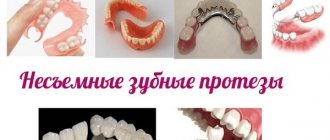
Bridges were used long before the formation of not only orthopedic dentistry as an independent discipline, but even dentistry in general. The first bridges were found during excavations of ancient tombs dating back thousands of years. The famous Phoenician and Etruscan dentures were the prototypes and the first attempts to implement this type of restoration of chewing efficiency. And this is not surprising: using remaining teeth to restore defects is the most obvious and logical method, and thousands of years later it turned out that this is also highly physiological. In restoring chewing efficiency, only implant-based structures can be compared with bridges, taking into account the advantages and disadvantages of both types of prosthetics.
Having stepped far ahead from the Etruscan prosthesis, modern bridges are made using a considerable number of methods using a wide range of different designs: starting from the soldered “bridge” that has become a thing of history and continuing with highly aesthetic and reliable all-ceramic bridges.
Structure of a bridge
The design of a bridge prosthesis includes, by analogy with the architectural structure of the same name, supporting and intermediate parts. The teeth surrounding the defect or directly adjacent to it are used as supports, in the case of cantilever structures, when the intermediate part has support on only one side. In turn, the intermediate part is fixed to the supporting parts and can be positioned differently in relation to the gingival margin:
— The intermediate part can be located according to the rinsing type, which is not the most aesthetic option, but is more convenient from a hygienic point of view and is used in the chewing group of teeth;
— The tangent type of the intermediate part is more aesthetic and is appropriate in the frontal part of the dentition:
— In the manufacture of ceramic or metal-ceramic structures, saddle-shaped or ovoid types of arrangement of the intermediate part can be used.
The use of the reserve forces of the periodontium of the supporting teeth is the most physiological way of transmitting chewing pressure, however, the lack of load on the bone in the area of the dentition defect contributes to atrophy of the alveolar process in this place.
In addition, the design of bridges in most cases involves the preparation of supporting teeth, which is an irreversible loss in the human body, which is why the choice of this type of prosthetics by the doctor must be justified, and otherwise the patient must be properly informed and motivated that the use “bridge” is not desirable for him and he should think about implantation
Soldered bridges
Yes, soldered bridges are practically a thing of history. With the development of precision casting methods using refractory models, computer modeling and milling, laser sintering and others, the design of a stamped-soldered “bridge” cannot meet modern criteria not so much for aesthetics as for the requirements of functional efficiency. Many soldered dentures do not “last” even a couple of years, and those that stand for a long time will significantly complicate both individual hygiene and the self-cleaning ability of the oral cavity.
Also, a considerable difficulty for both the orthopedic dentist and the dental technician is the creation of an adequate marginal fit, which affects the condition of the periodontium, further reducing the patient’s quality of life and complicating further re-prosthetics.
However, soldered bridges still remain one of the cheapest ways to restore defects in the dentition, which does not give the right to forget about this type of prosthetics, although the percentage of use of such structures is falling every year, along with an increase in the percentage of clinics refusing solder “bridges” .
What are bridges?
If several teeth in a row are severely damaged or missing, a bridge can be used to restore them.
This is a non-removable orthopedic structure, which consists of several artificial teeth connected in a row. It is fixed on supporting teeth located on both sides of the destroyed ones, or on specially installed implants. A bridge is a permanent structure consisting of dental crowns connected into a single unit, which is used to replace missing teeth. Fixation of this prosthesis can be done both on teeth rotated under crowns (located on the sides of the dentition defect) and supported by dental implants. As for the length of bridges, they can range from 3 to 14 units (the number of crowns in the prosthesis).
Metal-ceramic products: characteristic features
A metal-ceramic bridge is a complex dental structure that includes a metal base and an outer ceramic layer. In this case, the prosthesis frame can be made of cobalt-nickel or cobalt-chrome alloy, and can also contain precious metals.
Currently, designs based on the use of gold alloys are especially in demand. This allows you to get the most natural shade of the crowns and use them to restore lost units in the frontal zone. In this case, the frame can have a thickness of approximately 0.5 mm.
Advantages of metal-ceramic prostheses:
- Allowed for use in the frontal zone;
- The metal bridge has a solid base, which contributes to the high reliability of the product and ensures a long service life;
- The ceramic layer is resistant to abrasion;
- Can be repaired if cracks or chips occur.
It should be remembered that before fixing a metal-ceramic bridge, the supporting crowns are subjected to pulp removal and turning.
Construction of bridges
The main parts of a bridge are artificial teeth (sometimes simulating part of the gum) and attachments in the form of dental crowns, inlays or clasps. In appearance, all this resembles a bridge, hence the name of the prosthesis. Bridges are used to replace 1 to 4 consecutive missing teeth, depending on their type. At the same time, there must be healthy teeth to the right and left of the dentition defect, which can become a support for the prosthesis and withstand additional chewing pressure, which can reach several tens of kilograms.
The intermediate part of the bridge may have different principles of connection with the mucous membrane:
- Flushing. When there is space between the mucous membrane and the bridge. The washable bridge allows food to pass freely under the structure, facilitating hygienic care.
- Tangent. When the denture body touches the mucous membrane on one side, this is important for the anterior part of the teeth, where it is important from a functional, linguistic and esthetic point of view. A bridge of this design is usually installed on the front teeth.
