Hypersalivation in children is a process of increased salivation that occurs both at night and during the day. Babies from 3 to 6 months suffer from the pathology, and parents must be attentive and immediately identify the problem, since in children the disease is subject to adequate treatment.
If symptoms of hypersalivation occur in adults, this condition is already considered pathological. A synonym for the disease is ptyalism; its etiology may be associated not only with increased activity of the salivary glands, but also with swallowing dysfunction. For what reasons does pathology occur in children and adults, how to identify and treat it in time - will be discussed today.
How do children sleep?
The quality of sleep, the alternation of its phases and wakefulness change as the child grows older:
- In the first 3-4 months, the baby sleeps, as a rule, 16-18 hours a day. The child usually wakes up every 2-4 hours, as he feels hungry, and falls asleep when full. The feeding regimen does not depend on the time of day, since the child’s body does not react to the change of day and night. Night feedings at this age are considered normal. Starting from the 3rd week, infants begin to develop periods of wakefulness.
- After the first 3-4 months, the duration of night sleep increases, the child can sleep continuously for 5-6 hours.
- Periods of wakefulness increase as we get older, due to increased brain activity and functionality. Changes in sleep patterns (slower falling asleep, early awakening from naps) should not alarm parents as long as children remain active during periods of wakefulness and appear healthy. These changes indicate that the child has grown and needs a different sleep schedule.
The duration of sleep is individual for each child. It may be related to his temperament, physical and psycho-emotional state.
Is poor sleep a cause for concern?
Poor sleep in a healthy baby can signal that he wants to eat or drink, he needs to change diapers, or feel the warmth of his mother’s hands. In such cases, after waking up, the child groans, but after performing all hygienic procedures and feeding, he calms down.
Causes of sleep disturbances in children
Scientists say: interrupted sleep and frequent awakenings at night occur in 30% of children under the age of 3-4 months. In 20% of babies, night sleep disturbances are observed up to 6 months, and in 10% of cases, these disturbances persist into 1 year and later.
American neurologists and somnologists have developed a classification according to which sleep disorders in childhood are divided into two groups:
- Primary - problems with sleep and awakening are not associated with obvious external causes and are not accompanied by any painful manifestations.
- Secondary - caused by dysfunction of organs and systems of the child’s body (allergic reactions, emotional disorders, diseases of the ENT organs and digestive tract, and others).
Physiological features of children's sleep
Primary sleep disorders are most common in infants. The reason for difficulty falling asleep and frequent awakenings at night lies in the infant’s inability to fall asleep independently and in the inability to sleep continuously.
Favorable sleep conditions often help improve a child's sleep:
- Fresh air promotes sound, healthy sleep, so you should lull your baby to sleep in a well-ventilated room. Sleeping in the open air not only improves its quality, but also increases the child’s immunity and the child’s body’s ability to resist colds.
- Good sleep depends on the temperature in the room, the comfort of the pillow and blanket. The baby should not freeze or overheat while sleeping.
- Most babies from 2-3 months, waking up due to an uncomfortable position, can fall asleep without parental help, independently changing the uncomfortable body position in the crib. However, children with increased emotional sensitivity need the presence of their mother. Child psychologists and neurologists say: the desire to sleep with mom is a physiological need of the baby, and not a stupid whim. Mother's hugs contribute to the child's full mental development and normalization of sleep.
Treatment
The treatment process for hypersalivation in an adult is based on the results of examinations, and treatment includes the following points:
- Drug treatment aimed at normalizing the activity of the salivary glands - it includes drugs in the form of tablets and injections.
- Massage of the facial area - the most effective procedure is shown in patients who have experienced a stroke, because as a side effect they often experience dysarthria (pronunciation problems resulting from impaired innervation of the speech apparatus).
- Physiotherapeutic treatment - for hypersalivation, cryotherapy is used, this is a treatment using cold aimed at normalizing the swallowing reflex.
- Radiation therapy - allows you to block excessive saliva production by killing some part of the salivary ducts.
