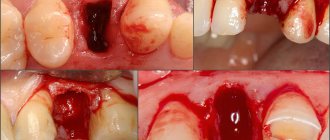
Tooth extraction is performed for medical reasons when it is impossible to save it. Surgery is performed under anesthesia. It can have varying degrees of complexity depending on the location of the dental unit.
If the operation is performed correctly, a clot will form in the socket within the first 24 hours after tooth extraction. It is necessary to protect the wound from infection and promotes accelerated tissue healing. If the blood clot does not form or becomes damaged, complications may occur. Find out how to prevent them and what to do if inflammation develops.
Stages of socket healing
The clot formed in the socket after tooth extraction plays an important role in tissue healing. Normally, recovery occurs in several stages:
- during the first day, a red blood clot forms, preventing the penetration of pathogenic bacteria into the wound;
- on days 2-3, the clot becomes white due to the growth of new epithelium;
- in the period from 4 to 8 days, granulations appear and completely replace the blood clot;
- in the second week after the operation, the blood clot completely disappears, the wound heals.
If the healing process of the hole is disrupted, complications may develop. One of them is alveolitis - an inflammatory process that occurs in 3-5% of patients after tooth extraction.
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
A tooth was pulled out and the bleeding doesn’t stop: what to do?
Contents: • Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery • What should not be done after tooth extraction?
• What can you do at home? • Professional help from a dentist Tooth pulled out
– the bleeding doesn’t stop, why does this happen? Tooth extraction is a dental surgery that is performed in a clinic. Any operation is accompanied by some blood loss. Tooth extraction is no exception, as damage to gum tissue and periosteum occurs.
Bleeding is a complication after dental surgery
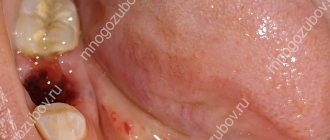
Socket bleeding can be quite difficult to stop. This problem occurs not only immediately after the operation, it can appear within a day.
Let's look at the reasons for this condition:
1. If the problem occurs immediately after removal, then this may be due to the fact that adrenaline has stopped working, and this provokes vasodilation. 2. If bleeding began after a certain time, then a common cause is the patient’s incorrect actions, which caused damage to the clot in the socket.
Local reasons include:
• damage to a wound or gum; • violation of the integrity of the interroot septum; • inflammation that has begun in the gum area at the site of the extracted tooth; • damage to the blood vessels located under the tongue. Common causes are mainly the patient's diseases, such as: scarlet fever, sepsis, blood diseases, hepatitis, hypertension.
What should you not do after tooth extraction?
After any surgical intervention, certain rules should be followed so as not to cause undesirable consequences.
For several hours it is prohibited:
• drink alcoholic drinks of any strength, because alcohol promotes vasodilation; • smoke; • Eating; • rinse your mouth with any liquid; • steam or take a hot shower, bath; • engage in physical labor or exercise in the gym.
How long does it take for blood to bleed from the socket?
A full-fledged clot is formed within 20 - 30 minutes.
If the bleeding continues when the patient is already at home, then there is cause for concern, so it is better to call the doctor and follow his recommendations. It is worth noting that some people confuse bleeding with ichor, which can be released from the wound for several hours after the removal procedure. If the secreted liquid is colorless or yellowish with a small amount of blood mixed in, then this is ichor. In this case there is nothing to worry about.
What can you do at home?
If bleeding begins after tooth extraction, and for some reason it is not possible to contact the dentist, then you need to help yourself.
The following manipulations may help solve the problem:
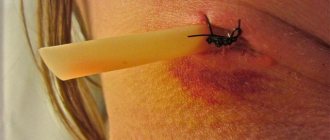
• A sterile swab should be placed on the resulting depression, then clamped with your teeth and held for approximately half an hour.
• If the bleeding does not stop, the tampon should be changed to one moistened with a 3% hydrogen peroxide solution, which helps stop the bleeding. • You can try applying cold to the cheek from the side of the extracted tooth. Cold constricts blood vessels, which helps eliminate this problem. Just remember: you can’t apply anything cold directly to the wound, as these actions can cause complications. • If the pain in the gum area is severe, then you can take painkillers, but without aspirin. This medicine thins the blood, which may cause bleeding. If the listed remedies do not produce results, and a person develops weakness or dizziness, then a visit to the dentist should not be postponed.
