This state cannot be called merely unpleasant or uncomfortable. Pulsating pain in a tooth can not only reduce a person’s quality of life - because of it, he may temporarily lose the ability to work normally, sleep, eat, etc. Dentists at the CrystalDent clinic urge all patients who are faced with this problem not to endure this condition in the expectation that it will go away on its own. The specialist strongly recommends immediately seeking help from a doctor and talks about the nature, causes, and methods of dealing with this problem.
Causes of throbbing tooth pain
It causes a feeling that at the site of its source someone or something is purposefully and monotonously hitting the nerve endings, tugging at them, causing them and the patient himself to shudder. This is approximately true, since it occurs due to mechanical irritation of a nerve bundle exposed for some reason, located in the soft tissues (pulp) of the tooth.
Throbbing pain can be either constant or occur periodically - when closing teeth, brushing them, touching them, eating, exposure to heat or cold, or any mechanical stress. It can last for several seconds or several hours, and in some cases it practically does not subside at all. In any case, this is a signal that urgent medical attention is required.
This, to put it mildly, unpleasant sensation may appear for the following reasons:
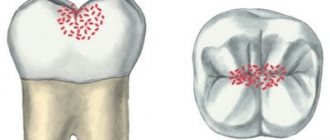
- Caries. This is one of the most common provocateurs of pain of this nature. When it occurs at an early stage, they can be almost imperceptible and short-lived. But as the problem progresses, they intensify, since the hard tissues that protect the pulp from external influences are gradually destroyed;
- Pulpitis. This pathology is a consequence of the destruction of hard dental tissues, which exposes the nerve of the tooth. Most often, this inflammatory process develops as a result of deep caries that has reached the final stages. With pulpitis, the patient feels severe throbbing pain in the tooth, which can radiate to the ear, temple, and even to the neck, eyes, and nose. It can make itself felt either periodically or not recede for a long time;
- Thinning, damage to tooth enamel. In such cases, a reaction of the nerve bundle to external stimuli is also possible;
- Mechanical damage to the tooth due to trauma. If, as a result of the latter, the hard tissues protecting the pulp are destroyed, it becomes exposed, and therefore reacts to any external influence;
- Periodontitis. This disease is an inflammatory process that occurs in the tissues around the apex of the tooth. In this case, the throbbing pain may intensify when touching not only the patient himself, but also the gum, which may also be inflamed;
- Periodontitis. With this pathology, inflammation develops in bone tissue, and, as a rule, this is a consequence of their infection;
- Incorrectly installed filling or insufficient treatment. Patients often complain that throbbing pain appears after filling, and in such cases the reasons may be different. For example, under a temporary filling it may appear due to the effect of a drug that kills the nerve that needs to be removed, and this option is normal. Once treatment is completed and a permanent filling is installed, this problem usually goes away. At the same time, during the treatment process, the doctor must be sure that pain is not a consequence of insufficient treatment. But there are also situations when throbbing pain appears even after the end of treatment. This may also be a variant of the norm - the injured tissues are still healing, and after a few days the discomfort will subside. If this does not happen, it is possible that the tooth was treated poorly (for example, the nerve was not completely removed or the pulp was injured by mechanical forces). It is also possible that a permanent filling is installed incorrectly, which literally puts pressure on the nerve bundle. In both of the latter cases, re-treatment and/or re-filling should be performed.
The problem can also appear after tooth extraction, and in some cases it signals infection of the hole that remains after it.
There are also situations when it is difficult for the patient to determine the localization of these sensations. To accurately establish it, sometimes an in-person examination by a doctor is not enough, but an x-ray will help do this.
Tooth removal
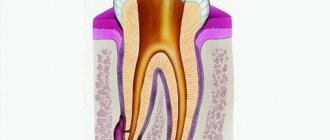
Depulpation (depulpation of a tooth) is the removal of pulp, connective tissue consisting of blood vessels and nerve endings. Removing the tooth nerve and cleaning the canals is designed to relieve the patient from pain, inflammation and further complications. However, the tooth, having lost its blood supply, becomes dead and, therefore, more fragile.
Dental treatment and nerve removal is one of the most common dental procedures. This is partly because patients turn to the dentist only in case of unbearable pain, when it is no longer possible to do without depulpation. Removing the nerve of the tooth and filling the canals allows you to preserve the natural tooth, which is a priority for endodontic treatment.
Indications for depulpation:
- extensive caries
- classic pulpitis and infectious pulpitis (bacteria penetrate through the root apex)
- trauma and damage to the tooth affecting the pulp
- if it is necessary to install crowns or classic bridges
Many patients who come to the dentist's office with toothache are interested in the question: is it possible to save the pulp? Today, there are methods of biological treatment (preservation of the entire pulp) and vital amputation (preservation of the root pulp), but many favorable factors must converge for them to be carried out. For example, biological treatment is not carried out after 25 years.
