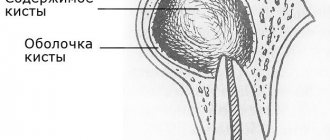
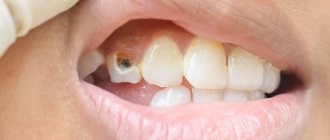
Patients with chronic periodontitis often encounter a situation where a cyst forms at the apex of the root - a cavity in the bone tissue filled with pus. Most often, a cyst develops due to infection in the root canals; sometimes the cause of a cyst is trauma, inflammatory processes in the periodontium (gums) and adjacent areas. It can also occur due to undetected caries, pulpitis or periodontitis, as well as due to poorly filled root canals.
Such a neoplasm may not bother a person for a long time. As a rule, a cyst makes itself felt during periods of weakened immunity, against the background of a cold. In such cases, the infectious process in the cyst cavity worsens, which leads to abundant pus formation. The patient feels acute pain, swelling and swelling of the gums appears, and a fever may appear. The main thing is to seek dental care on time. In these cases, resection of the apex of the tooth root and dental surgery to remove the cyst are used. However, you can often get by with therapeutic treatment.
When deletion is indicated
Modern dentistry strives to preserve teeth and their roots whenever possible, but this is not always possible. Dental surgeons remove teeth with cysts for the following indications:
- the infectious process was caused by an advanced form of periodontal disease;
- there is a vertically located crack on the root of the tooth or on itself;
- the dental root canals are impassable, as a result of which therapeutic treatment becomes impossible;
- severe tooth decay, and restoring it does not make sense (too expensive and time-consuming);
- the tooth is located entirely in the cavity of the neoplasm;
- the cyst has grown into the nasal cavity, or the size of the tumor is more than 10 mm;
- the root of the tooth has fused with the neoplasm;
- the tooth is very loose.
The dentist decides to remove a tooth with a cyst after a thorough examination of the patient, which includes examination, history taking, radiography or visiography.
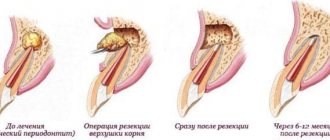
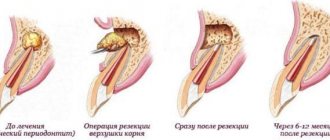
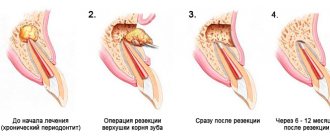
Cystectomy / root apex resection: indications, contraindications and causes
- The appearance of any neoplasm, for example, fibroma or other, larger than 1 cm.
- Incomplete or poor-quality root canal filling in the treatment of pulpitis, for example;
- Stump tab or pin in the dental canal;
- Damage to the root walls during tooth filling;
- Periodontitis, granulomas, cysts, fibromas;
- Perforation of the tooth root, fracture of the root or its apex;
- Curvature of the root canals or the apex of the tooth root;
- Presence of a foreign body;
- Inflammation near the site where the denture is installed;
- A fragment of a dental instrument in the canal;
Contraindications include periodontal disease, periodontitis, and the presence of a tumor at the location of the tooth.
Removing a tooth with a cyst: does it hurt or not?
In the “Optimal Choice” dental clinics, when removing teeth with benign formations at the roots, the latest anesthetics and modern equipment are used. Therefore, patients do not need to be afraid of anything at all. The doctor selects anesthetics on an individual basis; in some cases, general anesthesia may be recommended (we do not use it). Minor pain may occur after tooth extraction, when the anesthesia wears off. To relieve pain, your doctor may prescribe painkillers.
Why don't we remove the cyst with a laser?
After analyzing all the long-term results of the postoperative period from our department and partner organizations in Moscow, it was decided to abandon the further use of laser cyst removal.
When all the results were analyzed, it turned out that the positive disinfecting effect of the laser was seriously compromised by the longer recovery process. It has been determined that when removing a cyst with a laser, high-temperature exposure, forming burn areas, provokes inhibition of tissue restoration and prolongation of treatment time with a weak antiseptic advantage.
