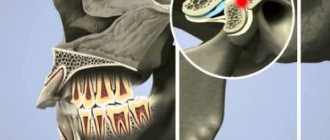
Is it possible to choke on saliva and die?
Yes, such situations are not uncommon. Most often, problems arise in preschool children. Usually these are infants, up to one year old. The fact is that up to 3 months, children do not have a developed cough reflex; they still swallow very poorly, so they can choke on milk or regurgitate masses.
Is it possible to choke on saliva and die?
- In this case, the child does not swallow, and some of the liquid remains in the mouth and may enter the trachea or respiratory tract. Up to 3 months, the situation is absolutely normal, which is why it is recommended to stand children up in a column after feeding so that leftover food and air can easily leave the mouth.
- However, if problems persist, if the child is more than three months old, you should consult a neurologist. Indeed, most often the problem is neurological; the child may have birth injuries. Due to neurological problems, the baby may not develop some reflexes, including the cough reflex.
- That is, the child cannot clear his throat or has problems swallowing. This is why some children spit up like a fountain after eating. This is also a consequence of a neurological problem.
- Therefore, you need to be constantly on guard with such children and under no circumstances put them to sleep in a separate room. The fact is that a child can choke at night and die. With such children it is necessary to sleep in the same room, preferably in the same bed, so that you can hear how they breathe, and if anything happens, provide first aid.
Choked on saliva
Why does a person constantly, often choke on saliva: reasons
A child choked.
This often happens if a person is in a hurry somewhere, talks while eating or laughs. In this case, you just need to eat more carefully, not talk a lot and discuss interesting situations after the meal. However, what to do if a person does not talk or laugh while eating, but still often chokes?
In this case, there are several reasons that contribute to the frequent entry of saliva or food into the trachea. In this case, medical assistance must be provided. In case of frequently recurring situations, you should consult a doctor.
A person constantly, often chokes on saliva, reasons:
- Parkinson's disease. This is a neurological disease that causes a person to be unable to swallow food normally. His swallowing reflex is impaired, food may go down the wrong throat. Most often found in older people.
- Damage to lymph nodes . This often happens after an illness, pharyngitis, laryngitis, or acute respiratory viral infection. In this case, the lymph nodes may be slightly enlarged, as a result of which the lumen of the esophagus and larynx narrows. Therefore, food may fall down the wrong throat.
- Violation of the integrity of the ligaments. Usually occurs after surgery, or after a person swallows an umbrella. As a result of the use of a foreign body, the ligaments are damaged, so the person cannot swallow normally, pieces of food do not fall into the esophagus, but into the trachea.
- Tumors or oncology of the larynx. Foreign objects, as well as tumors, can prevent normal swallowing of food. Pieces of food enter the respiratory tract, causing respiratory arrest or severe coughing.
Heimlich maneuver
Causes of choking while eating
Bulbar syndrome
A pronounced symptom occurs with bilateral damage to the nuclei of the caudal group of cranial nerves, which are responsible for the act of swallowing. Patients choke while drinking and self-feeding is impossible. There is no swallowing reflex, so saliva flows from the corners of the mouth. Choking is also caused by atrophy of the tongue muscles, which makes patients unable to chew food normally. The main diseases accompanied by bulbar syndrome:
- Stroke
. - Inflammatory and infectious causes
: Lyme disease, tick-borne encephalitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome. - Genetic pathology
: Kennedy disease, porphyria. - Damage to nerve cells
: syringobulbia and syringomyelia.
Myasthenia gravis
Choking with myasthenia gravis is associated with weakness of the muscles of the larynx, which contributes to the free flow of food masses into the trachea and bronchi. The disorder is pathognomonic in the bulbar form of the disease - patients choke while eating and drinking liquids. Characterized by variability of manifestations during the day, aggravation of symptoms after physical or mental fatigue. Similar signs are detected in half of those suffering from a generalized form of myasthenia gravis.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis
Swallowing disorders are observed in the later stages of the disease, after the development of muscle weakness in the limbs. At first, choking on solid food is observed; as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis progresses, patients constantly cough and gag while eating. The symptom is combined with speech impairment; saliva usually accumulates in the mouth, which patients cannot swallow.
