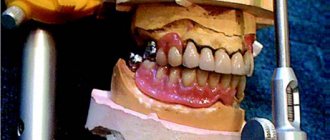
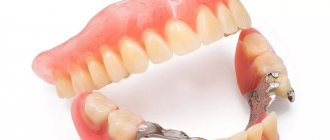
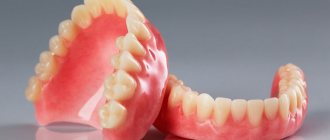
Removable dentures are a way to restore the integrity of the dentition. This type of prosthetics is used both for partial loss of teeth and for significant loss, when all or almost all teeth are missing. Modern removable dentures have good wear resistance and look aesthetically pleasing. They are divided into 2 main groups: full and partial.
Partial removable dentures come in the following types:
- clasp;
- conditionally removable;
- segmental;
- on telescopic crowns;
- immedia prostheses;
- lamellar.
What type of dental structure to choose is determined based on the individual characteristics of the jaw structure and the wishes of the patient.
In what cases should I contact
The reasons why you need to see an orthopedic dentist are varied. If severe tooth decay occurs, this is a serious reason to visit a doctor, because in addition to aesthetics, the functionality of the teeth may also suffer. Each tooth plays an important role in human life, so its destruction affects the functioning of the entire organism.
An orthopedic dentist is also necessary to ensure timely protection of the tooth from destruction. It is worth considering that not every type of prosthesis can completely restore a tooth. Many dentures are responsible for restoring only certain parts of the teeth. If a tooth has become fragile and susceptible to defects, then timely consultation with a doctor will prevent its further destruction.
Correction of small defects in the crown of the tooth also requires the help of a specialist.
Unfortunately, not all people can boast of perfect teeth. In some cases, the use of veneers will be an excellent solution to the problem. High-quality plates will help hide defects in the dentition.
Specialization
Surgeons perform surgical interventions, an orthodontist restores the correct bite using braces and removable or fixed plates, a periodontist treats inflammatory processes in the gums.
An orthopedic dentist is responsible for prosthetics and dental restoration.
Important: All highly specialized doctors work together, since any restoration of the oral cavity requires an integrated approach and comprehensive treatment.
Orthopedic dentistry techniques
An orthopedic dentist deals with microprosthetics, removable, fixed and conditionally removable methods of tooth restoration.
Microprosthetics involves the following procedure: when a tooth is destroyed and requires giving it a presentable appearance, an orthopedic dentist uses inlays and plates to restore part of the tooth. This type of prosthetics is most necessary for the front teeth. Today, prosthetic veneers are especially popular. Their service life is about 10 years.
Permanent prosthetics are larger and more durable than microprosthetics. An orthopedic doctor uses crowns and bridges to restore the chewing functions of the dentition. Orthopedic practice shows that in the case of the loss of one tooth, a crown will be an excellent solution, but if several adjacent teeth are missing, then it is much more effective to install bridges.
Removable prosthetics may not only be needed by older people. It happens that even teenagers need it. An orthopedic dentist installs a prosthesis in place of a lost tooth and thus prevents the curvature of healthy teeth.
A specialist can install complete or partial removable dentures, it all depends on the individual characteristics of the patient’s teeth.
Orthopedics as a field of medicine
Orthopedics treats diseases of the musculoskeletal system as a whole. Orthopedists restore spinal curvatures and treat flat feet. An orthopedic dentist eliminates disorders and restores the chewing-speech apparatus. With the help of prosthetics, the doctor restores the integrity of the jaw, which allows a person to chew food normally and communicate with others.
Symptoms
You should consult an orthopedic dentist if:
- absence (loss or removal) of one or more teeth;
- partial or complete destruction of the dental walls;
- mobility or increased sensitivity of teeth;
- diseases of the gums or bones, for example, periodontal disease, periodontitis;
- cosmetic defects in appearance: different size, irregular shape, enamel pigmentation, any other violations in terms of aesthetics;
- detection of temporomandibular joint disease (TMJ);
- recommendations from a therapist or other specialized specialist who issued such a referral after an examination.
Who is an orthopedic dentist and what does he treat?
This specialist specializes in restoring teeth. He is often confused with an orthodontist, however, there is a big difference between these doctors. An orthodontist straightens crooked teeth and corrects problematic bites using braces and removable plates. An orthopedist partially or completely restores teeth using dentures. He is often called a prosthetist.
An orthopedic dentist or prosthetist eliminates many problems, which makes the patients’ lives comfortable and of high quality:
Improves quality of life and restores psychological comfort.