The marketing benefits of “laser treatment” for business were not taken into account in this study. Thus, laser removal of cysts is no longer performed in our Center.
Types of deletion
A dental cyst can be treated using one of the following surgical methods:
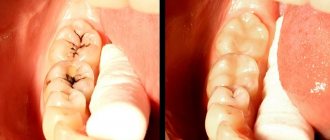
- Cystectomy is the most common way to remove cysts on teeth. During this operation, an incision is made on the gum, through which both the benign neoplasm and the apex of the tooth root with pathology are removed. The cystectomy procedure is usually performed under local anesthesia, after which the doctor prescribes antibiotics to the patient.
- Hemisection - this type of removal is used if a tooth with a cyst has more than one root, and at least one of them is pathologically changed. During this procedure, the cystic formation, the root of the tooth with pathology, and part of the tooth itself are removed. After this operation, a crown is placed on the tooth.
- Cystotomy is the most gentle type of surgical treatment for dental cysts, in which the doctor removes only the front wall of the tumor. The tooth body is completely preserved.
These techniques are an alternative to the complete removal of teeth with cysts. But it is not always possible to apply them. To completely remove teeth with benign tumors, the extraction method is used. The operation can be performed urgently or planned.
What do patients say about apex resection? Reviews are usually only positive!
“Resection of the top of the tooth took about an hour, the operation was performed under pain relief. It didn’t hurt very much near the tooth for about a month. A few months later I had to take an x-ray, the doctor showed that all the tissues had been restored."
“The cyst grew, they told me to remove it, it was a little unpleasant, but quite tolerable - the doctor quickly and accurately carried out the procedure. Everything was restored soon, now it’s completely unnoticeable that there was anything there.”
At Ritsa Dentistry, cyst removal operations are performed by experienced surgeons with extensive experience in performing such procedures. Therefore, you can rely on our professionalism and entrust the treatment of the cyst to our doctors.
What are the stages of the operation?
The procedure consists of the following steps:
- The desired area is numbed using conduction or infiltration anesthesia.
- The gum is peeled off from the wall using a rasp.
- The tooth is loosened and removed using forceps or an elevator.
- The dental unit is removed from the socket. In difficult cases, the tooth is first sawed into pieces using a drill, and then each of them is removed separately.
- The extracted tooth and socket are examined by a doctor.
- The cyst cavity is cleaned, and the wound is treated with antiseptic drugs.
- The wound is stitched up.
- Using an X-ray examination, the doctor makes sure that fragments, particles of the tooth and the removed tumor do not remain in the jaw.
- Antibiotics, anti-inflammatory drugs and anesthetics are prescribed.
Two to three days after the operation, you need to re-visit your dentist to monitor the condition of the tooth socket.
Rehabilitation period
After the procedure, swelling and pain occur, the temperature may rise, and the head may hurt. Acute symptoms are relieved with analgesics and anti-inflammatory drugs. Antibiotics are prescribed to prevent infection. They are also needed to prevent relapse and the formation of a new capsule under the extracted tooth.
Doctors recommend:
- eat liquid, soft food at a comfortable temperature;
- do not lick the blood clot;
- avoid high physical activity, temporarily stop playing sports;
- do not overheat the body (hot bath, sauna, bathhouse, beach, etc.);
- stop smoking and alcohol, as this has a bad effect on wound healing;
- rinse your mouth after eating;
- Use a soft-bristle toothbrush, avoiding the operated area.
It is useful to rinse your mouth with soda or salt solution, decoctions of chamomile, calendula, and oak bark. You can use pharmaceutical antiseptics: Chlorhexidine, Miramistin, Romazulan.
Possible complications
Among the common consequences of removing a tooth with a cyst may be the following complications:
- slight increase in body temperature;
- migraine;
- soft tissue swelling;
- toothache.
In order to alleviate the patient's condition, symptomatic treatment is prescribed.
If the doctor is insufficiently qualified or the patient does not comply with medical recommendations, the following complications may arise as a result of surgical intervention:
- infectious process in tissues;
- injury to nerve endings;
- profuse bleeding.
