Why do teeth rot in adults?
The development of caries and other dental diseases occurs under different circumstances, including:
- Insufficient oral hygiene or its complete absence.
- Poor nutrition, accompanied by the development of excess or deficiency of microelements and vitamins in the body.
- Failure to follow the rules of eating: chewing very cold or very hot food, combining hot and cold, biting into very hard foods.
- Disturbance of metabolic processes in the body.
- Endocrine diseases and temporary hormonal imbalances, due to which the protective properties of saliva are weakened.
- Pathological processes that occur during pregnancy and are associated with the outflow of nutrients from the mother’s body to the developing tissues of the fetus.
- Weak immune activity.
- Hereditary predisposition and improper formation of the dentofacial apparatus.
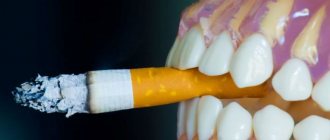
- The effects of nicotine and alcohol.
- The effect of toxic substances in unfavorable environmental conditions or harmful working conditions.
- Infectious processes due to injuries.
- The presence of untreated infectious processes in any part of the body.
When visiting a dentist, you rarely hear exactly why a particular dental disease has developed. Most often, unfavorable factors act on dental tissues in a complex manner and over a long period of time.
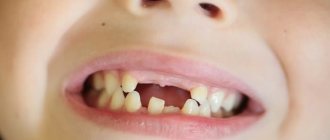
Why do children's teeth rot?
Teeth rot not only in adults, but also in children. In addition to the reasons described, children’s teeth are affected by additional factors that often arise due to the fault of parents:
- Improper nutrition of the mother during pregnancy, due to which the formation of bone and dental tissue of the fetus is abnormal.
- The effect of toxins and medications that enter the mother’s body through smoking, drinking alcohol or self-medicating.
- Long-term use of pacifiers and bottle nipples.
- Night feeding - at night, food particles linger in the mouth for a long time and rot due to the activity of bacteria.
- Late and incorrect teaching of children to maintain hygiene.
- Eating large amounts of sweets, the remains of which create favorable conditions in the mouth for the proliferation of microbes.
When is it necessary to remove a tooth root?
In all cases, the doctor decides individually whether the situation requires tooth root removal after carrying out diagnostic measures and examination using radiography or visiography. Among the most common indications for tooth root removal are the following:
- the patient suffers from aching and throbbing pain in the tooth;
- in the peri-root area there is some swelling of the gums;
- there are signs of inflammation;
- the root of the tooth is destroyed;
- third degree of tooth root mobility;
- tooth fracture is of increased complexity;
- the level at which the destruction of the dental crown is located is located below the level of the gums;
- a cyst was diagnosed.
If the rotting tooth root is not removed in a timely manner, it can give rise to a serious infectious process in the oral cavity, as well as bad breath. Problems will certainly affect healthy tissues nearby.
In some cases, even in the presence of inflammation and severe tooth decay, you can do without root removal. This will allow, after carrying out the necessary therapeutic measures, to restore or build up the tooth. The final decision on this issue is made by the dentist.
Treatment in dentistry
Whether a tooth can be treated depends on the severity of the carious process, so doctors first prescribe x-rays to patients. If the situation is not critical and the dentist can save the tooth from rotting, he carefully cleans it of accumulated deposits (plaque and stone) and begins treatment:
- Anesthesia is performed.
- All areas of enamel affected by the carious process are removed, and the rotting pulp must also be removed.
- The dental cavity is washed with an antiseptic.
- The integrity of the surface is restored with filling material. After the filling is installed and hardened, the patient must check the bite: if discomfort is felt, the excess layer of filling material must be removed.
Teeth that are rotting from the gums are treated in the same way, but photopolymer materials are usually used to fill them. They harden quickly, are characterized by increased strength and high aesthetics.
The dentist may prescribe an antibiotic to prevent the infection from spreading throughout the body. For severe pain, an analgesic is prescribed.
There are methods that can be used to prevent damage to dental tissues by cariogenic bacteria. Almost all dental clinics carry out remineralization - strengthening the enamel structure with special preparations. In a hospital or at home, you can perform fluoridation - saturating the enamel with fluoride.
Tooth root removal: painful or not?