- The introduction of botulinum toxin helps to stop the excessive activity of glands and ducts for a period of 3 to 6 months.
Surgical treatment is used in the most advanced situations; it involves the removal of several salivary glands. Only a doctor can recommend surgical intervention after a thorough examination and the absence of positive results from conservative therapy.
Treatment in children
If signs of hypersalivation appear in a baby at an early age, they may not signal the development of any serious pathology, but simply indicate underdevelopment of the necessary muscles of the face and oral cavity. Also, a problem may arise if the child does not know how to swallow the saliva accumulated in the mouth in time - to solve it, you need to teach the baby to close his mouth while swallowing, as well as in those moments when he is not eating or talking.
If a child is busy with important work (classes at school, kindergarten, requiring prolonged conversation), he sometimes needs to stop to swallow liquid. More radical methods of treating pathology in children include the following methods:
- Cryotherapy. Parents apply pieces of ice along the contour of the oral cavity to the baby; they need to be held for as long as the child can withstand - up to 60 seconds in a row.
- Mouth rinse. It is best to use medicinal herbs that have a calming effect - lavender, mint, sea buckthorn leaves. You can also rinse your mouth with unsweetened jelly, kefir or mineral table water (Borjomi, Essentuki).
- Speech therapy massage. First you need to find the hole under the jaw, place your index finger in it and make vibrating movements. Then you need to feel two points under the tongue and gently massage them counterclockwise for about 10-15 seconds. The next movement is circular, in those places where the jaw closes behind the ears. First, you need to massage these points when the child’s mouth is open, then when it is closed. The procedure should be completed with a palate massage.
- Dieting. This item does not include any special set of products, the main thing is that the diet contains carrots, apples, crackers (solid food that promotes sufficient salivation and full teeth growth). Young children should be introduced to solid complementary foods in the form of cookies, meat, and crackers, so that their salivary glands learn to process not only milk and cereal.
- Articulation exercises. Let the child throw back his head and imitate swallowing, yawning, and chewing food. Then he needs to open his mouth wide and hold in this position for 5-10 seconds. Inflating and retracting the cheeks, holding light objects (strips of paper, threads) with the lips are useful. You can frame the exercises as a game - let the child blow air into a glass of juice through a straw or through a curled tongue.
Accustoming your baby to solid foods (apples, carrots) is not only the prevention of hypersalivation, but also problems with teething, gastrointestinal diseases, anemia
All these measures will help not only for treatment, but also for the prevention of hypersalivation in children, which is not accompanied by serious pathologies. If the problem occurs against the background of concomitant diseases, then the baby must be shown to a doctor for a thorough diagnosis. According to 80% of young mothers, symptoms of hypersalivation appear in their children at the age of 3–9 months, while the process of teething occurs, and then the symptoms disappear on their own.
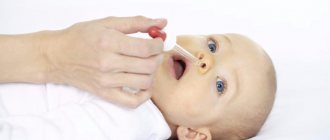
Many parents who trust homeopathic doctors buy the drug Belladonna for their children; taking 1 pea three times a day helps to survive the teething process painlessly and reduce the amount of saliva produced. Signs of pathology in adults require examination by an experienced specialist who, if necessary, will refer the patient for consultation with specialist doctors, because increased salivation in adults and old age indicates serious diseases (if the symptom occurs regularly and not just once).
Excessive stress on the baby's psyche
Overexcitement or overtiredness of a child often leads to disruption of the process of falling asleep. To avoid this problem, parents should exclude the influence of negative factors on the baby’s nervous system:
- The following can overstimulate the nervous system: watching cartoons before bedtime, noisy games, so mothers should control what their children do before bedtime.
- The emotional state of the mother affects the quality of the child’s sleep, as her irritability, increased anxiety, and negative emotions affect communication with the baby. Impressionable children suffer from an uncomfortable psychological environment in the family, which can also lead to sleep disorders. A loving, calm mother and harmony in the family are a guarantee of children’s peace of mind and their mental health.
