The goal of prosthetics at CLINIC IN is the aesthetic and functional restoration of teeth with a high degree of reliability and comfort. In fact, prosthetics is the final point of complex dental rehabilitation, by which we can mean the completion of sanitation and the final improvement of the oral cavity. In this article we will talk about what you need to know about preparing for dental prosthetics: what it is like, how materials and methods of modern dental restoration differ, what principles and rules are followed, how decisions are made about choosing the type of denture, etc. We hope that it will help you make your upcoming consultation with an orthopedic dentist more productive and thoughtful.
Chief's Comment: Before we get started, I'd like to add a quick comment to this article. It is fundamentally important to me and our employees that you have the most realistic picture of our work. The Internet and television are full of advertisements about “teeth-in-one-day” or “ceramic crown for 3,000 rubles,” but none of you have seen such treatment in person. No one has seen the long-term results of such treatment. No one knows whether it is possible to implement what the advertisement suggests in your case, and whether you will pay as much as indicated in the advertisement. This article is a current reflection of real practical experience. Yes, this is exactly how all good dentists work, including ours. No matter what stage you are at now or perhaps just about to start with prosthetics, you should have honest, truthful and confirmed information on all aspects of it. And we will be happy to provide it to you, understanding the full responsibility for what is written and the obligations assumed. Well, you can ask your questions and get honest and detailed answers in the comments to this article.
What can be done about missing teeth or teeth that need to be extracted?
Traditionally, all existing options for restoring missing teeth can be reduced to two groups: removable and fixed prosthetics.
The differences are simple: any removable prosthesis yourself without the help of a doctor, while fixed prosthetic structures either cannot be removed at all, or this can only be done with the help of a doctor.
For example, you can remove a removable laminar denture without the participation of a doctor. And put it on exactly the same way, without helpers:
More advanced versions of removable dentures are trying to be made more compact, and for this purpose almost all plastic is replaced with metal - this creates a more compact (and therefore more comfortable) removable denture, called clasp.
Often, a clasp denture is made with special locks (attachments) and clasps (claws) so that it is more accurately and reliably fixed to the remaining teeth. Yes, such a prosthesis is much more convenient than a removable plate prosthesis; it does not rest on the gums, but at the same time it significantly loads the teeth (therefore, they often have to be taken under crowns and combined into bridge structures).
Removable prosthetics can also be implemented using dental implants.
So, to fix a removable denture (if, for example, it dangles and does not stay on the jaw), you can use a pair of implants with special locks.
At the same time, the prosthesis does not dangle and does not rub the gums. In the case of an increased gag reflex, it can even be slightly reduced without losing stability. However, the service life of such a prosthesis is still limited by wear, and it must be periodically repositioned.
Therefore, with a large number of implants (minimum 4 units), it is possible to create a removable prosthesis with fixation on a beam.
A beam (or two beams) firmly fixed to the implants with locks evenly distributes the load on the implants, while the prosthesis itself can be significantly reduced in size - in fact, it is almost no different from a fixed one. Therefore, it is easier to get used to, and it lasts much longer than any other removable structure.
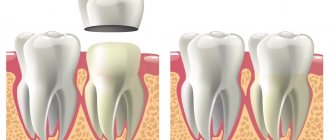
Fixed prosthetics require a reliable support, which can be either natural teeth or implants.
In the case of making a bridge based on natural teeth, the latter are very carefully ground down. To do this, they use special tools with relatively low speeds and very good cooling - this avoids thermal injury to the dental pulp, therefore, it is not at all necessary to depulpate the abutment teeth (as was done before). Most often, it is possible to avoid removing the nerve altogether, and a living tooth can better withstand the load and last longer.
However, even perfectly prepared teeth, onto which a perfectly made bridge is fixed, turn out to be overloaded - if previously they received chewing load only from their own surface, now they bear it also from missing teeth.
The higher the load on the tooth, the higher its wear. Especially. if the tooth is depulped (the nerve is removed from it). Therefore, some doctors try to distribute the load as much as possible from missing teeth to as many remaining teeth as possible.
From the point of view of our clinic and our orthopedists, this approach does not look entirely rational from a medical and economic point of view. And really, is it worth intervening, grinding, and sometimes depulping several teeth to restore one missing one?
And this is where dental implants come to our aid. Dental implantation is one of the main areas of our activity.
