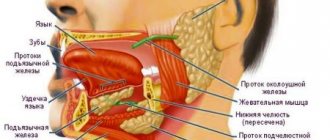
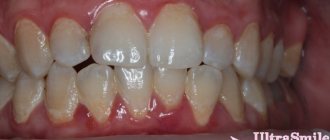
Diseases of the gastrointestinal tract have a complex effect on the health of the entire digestive system, which includes the oral cavity. First of all, this effect is due to a lack of vitamins and minerals, which leads to inflammatory processes, and in addition, aggravates existing oral diseases.
Of course, in such cases, treatment of the problem should be comprehensive - you should also contact a dentist
, who will eliminate the manifestations of diseases in the mouth, and to an endocrinologist, who will directly eliminate the root of the disease.
Let's look at the main examples of gastrointestinal diseases that directly affect the condition of the oral cavity and teeth.
Oral disease:
Aphthous stomatitis
- characterized by the appearance of point inflammations in the oral cavity, which are called aphthae.
These manifestations are quite painful and interfere with comfortable eating. Treatment of tongue ulcers lasts from one week to a month. As a rule, aphthous stomatitis leaves raised scars. Stomatitis
- inflammatory manifestations are covered with a gray-white film.
With daily rinsing it goes away within a week. Herpetic stomatitis
is expressed by the formation of small ulcers that are similar to herpetic manifestations on the lips.
The boundaries of inflammation are blurred and mainly affect the lower part of the tongue. They heal within 8-14 days, scars are not visible. Fungal stomatitis
(popularly called thrush) is most common in young children.
Easily treatable at home. Recurrent periadinitis
- first, compactions form on the submucosa, and then ulcers with raised edges appear.
Such manifestations are quite painful, form on the edges of the tongue, gums and lips, and take several months to heal. This type of ulcer on the tongue in adults and children can only be treated with the strict supervision of specialized specialists. Bernard's canker sores
- the most common ulcers on a child's tongue, manifests itself in the form of a plaque with a yellow tint. The reason is failure to maintain good oral hygiene. Treatment of ulcers is carried out within a week.
Is my tongue my doctor? What diseases can be identified by the organ of taste?
The tongue is one of the most important organs in the body. It contains receptors that allow you to recognize all shades of taste of products entering the oral cavity.
As scientists noted back in ancient times, human language has a connection with various organs of the body. When diagnosing, they divided it into conventional parts: basal, middle and tip. And they believed that in case of pathology of a particular organ, the lesion would be observed strictly in one of these areas. AiF.ru looked into what diseases leave their mark on the language together with Professor, Doctor of Medical Sciences, head of the laboratory for the development of an interdisciplinary approach to the prevention of chronic non-infectious diseases of the Federal State Budgetary Institution "State Research Center for Preventive Medicine of the Ministry of Health of Russia", expert of the National Health League Mehman Mamedov .
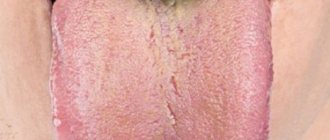
Color spectrum
When examined by a doctor, you are often asked to show your tongue. And they do this not out of idle curiosity. After all, even by the color of the tongue it is quite possible to determine whether there is a particular disease. For example, the tongue of a healthy person should be pale pink: this is what is accepted as the norm. If there is a white coating on the tongue, we can talk about fungal infections of the body or disorders of the gastrointestinal tract. A gray tongue is usually the result of chronic pathologies. Bright red - will indicate infectious and inflammatory processes in the human body; if the red color has a shade of scarlet, doctors will suspect problems with the circulatory system. A burgundy tint is a clear sign of an acute infectious process. The tongue is part of the gastrointestinal tract, and is also connected with the respiratory system, because located in the oral cavity. With stomach and duodenal ulcers, problems with the gallbladder, liver and intestines, there may be changes in the color of the tongue. Each disease has its own manifestations - in some places it can be more contrasting, in others it can be lighter.
It also happens that the color of the tongue changes to blue and purple. In this case, they talk about problems with the lungs or severe kidney ailments. Yellowing of the tongue is not only a characteristic feature of a heavy smoker, but also a signal of problems with the gastrointestinal tract. If there is a lack of vitamins in the human body, the tongue may completely lose color.