Due to the absence of one or more teeth, the patient loses self-confidence and feels constant discomfort when communicating with others.
Please note : Psychological complexes and stress can also cause pronounced defects in the dentition, for example, large gaps or chips. The person stops smiling widely, speaking openly and constantly controlling the position of his lips. Such tension can provoke the development of side diseases of the nervous system.
Restores chewing function
Chewing food thoroughly is the key to a healthy digestive system. Chewing dysfunction disrupts the functioning of the entire dental system, reduces muscle tone and slows down blood circulation in soft and bone tissues. The faster the doctor fixes the problem, the faster the patient’s general condition will improve. If the situation is neglected, an inflammatory process may develop, which will lead to periodontitis or periodontal disease.
Saves teeth
Let's imagine a situation: a patient came with dental tissue almost destroyed to the ground, which makes it impossible to install a filling, but the roots remained healthy. Common causes are advanced caries or injury. You can try to stop the destruction process by preserving the roots and nerve endings. An orthopedic dentist also deals with such cases.
Treats edentia
Patients who are missing all their teeth also turn to an orthopedist. He makes removable or fixed dentures and places implants that replace natural teeth. This is not just an opportunity to chew, but a complete return of communication skills and a comfortable stay among others.
The medical practice of the orthopedic office includes:
- restoration of tooth enamel and bone tissue while preserving its own root and nerve canals;
- installing a protective crown on a decaying tooth to stop further shedding and delamination of tissue;
- production and installation of prostheses;
- elimination of aesthetic defects in the dentition, such as cracks, chips, irregularities, pigmentation.
Medical protocols are clearly defined, so orthopedic dentists in qualified clinics always follow established rules and treatment regimens. This allows you to avoid negative consequences and dangerous side effects.
What does an orthopedic dentist do?
The area of competence of the prosthetist includes:
Installation of fixed dentures
Such structures include crowns, inlays, and veneers. These designs are securely fixed and are worn constantly.
Metal-ceramic crowns
The most common type of fixed prosthesis. At the base is a cap made of an alloy of cobalt, chromium and titanium, which is coated with a ceramic composition. This design imitates healthy teeth, lasts from 5 to 10 years and is quite affordable. Safety depends on the presence of impurities in the material, which can cause oxidation and inflammation of the gums.
Zirconium dioxide crowns
One of the most advanced techniques. The cap, shaped like a tooth, is made of zirconium dioxide, which is covered with ceramic on top.
This material does not cause allergic or oxidative reactions. It does not interact in any way with the soft tissues of the gums. When making prosthetics, computer modeling is used, which creates a crown of the most accurate shape and size. The number of possible shades is much greater compared to conventional metal ceramics, so the artificial tooth will not stand out among the natural dentition.
Solid ceramic crowns
There is no metal in such designs, which allows you to fully convey all the shades of the tooth. These crowns are placed on the front teeth.
Installation of removable dentures
Clasp prosthetics are suitable for cases where it is impossible to install fixed structures, and the patient does not have money for implantation. It is an arch with two supports that hold artificial teeth. The orthopedist fixes it to the upper jaw.
The undoubted advantages of clasp dentures are low prices and the absence of surgical intervention. There are quite a lot of disadvantages. Firstly, it takes a long time to get used to the prosthesis. Secondly, it must be removed and cleaned daily. Thirdly, the jaw does not receive full load when chewing food, the blood supply deteriorates and the bone gradually sags. Therefore, removable dentures need to be changed quite often.
Implantation
This is the method that doctors recommend to all patients who have lost one or more teeth. Implants not only maintain a beautiful appearance, but also contribute to the health of the patient.
Regardless of the chosen method of prosthetics, all installed structures must be:
- made taking into account the individual characteristics of the patient;
- designed for long term use;
- safe for health and solve aesthetic problems.
An integrated approach to treatment
Let us once again emphasize the important connection between the orthopedist and other specialized doctors. First, the therapist sanitizes the oral cavity, removes plaque and stones, and treats inflammatory processes in the gums and oral mucosa.
Surgeons remove the roots of teeth that are no longer subject to therapeutic treatment and implant an implant into the patient’s jaw for further manipulation by an orthopedist.
The orthopedic dentist works closely with dental technicians who are responsible for making dentures in the laboratory.
Patient reviews will help you choose a competent orthopedic dentist. It is important to establish complete trust and mutual understanding between the doctor and the patient. Your health and beautiful smile largely depend on this.