The essence of using implants for fixed prosthetics is extremely simple - just like teeth, they create a stationary, reliable and, most importantly, universal support for a denture. Thus, the use of implants allows for the widest range of dental prosthetic options:
The implant does not have a connective tissue ligament surrounding the natural tooth. From a biophysical point of view, a dental implant is a continuation of bone tissue. The chewing load, sometimes quite significant, is transmitted and distributed in the jawbone, bypassing the periodontal ligament and mucous membrane - this explains the long service life of the implant, much longer than that of natural teeth under crowns. And this gives us the opportunity to provide appropriate guarantees for the work we have done. Of course, subject to following certain recommendations.
Dentist-therapist
It all usually starts with this dentist. People come to him when they are worried about toothache or other symptoms associated with the maxillofacial area. He conducts diagnostics and an initial examination, establishes a diagnosis and prescribes treatment, and gives referrals to specialized specialists. His competence includes standard problems: caries, infectious diseases and inflammatory processes in the oral cavity.
Dentist-therapist:
- cleans channels;
- removes nerves;
- installs seals;
- removes tartar and plaque;
- restores teeth;
- performs sanitation of the oral cavity before prosthetics or other dental procedures.
What materials are used in dental prosthetics?
In this section we will talk specifically about materials for dentures, because with implants everything is simpler and is described here>>. In short, almost all existing dental implants are made from bioinert titanium alloys; contrary to popular belief, “pure titanium” is not currently used for the production of implants.
The artificial tooth itself, or denture, can be made from different materials or combinations thereof.
Thus, acrylic and, in some cases, nylon, which is more comfortable to use, are traditionally used for removable dentures. Special dyes and, in some cases, artificial fibers are added to it in order to imitate the gum mucosa as best as possible. The color of the prosthesis is a matter of the patient’s wishes. Sometimes, in case of allergies, they are made transparent, without any dyes at all. At the same time, the teeth themselves are usually manufactured at the factory and end up in the dental laboratory in the form of ready-made sets. They can be plastic, composite, porcelain, with varying degrees of detail and naturalness. The stronger and more natural artificial teeth look, the more expensive they are, of course.
Accordingly, the dental technician selects a headset that is suitable in color and shape (and this is also a matter of the patient’s wishes). First, they are tried on a wax model, and then glued into an almost finished prosthesis base - and the result is beauty!
Composite materials are used to manufacture temporary prosthetic structures. They are sometimes confused with plastic, but composite is still not plastic. In contrast, it contains particles of solid inorganic filler, usually quartz or aluminum oxide, which gives it mechanical strength. Therefore, composite crowns last longer and wear out less, unlike plastic teeth.
Previously, just a few years ago, temporary composite crowns were made by polymerization, much like how dentists make fillings. Now, with the development of digital technologies, the situation has changed - and the process of making temporary crowns on natural teeth and implants is practically no different from making ceramic or zirconium oxide dentures - a scanner, computer modeling, a special milling machine and final finishing by a highly qualified dental technician are used.
Yes, this is somewhat more complicated and expensive than simply sticking filling material onto a model, but such crowns turn out to be much denser, more durable and aesthetically pleasing. And temporary crowns on implants can generally last for several years, if necessary.
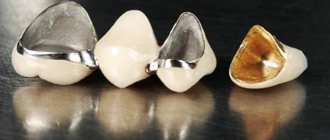
Permanent crowns supported by natural teeth can be divided into two groups: framed and frameless .
Frame crowns contain a cast (old-fashioned) or milled (modern technology) frame, onto which ceramic mass is applied successively, in layers.
The frame itself can be made of different materials, depending on the task and patient preferences:
- made of metal (chromium-cobalt alloy, titanium, zirconium, precious metals, etc.), thus we obtain the well-known cermets.
- from oxides (zirconium oxide, aluminum oxide, etc.), this is how metal-free crowns are obtained, erroneously popularly called “zirconium oxide”, “zirconium”, etc.
- made of ceramics (the same pressed ceramics E-max). It should be noted that it can be used to make both a crown frame and an entire crown; the latter is used in cases where it needs to be done beautifully, but super-duper-megaesthetics is not required. For example, when making crowns in the side of the jaw.
Frameless crowns are made mainly from ready-made ceramic blocks by milling; the technician only needs to make minor color and shape corrections.
This is the most advanced, most complex and expensive technology that makes it possible to produce very thin (with a wall thickness of 0.2 mm) restoration crowns and, therefore, preserve tooth tissue to the maximum. For the high-quality and aesthetic production of such prostheses, very expensive equipment and highly qualified specialists at all stages are required - fortunately, our dental center has all this.