Somatic diseases
To identify somatic problems that lead to sleep disturbances, you should contact your pediatrician. Timely treatment will eliminate the cause and normalize the baby's sleep.
Abdominal colic is a common cause of poor sleep and whims in a child. When the spasms pass, the baby calms down and sleeps peacefully. Such disorders are temporary and are associated with the characteristics of the digestive system of infants.
The most common cause of persistent sleep disorders in children under 1 year of age is rickets. Its development is caused by a deficiency of vitamin D, as a result of which the metabolism of calcium and phosphorus is disrupted. Starting from 3-4 months (sometimes from 1.5 months), signs of increased neuro-reflex excitability appear:
- fearfulness, irritability;
- frequent shuddering, especially when falling asleep;
- severe sleep disorders;
- increased sweating during feeding and sleep.
The child's condition improves after the pediatrician prescribes a therapeutic dose of vitamin D.
Sleep-disordered breathing in children
Obstructive breathing disorders during sleep can be assumed when a child's parents or relatives notice respiratory arrests during night sleep. A shortened breathing period is usually caused by a blockage of the airways. Tonsillitis and adenoids in children can grow to a size larger than the lumen of the child's respiratory tract. Inflammation and infection of the lymphoid tissue of the nasopharynx, located on the sides and back wall of the pharynx, lead to their growth and blockage of the airway.
During episodes of blocked breathing, the child may appear to be struggling to breathe (the chest rises and falls during breathing phases), but air does not enter the lungs. Often these episodes are accompanied by spontaneous premature awakening of the child in order to compensate for the lack of breathing. Such periods of respiratory blockage (obstruction) occur several times during the night and cause disruption to the child’s sleep physiology.
Sometimes, due to the inability to carry air and oxygen into the lungs to ensure proper breathing, a decrease in the level of oxygenation of the blood occurs. If these situations are prolonged, there is a risk of severe dysfunction of the heart and lungs.
Obstruction of night breathing is most often detected in children aged 3 to 6 years. Often observed in children with Down syndrome and other congenital pathologies that cause disruption of the movement of air through the respiratory tract (for example, an increase in the size of the tongue or an abnormal decrease in the lower jaw).
What are the causes of obstructive sleep apnea in children?
In children, the most common cause of airway obstruction during sleep is enlarged tonsils and adenoids, which obstruct normal airflow at the level of the upper respiratory tract. Infectious processes contribute to an increase in the size of these lymphoid formations. Large adenoids can even completely block the nasal passages and make it impossible to breathe freely through the nose.
There are many different muscles in the structure of the head and neck that help keep the airways open when you are awake to allow air to pass through when you breathe. When a child falls asleep, muscle tone physiologically decreases, thus allowing the tissues to collapse and impair breathing. If the respiratory flow is partially blocked (by enlarged tonsils) during wakefulness, then during sleep the airways may be completely closed to air.
Obesity can also lead to airway obstruction during sleep. While it is a leading cause in adults, obesity is less likely to cause sleep apnea in children.
A rare cause of obstructive sleep apnea in children is tumors or growth of other tissues in the airways. Some syndromes or birth defects, such as Down syndrome or Pierre-Robin syndrome, can also cause obstructive sleep apnea.
What are the symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea in children?
You can point out the most typical symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea, but these symptoms may manifest differently in each child.
Symptoms of sleep apnea include:
- Periods of absence (cessation) of breathing. In this case, the chest will move in and out, but air and oxygen do not pass through the mouth and nose into the lungs. The duration of these periods varies and is measured in several seconds or more.
- Mouth breathing, snoring, just noisy breathing. Breathing through the nose can be completely blocked by enlarged adenoids or tonsils. The child may have a specific “nasal” voice.
- Sleep does not give the child proper rest. This can occur in the presence or absence of obvious periods of awakening during night sleep.
- Increased daytime sleepiness or excitability. Due to the reduced quality of night sleep, the child has difficulty waking up in the morning, is drowsy or hyperexcitable during the waking period.