First aid for throbbing tooth pain
These sensations are sometimes unbearable, and in order to calm them down a little, various painkillers are used.
The following medications can be used:
- Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). Such medications can relieve pain for several hours. In addition, they have anti-inflammatory effects. The most effective painkillers in this category are Ibuprofen, Ketanov, Ketorolac, Ketorol;
- Derivatives of phenylacetic acid. These drugs have not only analgesic, but also anti-inflammatory effects. Their most popular and effective representatives are “Aceclofenac”, “Diclofenac”;
- Such remedies as “Indomethacin”, “Nise” also help to temporarily eliminate throbbing toothache;
- If the sensations are not too pronounced, Paracetamol, Aspirin, and Analgin will help temporarily numb the tooth.
There are also folk remedies that help relieve pain for a short time:
- Ice. It is wrapped in cloth or gauze and applied to the cheek;
- Rinse with soda solution. To prepare it, 1 tsp. soda is dissolved in a glass of warm (but not hot) water, and the resulting composition is rinsed in the mouth. You can add a little iodine (a couple of drops) and salt to the solution;
- Rinse with sage decoction. It is prepared by pouring boiling water (1 cup) over the herb (0.5 tsp), and then sending the mixture to a steam bath for a third of an hour. When the broth has cooled (but it should not become cold), it is decanted and used for rinsing.
Using any methods of pain relief, first of all, you need to carefully clean the oral cavity and the diseased tooth itself from plaque, using toothpaste and a brush.
It is very important to consider the following points:
- The use of painkillers is not a treatment, but only a temporary elimination of symptoms to alleviate the patient’s condition before his visit to the dentist;
- The given examples of drugs and traditional methods are not universal and guaranteed to be effective. In some cases, using any of them can even be harmful. Be sure to contact your doctor to see what steps you can take to relieve your condition. Only a doctor can determine the means that will help do this in each specific case.
Some patients, feeling that the pain has subsided, believe that the problem has passed. This is a big misconception! Eliminating symptoms does not eliminate the disease, so a visit to the dentist is inevitable if you do not want to allow the pathology to rapidly progress and lead to more serious consequences.
How does tooth depulpation occur before prosthetics?
The decision about whether to perform depulpation or not is made by the doctor. The main diagnostic method is x-ray. It shows the presence of inflammation, the condition of the roots, and the thickness of the dentin. Another method is a visual examination, which evaluates the condition of the oral cavity and the physical location of the teeth. Based on clinical data, a treatment plan is drawn up. If a decision is made to remove the nerve before prosthetics, the procedure follows the following algorithm:
- Anesthesia
. Most often it is an injection into the gum. In some cases, sedation may be performed. - Removal of affected tissue
. If there is no caries, then this stage is skipped. - Opening access to the pulp and canals
. To do this, the dentist has to remove part of the hard tissues - enamel and dentin. - Removing pulp
from the pulp chamber. This is a simpler stage. - Extraction of loose pulp
from canals. This is a difficult stage. The manipulation is carried out blindly; how thoroughly he cleans the canals depends on the skill of the doctor. - Treatment of canals
with an antiseptic solution - Drying the surface
- Canal filling
. They do this to prevent pathogens from entering the canal. - Applying a gasket
to isolate the channels. For this purpose, different types of dental cements are used. - Temporary filling
. Only necessary when using medication. A temporary filling is placed for a period of up to 14 days. It can be easily removed if complications arise and additional treatment is needed. If no problems arise, move on to the next step. - Replacing a temporary filling
with a permanent one. Filling is carried out with durable composite materials. - Grinding away excess filling
. - The finishing touch is polishing the filling
.
This is vital removal. No preliminary manipulations are performed with the neurovascular bundle; the amputation is performed live.
The devital method involves mummification of the pulp followed by its removal. After access to the pulp is opened, a paste containing paraformaldehyde is placed into the hole. Or, as people say, arsenic. Then the paste is carefully isolated, covered with a temporary filling and waited until the neurovascular bundle mummifies. After 3-7 days, the cavity is opened again and the pulp is removed. The canals are processed and sealed. This method is rarely used due to the risk of toxins getting into other tissues.
During the work, control images are taken to monitor the quality of canal blockage.
Professional treatment
Its tactics and volume are determined by the doctor, and it depends on the causes of the problem and the condition of the diseased tooth. After an in-person examination, if necessary, the specialist sends the patient for an x-ray in order to accurately determine the location of the lesion and examine the condition of the root and dental tissues.
