simple rules, the swelling will go away quickly enough and there will be no need to visit the dentist.
Types of complications
The most serious problems can appear during the fusion of the implant surface with the jaw bone: re-implantitis, rejection.
Reimplantitis
This is an inflammation of the tissues that are located next to the artificial tooth. The cause of reimplantitis is the entry of pathogenic bacteria into the cavity between the body of the implant and the gum. This happens if the wall of the paranasal sinus is damaged, there are foci of inflammation in the adjacent tooth, there was an error when closing a postoperative wound, or the crown was made inaccurately. But most often the cause of reimplantitis is poor oral hygiene.
The disease is accompanied by increasing pain, bleeding, and swelling. It is very important to treat it as early as possible, or the disease will become chronic. Gradually, the infection will “eat away” the bone, causing the implant to begin to wobble. In this case, it will have to be removed and then the hole should be treated.
Reimplantitis occurs infrequently - in about 1-2% of cases, but it should be taken seriously.
Rejection of an artificial tooth
Bone tissue may not accept a titanium rod. Most often this occurs due to infectious processes, lack of bone tissue, surgical errors, exacerbation of chronic diseases, and smoking after surgery. Very rarely, rejection may be due to an allergy to titanium.
The beginning of the process is accompanied by increased pain in the surgical area and loosening of the implant. In this case, the tooth is removed and a course of vitamins is prescribed to strengthen the bone tissue. After one to two months, the implant can be re-implanted.
The chance of a new tooth being rejected is 1%.
When to see a doctor
If you have followed all the rules, carried out all the procedures aimed at reducing swelling, and your condition continues to worsen, then this is a sure sign that you need to urgently consult a dentist. Immediate medical attention is required if:
- the next day the swelling increased, and the pain did not decrease;
- the temperature has risen, general health has worsened;
- opening the mouth is accompanied by painful sensations, and the smell of rotting from the hole is felt.
All these symptoms should prompt an immediate visit to the dentist to avoid serious consequences.
Swelling after resection of the root apex
What is resection? Postoperative period
Recommendations in the postoperative period
Any competent dentist will try to keep the tooth alive, even if a cyst or other inflammation has formed at the top of the root. Fortunately, today doctors have more and more opportunities for this; for example, they can remove a cyst without depulping the tooth. This operation is called resection of the apex of the tooth root. However, swelling often appears after it. Is this normal and what should I do?
Flux - treatment in children
If a child has flux, you should never give him medications on your own, and especially antibiotics. Only a dentist can prescribe a medicinal course of treatment. Antibiotics destroy both pathogenic and beneficial bacteria that help fight infection, so the unauthorized use of such serious drugs can lead to negative consequences for the child’s entire body.
Treatment of gumboil largely depends on the causes of its occurrence. So, this process is not much different from the treatment of periostitis in adult patients. As a rule, to begin with, the specialist makes a small incision in the area of the inflammation and ensures the outflow of pus using a special drainage system. The treatment then continues at home under the supervision of parents. Most often, a complex of medications is prescribed, but in some cases, a specialist may allow you to limit yourself to rinsing with special decoctions and solutions.
Ways to solve the problem
A detailed x-ray examination is carried out on a computed tomograph in macro mode, the doctor determines whether there is inflammation or whether it is just panic from noticeable swelling. After assessing the clinical situation, the doctor will prescribe treatment aimed at eliminating the cause of the swelling.
- In severe cases, repeated surgical intervention may be resorted to (in case of implant rejection, purulent complications).
- In cases where the swelling does not bother the patient too much and gradually decreases during the first 7-10 days, additional medical intervention is not required and this symptom will disappear on its own as the tissue heals.
Patients often come to our Center with complications after unsuccessful operations. We specialize in helping with problems related to maxillary sinus dysfunction. The specialized ENT department is equipped with the necessary equipment to eliminate sinus lift complications.
Antibiotics for flux
As noted above, flux is a consequence of a bacterial infection, which is often treated by taking antibiotics. Many, at their own peril and risk, try to cope with inflammation by independently taking quite strong medications that can cause serious damage to the health of the entire body. Effective and at the same time safe treatment of flux with antibiotics can only be prescribed by a qualified specialist.
Antibiotics for flux are prescribed by a doctor individually. Self-use of strong medications is fraught with serious consequences for the entire body.
Antibiotics, like anti-inflammatory drugs, are used in dentistry for flux as part of complex maintenance therapy. The only way to stop the inflammatory process and remove the pus is surgery. Antibiotics are usually prescribed at the very beginning of treatment if the disease is in the earliest stages of its development, but identifying such inflammation at the initial stage can be quite difficult. As a rule, the dentist is able to detect the very first signs of periostitis by accident, for example, during a routine examination of the oral cavity. The specialist prescribes antibiotics for flux individually, depending on the characteristics of the patient’s body and the general clinical picture.
How many days does tooth flux last?
Waiting for the flux to disappear on its own is, to say the least, naive. Some patients believe that if the flux bursts and pus comes out of the wound, then further treatment may not be carried out at all. This is a big mistake, since complete removal of pus requires special drainage, as well as complex therapy and subsequent treatment in the dentist’s chair. With timely and correct treatment, the flux disappears on average in 12-14 days; rehabilitation after severe periostitis can take more than a month.
Diagnostics
Before proceeding with dental flux treatment, the doctor must conduct an appropriate diagnostic examination. The exact diagnosis is determined based on data obtained during a clinical examination and x-ray diagnosis. Laboratory tests allow you to accurately determine the stage of the inflammatory process. Only after making an accurate diagnosis will a specialist be able to decide what to do with gumboil and which method of treatment in this particular case will be optimal.
How to treat flux?
If your tooth hurts and gumboil appears on your cheek, you shouldn’t panic and look for something to rinse your mouth with. “Grandmother’s” treatment methods really help get rid of acute pain and relieve some swelling, but they have not yet helped anyone cope with purulent compaction, which is the main danger. How and with what to treat flux? How to remove gumboil in case of gum inflammation? Only a qualified dentist can give detailed answers to these and other questions.
Self-medication with folk remedies will only help dull the pain and relieve swelling a little. Only a qualified dentist can completely remove pus and eliminate the cause of inflammation.
How is flux treated in dentistry? Currently, there are two main methods of treating gumboil on the cheek:
- Opening the pus sac, in which the doctor removes the accumulated pus through a small incision. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. After removing the pus, the specialist installs a drainage at the site of the incision - a special rubber strip that ensures the outflow of pus and prevents the wound from healing ahead of time.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal is necessary if the inflammation is a consequence of caries or a crack in the tooth.
Often in advanced stages of the disease there is a need for tooth extraction. Typically, this procedure is carried out when there is deep destruction of the causative tooth or if there is a large infected area between the tooth and the gum. Removal is also used if there is a sufficiently large crack in the tooth that cannot be treated.
Typically, the doctor begins by making an incision into the periosteum or lining of the mouth. The causative tooth is usually removed gradually, that is, in parts. For this, a special dental saw or laser is used. Modern equipment has made it possible to make the procedure for tooth extraction quick and completely painless, so there is no need to be afraid of treatment. After the operation, the sharp edges of the incision are smoothed, which is then washed with peroxide or other antiseptic agents and fixed with sutures.