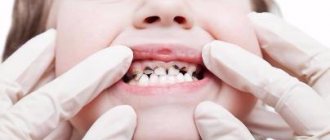
When visiting a dentist, you have probably heard them more than once say such phrases as, for example, “lower left five” or “16th tooth” or “2nd premolar.” Experienced patients know that this is the numbering of the teeth, which is necessary for the doctor to describe the condition of the oral cavity when filling out the card. There are several systems used in dental practice for this purpose.
Location of teeth by numbers
Despite all the individual characteristics of each person, the location of the teeth and their name are the same for everyone. This is explained by the fact that dental elements begin to form long before birth (approximately 2-3 months of embryogenesis), and at birth the child has all the dental buds located deep in the jaw.
In both adults and children, the dentition is symmetrical - the upper and lower jaws have the same number of teeth of the same name (the reference point is the midline of the face).
The table shows the order of the teeth and their correct name.
| Serial number | Dairy | Permanent |
| 1 | central incisor | central incisor |
| 2 | lateral incisor | lateral incisor |
| 3 | fang | fang |
| 4 | first molar | first (small) premolar |
| 5 | second molar | second (small) premolar) |
| 6 | — | first (large) molar |
| 7 | — | second (large) molar |
| 8 | — | third (large) molar |
As can be seen from the table, only the front teeth (incisors and canines) have the same names and locations in children and adults. The rear (or “root”) have significant differences.
Teeth of ancient people
The dentofacial apparatus of prehistoric and modern humans differs significantly. Ancient people had more than 36 teeth, protruding fangs and a massive jaw. This was explained by the need to chew rough food and raw meat. With the addition of thermally processed foods to the diet, the dentition began to change. The canines were the first to transform, becoming aligned with the bite line. Then the jaw arch narrowed, the interdental spaces disappeared, and the teeth themselves decreased in size. Currently, 32 teeth in humans are the norm, but third molars are considered to be an atavism.
Interesting fact!
The teeth of ancient man cannot be called aesthetic, but they were healthy. According to scientists, cavemen never suffered from caries and other oral diseases.
Why is tooth numbering necessary?
All human teeth have their own specific location according to numbers. But how can you understand whether it is located on the upper or lower jaw, or on the left or right? You can use full formulations (for example, the first permanent molar of the upper jaw on the right). But such cumbersome names create certain difficulties for dentists and can often cause mistakes, which are especially dangerous if the patient is undergoing extraction of a diseased tooth.
In order to optimize the work of doctors and simplify the designation of tooth numbers as much as possible, special numberings were invented.
Dimensions of human teeth
The upper central incisors are twice as wide as their antagonists. The remaining dental units of the same name have approximately equal parameters. The size is determined using special tables with the optimal size and permissible deviations. Experienced doctors calculate proportions by dividing the length of a person’s teeth by the width. A result of about 0.75 millimeters is considered close to ideal. For more detailed diagnostics, other professional formulas and techniques are used.
Size deviations from the norm occur due to improper formation of the jaw, fusion of tooth buds, or genetic predisposition. Teeth that are too large are called macrodentia, and abnormally small teeth are called microdentia. Pathologies are accompanied by problems with bite and chewing functions, but can be successfully corrected by a dentist.
Interesting fact!
The longest tooth in the world belongs to an Indian teenager. The size of its crown is almost four centimeters. About a year ago, the tooth was removed, and the young man was included in the Guinness Book of Records.
Tooth numbering schemes in dentistry
Currently, tooth numbers in dentistry are systematized according to several schemes:
- Universal numbering system.
- Square-digital or Zsigmondy-Palmer system.
- Haderup system.
- American numbering or alphanumeric system.
- European numbering Viola or WHO system.
Let's take a closer look at the features of each of them.
Universal system
This numbering scheme is based on assigning each permanent tooth a specific number from 1 to 32. In primary occlusion, each tooth has its own letter. In this case, the count is carried out from the right half of the upper jaw clockwise from the wisdom tooth.