Professional dental care
The doctor will assess the situation and take action to stop the bleeding. What should a patient be prepared for? If there is bleeding from the soft gum tissue, the dentist may use sutures to close the wound.
If blood flows out of a blood vessel, then a tampon soaked in a special agent is placed into the tooth wound, the vessel is compressed, and the tampon is left in the hole for 5 days.
If the use of local remedies is ineffective and the bleeding does not stop, then the doctor may prescribe general medications that accelerate blood clotting. But the use of these medications is possible only after examination and testing.
Prevention of bleeding
To reduce the risk of all kinds of complications, you must adhere to some rules before tooth extraction: • Approximately two days before surgery and after, you should definitely stop smoking. • If the patient has hypertension, it is necessary to take medications to stabilize blood pressure, and also measure it before and after this dental procedure. • If the patient is taking blood thinning medications, they should be stopped a few days before surgery as they reduce blood clotting.
Signs of inflammation
The inflammatory process in the socket occurs when a blood clot is damaged and the wound becomes infected. The following signs indicate its development:
- pain of varying intensity - aching, throbbing,
- fatigue and severe weakness,
- rise in temperature to subfebrile levels,
- unpleasant odor and taste in the mouth,
- pain when touched, contact with hot and cold,
- discharge of pus,
- difficulty chewing, swallowing, opening the mouth.
With alveolitis, the socket may become dry and a greenish or yellowish coating may form. If a blood clot falls out and pain occurs, do not put off visiting the dentist. It is easier to stop the inflammatory process at its beginning. The doctor will curettage the hole, treat the wound with an antiseptic solution, and prescribe antibacterial drugs.
Causes of prolonged bleeding
Experts identify many reasons that can lead to resumption of bleeding. Primary can begin due to vascular injury received during the procedure, hypertension, sudden surges in pressure, and even due to severe stress.
Also among the provoking factors are the use of Aspirin and other blood thinning drugs, hormonal imbalance or the usual increase in estrogen levels in women. Pathology can also develop if the rules of oral care are not followed, rinsing too vigorously, accidentally injuring the gums with the tongue or foreign objects, or eating too hard or hot food.
Another reason for close monitoring of the patient’s condition after surgery is tooth extraction due to existing gumboil or cyst. Tissues in which there is inflammation usually have greatly dilated blood vessels. You can also encounter unpleasant consequences with blood diseases, for example, with anemia or hemophilia, with diabetes mellitus, atherosclerosis, etc. To reduce the risk of bleeding in the first few days after surgery and before it, you do not need to drink alcoholic beverages.
Prevention of complications
In order for a blood clot to remain in the socket after tooth extraction and healing to be successful, you need to follow several recommendations:
- do not drink or eat food for two hours after tooth extraction,
- do not touch the hole with your tongue or cutlery,
- on the first day, do not rinse your mouth, do not smoke, limit physical activity,
- exclude hot food, alcohol, carbonated drinks from the diet for several days,
- do not take a hot bath, refuse to visit the sauna,
- Brush your teeth with a soft-bristled brush.
Bleeding from the socket after tooth extraction
Often, after tooth extraction, bleeding occurs from the socket (hemostasis), which occurs due to rupture of ligaments and capillaries (blood vessels). The complication may appear immediately, or maybe after a few days. Hemostasis can be stopped using a gauze pad, which the doctor places on the bleeding area for 15-20 minutes. During this period, a clot forms in the socket, after which the bleeding usually stops. If this does not happen, then stopping is done in other ways: by suturing with catgut, using hemostatic paste (sponge), applying fibrin film, or using special preparations in the socket.
Recommendations after tooth extraction
After the tooth is removed, the patient is allowed to go home if there is no bleeding from the socket. The doctor gives the patient the necessary recommendations, which must be strictly followed. If these rules are followed correctly, bleeding can be avoided.
- At least three hours should pass from the moment of tooth extraction to the first meal.
- It is strongly recommended not to smoke within three to five hours after tooth extraction.