Based on a preliminary study, the following assistance can be provided to the patient:
- Treatment of caries;
- Depulpation of the tooth with treatment and subsequent filling of the dental canals;
- If its tissues are severely damaged, it may be necessary to install a crown or other types of prostheses (for example, veneers, lumineers);
- If the cause of the pain lies in a root disease, if possible, it is treated by opening the canals. It is possible that resection of its apex will be required to eliminate the source of inflammation and preserve the tooth;
- In some cases, it is not possible to avoid completely removing the latter.
If discomfort occurs after filling, and the reason lies in improper treatment, the filling is opened, the canals are treated, if necessary, and then the filling is repeated.
Tooth hurts after root canal filling
Dental clinic patients are often concerned about the question of why their tooth hurts after inserting filling material into the tooth canal after removal of the nerve. Since any intervention in the body has its consequences, toothache is an “echo” of the filling procedure.
The most common reasons for a tooth to ache after root canal filling are:
- burns and overdrying of dentin;
- allergic reaction to filling material;
- depressurization of the seal;
- change in bite;
- exposure to polymerization lamps;
- shrinkage of the filling.
After the procedure, the dentist usually advises you on how long the tooth under the filling hurts. However, if you feel increasing pain in a filled tooth for more than 2 weeks, you should urgently consult a doctor. Such pain can occur when an instrument breaks off in the canal, root perforation, or improper treatment of pulpitis.
Prevention
No one is immune from diseases and the discomfort associated with them, but measures can be taken to reduce the risk of encountering them. In the case of dental problems, including throbbing pain in the tooth, they are as follows:
- Inspect your mouth regularly to detect early caries early. If you notice it, contact your doctor immediately to get it eliminated as quickly as possible. At the initial stages of its development, it is possible not only to preserve the tooth, but also the nerve in it, which means that it will remain “alive” and will last for many years;
- Regularly visit the dentist - he will see with a professional eye possible problems that the patient himself did not notice, and immediately begin treatment;
- Strictly adhere to the rules of oral hygiene - you need to brush your teeth twice a day, doing it thoroughly and for at least 2-3 minutes. After eating, use dental floss and special rinses;
- Don't skip professional oral cleaning. With its help, it is possible to remove plaque that a regular toothbrush cannot cope with. It often becomes the cause of the development of caries, other dental problems and all their negative consequences;
- As soon as pain makes itself felt, do not delay in seeing a doctor. They are always a “bell” that a pathology is developing, but it will not go away on its own, and without the help of a specialist it will only get worse.
The dentists of the CrystalDent clinic draw the attention of patients to the fact that it is very important to find an experienced, responsible doctor who can provide professional assistance to the required extent, and not only quickly relieve pain, but also save the tooth, do everything to ensure that it served for many more years.
Kostyuk Anna Vladimirovna
Orthopedic dentist of the first category
Did you like the article?
Rate: (no rating)
Loading…
Modern method of depulpation
Today, depulpation is carried out using a pulp extractor - a thin metal rod with teeth that can penetrate even remote areas of the root canals. The apex locator device helps determine the depth of the canal to reduce the risk of injury. After the procedure, a temporary filling is usually installed, but a permanent one can also be installed if the doctor does not see the risks of complications and has high-precision instruments on hand, for example, a dental microscope.
Symptoms of the lesion
The cause of the formation of a pathological process can be carious lesions, inflammation of soft tissues, or mechanical damage to the teeth. The main symptoms include severe aching pain that can radiate to the temporal tissue. You may experience bad breath. The painful area may react acutely to hot and cold foods. With the development of the pathological process, swelling, inflammation of the pulp chamber, and the formation of pus may be observed over the course of several days.
Many patients often wonder whether the nerve in a tooth can die on its own. Yes, maybe, if the destructive process has gone far enough. The main symptom will be a sudden cessation of pain. However, without timely dental intervention, the infection can spread further and affect the trigeminal nerve, leading to trigeminal neuralgia. The consequence will be impaired facial expressions, facial distortion and other anomalies.
Is it painful to treat pulpitis?
Pulpitis is actually an acute inflammation of the nervous tissue, so any manipulation of a diseased tooth can cause significant discomfort to the patient. However, the use of modern painkillers can reduce pain to a minimum. The least painful are conservative and devital surgical methods of treatment. Sometimes pain may persist for some time after treatment; in this case, the doctor may prescribe the patient to take painkillers. However, severe or prolonged pain after pulpitis treatment is often a sign of improper treatment and requires a second visit to the dentist.
Prevention of pulpitis is compliance with the rules of oral hygiene. Use toothpastes with sufficient mineral content, since thinned enamel is less resistant to initial caries and, as a result, inflammation of the pulp. Thus, Asepta Plus remineralization toothpaste will provide additional supply of minerals to the tooth, which is an excellent prevention of diseases of the teeth and gums.