The dental formula of a permanent set according to the universal system looks like this:
Milk teeth are marked according to the same principle, but only using letters of the Latin alphabet:
Zsigmondy-Palmer system
This numbering is the most imperfect, since it still indicates the teeth under numbers without a more precise indication of their location. At the same time, Arabic numerals from 1 to 8 are used for the permanent set, and Roman numerals (IV) are used for numbering dairy products.
The digital system does not exclude errors when carrying out diagnostic or therapeutic measures, therefore, today it is used only by orthodontists (for example, when installing and marking braces) or maxillofacial surgeons. And entries on it in the patient’s medical record are made only on a special diagram.
Haderup system
Numbering according to the Haderup system also applies to digital numbers. To designate the teeth of an adult, Arabic numbers 1-8 are used with a plus or minus sign in front of them. The “+” sign is used to number the upper ones, and the “-” sign to indicate the lower ones.
The numbers of children's teeth are similarly written in Arabic numerals with the signs “+” or “-”, but at the same time the number “0” is placed in front of them.
The inconvenience of such a system is the need to indicate the location of the tooth on the left or right side of the jaw.
American alphanumeric system
This numbering is widespread in the USA. The alphanumeric system is based on assigning a letter value to each group of teeth (capitals for a permanent set, and capitals for a primary set), as well as a digital code that indicates the location of the tooth in a correct bite.
Letter meanings of teeth:
- I (i) - permanent (deciduous) incisors;
- C (s) - permanent (deciduous) fangs;
- P - premolars (absent in primary dentition);
- M (m) - permanent (deciduous) molars.
American numbering also does not take into account the left- or right-sided position of the tooth, which can cause certain difficulties.
European international numbering Viola
Today, this is the newest and most advanced teeth numbering system. Its essence lies in the fact that the jaws are divided into segments (2 on top and 2 below), each of which is assigned its own number. For adults, numeric values are used 1-4, and for children - 5-8. As a result, each tooth receives a two-digit number, the first digit of which indicates a specific segment, and the second - a serial number.
The convenience of the Viola system lies in the absence of cumbersome names while accurately indicating the location of the required tooth and the minimal risk of error. This numbering is indispensable when sending a patient for an x-ray, as well as when identifying teeth on a panoramic image.
Features of treatment of individual groups of teeth
The treatment tactics for incisors, canines, premolars, molars of the upper and lower jaws are different. Each tooth carries a different load. One part of the row is visible when you smile, while the other remains invisible to others. Let's look at the features of treatment for each area of the oral cavity.
Treatment of wisdom teeth
Eights are the outermost molars in the row. They erupt later than others, practically do not participate in chewing food, and regularly cause trouble. 1, 16, 17, 32 teeth can erupt incorrectly, displacing the entire row, injuring the gums, and causing the formation of a soft tissue hood. This increases the risk of plaque accumulation and tooth decay.
| Features of wisdom teeth treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| Do I need to remove wisdom teeth? | In most cases, this is necessary and recommended. |
| Is it possible to treat caries on the 8th tooth? | If they do not disturb the structure of the dentition or cause discomfort, then after consultation with a doctor you can do this. |
In most cases, eights must be removed. If they grow at an angle, disrupt the bite, displace other molars, cause discomfort, or have underdeveloped enamel, it is recommended to get rid of them as quickly as possible. Extraction of teeth 1, 16, 17, 32 does not affect the chewing function or appearance of the patient.
Is caries of eights curable? If they have a normal structure, do not cause discomfort, and are involved in chewing, superficial caries can be treated using the traditional method - drilling, installing a filling. The procedure is performed at the request of the patient. If a person refuses conservative therapy, the extreme molars are removed.