- On the day of surgery, avoid physical activity and lifting heavy objects.
- Also, on the day of removal, you should not eat hot food, steam or take a hot bath.
- When brushing your teeth, be especially careful on the side where the tooth was removed.
- Do not take medications that contain aspirin (this drug thins the blood).
- The next day after surgery, carefully rinse your mouth with a warm, weak solution of potassium permanganate, chlorhexidine or furatsilin. This cannot be done on the day of removal.
- To speed up healing, you can carefully rinse your mouth with decoctions of medicinal herbs (chamomile and sage), and also lightly lubricate it with sea buckthorn oil.
- Do not touch the wound with your fingers (even your tongue), stay as far away from drafts as possible.
It often happens that bleeding from the socket appears several days after the operation. There may be several reasons for this: a complex removal procedure, accidental injury, poor blood clotting, a jump in blood pressure, problems with a herbal clot, as well as failure to follow the rules recommended by the doctor.
How to stop bleeding from a socket after tooth extraction
If bleeding from the socket of an extracted tooth occurs far from the clinic, then you can stop the bleeding at home yourself. To do this, you need to use the following method: make a thick tampon from a sterile medical bandage, moisten it slightly (preferably with lukewarm boiled water), then carefully apply it to the bleeding area and close your teeth. The tampon should not be too large, otherwise it will put too much pressure on the blood vessels. Then take a quiet position, sitting or lying down, and try to relax while continuing to close your teeth.
You can also replace the tampon with a bag of black tea - thanks to the tannins included in the composition, the blood stops faster. But if these methods do not help, then it is possible that a large vessel is damaged. Then you can try this method: mix one spoon of salicylic acid solution with two spoons of peach oil and seven spoons of beeswax. Heat the mixture to a boil, cool, pipette and drop into the well. The mixture will harden and turn into a protective film that will stop the bleeding. It is better to place a cotton swab on top of the resulting film.
If this method does not help, and the bleeding does not stop, contact a specialist immediately! Otherwise, everything can end in blood loss and even life-threatening.
Why is it important how long it takes to bleed after tooth extraction?
Stopping bleeding indicates the beginning of the formation of a dense clot. It is needed to protect the wound surface from the penetration of bacteria and microbes. It also serves as a mechanical barrier for particles of food and drinks.
If the blood does not clot, the socket will be unprotected. Pathogenic microorganisms will begin to penetrate into the bare bed. It will secrete ichor (this is indicated by the salivary fluid acquiring a characteristic pink hue). In this case, recovery after surgery will take a long time and, most likely, will be accompanied by various complications.
Why you don’t need to remove white plaque after tooth extraction
In some cases, patients intentionally or accidentally remove a blood clot or fibrinous film from the socket. This is not necessary, since removing a clot or film can provoke negative processes.
First of all, an open wound provides access for bacteria to the circulatory system and tissues of the maxillofacial apparatus. Infection can cause serious consequences and require long-term treatment with antibiotics. Also, removing the clot and white plaque increases the pain, since an open wound is more sensitive to any irritants, including drinking drinks and food, during a conversation.
Finally, plaque on the gums after tooth extraction does not need to be cleaned off because this can cause re-bleeding and prolong the wound healing stage.
In any case, there is no need to intentionally remove plaque; this can cause:
- serious complications;
- severe pain;
- improper gum formation;
- long recovery process after tooth extraction.
To avoid accidentally damaging the socket, blood clot or fibrinous film, you must follow the recommendations given by the doctor after the operation.
When white plaque on a wound after tooth extraction requires examination by a doctor
Despite the fact that white plaque after wisdom tooth removal is a natural reaction, the patient needs to conduct a daily self-examination of the oral cavity and consult a doctor for help if alarming symptoms appear.
You should consult a doctor if:
➢
on the 3rd - 4th day the pain does not decrease, it becomes throbbing and intense;
➢
a white, reddish or yellow mass or liquid is released from the wound;
➢
swelling of the gums has intensified or spread to the face;
➢
body temperature rose above 38 degrees.
These signs indicate possible infection or complications. After examining the oral cavity, the dentist, if necessary, may prescribe a course of antibiotics or surgical cleaning of the socket cavity.