The search for optimal materials for dentures does not stop to this day - new alloys (for example, tantalum), new high-strength materials for aesthetic prosthetics (various silicates and ceramic masses) are appearing, which, on the one hand, satisfies the highest aesthetic needs of our patients, on the other hand on the other hand, it makes our work more and more difficult every day. But it's worth it, isn't it?
The use of implants as a support for artificial teeth makes some adjustments to prosthetic technology.
Technically, we can make the same crowns for an implant as for natural teeth, but for this we will need additional components. And that's why.
An implant, from a technical point of view, is just an artificial root. As we wrote above, this is just a universal support to which you can screw whatever you want.
Conceptually, there are two options for fixing permanent prosthetic structures on implants:
- – with screw fixation , a separate crown or denture is fixed to implants or abutments using screws.
This is the safest option, which, however, requires very precise placement and selection of implants according to axes and sizes. Currently, screw fixation is a priority for most clinical cases. - cement fixation is used in situations where for some reason it is impossible to use a screw fixation - for example, when fixing crowns on implants in an aesthetically significant area
A special abutment is used for it, which allows you to compensate for the angle of inclination of the implant. Like the crown, it is made separately and individually from various materials: cobalt chrome, titanium or precious alloys, zirconium oxide, aluminum oxide, etc.
A separate article about prosthetics on implants will soon be published on our website, in which we will tell you the details of this technique. In general, this topic would be enough for an entire website or a separate book, so it is not possible to fit it into the framework of a small introductory article.
Dental surgeon
This doctor comes to the rescue if conventional treatments are ineffective and drastic solutions are needed that require surgical intervention.
Dental surgeon:
- removes teeth, tumors and cysts;
- eliminates acquired and congenital defects;
- opens foci of abscess and other inflammations;
- prepares the jaw for prosthetics and performs implantation;
- deals with restoration and plastic surgery of the jaw, as well as any other operations in the oral cavity.
What determines the quality of prosthetics?
Advertisements that litter the Internet tend to focus on materials. For example:
- “Metal ceramics for 3,900 rubles!”
- “Zirconium crowns for 5,000 rubles, subsequent tooth extraction is free!”
- “Removable denture for 10 thousand”,
and so on.
Meanwhile, the role of materials in the quality of manufactured prostheses is greatly exaggerated. Ordinary metal-ceramic crowns can be made more aesthetically pleasing than ceramic ones, and they will be very different from each other, because it depends on who made them and how.
Let's show a simple example:
Therefore, we would highlight the “quality triad” - three components that determine how functional, aesthetic and durable your new teeth will be:
Total, by points:
- original components are necessary primarily for implant prosthetics. Now, for almost every implantation system, Chinese counterfeits are produced, and with the increase in the accuracy of digital milling machines, doctors and laboratories have the opportunity to produce the same abutments almost on the knee.
However, no one is yet able to replicate the original dimensions and alloys (the latter is important to avoid galvanism and corrosion). Therefore, all manufacturers of implantation systems will void the warranty if, during the examination of the doctor’s joint, any left-handed screw or abutment is found. Our dental center CLINIC IN works directly with the world's largest manufacturer of implantation systems, Dentsply Sirona Implants, we do not need to use counterfeit products to save money. Therefore, all our work, all original components we use, are covered by the manufacturer’s warranty. You can read more about this here>>. - highly qualified dental technician and well-equipped dental laboratory. Indeed, it is unlikely that we can offer you digital technologies if our laboratory does not have special equipment and trained personnel.
In addition, each dental crown, each prosthesis is, in fact, a piece of art - and the extent to which the dental technician masters this art will depend on the aesthetics of the final product. Making highly aesthetic dentures is a unique fusion of art, good taste and engineering. And, unfortunately, few dental technicians can offer a job worthy of you. And those who are, as a rule, are in great demand, so they ask for a lot of money for their services. Through a lengthy search and a very strict selection, our orthopedic doctors, David, Kirill and Ivan, selected four dental laboratories from thirty candidates, the quality of which would suit us and our patients. Yes, such work is not cheap, but you will never guess the artificial teeth in the smiles of our friends. We will definitely tell you about our partner laboratories in one of the future articles, since the manufacture of dentures is a very interesting and extensive topic. - a medical specialist is, in a way, the chief architect of any dental rehabilitation. His task includes not only preparing teeth and implants for fixing restorations and prostheses, but also managing the entire process of patient treatment - it is the orthopedic dentist who determines the placement scheme of implants, together with the dentist-therapist makes a decision on the preservation/removal of teeth, and gives recommendations on the form and the color of future crowns, and in some cases models them independently. Their service life largely depends on the orthopedic dentist’s understanding of the rules of prosthetics on implants, so when planning implantation, he is always somewhere nearby.