If there is significant damage to the visible part of the figure eights, their removal is indicated. Artificial crowns are not installed on them due to their location and anatomical features. For acute pain, the only way to solve the problem is extraction. The figure eights are located in the far corners of the oral cavity, which makes depulpation and endodontic treatment impossible. Lack of visibility and access to instruments prevents nerve removal and canal filling.
Extreme molars are unreliable and often destroyed, so they are not recommended for use as a support for bridges. If eights are lost, prosthetics are not performed; there is no such need or possibility.
Treatment of molars
2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth are molars that bear the main load when chewing. They are large, with a wide crown, have several roots, so they are firmly held in the jaw. They are not visible when you smile, but the defeat or absence of one of them causes severe discomfort to the patient. When treating this group, they pay attention to strength and strive for complete restoration of function.
| Features of treatment of molars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment methods are there if a molar is severely damaged? | In case of severe destruction of molars, ceramic inlays are most often used. |
| Which crowns are best for molar prosthetics? | More often, patients are recommended to install metal-ceramic crowns in the molar area. |
| What to do if you lose molars? | The best option in this case is implantation; patients also consider removable dentures. |
The main method of treating caries of sixes and sevens is drilling and filling. If the process does not affect the canal with the neurovascular bundle, the doctor drills out the affected areas and closes the defect with a filling made of composite materials. If the affected area is large, it is advisable to use ceramic inlays. They are made from impressions for each patient and close the cavity formed after treatment. The use of inlays allows you to increase the service life of the molar and ensures its resistance to chewing loads.
If the visible part of the six or seven is significantly destroyed, but the root is preserved, restoration is carried out using a crown. The best material for prosthetics of 2, 3, 14, 15, 18, 19, 30, 31 teeth is metal ceramics. Such designs are very durable and allow you to chew even hard food. A thin strip of metal that is visible between the metal-ceramic crown and the gum is not a disadvantage when restoring molars. It is completely invisible because these teeth are not located in the smile area. You can choose crowns made of zirconium dioxide, but they will cost more than metal-ceramics. Ceramic structures are not installed on chewing teeth.
The loss of molars affects the condition of the gastrointestinal tract and leads to displacement of the entire dentition, so prosthetics are necessary. To replace 6-k bridges, bridges are often used. If nearby units can serve as support, this is the fastest, least expensive, painless option for restoring mastication. For multiple defects, removable clasp and plate prostheses are used.
The optimal way to replace molars is implantation. The condition of adjacent teeth does not matter. With the help of titanium structures, it is possible to restore both one and several units. In most cases, root-shaped prostheses are used for prosthetics. They are able to withstand heavy loads. Such implants can serve as a support for artificial crowns and bridges.
Treatment of premolars
Teeth 4, 5, 12, 13, 20, 21, 28, 29 are premolars. They also perform the function of chewing, but are not as large and massive as molars. Some premolars are located in the smile zone, so when treating them, not only strength and functionality are important, but also beauty and naturalness.
| Features of treatment of premolars | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What to do if premolars are destroyed? | In case of significant destruction, ceramic inlays or crowns are used. The best material for premolar restoration is zirconium dioxide. |
| What to do if there are no premolars? | In this case, there are several treatment options - bridge structures, butterfly prosthesis or implantation of a missing tooth. |
The most common lesion of fours and fives is caries. Destruction occurs especially often in patients with deep fissures and narrow interdental spaces.
Due to the location of small molars, caries on them can be noticed in the initial stages. Sometimes even patients themselves pay attention to the problem and seek dental help. If a carious lesion is detected at the spot stage, modern clinics carry out treatment without drilling using the ICON system. Careful removal of damaged enamel using an etching gel allows you to save the tooth, and sealing the cavity with a special compound stops further destruction. For deeper lesions, destroyed tissue is removed using a drill or laser. Small defects are restored with durable photopolymer materials. You can choose the shade of the filling that perfectly matches the color of the enamel. In case of significant destruction, leading dentists recommend using ceramic inlays, which are made in a dental laboratory using individual impressions.