Mental illness
In this case, choking has no organic cause. Symptoms are caused by dysfunction of the cerebral cortex and inappropriate behavior in severe mental disorders. Patients choke on both drinks and solid food, and sometimes fluid flows through the nose. At the same time, a painful paroxysmal cough begins, soreness and discomfort occur in the throat.
Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)
Normally, a person swallows food while exhaling, when the airways are closed by the epiglottis and soft palate. In COPD, there is indiscriminate contraction of the muscles of the pharynx and larynx, resulting in a reflex inhalation when swallowing food. An attack of severe coughing begins, which is associated with irritation of the larynx with pieces of food.
Rare causes
- Developmental anomalies
: hypoplasia of the larynx, cleft palate. - Gastrointestinal pathologies
: diaphragmatic hernia, reflux esophagitis. - Traumatic rupture of the vagus nerve
.
How to provide first aid if a person is choking?
There are several basic rules and techniques that should be followed to perform first aid. It is necessary to pat between the person's shoulder blades. This will help if he coughs.
How to provide first aid if a person is choking:
- This means that pieces of food have partially blocked the respiratory tract, the trachea, so some air comes in, but in sufficient quantities. Blue discoloration may be observed in the lower lip area. This means there is not enough oxygen.
- Few people know how to perform these taps correctly. Most often, strong punches are delivered when a person is in a standing position. This is wrong and only makes the situation worse by pushing pieces of food even deeper into the respiratory tract.
- In this case, they will be more difficult to remove. Therefore, the best option is to ask the person to bend forward and strike with the palm of the hand in the area between the shoulder blades. It is necessary that the movements be in the direction from the lower back to the neck. That is, as if pushing and sliding, and not direct pats.
Choked
I accidentally choked on my saliva and can’t clear my throat: what should I do?
In this case, there is no one to provide first aid; you will have to save yourself. The main thing in this situation is not to panic.
I accidentally choked on saliva, I can’t clear my throat, what should I do?
- Of course, most often a person is lost, he is in a state of stress, and does not quite understand what needs to be done. However, there are simple manipulations that will help remove pieces of food from the respiratory tract. To do this, take a chair and place it.
- Rest your chest on the back so that it is in the area between the lower ribs and the navel. Now try to lean in such a way that the back of the chair hits this area.
- Hanging your head forward so that a slope is formed, pieces of food will easily leave the larynx. If this does not help, you can perform the Heimlich maneuver yourself. To do this, you need to place your palm bent into a fist in the area of the diaphragm.
- In this case, the second hand should clasp this fist. Now strike from the bottom up, while leaning forward. This way, you will create favorable conditions for pieces of food to leave the trachea.
Where does the crumb go when a person chokes?
Where does the crumb go if a person chokes? In the human body, there are two openings in the throat: the esophagus and the trachea. If a person talks or rushes while eating, food may go down the wrong throat. That is, instead of the esophagus it enters the trachea. This is what provokes a strong cough; if the pieces of food are large, then suffocation.
Heimlich maneuver
Classification of dysphagia
The act of swallowing is extremely complex and involves many different muscles and nerves. And any disturbance in this well-coordinated mechanism can cause swallowing problems. In clinical practice, there are three main types of dysphagia:
- Oral
It is called high, the cause is hidden directly in the oral cavity. For example, this type of difficulty swallowing is associated with tongue weakness after a stroke. Signs include difficulty chewing food and problems redirecting food from the mouth further down the esophagus.
- Pharyngeal
The causes are hidden in the throat, and are associated with neurological diseases that affect the nerves, for example, it can be a symptom of Parkinson's disease or amyotrophic lateral sclerosis.