Preparing for an appointment and how to see a doctor
It is not recommended to drink alcohol before seeing a specialist. The presence of alcohol in the patient's blood negatively affects the effect of anesthetic drugs. If the patient is sick, then you should postpone your visit for a while. Before coming to the dental office, you should thoroughly brush your teeth. Therefore, it is advisable to discuss the time of your appointment with the dentist in advance.
At the first consultation, the doctor must determine the degree of damage to the patient’s masticatory apparatus. Before starting orthopedic treatment, complex surgical and therapeutic treatment of the oral cavity is carried out. This makes it possible to carefully prepare the soft and hard tissues of the patient’s maxillofacial area for upcoming procedures. Treatment of the following diseases is mandatory:
- Pulpitis,
- Caries,
- Scar changes in the mucous membrane,
- Stomatitis, gingivitis, periodontitis.
During the appointment, the orthopedic dentist examines the patient’s oral cavity and listens to complaints. The inspection can be visual and instrumental. Next, the doctor takes impressions and photographs the dentition. If necessary, a consultation with a dental surgeon is scheduled. Based on the data obtained, the doctor draws up a further treatment plan for the patient.
How to prepare for the procedure
Dental prosthetics is preceded by a number of preparatory measures:
- radiography of the jaw - to assess the condition of the oral cavity and identify pathologies that cannot be detected during a classic examination;
- studying the general condition of the patient in order to exclude contraindications to the procedure.
The dentist also preliminarily performs:
- removing plaque;
- dental cleaning of plaque from the subgingival area;
- polishing teeth and coating them with fluoride preparations.
Before prosthetics, therapy for inflammatory processes in the oral cavity, treatment of caries and other pathologies is mandatory.
If necessary, old filling materials are replaced with new ones and dental canals are treated.
Diagnostic methods
Based on the individual characteristics of the patient’s teeth, the doctor selects appropriate research methods. A panoramic photograph of the jaw, an orthopantomogram, or an x-ray of one or more teeth may be offered. A couple of months after prosthetics, the patient will need to take a control photo to evaluate the work performed.
After conducting instrumental diagnostics, the orthopedic dentist can prescribe consultations with other specialized specialists, for example, an orthodontist. After all the data necessary for treatment has been collected, the doctor draws up a plan for further therapy for the patient. All responsibility for the correct selection and production of an individual prosthesis lies with the orthopedic surgeon.
Features of the procedure
Removable orthodontic structures are made of artificial materials: acrylic plastics or nylon. The orthodontist, together with the patient, selects the shape and color of the teeth, a suitable shade. During the first fitting of the wax sample, it is possible to adjust the position of the structure and make the necessary changes. After putting on the finished prosthesis, the patient may feel discomfort. The specialist corrects the identified deficiencies.
Getting used to the design takes some time. During this period, it is important to follow the dentist’s recommendations and perform all necessary hygiene procedures. A high-quality and correctly selected denture allows you to quickly restore chewing functions.
The structure needs periodic cleaning, ideally after every meal. It can be removed or left in the mouth at night.
What can be done about missing teeth or teeth that need to be extracted?
Traditionally, all existing options for restoring missing teeth can be reduced to two groups: removable and fixed prosthetics.
The differences are simple: any removable prosthesis yourself without the help of a doctor, while fixed prosthetic structures either cannot be removed at all, or this can only be done with the help of a doctor.
For example, you can remove a removable laminar denture without the participation of a doctor. And put it on exactly the same way, without helpers:
More advanced versions of removable dentures are trying to be made more compact, and for this purpose almost all plastic is replaced with metal - this creates a more compact (and therefore more comfortable) removable denture, called clasp.
Often, a clasp denture is made with special locks (attachments) and clasps (claws) so that it is more accurately and reliably fixed to the remaining teeth. Yes, such a prosthesis is much more convenient than a removable plate prosthesis; it does not rest on the gums, but at the same time it significantly loads the teeth (therefore, they often have to be taken under crowns and combined into bridge structures).
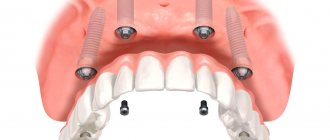
Removable prosthetics can also be implemented using dental implants.
So, to fix a removable denture (if, for example, it dangles and does not stay on the jaw), you can use a pair of implants with special locks.
At the same time, the prosthesis does not dangle and does not rub the gums. In the case of an increased gag reflex, it can even be slightly reduced without losing stability. However, the service life of such a prosthesis is still limited by wear, and it must be periodically repositioned.
Therefore, with a large number of implants (minimum 4 units), it is possible to create a removable prosthesis with fixation on a beam.