The destroyed outer part of the premolar is an indication for the installation of crowns. If only the root remains, a stump tab is installed to securely secure the prosthesis. The choice of crown material depends on the financial capabilities of the patient. The best choice is zirconium dioxide. Such designs are aesthetic and resistant to chewing loads. Their only drawback is their high price. Metal ceramics are available to everyone. It is strong and durable, but the strip of metal under the gum can be very noticeable for some. Ceramics are not suitable for fours and fives. This material is too fragile; with intensive chewing, chips will quickly appear on it.
The absence of premolars in a person is immediately noticeable to others. When they are lost, most turn to dentistry for prosthetics. If you want to quickly restore chewing and restore an attractive smile, installing an inexpensive bridge will help. The design consists of several interconnected crowns made of metal ceramics or zirconium dioxide. The outer crowns are placed on the supporting teeth, and the middle ones cover the defect in the dentition. The main disadvantages of this type of prosthetics are the need to grind healthy teeth and uneven distribution of load on the jaw.
If installing a bridge is not possible, the prosthetist will suggest a removable clasp prosthesis. Typically, the design is used when several teeth are missing. This method saves the budget and has virtually no contraindications. Lightweight butterfly prostheses are used to temporarily replace the defect. They last no more than six months, but this is enough for patients who are awaiting the manufacture of a permanent prosthesis or implantation.
The best method of replacing a lost premolar is implantation. If there are no contraindications and your budget allows, it is better to choose this modern method. A titanium rod is inserted into the jaw bone tissue and becomes a support for an artificial crown. To install such a prosthesis, you do not need to grind down the adjacent teeth. In addition, the load during chewing is distributed physiologically. Externally, an artificial premolar is difficult to distinguish from your own. Even a dentist will not always do this at first glance.
When treating 4- and 5-k, it is important to maintain a balance between practicality and aesthetics. For this reason, this group is the most difficult for dentists.
Treatment of fangs
There are four fangs in the oral cavity. These are 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth according to the universal numbering system. They have a different shape from other teeth, so during restoration it is necessary to have experience working with this group.
| Features of canine treatment | |
| Question | Dentist recommendation |
| What treatment options are there for lost fangs? | In this case, implantation of the lost canine is recommended. |
| How can you correct abnormally growing fangs? | After consultation, the patient is offered options for either orthodontic treatment or the installation of veneers or crowns. |
The fangs do not bear the chewing load. They help you bite off small pieces of food. In the process of evolution, the role of fangs in humans was lost; we do not use them to hold food or tear it into fragments. That is why the treatment of triplets is aimed at restoring their natural appearance.
In case of carious lesions, the preparation of fangs is carried out carefully, trying to preserve healthy tissue as much as possible. This will allow for high-quality restoration. With superficial caries, it is possible to preserve the volume of hard tissue necessary for high-quality filling, but deep lesions serve as an indication for installing a crown. To maintain a natural smile, it is recommended to use structures made of ceramics or zirconium dioxide.
If 6, 11, 22, 27 teeth are lost, implantation is recommended. Manufacturers offer titanium prostheses of a special configuration, taking into account the anatomical features of the jaw. Such prostheses are already classic, they have a special thread that allows you to securely fasten the structure in the narrow alveolar process.
A popular dental service is canine shape correction. Some patients have teeth that are too long, pointed, or significantly narrower than the incisors, which makes the smile less attractive. The best way to give the fangs the ideal shape is to use ceramic onlays made from individual impressions, as well as modeling with composite materials.
How to determine the tooth number - practice with examples
Determining which teeth numbers are quite simple, you just need to practice a little with examples.
Tooth number 37 - which one is it?
To an unknowing person who is not familiar with the numbering systems in dentistry, it may seem that we are talking about an extra 5 teeth in the mouth. But that's not true. According to the Viola system, teeth with numbers starting with three are located on the lower jaw on the left. And serial number 7 corresponds to the second molar. This means the 37th tooth is the second lower molar on the left.