- Esophageal dysphagia
Or weak, in which the causes are hidden in the esophagus.
Its appearance is associated with blockage or irritation of the sphincters. Pain when swallowing and difficulty swallowing are different conditions, but can be inextricably linked.
What to do if you choked on water?
The most dangerous situation is when a person does not cough, chokes on water, but simply turns blue and cannot breathe. The main mistake is trying to take deep breaths. In this case, the liquid is pushed deeper into the airways and completely blocks them, causing suffocation.
Therefore, it is necessary, on the contrary, to take quick and sharp exhalations. That is, how to cough, helping yourself with the abdominal muscles. You are trying to push out pieces of food without inhaling, but rather exhaling. It is advisable to lean forward so that the fluid leaves the trachea freely.
What to do if you choked on water:
- If you are in a room and a person is not breathing, quickly turns blue, and grabs his throat, this means that there is very little time. After about one minute, the person will turn blue and experience clinical death due to respiratory arrest.
- What should be done in this case? Tapping on the back is unlikely to help. The ideal option is the special Heimlich maneuver. To do this, you need to place your fist in the abdominal area, between the navel and lower ribs, and clasp the fist with your other hand.
- This way, your chest will fit snugly against the victim's back. Now try to tilt it forward so that your head also hangs down. Use sharp movements to apply pressure to this area.
- On average, you need to do about 5 pressures. In this case, with sharp pressure, the water will quickly leave the trachea. However, this method may not work if the person is overweight or is pregnant. In this case, pressing on the abdominal area is dangerous or completely useless, or because of the thick layer of fat, which will not allow it to affect the respiratory tract.
- It is necessary to grab the area immediately under the chest, and also perform sharp pressing movements, from bottom to top, as if pointing to the remaining food in the direction in which they should move. You can lay a person on an oblique surface, head down, and perform tapping movements with your palm in the area between the shoulder blades.
First aid
Causes
Dysphagia is a symptom that accompanies serious illnesses. But if difficulties appear once, we can hardly talk about a serious pathology. It’s another matter when such symptoms persist for a long time and are chronic – this is a reason to visit a doctor. One possible cause may be amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, an incurable form of progressive neurodegeneration. In this case, the nerves in the spine and brain gradually lose the ability to perform their functions. Diseases of the nervous system that are characterized by difficulty swallowing include achalasia, when the muscles of the esophagus cannot relax enough to allow food to pass into the stomach. Coordination of the esophageal muscles is impaired - diffuse spasm.
Eosinophilic esophagitis is an increase in the level of eosinophils, blood cells that begin to grow uncontrollably and attack the gastrointestinal tract. Characteristic symptoms include repeated vomiting and difficulty swallowing food. Parkinson's disease and parkinsonism syndromes are gradually progressive degenerative neurological diseases that lead to impairment of the patient's motor skills. These changes also affect the centers that control the act of swallowing.
Autoimmune and other causes
In addition to neurological diseases, there is a whole list of autoimmune and other diseases, the symptoms of which can be dysphagia:
- Scleroderma
This is a group of rare diseases in which the skin and connective tissue that forms the digestive tract (and not only) becomes denser and tougher.
- Multiple sclerosis
The body's own immune system attacks the myelin sheath of the nerves, resulting in multiple symptoms depending on the location of the damaged nerves.
- Myasthenia gravis
This is a severe autoimmune disease that affects a person's nerves and muscles. Over time, it only progresses and leads to death.
- Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Due to constant irritation of the esophagus, oral cavity and sphincters, strictures of the esophagus can form, which disrupts the act of swallowing and makes it difficult.
- Oncopathologies and their treatment
Esophageal cancer is one possible cause of this symptom, and difficulty swallowing may be an early sign. Radiation therapy, as a method of complex treatment of oncological pathologies, especially of the head and neck, can also cause swallowing disorders.