A beam (or two beams) firmly fixed to the implants with locks evenly distributes the load on the implants, while the prosthesis itself can be significantly reduced in size - in fact, it is almost no different from a fixed one. Therefore, it is easier to get used to, and it lasts much longer than any other removable structure.
Fixed prosthetics require a reliable support, which can be either natural teeth or implants.
In the case of making a bridge based on natural teeth, the latter are very carefully ground down. To do this, they use special tools with relatively low speeds and very good cooling - this avoids thermal injury to the dental pulp, therefore, it is not at all necessary to depulpate the abutment teeth (as was done before). Most often, it is possible to avoid removing the nerve altogether, and a living tooth can better withstand the load and last longer.
However, even perfectly prepared teeth, onto which a perfectly made bridge is fixed, turn out to be overloaded - if previously they received chewing load only from their own surface, now they bear it also from missing teeth.
The higher the load on the tooth, the higher its wear. Especially. if the tooth is depulped (the nerve is removed from it). Therefore, some doctors try to distribute the load as much as possible from missing teeth to as many remaining teeth as possible.
From the point of view of our clinic and our orthopedists, this approach does not look entirely rational from a medical and economic point of view. And really, is it worth intervening, grinding, and sometimes depulping several teeth to restore one missing one?
And this is where dental implants come to our aid. Dental implantation is one of the main areas of our activity.
The essence of using implants for fixed prosthetics is extremely simple - just like teeth, they create a stationary, reliable and, most importantly, universal support for a denture. Thus, the use of implants allows for the widest range of dental prosthetic options:
The implant does not have a connective tissue ligament surrounding the natural tooth. From a biophysical point of view, a dental implant is a continuation of bone tissue. The chewing load, sometimes quite significant, is transmitted and distributed in the jawbone, bypassing the periodontal ligament and mucous membrane - this explains the long service life of the implant, much longer than that of natural teeth under crowns. And this gives us the opportunity to provide appropriate guarantees for the work we have done. Of course, subject to following certain recommendations.
Rubric “Question and answer”
Who is a dentist?
The concept was used in the 20th century and is now considered obsolete. Previously, the term was used to describe dentists who did not have a special higher education. In foreign countries, a dentist is a dentist who has received secondary education in his specialty. This term can be used to describe a dental laboratory specialist, a dentist, or a paramedic.
Can a dentist perform the duties of a dentist?
The answer to the question will be negative, since the dentist does not have the necessary skills and knowledge to carry out the procedures that are the responsibility of a dental therapist.
Dental prosthetics as an art with a long history
If you are worried about searching for reliable dental prosthetics, then we hasten to please and reassure you - you are on the website of the best private dental clinic in Russia. Our clinics have confidently taken the place of the all-Russian leader in prosthetics
and implantation since 2021.
1,120
dental clinics from
106
took part in the all-Russian ranking “Best Dentistry in Russia” for 2020, according to the Kommersant Publishing House and the expert magazine Startsmile .
The quality of the clinics' work was assessed using more than 240 (!) criteria
. The TOP rating of the best dentists in Moscow and Russia helps people from different parts of the country choose dentistry where they are guaranteed to receive the highest quality medical care.
Categories of dentists
After a certain period of time, the doctor can improve his qualifications. The category largely depends on the doctor’s work experience and the completion of additional training courses. There are 3 categories in total that a dentist can receive:
Dental diseases, their names and photos
- Second. Awarded to people whose work experience is more than 3 years after certification. To obtain a category, a doctor must be savvy in both theoretical and practical skills.
- First. Given to dentists who have worked in their specialty for more than 7 years. In this case, he needs to study related disciplines related to prosthetics, dental work, etc.
- Highest. Issued to doctors whose work experience exceeds 10 years. Doctors of this level of training have advanced theoretical and practical knowledge and skills.
Not only the doctor’s knowledge, but also his salary depends on the category. Some dentists only treat children. They can eliminate small cavities caused by a child's excessive consumption of sweets or poor oral hygiene.
In some cases, the dentist is unable to provide assistance to a small patient. This is due to several factors:
- A child's jaw is different in structure and structure from an adult's.
- The dentist does not have special equipment and devices for treating pulpitis or complicated caries.
- Lack of drugs necessary for therapy.
- Inability to find an approach to the child.
If one of the listed problems is present, the child is referred for treatment to a pediatric dentist. In most cases, a dentist can also cope with simple caries in a baby. The dentist also conducts preventive examinations of children 2 times a year.
Uncomplicated caries in a child