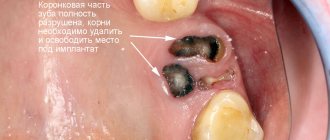
- Complex tooth extraction
The operation to remove a tooth can be simple or complex (accompanied by an incision in the gum), and its duration can vary from several minutes to an hour. In addition, tooth extraction in children and adults, as well as in people with any diseases, may have some features and nuances. On average, the operation takes about 30-40 minutes and includes the following steps:
- Anamnesis collection. The first stage, during which the doctor finds out whether the patient has any diseases, as well as allergic reactions to medications - this makes it possible to select the optimal anesthesia option in this case.
- Anesthesia. The dentist administers an anesthetic drug to the patient, and in standard cases, carpules are used for this purpose. Their duration of action can range from 40 minutes to several hours.
- Preparation. Using a special tool, the gum is peeled away from the tooth - this approach avoids injury to soft tissue during the removal process.
- Tooth swinging. At this stage, the doctor applies forceps to that part of the tooth that is located above the bone tissue, and, tightly squeezing the handles of the instrument, begins to loosen it. This requires some physical effort and is necessary in order to destroy the ligaments with which the tooth is attached to the bone.
- Tooth extraction. As a result of the previous stage, the tooth becomes mobile and can be removed from the socket. After this, the hole must be inspected and all bone fragments removed from it.
- Hole processing. If the operation was carried out against the background of purulent inflammation, then the hole must first be washed with an antiseptic, and then an anti-inflammatory drug should be placed in it. In addition, to quickly heal the gums and prevent complications, sutures are sometimes placed on it.
After removal, the patient must follow all doctor’s recommendations and take prescribed medications. If within 24 hours after the operation the hole begins to bother you greatly, you should definitely consult a doctor, since any discomfort may be a symptom of a complication called alveolitis.
Types of tooth extraction
In medical practice, all removal procedures are divided into:
Easy removal
The doctor manages to extract the entire tooth using special forceps; its duration is up to 5 minutes. This is how single-rooted teeth or teeth affected by periodontitis are removed.
Difficult removal
To extract a tooth, the doctor uses auxiliary tools (most often an elevator), and the entire extraction process takes up to 15 minutes. It is most often performed when a part of the root or crown is broken during the removal of multi-rooted teeth.
Atypical removal
It has no clear boundaries in terms of time and extraction method and implies a complex and multi-stage procedure. For this, the doctor can use a bur, an elevator, forceps, a chisel, surgical sutures and needles to close the wound. Often such removal requires from 30 minutes to 2 hours.
This division is reflected both in the cost of the removal itself (due to the various labor costs of the doctor) and in the rehabilitation period:
Simple removal results in minimal damage to surrounding tissue. At the same time, squeezing them with an instrument (and stopping full blood circulation in this area) lasts no more than 5 minutes, and does not in any way affect the subsequent healing of the wound. If you follow the recommendations, the risk of complications is minimal.
Complex removal involves the use of more aggressive instruments and prolonged compression of the walls of the bone alveolus. After it, there may be difficulties with the formation of a blood clot and the development of alveolitis of the “dry socket” type, which is supervised by taking anti-inflammatory drugs and applying turunda with iodoform.
Atypical removal is a surgical intervention in which the doctor violates the integrity of the mucosa, periosteum, or a certain part of the bone. Pressure on tissue can last up to 2 hours, which greatly affects tissue microcirculation. Sometimes a hemostatic sponge is used to stop socket bleeding during such removal. The wound is sutured, which ensures the tightness of the hole and protects it from the development of alveolitis, but it is important to maintain a hygienic regime to avoid infection on the soft tissue.
The doctor’s further tactics, his prescriptions and recommendations for the recovery period depend on how the tooth was removed.
The essence of the technique
When pulling a tooth, it can not only be moved vertically, but also tilted in the desired direction.