Symptoms of dysphagia
Many patients are not even aware of the presence of a problem, and those signs of dysphagia that arise remain without proper attention. Delay in treatment and diagnosis
increases the likelihood of developing aspiration pneumonia, exhaustion and dehydration. Therefore, if you experience choking when eating, coughing, even vomiting, increased salivation, if food constantly gets into the “wrong throat,” you need to consult a doctor and begin an examination. Obvious signs of pathology include persistent heartburn, hoarseness, unexplained weight loss, and the inability to control salivation.
What examination is needed
The examination begins with clarifying complaints: when difficulties appeared, whether there are other symptoms, it is necessary to study concomitant diseases.
This data is enough for the doctor to suggest one reason or another, but to confirm the diagnosis, additional examination methods and the involvement of several specialists are necessary.
The act of swallowing is examined to understand what is causing
the difficulty. Visual research methods with the introduction of contrast agents will help to visually assess the picture, identify structural changes and formations. CT and MRI will help complete the picture. An endoscopy may be necessary, which may allow for a biopsy. This examination method is mandatory if the development of oncopathology is suspected.
Treatment of dysphagia
Treatment tactics are determined by the cause of difficulty swallowing, the type, condition of the patient and a number of other factors.
Since difficulty swallowing is most often caused by neurological diseases, treatment is complex and requires an integrated approach. But it will improve the condition and reduce the severity of symptoms. A speech therapist may recommend swallowing therapy. During the learning process, the muscles involved in the act of breathing and swallowing become stronger and more resilient. To ensure you are getting all the essential nutrients, vitamins and minerals, your doctor will recommend making dietary changes. All food that reaches the table must be liquid or semi-liquid. In difficult cases, feeding through a feeding tube may be required. This need is determined by the doctor after examining and assessing the patient’s condition. In difficult cases, surgical intervention may be required, especially if the cause of difficulty swallowing is cancer or structural disorders when the esophagus needs to be expanded. Text: Yulia Lapushkina
I choked on food, what should I do?
What should you not do when a person is choking? As stated above, under no circumstances should you strike hard on the back when a person is in an upright position, that is, standing straight. On the contrary, it pushes pieces of food deep into the respiratory tract, which blocks breathing and can aggravate the situation.
I choked on food, what not to do:
- Under no circumstances should you give a person a drink of water when he is coughing; this will aggravate the situation and, along with pieces of food, water may enter the larynx and trachea.
- Under no circumstances should you begin chest compressions or artificial respiration if foreign objects have not been removed from the larynx.
- First, it is necessary to remove the foreign object, then provide resuscitation procedures, chest compressions and artificial respiration. If you immediately begin artificial respiration, you will insert a foreign object even deeper into the trachea and respiratory tract.
Choked
As you can see, resuscitation procedures for removing a foreign body from the respiratory tract are quite simple. The main difficulty is that the victim panics, and those around him do not know what to do. The main thing in such a situation is not to get confused.
Treatment
Help before diagnosis
If the disorder occurs occasionally and is caused by the habit of talking while eating, specific therapy is not required. The appearance of regular choking while eating, as a result of which a person cannot eat normally, indicates severe damage to the brain or other systems, which requires qualified medical care.
Conservative therapy
Medical tactics consist of eliminating or slowing down the progression of the underlying disease that caused choking. For myasthenia gravis, physiotherapeutic methods and massage are indicated to improve muscle function. In severe situations, when independent food intake is impossible, parenteral nutrition is provided. For etiotropic and pathogenetic treatment, drugs such as:
- Anticholinesterase drugs
. Medicines from the proserin group improve neuromuscular transmission processes and eliminate the causes of choking. To achieve a lasting clinical effect, they are taken for several years. - Glucocorticoids
. Hormones are used in severe forms of encephalitis to prevent brain swelling. They are also recommended for rapid progression of myasthenia gravis and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis. - Antipsychotic drugs
. Prescribed for serious mental disorders, which are accompanied by swallowing disorders and food getting into the larynx. Antipsychotics and tranquilizers are effective for quick relief of symptoms.