It is worth considering that a shade that is too dark and saturated is a sign of problems that require immediate medical intervention, or even hospitalization.
Additional factors
However, not only color matters. If the tongue is too dry, the following diagnoses may be made: dehydration, intestinal obstruction, peritonitis. Often, dry tongue is observed with an increase in body temperature. If the situation approaches critical, the taste organ may even crack due to dryness. In this case, an additional threat is created: it is easily infected with bacteria, resulting in suppuration and severe inflammation.
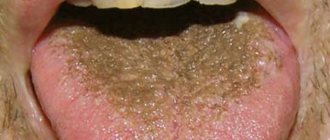
The type of coating on the tongue is also of particular importance. So, if it is thin, it means that the disease is in the initial phase, and if it is frankly fatty and thick, then the problem most likely lies in pathologies of the gastrointestinal system: this usually happens if mucus has accumulated there and food stagnates. A spotted and purple coating indicates the development of blood stagnation. Malfunctions in the digestive system will cause the tongue to become slightly swollen and wet. In this case, it is recommended to be checked for gastritis, cholecystitis, ulcers and even appendicitis.
Doctors pay special attention to the place where plaque accumulates. So, if it is more adjacent to the root of the tongue, then problems are noted in the large intestine: most likely, many human waste products have accumulated there and cannot find a way out. Plaque in the middle indicates problems in the small or duodenal intestine or stomach. If the plaque is so thick and the tongue is so swollen that you can see teeth marks along the edge, you need to reconsider your diet: with a high degree of probability it can be said that the intestines cannot cope with the food that a person eats.
The presence of deep wrinkles and cracks located transversely should alert you and send you to a neurologist - as a rule, this problem manifests itself with a predisposition to vascular disorders of the brain.
The tongue can even indicate serious cardiac and vascular problems, which may occur without any symptoms for some time. For example, a tongue that is slightly shifted to the side or slightly bent will indicate a hemorrhagic stroke, cerebrovascular accidents, or problems with the functioning of the cerebellum.
An increase in the volume of the taste organ may be a consequence of problems with the thyroid gland, malfunction of the pituitary gland, or mental disorders.
Shaky and grainy
Sometimes a person may notice that his tongue... trembles. This condition indicates nervousness and problems with the central nervous system. In such a situation, doctors recommend changing the psychological environment, as well as working on your lifestyle. It is also worth checking with a doctor if your sense of taste begins to decrease. After all, it does not develop out of the blue: there must be a reason why a person no longer feels the tastes to which he is accustomed. Moreover, it is important to understand that there are certain zones and areas on the tongue that are responsible for the reaction to different tastes: spicy, salty, sweet, etc. If a malfunction is noted in any of the parts, this may indicate that the nervous system is suffering. or endocrine system. Loss of taste in the taste buds of the tongue manifests itself as a result of metabolic disorders in the human body, as well as malfunctions of the central system of various etiologies, the development of anemia and the presence of cancer.
Also, people often begin to notice that the tongue has become rougher: this is due to an increase in the size of the papillae on the surface of the organ. When swollen papillae are localized at the tip, it is worth being examined by a cardiologist. If the tongue becomes “spiky” around the edges, you need to check the liver. An affected middle part of the tongue indicates problems in the stomach and intestines. At the same time, you should not rejoice when the tongue becomes smooth and “mirror-like”. After all, this is also a pathology. This happens with anemia, exhaustion or severe pathologies of the stomach.
Trauma to the oral mucosa.
- Incorrectly selected dentures or orthodontic devices.
- Injuries due to improper brushing of teeth.
- Injury to the tongue with sharp medical instruments.
- Irritation of the mucous membranes with acidic foods or concentrated medications.
- Chipping of damaged teeth causes trauma to the tongue.
The causes of ulcers on the tongue in an adult, caused by trauma, are not as problematic as diseases of the oral cavity, but the threat can be the penetration of viral infections through wounds and microcracks, which will lead to a more serious disease. Many people know how to treat ulcers on the tongue of this group - maintain strict oral hygiene during the initial injury. Solutions that have disinfecting abilities (chlorhexidine, chamomile decoction, calendula infusion) will cope best with this.