What is the cost of nerve removal?
Over the phone, the administrator can tell the patient only the minimum possible cost, which is estimated at a simple depulpation of an “ideal” single-canal tooth. What if there is a need to treat pulpitis in three-canal molars?
- The final cost will include the passage, expansion and cleaning of each of the channels.
- If the canals turn out to be narrow and curved, the doctor will have to work for about two hours, monitoring the endodontic process using intermediate images on a visiograph or regular x-rays, paid separately.
- Mandatory stages of treatment will be filling the canals and installing a temporary and final filling.
- The price list will include the price of the local anesthesia used or the cost of dental treatment under general anesthesia .
There may even be a need for a second, and in some cases, a third visit to the doctor - in complex cases it is impossible to insure against force majeure.
Want to avoid unexpected costs? Follow all the rules of oral hygiene, do not cause caries and visit the dentist regularly!
Quick appointment Free consultation
Primary canal treatment and installation of a temporary filling
High-quality treatment of tooth pulpitis involves preliminary mechanical expansion of the root canals and their subsequent filling, first temporary and then permanent. The channels are also expanded with a special tool using K-files or reamers. In order to make the necessary expansion, the doctor carefully rotates the K-file and its cutting edges remove chips from the canal walls. It is necessary to increase the size of the canal manually in order to subsequently perform a high-quality filling.
All canals are processed in a similar way to the depth determined by the apex locator and control radiography. During the mechanical treatment, the canals are also constantly washed with antiseptic agents to eliminate the risk of infection entering the root part of the tooth, as well as to eliminate chips removed by manipulation.
After the channels are properly expanded, they are thoroughly washed again, dried, and pads impregnated with an antiseptic drug are placed in them. A temporary filling is placed on the tooth.
Complications and consequences that will not keep you waiting if your teeth are not treated
A far-fetched fear is extremely harmful: because of it, patients often take the situation to extremes and go to the doctor only when the disease spreads to neighboring teeth and gums, and serious intervention is required.
Deterioration of the general condition of the body
There is a misconception that bad teeth have no effect on the body as a whole. And that “one day the moment will come...” - the teeth will be cured, and there can be no complications. The immune system actually copes with the infection up to a certain point, and the problem is localized in the oral cavity. But one day the strength of the immune system weakens, because... he receives no help from outside. General intoxication of the body develops, which is poorly diagnosed, but manifests itself very clearly.
Intoxication is expressed in constant fatigue, fluctuations in body temperature, etc. The prolonged presence of rotten teeth leads to the following consequences:
- 1. Cardiac dysfunction. Endocarditis is an inflammation of the inner lining of the heart, which can only be treated surgically;
- 2. Loss of appetite. Impaired functioning of the gastrointestinal tract due to the entry of harmful microorganisms into it with saliva. Development of gastritis, food intoxication;
- 3. Frequent headaches due to tooth decay at the base of the root;
- 4. Many doctors are sure that bad teeth can cause problems with bone tissue and harm the musculoskeletal system. Arthrosis and polyarthritis often develop;
- 5. It has been scientifically proven that rotting of large chewing teeth leads to hair loss on the back of the head; destruction of small chewing units leads to baldness of the temporal part;
- 6. Rotting of any bone in the skull leads to brain damage;
- 7. Hearing impairment;
- 8. Poor condition of the skin;
- 9. An advanced putrefactive process spreads to the sinuses and can provoke chronic tonsillitis, hyperplasia of nasopharyngeal tissue, etc.
Pulpitis is a consequence of caries
The most common complication of caries is pulpitis. In fact, it is a natural consequence of caries and does not threaten a healthy tooth. With pulpitis, the dental nerve becomes inflamed; the disease is characterized by particularly severe pain when pressing on a tooth (biting on food).
A person can determine for himself when caries turns into pulpitis. With caries, pain appears only if a certain irritant acts on the diseased tooth. The unpleasant sensations disappear as soon as the irritant is eliminated. With pulpitis, pain can occur on its own. It can only be eliminated by the intervention of a doctor. A pain reliever will also help, but this is a short-term measure that loses effectiveness with frequent use. Taking painkillers is allowed only when it is not possible to visit the dentist. Their effect is only to relieve or weaken the pain syndrome; they do not have a therapeutic effect.
Periodontitis
If for some reason pulpitis has not been cured, the disease develops further. The ligaments that attach the tooth to the bone are affected.
Periodontitis has 2 phases:
- 1. Acute, characterized by severe pain;
- 2. Chronic – this phase may practically not appear.