Our dental center employs highly qualified dental specialists who have undergone rigorous selection and testing with fire, water and copper pipes.
They can handle prosthetics of any complexity and any option, no matter what you choose. But, most importantly, they understand and accept your wishes, take into account your characteristics and needs, they restore YOUR teeth, not their own, so all their experience, all their competence and all their arsenal of means are aimed at achieving only one goal - you must like the result, first everything, to you. Chief's comment: The ability to hear and understand your patient is perhaps the main quality for a dentist involved in the aesthetic and functional rehabilitation of a smile. In the end, if function can be calculated and adjusted, then aesthetics is a subjective and individual concept for each of us. Just as there are no specific standards of beauty, there is no one generally accepted idea about the aesthetics of a smile. It’s the task of our doctors to figure this out and take into account what you need. It is their direct responsibility to realize what you want without loss of functionality, durability, reliability and comfort. That is why such doctors work for us.
In what cases is it worth going to a specialist?
You should contact a professional if you have the following deviations:
- The dental unit can no longer be restored. If neither fillings nor other treatments help, then you should at least consult an orthopedic dentist. This situation occurs especially often when the baby has severe caries.
- Fluorosis. If there is too much fluoride in a child's body, tooth damage cannot be avoided. So if you don’t want inflammation to occur, have the damaged area removed by an orthopedic dentist.
- The child has consequences of dental trauma. For example, a child knocks out or severely damages a tooth. In this case, the doctor will help restore the damaged tooth element.
- Too early loss of baby teeth. With this problem, the molars may not have enough space to erupt and secure. The doctor will help you choose a retainer for the child that will preserve space for the formation of the radical elements.
How to make an appointment?
You might be interested to know that 90% of an orthopedic dentist’s time is spent talking, examining, photographing, discussing, making all kinds of corrections, drawing up treatment plans, and only ten percent is spent directly on manipulations related to prosthetics.
Therefore, before your first meeting with an orthopedist, try to be as specific as possible about your wishes regarding future dental restoration. The better you imagine it, at least for yourself, the easier, faster and, most importantly, cheaper your treatment will be.
Also, don’t wait until your old dentures become unusable and fall off on their own. The appearance of mobility of crowns both on natural teeth and on implants is always a bad sign; this mobility will not go away on its own, and its increase can lead to subsequent loss of both teeth and implants.
Usually, at the first prosthetics meeting, only diagnostics are carried out - to a greater extent, this is a conversation and discussion. Also, during the consultation, pictures and photographs of the teeth are taken so that there is something to talk about in detail. And draw up a treatment plan, the so-called “road map”, which will include all the necessary procedures, from caries treatment to bite correction and implantation. And sometimes one meeting is not enough for this - so, before starting a large and complex work, one, two or three consultations are held, including consultations with other dental specialists.
All this time, the orthopedic doctor is trying to answer the question:
“How to fulfill all your wishes for the beauty and functionality of your teeth as rationally, reliably and durablely as possible?”
Indeed, it is very easy to make your teeth “simply beautiful” - remove everything, make two removable dentures - and you will have “beauty”! How to live further with this beauty, how to chew, smile, talk, kiss - another, more complex and delicate question. That is why high-quality and reliable dental prosthetics is somewhat more than “metal-ceramics for three thousand rubles,” and an orthopedic dentist is not just a “teeth sharpener” and an “impression machine.”
Be prepared for the fact that consultations on prosthetics are usually long. They take at least 45 minutes. As we wrote above, a consultation with the involvement of other specialists may be required, so have a reserve of time.
It is unlikely that at the first consultation the doctor will remove your old dentures (if they have not completely fallen apart) or grind your teeth. But, to fully assess the clinical situation, some examination may be required, namely:
- photographing and drawing up a photo map (at CLINIC IN – free of charge)
- taking impressions and making diagnostic models of the dentition (in CLINIC IN – from 3500 to 5000 rubles)
- X-ray examination - computed tomography (4,200-2,100 rubles), orthopantomography (2,200-1,100 rubles), targeted photographs of teeth (550-240 rubles)
The consultation itself in our clinic costs from 0 to 2,000 rubles. But for good people it is always free.
Dentist orthopedic dentist: who is he and what does he do?