What number corresponds to the upper right wisdom tooth (eight)?
The third molar will be designated differently in different systems.
- In the universal number scheme - number 1.
- According to the Zsigmondy-Palmer scheme - “upper right eight”.
- According to the Haderup system - “+8 on the right”.
- In the American scheme - “upper M3 on the right”.
- According to the Viola system - number 18.
For a school-age child, the dental formula says that next to tooth 21 there is tooth 62. How can this be?
In children at 6-7 years old (less often at 8-9 years old), the replacement of milk teeth begins. Therefore, both teeth from a temporary set and already erupted permanent teeth can be located in the mouth at the same time. In this situation, they are numbered according to the Viola system, and their numbers indicate that the central upper incisor on the left (number 21) has already been replaced by a molar, but the lateral incisor is still from the primary bite (therefore it is marked under number 62).
Human wisdom teeth
A “wisdom tooth” is the third outer molar with three to five roots. In structure it is no different from its “neighbors”. To the question “How many wisdom teeth does a person have?” cannot be answered unambiguously. They erupt around the age of twenty, one on each side of both jaws. However, there are people without wisdom teeth. This is a variant of the norm, since in the process of human evolution the need for the “eight” disappeared, and the structure of the jaws underwent corresponding changes. Today, third molars are considered a vestigial organ.
Numbering for an abnormal number of teeth
If a person has a normal number of teeth in his mouth, then their numbering does not cause difficulties and remains constant both at a young age and after 60 years.
If some teeth are lost (for example, due to various diseases or developmental anomalies), then in the dental formula next to the corresponding number its absence is simply indicated.
But there are diseases of the dental system, which are characterized by an increase in the number of teeth with an atypical arrangement. With such options, the use of any numbering schemes is difficult and most often dentists refuse to use them. In this case, complete information about the number of teeth, their description and location is entered into the patient’s medical documentation.
The structure of the human tooth
Anatomy
From an anatomical point of view, a human tooth consists of three parts.
- Crown.
The visible part protruding above the gum. It has four sides: the occlusal, or cutting edge, in contact with the antagonist teeth; contact wall adjacent to adjacent dental units; vestibular and lingual surfaces facing the lips and tongue, respectively. - Root.
Fixed in the socket by connective tissue, located in the recess of the jaw. As a rule, premolars have two roots, and molars have three, four or even five. The remaining dental units have one root canal. - Neck.
It is located between the coronal part and the root of a human tooth, surrounded by periodontium.
Histology
What are human teeth made of? Let's look at the cross-section of the structure of a human tooth.
- Enamel.
A transparent protective coating of the crown, almost entirely consisting of inorganic microelements. - Dentine.
The hard base of the tooth, containing 80% mineral components and 20% organic substances. The shade of dentin is responsible for the color of dental units, as it shines through the enamel. - Cement.
The bone tissue covering the tooth root. Plays the role of a fastening element connecting the tooth to the alveolus. - Pulp.
Soft tissue filled with bundles of nerves and capillaries. Painful sensations during caries are explained precisely by the presence of nerve endings.
Scheme for adults
The adult system can be divided. Unit numbers are determined for the lower and upper jaws based on center to right and center to left. The first two incisors in dentistry are numbered as No. 1 and No. 2. There are eight incisors in total. Under No. 3 are the fangs, there are four in total. Then numbers 4 and 5 follow - these are premolars. Numbers 6 and 7 are molars and other chewing units. The last units of the dentition, which dentists call “eights,” grow later than others. You may notice that the names are not clear and vague. Therefore, having heard about the need to fill molar number 7, it is impossible to determine exactly which tooth, on the right or left, is meant and on which jaw it is located. Digital designation undoubtedly simplifies the work of doctors, but there is still a division of the jaw into segments. The parties are determined not by the patient, but by the doctor. Teeth numbering in dentistry, photo diagram can be found on the Internet. Dentists use similar products in their daily activities.