Causes of peptic ulcer
- The presence of Helicobacter pylori in the stomach and duodenum, which is the main etiological factor in the occurrence of ulcers. The influence of other bacteria has not been proven
- Eating disorder
- Alcohol and tobacco abuse
- Long-term use of drugs that affect the gastric mucosa, the main ones: NSAIDs and glucocorticosteroids (prednisolone)
- Emotional overstrain, stress
- Genetic predisposition
- Metabolic disorders
- Hypovitaminosis
Ulcers on the tongue are caused by common diseases.
Ulcers are caused by viral diseases, stomatitis, deterioration of the immune system, and exhaustion of the body. In this case, ulcers under the tongue, active salivation, unstable temperature, sweating, and bad breath are characteristic. The inflammations are covered with a greenish coating with jagged edges. Ulcers caused by pulmonary tuberculosis. As a rule, it provokes oral tuberculosis. This disease is characterized by loose ulcers with raised edges. Vivid symptoms of oral tuberculosis will be fever, lethargy, and mild nausea. Mouth ulcers are caused by an infectious disease such as syphilis. Inflammation accompanies the entire cavity - tongue, lips, palate, throughout the entire period of the disease, except for the incubation period. Ulcers on the tongue are not accompanied by severe pain, but heal in 2 to 4 months and leave pronounced scars.
Ulcers on the tongue, lips, cheeks, gums, palate due to HIV disease.
These manifestations are inevitable with such a diagnosis, although with careful monitoring and drug support they are treatable. Oral ulcers of the last group are the most risky category of diseases that are provoked by serious illnesses. Recovery is possible through systemic treatment and constant monitoring of both medical workers and the patient himself. This article is for informational purposes only, please consult your doctor for details!
Symptoms of peptic ulcer of the stomach and duodenum
- Aching or cramping pain, low intensity in the epigastric region, often occurs on an empty stomach or immediately after eating
- Constant heartburn, especially at night and in the morning, sour belching
- Nausea
- Belching with air, sour or bitter taste
- Heaviness in the epigastric region after eating, a feeling of rapid filling of the stomach
- Decreased appetite
- When bleeding from ulcers, vomiting appears like “coffee grounds”, dark stools (melena)
- With perforation of ulcers - severe, dagger-like pain in the epigastric region, nausea, vomiting, painful tension in the abdominal muscles
Methods for diagnosing stomach ulcers
In the diagnosis of gastric ulcers, instrumental diagnostics and laboratory methods are used. The main importance is attached to the endoscopic method - EGDS (gastroscopy).
Gastroscopy
Gastroscopy allows you to identify ulceration, clarify its location, size and depth, and determine whether bleeding is occurring. Gastroscopy also makes it possible to evaluate the relief and elasticity of the mucosa.
More information about the diagnostic method
X-ray
For stomach ulcers, a diagnostic method such as fluoroscopy can be used. Fluoroscopy is a real-time X-ray examination. The patient's stomach is filled with a contrast agent. Using X-rays, an image of the contours of the stomach is obtained. You can evaluate the dynamics of the passage of the contrast agent. In case of a gastric ulcer, examination reveals “niches” - a persistent accumulation of contrast agent on the relief of the mucous membrane or on the contour of the organ wall.
General blood analysis
With a peptic ulcer, you should expect that a general blood test will show an increase in the number of red blood cells, an increase in hemoglobin and a slowdown in ESR.
More information about the diagnostic method
Fecal occult blood test
The standard of examination for suspected gastric ulcers usually includes a stool occult blood test.
Detection of Helicobacter pylori
The cause of the inflammatory process in the stomach may be the bacterium Helicobacter pylori. In order for the treatment to be effective, it is necessary to establish its presence in the patient’s stomach. For this purpose the following may be carried out:
- taking a biopsy of the gastric mucosa during endoscopy for subsequent microscopic or cultural examination;
- urease breath test;
- stool analysis for detection of Helicobacter pylori antigen;
- serological blood test;
- PCR diagnostics.
Sign up for diagnostics To accurately diagnose the disease, make an appointment with specialists from the Family Doctor network.