In modern dental clinics there are many highly specialized doctors who provide medical care only for a certain type of diseases of the maxillofacial system.
A dental surgeon performs all necessary operations, an orthodontist corrects the bite using braces, a periodontist treats periodontal inflammation, and an orthopedic dentist does almost everything related to prosthetics, namely, installs dentures to restore teeth. This article will tell you in more detail about the most popular dentist - an orthopedist, and will also help you understand other specialties of dentists, which you can make an appointment with at the Dr. Stepman" on Universitetskaya metro station, Lomonosovsky Prospekt.
Total:
However, before you click this link to schedule an appointment with any of our podiatrists, here's a quick recap:
- You shouldn’t believe advertising that promises a Hollywood smile in one day. Functional and aesthetic rehabilitation is always a complex, expensive and lengthy process, sometimes taking several years and requiring the participation of a number of dental specialists.
- The key point that determines the timing of treatment is the adaptive capabilities of our body. It will take some time before he perceives the dentures as well as his own teeth. In other words, the dental system must be reprogrammed and adjusted. This takes most of the time and effort of doctors.
- The main factor influencing the cost of an artificial crown, inlay or veneer is its aesthetics. How beautiful it looks and whether it can be distinguished from other teeth. There are only a few specialists who can create beautiful teeth so that no one would ever guess, and their work is very expensive.
- The more laboratories and dental technicians an orthopedic doctor has in his arsenal, the better. Each dental technician, each dental laboratory has its own style, its own traditions, sense of taste and aesthetics. And we, for example, knowing the patient’s wishes, select for the work a dental technician who could fully satisfy them.
- When using implant-supported prosthetics, it is very important to use original components of implant systems. And it's not just a matter of warranty. Counterfeit parts do not have the required accuracy; they are often made from cheap alloys, and this is fraught with both endless breakdowns and the appearance of galvanism and corrosion.
- It is the orthopedist, based on the prosthetic design chosen together with the patient , who determines which teeth to save/retreat/remove, how many implants and in what places they need to be placed, etc. For this, examination data and special computer programs are used.
- The popularity of implants is largely due to their reliability and versatility. In fact, with the use of implants, it is possible to recreate both a single tooth and an entire row of teeth. But this does not mean that your teeth should not be protected and treated.
- CLINIC IN dentists can carry out rehabilitation of any complexity. But in order to fulfill your wishes, we need to at least know them. Therefore, get ready for a large number of questions to which you will need to give specific and clear answers.
- “like” and “dislike” are essentially two criteria for assessing the dental treatment performed. We try to make sure you like the result. And in order to achieve this, do not hesitate to say what you “don’t like” or “don’t like” or “don’t feel comfortable with.” It can be fixed. Well, if one of our employees does not hear this, you can always contact the boss directly. And he will achieve justice.
And now you can call and make an appointment for a consultation on prosthetics!
Welcome to CLINIC IN!
What tests should be taken to install prostheses and implants?
Implantation is a full-fledged operation, albeit a minimally invasive one, so before it it is necessary to undergo tests so that the doctor can make sure there are no contraindications. Basic laboratory tests include:
- general blood analysis;
- analysis for infectious diseases - HIV, hepatitis, syphilis, to ensure the safety of treatment;
- a platelet test that determines coagulability is prescribed if the patient suffers from increased bleeding gums;
- If diabetes mellitus is diagnosed, a blood glucose test is prescribed.
In some cases, consultation with other specialists may be required. They are usually necessary if there are chronic diseases - cardiovascular, respiratory tract and others.
Free prosthetics if you have a compulsory medical insurance policy does not give you the right to choose a doctor
Post-operative care
Proper oral care will help consolidate the results and avoid side effects in the postoperative period. The duration of this period does not exceed 2 weeks. Important rules to follow:
- You need to brush your teeth at least 2 times a day. To remove hard-to-reach stains, it is recommended to use dental floss.
- You need to rinse your mouth 3 times a day using rinses recommended by your dentist.
- The use of anti-inflammatory and painkillers should be agreed with the attending physician.
- The denture should be cleaned as thoroughly as possible. You need to pay attention to all parts, and especially in the area near the root.
Clean the superstructure thoroughly from all sides. It is recommended to carefully clean the main part of the denture with a soft toothbrush and a minimum amount of toothpaste. The presented rules apply to removable and fixed prostheses.
Be careful! Lack of care after surgery can cause inflammation and deformation of the bone tissue at the attachment site. Be sure to follow the specialist's recommendations.