Most often, the situation in which tooth root removal is indicated occurs when the pulp is dead. To avoid pain and discomfort, the “Optimal Choice” dental clinics use modern high-quality local anesthesia before tooth root removal and other manipulations. Therefore, you should not be afraid of pain and put off visiting the dentist for the indefinite future. Today the procedure takes place with a minimum of discomfort.
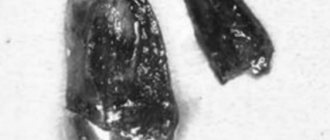
How to pull out the remaining root in the gum
It is always easier for a dental surgeon to remove the entire tooth than just the remaining root parts.
First, the doctor carries out diagnostic measures, which include:
inspection;- reorganization;
- taking pictures.
If he deems it necessary, he may ask the client to take a blood test. On the appointed day, the patient is given an anesthetic. Local anesthesia is usually sufficient. When the anesthetic takes effect, the hard fragments are removed using special forceps. When the gums are completely overgrown, they are first excised, and the bone tissue is drilled out to gain access to the root zone. After this, using a dental elevator, all detected particles of the missing unit are removed. Such an operation is certainly complex and traumatic. Upon completion, stitches are applied.
Types of deletion
To remove a tooth root, your dentist may use one of the following methods:
- tongs;
- using an elevator;
- using a drill.
Tooth root removal using forceps is most often used. For the upper roots, tools with straight ends are best, and for the lower roots, beak-shaped models are best. Bayonet pliers are universal and are suitable for all cases. If the tooth is single-rooted, then the rotation method, that is, rotation, is suitable for root removal. If a tooth has several roots, luxation is required.
If the roots are located far away, it may not be possible to remove them with forceps. Then various elevators are used, which operate on a principle similar to levers. The root is twisted out using this tool, and part of it appears on the surface. After this, it is already possible to remove it using forceps. Elevators come in corner and bayonet types. The former give good results on the roots of the lower teeth and their remains, while the latter are often used to remove “figure eights”.
If there are some peculiarities in the location of the roots or their strong “ingrowth” into the bone, the dentist will need a drill. The procedure can take quite a long time and requires high professionalism, however, like all types of medical care. Depending on the severity of the problem, removal surgery may be performed using one of the following methods:
- root hemisection—one of the roots of the tooth is removed;
- root extraction - it is completely removed.
Indications for surgery
Today, dentists prefer tooth-preserving operations. Therefore, even if there is only one root left, they first study whether it can be used as a basis for future prosthetics. However, in medical practice there are often situations when the removal of a decayed tooth must be carried out without fail.
This is possible if:
the tooth base has become very loose due to advanced periodontitis;- fracture diagnosed;
- a cyst has been discovered that cannot be removed in isolation;
- a fragment of the crown that extends deep under the gum has broken off;
- a part remained after the unit was carelessly removed.
Milk units should ideally fall out on their own. They are pulled out when the coronal part is completely damaged by caries, loosened or fractured, or a carious process that has spread under the gum.
Stages of the procedure
First, the dentist must conduct a diagnostic examination, examining the root of the tooth and the patient’s oral cavity. Particular attention is paid to the condition of the gums and the presence of inflammation. A survey and medical history allows you to choose the best method of anesthesia that will not cause an allergic reaction.
Then the doctor, based on the condition of the tooth root, selects the extraction method and prepares the instrument to be used.
An injection with an anesthetic is made into the gum in the area of the affected tooth root, and further procedures to remove the root using the chosen method are carried out after the anesthesia has taken effect.
After the tooth root is removed, the oral cavity is treated with an antiseptic, then an anti-inflammatory agent is applied to the treated area. If an incision was made in the gums, it is necessary to apply sutures. They are removed after a week. After tooth root removal, the patient is prescribed analgesics and antibiotics.
Why do teeth rot?
Unfortunately, almost any patient can experience tooth decay. Causes of pathology:
- mechanical or chemical injury to the enamel or crown, leading to rapid destruction of dentin and pulp;
- poor oral hygiene - lack of regular brushing, incorrect selection of toothbrushes and toothpastes;
- bad habits - alcohol abuse, frequent smoking, drugs;
- poor ecology - for this reason, rotten molars are increasingly diagnosed among residents of megacities;
- unbalanced diet - a small amount of vegetables and fruits in the diet, excessive consumption of sweet and flour products;
- lack of vitamins and minerals - primarily a lack of fluoride and calcium;
- heredity - genetic predisposition to the rapid destruction of enamel and dentin;
- untreated dental diseases - advanced caries, pulpitis, gum and periodontal diseases;
- general decline in immunity - teeth often rot during serious chronic diseases of internal organs and systems, during pregnancy, and during periods of active growth in adolescents.