To avoid this, you must contact only trusted dentists with good experience and clinics with modern equipment, and also follow all recommendations given by your doctor.
Is it possible to eliminate pathology at home?
Since the infection affects the dental root, it is impossible to cure yourself without a visit to the doctor. Traditional methods should be used as adjuvant therapy. To reduce the inflammatory process, it is recommended to rinse the oral cavity at home. The simplest rinsing solution can be prepared from water and a mixture of salt and soda. Herbal decoctions with antiseptic and anesthetic properties have proven themselves to be effective. To prepare the solution, you can use sage leaves, chamomile, horsetail, and alcohol tincture of calendula.
After brewing the plant material, the composition should be stored in the refrigerator. Before use, the mixture is slightly warmed. It should not be cold or too hot.
Preventive measures
To ensure tissue healing proceeds faster and serious complications do not arise, a number of recommendations must be followed. Dentists at the Optimal Choice clinic give the following advice to their patients:
- For several days after surgery, rest is required; any physical activity (even light) is contraindicated;
- avoid hot water procedures, including baths, steam baths, saunas, and do not use hot compresses;
- You cannot use active mouth rinses for 2-3 days; if necessary, they can be replaced with oral baths with infusions or decoctions of medicinal herbs (with oak bark, calendula, eucalyptus, sage), furatsilin, chlorhexidine, etc.;
- do not drink alcoholic beverages or smoke for 2-3 days;
- Taking medications prescribed by a doctor is mandatory.
Compliance with these rules, as well as regular visits to the dentist for preventive examinations and at the slightest unpleasant symptoms, will allow you to avoid serious negative consequences and significant financial expenses for dental services.
Alternative Methods
A neoplasm localized at the root apex can be treated conservatively if its diameter does not exceed 8 mm and the root canals are not sealed. In this case, access to the affected area is through the crown.
Therapeutic treatment
The root canal is depulped, cleaned, and expanded. The cavity is cleared of purulent masses, treated with antiseptics, and filled with a special paste. After treatment, the canal and crown part of the tooth are filled. You need to be examined within a month to rule out relapses.
Laser treatment
It is carried out similarly to the previous method, only the capsule is exposed to a laser. Laser beams quickly remove the tumor and disinfect the cavity. After such a procedure, the recovery period is easier and faster, and complications are minimal.
Experts' opinion
Question: Is it possible to avoid the occurrence of a cyst on a tooth?
Answer : The etiology of the formation of a cyst at the root of a tooth can be different. At the initial stages, treatment of this pathology does not pose a serious problem. Therefore, it is very important to be regularly examined by a dentist, and also to take x-rays or visiography at least once a year to identify any pathologies of the dental system. New growths, if present, will also be visible on the images. To reduce the likelihood of tumors appearing, if any diseases of the oral cavity and nasopharynx occur, it is necessary to treat them in a timely manner: develop the habit of regularly rinsing your mouth with antiseptics, and learn to brush your teeth correctly. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle, a balanced diet, a strong immune system and preventive dental examinations are the key to dental health.
Question: Is it possible to get rid of a cyst on a tooth at home on your own?
Answer : We do not recommend self-medication if you have any pain or unpleasant symptoms in the oral cavity. Any discomfort may be a sign of a serious illness that requires medical attention. If it is not possible to urgently visit the dentist, then to reduce pain you can use the following rinses: herbal decoctions (yarrow, calendula, sage, chamomile, oak bark), a solution of baking soda or salt, vodka, tea tree essential oil. This may help reduce pain, but in any case you should see a doctor as soon as possible.
Causes of the disease
A lesion occurs when an infection enters the dental canals. This can happen for various reasons:
- Caries, other diseases of the oral cavity;
- Violation of technology when installing a pin, filling canals, endodontic procedures;
- Complications of sinusitis and other infectious diseases.
Very often, suppuration occurs as a result of a jaw injury. People who practice various types of martial arts and participate in street fights are at risk. You can injure the dental system at home by cracking nuts.