This is possible due to a number of anatomical features of the structure of the root part of the organ, as well as due to the use of a certain force. Experts strive for the appearance of so-called pressure zones, which ensure the occurrence of histological changes.
It is necessary to understand that this procedure cannot be carried out in several sessions. As practice shows, it takes several months to finally restore the normal physiological position.
Although there are exceptions for some patients. One of the main factors determining the speed of this process is the age of the patient.
How is tooth extraction performed?
Before removal, the doctor conducts a survey to find out if the patient is allergic to anesthetics and medications. The doctor also asks the patient about the presence of trophic diseases (diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis) and pathologies of the cardiovascular system (hypertension, arrhythmia, etc.). This is necessary for the correct selection of anesthesia.
Then the doctor administers anesthesia (usually conductive torus for the lower jaw and infiltration for the upper jaw) and waits for the effect to occur.
Simple removal consists of 5 steps:
- applying forceps to the tooth;
- moving them so that the cheeks are under the gum;
- tool fixation;
- luxation (swinging) - necessary to detach the periodontal ligament, which holds the tooth in the bone;
- traction (luxation) - removal of a tooth from the alveolus. This is done by tilting the tooth in the direction of least resistance (where the alveolar wall is thinner) and simultaneously pulling the tooth outward.
For complex extractions, the doctor uses an elevator - a chisel-shaped instrument with a pointed end, which is carefully inserted into the hole and, with its help, pushes the tooth out from the top of the root.
In the process of atypical removal, a surgical field is formed: the doctor dissects the mucous membrane, peels off the flap with the periosteum and removes the bone substance located above the tooth. The tooth itself is removed using an elevator, but often during the removal of wisdom teeth, the doctor is forced to saw it into pieces with a drill, extracting each root and crown separately.
Indications and contraindications for manipulations
There is a clear list of indications and contraindications for such treatment. The doctor will definitely prescribe traction if the cause of the anomaly is:
- avitaminosis;
- early loss of baby teeth;
- improper jaw development;
- somatic weakness;
- genetic pathologies.
It is possible to use the technique in patients who are unsystematically engaged in treatment: they do not comply with the schedule for prosthetics and tooth extraction.
Traction is not performed if:
- in the jaw row there is no free bed for a future full tooth;
- There are no teeth next to the damaged one.
Also, the doctor’s refusal to perform the manipulation may be due to the inability to install an intracanal pin.
Recommendations after removal
Regardless of the method by which the tooth was removed, in the first 2 days the patient must observe a special diet, activity and hygiene. This is necessary to preserve the blood clot in the wound, which helps maintain the sterility of bone tissue and promotes its regeneration.
In the first 48 hours after removal you cannot:
|
Failure to comply with these recommendations most often causes the clot to fall out of the socket and the development of alveolitis or bleeding.
After tooth extraction it is recommended:
- make oral baths from chamomile and sage decoctions (the decoction prepared according to the instructions is taken into the mouth and held there for 10 minutes, without rinsing or moving the tongue) 2-3 times a day;
- take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (especially after atypical removal, when the tissue is severely damaged and swelling occurs) - nimesulide, diclofenac sodium, ibuprofen, paracetamol, etc. (it is important that the medicine does not reduce blood clotting).
Sometimes patients need preliminary preparation for removal. People taking aspirin and other medications that impair blood clotting should stop taking them a week before the procedure. For those who suffer from increased excitability and anxiety, you can start taking valerian or motherwort 1-2 weeks before removal, having previously agreed with your dentist and your therapist.
Even if the removal was painless and quick, you should not ignore the doctor’s advice. The right approach to rehabilitation will help you avoid complications and recover faster.
Possible problems
The pulling process is associated with various possible problems that must be adjusted as treatment progresses. Due to the application of significant forces, locks or buttons can become unstuck, so the attachment is carried out with special care.