When does a child's molars come out?
Most parents are interested in the question: at what age do children’s molars begin to erupt? The first buds form in the fifth month of pregnancy. The exact timing of their appearance has not been determined and depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. Nevertheless, an approximate scheme for the eruption of molars in children exists. If the appearance of a permanent tooth is delayed for more than six months from the extreme threshold (especially after the loss of a baby tooth), consult a specialist. The doctor will take control of the process and be able to identify complications.
Complications during teething
- Delay in the appearance of permanent teeth.
This may be due to genetic characteristics, immune system problems and a number of other diseases. - Uneven teeth and other malocclusions.
- Hyperdentia.
The child’s molar tooth (or teeth) grows in the second row. Hyperdentia, or supernumerary of teeth, is a fairly rare phenomenon, but requires the intervention of a dentist to eliminate the risk of malocclusion in a child.
Is it worth getting an implant?
The absence of the sixth tooth threatens:
- displacement of neighboring units;
- advancement of antagonists on the opposite jaw.
Neighboring and antagonist teeth will slowly shift, which threatens to expose the roots, the appearance of wedge-shaped defects at the gum itself, exposure of the neck, which is sensitive to changes in temperature of water and food, and pain. In addition, there will be a change in the bite, since the teeth will be out of place. Therefore, it is necessary to place an implant to maintain healthy teeth and correct bite.
Molars in children: symptoms of eruption
- Fever. When teething in children, body temperature may rise, usually not higher than 38 degrees.
- Itching and pain at the site where the molar appears. Various gels and ointments, as well as gum massage, will help relieve children from unpleasant sensations.
- Increased salivation and runny nose.
Important!
The growth of molars in children, especially at the initial stage, leads to weakened immunity. Take vitamins and do not forget about preventive visits to the dentist.
Guarantees
In our Center, implants are installed with a lifetime warranty from the manufacturer - Nobel Biocare. We provide guarantees:
- lifetime for the installation of implants;
- 1 year for crowns.
The warranty program includes a complex for the implant, surgery, bone reconstruction and prosthetics.
The guarantee is valid provided that the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations, care rules and regularly visits the dentist.
Dental formula for anomalies
Standard types of numbering can be used when there is a lack of teeth: their absence as a result of illness, age-related changes or developmental pathologies is described after indicating the number.
But there are anomalies in which the classical formula changes:
- Irregular shape or size: when one tooth takes the place of several or, on the contrary, grows smaller than expected, the entire dentition is displaced.
- Change in quantity: an excess of masticatory organs deforms the dentition due to a change in position and underdevelopment of the teeth.
- Incorrect location: cutting in the wrong place hinders the development of “neighbors” and may affect their number and shape.
In case of such pathologies, an individual dental formula is drawn up for a person, taking into account the number of different chewing organs in the oral cavity.
Numbering is not used in such cases: when describing the condition and pathologies in the patient’s medical record, the doctor uses the full name of the tooth, and also indicates its position, shape and other characteristic features.
These are the basic principles by which teeth are counted in dental offices. Knowing the decoding of all the meanings, you will be able to understand what exactly is hurting you and which masticatory organ will be treated.
Price
Our Center has a case payment system, which means that the case includes all materials and necessary manipulations.
The cost of implant installation includes:
- implant and superstructures;
- work of an implantologist;
- anesthesia;
- basic bone building complex;
- primary and repeat CT.
The price of implants varies depending on the type of bone. Nobel Biocare PMC (cheaper) is intended for weak tissue, and Nobel Biocare Conical Parallel CC (more expensive) is intended for dense tissue.
The cost of the crown includes:
- production of a prosthesis by a technician;
- taking impressions;
- installation of a crown.
Tooth extraction (for simultaneous implantation), bone grafting or sinus lifting are paid separately. Prices for services can be found here.