- Hyperactivity during daytime wakefulness. There may be problems with behavior, schooling or social problems.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea may resemble other conditions or medical problems. You should always consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis.
How to treat obstructive sleep apnea?
The treatment method for obstructive sleep apnea will be chosen by your doctor based on several points:
- child’s age, health status, medical history
- causes of airway obstruction
- the possibility or impossibility of carrying out specific procedures, treatment and examinations for your child
- prognosis of the course of the disease
- Your opinion and preferences in treatment will also be taken into account
Treatment of obstructive sleep apnea is based on the causes of its occurrence. Since the most common cause is enlarged adenoids and tonsils, treatment consists of surgical removal. Your otolaryngologist will discuss with you the stages of treatment, the risks and the need for a particular treatment.
If the cause of the disorder is obesity, treatment will be less invasive, including weight loss and, in some cases, the use of CPAP therapy (a special mask during sleep to keep the airways open) may be necessary. This mask creates increased air pressure (CPAP) in the airways. The device is not fully adapted for children and can be difficult for a child to tolerate, since he or she must sleep wearing a mask.
How is obstructive sleep apnea diagnosed?
You should see a doctor for evaluation if your child's breathing becomes noisy during sleep or snoring becomes noticeable. You may be advised to consult an otolaryngologist.
In addition to a general clinical examination, diagnostic procedures may be recommended:
- completion of a sleep questionnaire (by parents, possibly with the help of a doctor)
- examination of the upper respiratory tract by an ENT doctor.
- -Sleep study using polysomnography. This is the best method for diagnosing obstructive sleep apnea, or the “gold standard”. This test can be carried out on a large number of children, however, some of them, especially young ones, may have difficulties due to the child’s lack of cooperation during the test. Two types of studies are possible: polysomnography or cardiorespiratory monitoring (for young children - using a reduced number of electrodes). The child will sleep in a specialized laboratory. During the study, a number of parameters will be recorded:
- brain activity
- electrical activity of the heart
- blood oxygen content
- movements of the chest and abdomen
- muscle (motor) activity
- amount of respiratory flow through the nose and mouth
During sleep, all episodes of apnea or hypopnea will be recorded:
- apnea – complete absence of respiratory flow
- hypopnea – partial decrease in air flow through the upper respiratory tract with a significant decrease in oxygen in the blood
Based on laboratory testing, sleep apnea becomes significant in children if more than 10 episodes are observed per night, or one or more episodes every hour. Some experts define problems as significant if a combination of one or more episodes of apnea and/or hypopnea are recorded every hour.
Symptoms of obstructive sleep apnea may reflect other conditions or medical problems. In any case, consultation with a pediatrician is necessary.
Neurological causes of sleep disturbance
Sleep disorders associated with disruption of the central nervous system are caused by the following reasons:
- the baby was born prematurely;
- During pregnancy, the woman suffered serious illnesses and took potent medications;
- As a result of a complicated birth, the child was born with asphyxia and various physical impairments.
In such situations, the formation of the nervous system occurs differently in each child. Its defeat is necessarily accompanied by behavioral and mental disorders, and sleep problems. To determine the level of damage, the nature of the disease, and exclude other causes, you should contact a pediatric neurologist.
Reasons for development
The nature of ptyalism may be true or false. True hypersalivation is distinguished by the fact that during the day a person secretes several times more saliva than should be secreted normally. The false form is characterized by a violation of the swallowing function, while the patient feels that a copious amount of saliva has accumulated in his mouth.
Doctors believe that the causes of hypersalivation in an adult may be the following:
- stomatitis - the flow of saliva is provoked by irritation of the oral mucosa, when it is painful for a person to swallow and simply touch the affected surface;
- Parkinson's disease;
- poor blood supply to the brain, vascular pathologies, malignant neoplasms;
- stomach ulcer;
- helminthic infestations;
- the period of gestation in women, especially if pregnancy occurs against the background of severe toxicosis;
- stroke;
- poisoning with salts of heavy metals - mercury, lead, iodine;
- epidemic encephalitis.