When rotating the crown by 90°C or more, it is important to predict the trajectory of movement so that the tooth does not rest against the roots of neighboring elements of the dental arch. At the very beginning of advancement, it may turn out that the impacted tooth has fused with the jawbone. This phenomenon is called ankylosis. It is possible to separate these two structures surgically only in the case of partial fusion. To avoid this problem, a thorough diagnosis is necessary.
If the rate of movement increases beyond what is necessary, a complication may occur in the form of resorption of the root, periodontal ligament and surrounding bone tissue. For this reason, the speed of movement and traction force should be monitored by an experienced orthodontist who can find the optimal speed.
Prices for tooth extraction
| Name | Price |
| Consultation | For free |
| Use of bone material | 4,000 rub. |
| Simple tooth extraction | 2,700 rub. |
| Removal of periodontitis tooth | 1,000 rub. |
| Tooth extraction is complicated | 3,200 rub. |
| Removal of a dystopic wisdom tooth | 4,000 rub. |
| Removing a tooth fragment | 500 rub. |
| Removal of exostosis in the area of 1 tooth | 2,500 rub. |
| Removal of cysts and benign formations | 3,500 rub. |
| Treatment of alveolitis | 1,200 rub. |
| Lengthening the clinical crown of a tooth | 5,000 rub. |
| Free flap gum grafting | 8,000 rub. |
| Removing stones from the ducts of the salivary glands | 3,500 rub. |
| Splinting for a jaw fracture | 15,000 rub. |
| Socket curettage | 200 rub. |
| Filling the hole with a medicinal substance (Alvogil, al-vostaz, hemostatic sponge) | 200 rub. |
| Resection of the apex of the tooth root | 4,500 rub. |
| Removing a foreign body from the canal | 1,500 rub. |
Duration of treatment
The time it will take to pull out is difficult to predict exactly. It depends on the following characteristics:
- Patient's age . As a rule, the younger the patient, the faster all changes in the area of the dentofacial apparatus occur.
- Clinical picture . If the stretching is carried out for a dystopic element, then it will require more time to turn and give the correct orientation.
Usually the course lasts from six months to two years, without taking into account the preliminary correction of the dentition at the preparatory stage.
Why is retention dangerous?
A partially erupted tooth is covered with a “hood” of adjacent tissues, under which food debris collects and colonies of pathogenic microflora develop, which can provoke purulent inflammation. With complete retention, another problem arises: a tooth embedded in the tissues constantly affects its “neighbor,” causing it to move from its correct position. The situation may sooner or later become more complicated:
- caries of adjacent teeth and resorption of their roots;
- malocclusion, crowded teeth and other dental anomalies;
- pulpitis and periodontitis;
- periodontal cyst;
- pericoronitis (inflammation of the gingival “hood”) and its complication, periostitis;
- purulent lymphadenitis;
- inflammation of the trigeminal nerve;
- abscess and phlegmon.
Therefore, when diagnosing retention, the patient is offered the optimal way to solve the problem.
What can be done about an impacted tooth?
- According to indications, based on the general clinical situation, removal of an impacted wisdom tooth may be recommended (especially for patients undergoing treatment with braces for an abnormal bite).
- In some cases, not accompanied by obvious problems, when removal is not necessary, the doctor will suggest observing the tooth.
- Healthy impacted incisors and canines located in the smile zone, subject to certain conditions, can be “pulled out” from the dental tissues and returned to the dentition.
What are impacted teeth?
Retention of primary and molar teeth occurs for several reasons:
- with an abnormal location of the tooth germ;
- when there is not enough space in the dentition for tooth eruption;
- when a tooth is blocked by “neighbors” who have taken its place.
Depending on the complexity of the pathology, the tooth can be completely covered by gingival and bone tissue (full retention) or partially protruding from the gum mucosa (partial retention). It can be located in its place - vertically, horizontally or at an angle, or outside the border of the dentition (impacted dystopic tooth). Sometimes teeth even grow upside down.