Possible complications
Among the most common complications that occur during tooth root removal are the following:
- dislocation of the jaw, if the doctor has little experience;
- inflammatory process in the hole;
- penetration of bone particles into it;
- damage to teeth located next to the one being removed;
- allergy to anesthesia;
- heavy bleeding.
If you do not skimp on dental services and contact an experienced specialist, as well as follow all medical recommendations, then the risk of complications is minimized.
Preventive actions
The main prevention of possible complications after tooth root removal is the patient’s compliance with all recommendations given by the dentist. These include:
- after the operation, you need to press the gauze swab tightly against the hole for 15-20 minutes and then remove it;
- During the day, it is necessary to treat the fresh wound very carefully so as not to disturb the formed clot. For example, you will have to give up mechanical teeth cleaning;
- for five hours after surgical removal of the tooth root, you should stop drinking hot foods and eating;
To avoid inflammation, you should contact your dentist again at the slightest suspicion.
Bridges
The good old classic that dentists offer when they see that a root is missing. Bridges do not need to be removed from your mouth every day to be cleaned, unlike removable dentures, they will last 10-12 years with proper care and are much better at restoring chewing function. Modern materials are quite effective at restoring a beautiful appearance to a smile. The price and production time of such a prosthesis is higher than that of a removable prosthesis, but lower than that of an implant.
What are the disadvantages of this technique?
- With classic prosthetics relying on your own teeth, due to the uneven distribution of the load during chewing, the supporting teeth under the bridge gradually begin to collapse.
- Bone atrophy also does not stop.
- The denture requires special cleaning products - pipe cleaners, brushes, etc., otherwise food debris and plaque will accumulate under it.
- The implant-based method is not always possible - if one tooth or two in a row is lost, the doctor will not remove adjacent healthy teeth in order to put implants in their place.
Experts' opinion
Question: After removing the root, the doctor told me to rinse my mouth. What means can be used for this?
Answer : Among the most accessible means for rinsing the mouth after tooth root removal are: a weak salt solution (you can use a mixture of salt and baking soda in equal proportions), miramistin, chlorhexidine, a weak solution of potassium permanganate (light pink), a decoction or infusion of medicinal products herbs (chamomile, sage, eucalyptus, calendula). Oak bark helps very well. It must be remembered that active rinsing cannot be carried out on the first day after surgery. During this period, you just need to put the product in your mouth and hold it for a few minutes, then spit it out.
Question: Is it possible to remove a tooth root yourself at home?
Answer : Doctors at the Optimal Choice dental clinics recommend that you never try to remove a tooth root at home on your own, but if you have the slightest problem with your teeth, visit a dentist as soon as possible. It is not worth saving on your health, since such savings may entail large expenses in the future. At home, it is not possible to painlessly, efficiently and correctly remove the root of a tooth using improvised means. This can only be done in a clinical setting.
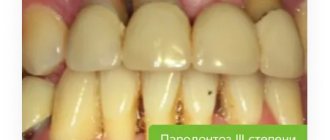
Rotten teeth: consequences for the body
A rotten black tooth is a direct path to the dentist. The doctor will make a diagnosis and provide treatment. But what happens if you don’t remove a rotten tooth? In cases where the tooth has rotted down to the gum, the consequences will affect the patient’s entire body:
- constant fatigue, apathy, frequent colds and ARVI - due to general intoxication due to infection and decreased immunity;
- deterioration of heart function - development of the disease endocarditis, inflammation of the inner lining of the heart;
- problems with the gastrointestinal tract - loss of appetite, gastritis, ulcers, dysbacteriosis;
- damage to the trigeminal nerve - chronic migraines, memory impairment, Alzheimer's disease;
- disruption of the musculoskeletal system - development of arthrosis, polyarthritis;
- problems with appearance - hair loss, deterioration of skin condition;
- decreased hearing quality.
A serious consideration of the question of what rotten teeth affects demonstrates the interdependence of all organs and parts of the human body. Deterioration of the oral cavity is a path to heart attack, thrombosis, abscesses and other diseases.