Unlike an adult disease, a child drools from the mouth more often for physiological reasons, for example, during the eruption of baby teeth - between the ages of 4 and 12 months. At an
older age, if a child drools, this symptom cannot be ignored, it may indicate the following diseases:
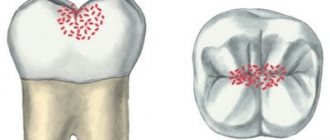
Symptoms of inflammation of the salivary glands
- cerebral palsy;
- disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system - salivation during sleep is observed, for example, with the disease PPCNS (perinatal damage to the central nervous system) or PEP (perinatal encephalopathy);
- malocclusion;
- pathologies of the nasopharynx and ears - sinusitis, sinusitis, proliferation of adenoids, acute tonsillitis;
- ulcerative stomatitis - when painful ulcers form, the baby finds it difficult to swallow saliva, at night it flows down the cheek, while the baby refuses to eat and sleeps poorly (irritated mucous membrane causes severe discomfort);
- Gingivitis is an inflammation of the soft tissue of the gums. Why do you drool while you sleep? This is the body’s protective reaction to an acute process; during sleep, the mucous membrane tries to recover on its own and wash out the infectious agent from the oral cavity;
- intoxication of the body.
In any case, if an adult or child suffers from increased salivation, it is necessary to consult a doctor; treatment of hypersalivation depends on the underlying cause. Most often, when the underlying problem is eliminated, for example, after treating stomach problems or helminthic infestations, the disease goes away on its own.
Causes of nocturnal hypersalivation
The secretion of saliva in a dream can be a separate symptom of the disease, while during the day a person does not experience increased work of the glands, and he himself only guesses about the problem from a wet pillow or his relatives tell him about it. Most often, such problems arise due to the predominance of the parasympathetic part of the central nervous system, since it is responsible for the functioning of the salivary glands.
Under its influence, saliva becomes too liquid, and a person does not have time to swallow it in a dream.
The most common reasons why a sleeping person has saliva flowing from his mouth:
- difficulty breathing through the nose - problems can arise from ENT diseases (runny nose, sinusitis, sinusitis), allergic reactions, curvature of the bony nasal septum;
- abnormal structure of the jaws - an incorrect bite does not allow the bones to fully close, as a result, saliva flows directly onto the pillow during sleep (this phenomenon is often observed in older people, they suffer from dysfunction of the jaw joint and relaxation of the lower jaw);
- sleep disorders.
The amount of saliva produced may increase even once; this situation is not considered pathological. For example, if a person is too tired or has experienced emotional shock. At the same time, he fell fast asleep, his body was completely relaxed, his mouth opened and a small amount of saliva flowed out.
The same problem is observed in people under the influence of alcohol or after heavy consumption of nicotine - if you drink and smoke before going to bed, it is quite possible that a one-time problem with increased salivation will arise
If there is increased salivation at night in an adult, diabetes mellitus, disease of the thyroid gland, pituitary gland or hypothalamus can be suspected. In this case, the neuroendocrine system reacts violently to any stimulus during the day, and at night responds with increased production of saliva.
Help from a neurologist for sleep disorders
If there are sleep disturbances or any suspicion of a neurological pathology, the child should be shown to a specialist. The doctor conducts a comprehensive examination, which makes it possible to detect deviations from normal development and determine the disease. The difficulty in diagnosis is that some diseases of the central nervous system cannot be detected before the age of 1 year, sometimes even until the age of three.
Treatment is aimed at calming, relaxing, normalizing sleep, and correcting behavioral characteristics. Complex therapy for neurological disorders includes:
- massages;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- baths with sedatives.
In some cases, the child is prescribed medication.
We draw the attention of parents that most often sleep disorders are not associated with serious problems and only require correction of the baby’s sleep pattern. However, if your child continues to sleep restlessly, you should consult a doctor about this problem. If you are looking for a qualified pediatric neurologist in Kaliningrad, contact the Edkarik children's clinic.