- Saddle-shaped. When the bridge is completely connected to the mucosa, the joint is connected to the joint. This is not the best option in terms of functionality and reliability, but there are cases when you cannot do without it, for example, in the area of the front teeth.
The use of inlays for attaching prostheses
To fix bridges, it is allowed to use special inlays made of ceramic or metal material. In this case, there is no need for total grinding of the supporting crowns: it is enough to make a small ledge on the chewing side of the dental unit.
The installation of such products is recommended only to reproduce 1 lost unit in the presence of healthy nearby crowns. In addition, due to the insufficient stability of structures on inlays, sometimes it is necessary to fix the crown at one edge.
Materials for the manufacture of bridges
Dental bridges are usually made from the following materials:
- Metal is a classic durable option and has been the only option for many years. It lasts a long time, easily adapts to different chewing loads, but it is too unsightly, so it is mainly placed only on the back teeth. It's the cheapest;
- Sintered metal is a more expensive option with better aesthetics. It is a metal frame with a ceramic coating that makes the structure white and similar to natural teeth. Still quite durable, although inferior in aesthetics to other options;
- All-ceramic dentures are very aesthetic prostheses, but they are expensive and fragile. Due to their lack of structure, they can create natural color and translucency of teeth, but cannot withstand heavy chewing loads. Recommended to be placed in the front of the jaw;
- Zirconium dioxide is a modern material, but at the same time extremely durable and aesthetic. Unfortunately, it is very expensive, but it lasts a long time and, as a result, is quite inexpensive.
- Combined designs: combine metal and metal-ceramics. They are placed if part of the teeth falls into the smile area, then they are covered with ceramics for better aesthetics, leaving metal teeth invisible to save money;
- Metal-plastic is an inexpensive option in which the metal is covered with white plastic to match the color of the teeth. It does not provide sufficient aesthetics and deteriorates quickly, so it is rarely used;
- Plastic is a material for temporary bridges that are installed before making permanent ones. Not suitable for regular wear due to its fragility and tendency to accumulate harmful bacteria.
The material is usually selected in accordance with the wishes and financial capabilities of the patient, as well as depending on the area of prosthetics.
Price
The approximate cost of a solid-cast bridge varies from 7,000 rubles. The price differs depending on the length of the defect and the metal alloys used.
The cost will be higher if the structure is additionally coated with ceramics to improve the appearance. Also, the price differs for combined dentures and products with veneering.
To choose a prosthetic method, consult an orthopedic dentist. The doctor will conduct the necessary research, select which prosthesis is best suited in a particular situation, and tell you about all the intricacies of subsequent prosthetics.
Indications and contraindications for the installation of bridges
Direct indications for the installation of bridges are the absence of a chewing tooth or one to four front teeth with supporting teeth on either side of them that can withstand heavy loads. Dentures with a bridge have a number of relative and absolute contraindications. This includes:
- no more than 4 incisors, 2 premolars, 1 molar in a row;
- bruxism (involuntary grinding of teeth, the damage of which can be neutralized by wearing special mouthguards);
- bite pathology (in this case, orthodontic treatment will have to be carried out before prosthetics);
- periodontitis and severe periodontal disease;
- pathological abrasion of hard dental tissues;
- diseases of the bone tissue of the upper jaw (for example, osteoporosis, osteomyelitis);
- acute inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity;
- poor oral hygiene.
This may also include general contraindications to surgery itself: for example, problems with blood clotting, allergies to painkillers, acute chronic diseases, taking anticoagulants, mental illness and much more.
Free consultation
Our specialists will conduct a free consultation and select the best treatment option for you.
Sign up now! Online registration
+7 (495) 649-41-19
Content
1 Indications for bridges and limitations for their use
2 Features of installing a fixed bridge 2.1 Method of grinding dental units for a future prosthesis
2.2 Preparation of supporting units for installation of prostheses
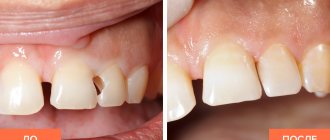
3 Bridges, before and after photos:
4 Which bridge structures should be preferred?
5 Solid structures
6 Metal-ceramic products: characteristic features
7 Ceramic fixed bridge: features 7.1 Some “cons” of zirconium bridges
8 What are the features of adhesive bridges?
9 Use of inlays for fastening dentures
10 Bridge prosthesis on implants
11 Basic rules of care
12 Price for a bridge
Stages of installing a dental bridge
- Examination and diagnosis.
This stage is very important. This allows you to eliminate any restrictions and determine the type of bridge the patient needs. The doctor will examine the entire mouth. He will direct you to a targeted x-ray if it is a specific tooth, or rather a CT scan (images that are more precise and less radial) to see the teeth in all projections. You may also need a panoramic x-ray to see the entire situation. These technologies are available at the Implantmaster clinic. Our specialists have the ability to model a new smile in 3D. This way, the patient will see the results that can be achieved. Additional tests may be prescribed. Based on the data obtained, a further treatment plan is formed.
- Preparing the oral cavity for prosthetics.
The design will last a long time if the patient does not have untreated teeth, gum inflammation, tartar and soft plaque. Preliminary treatment of caries and cleaning of the oral cavity is carried out, during which all dental deposits are qualitatively removed.
- Prepare your teeth before placing a bridge.
The selected teeth are ground under the holder and, if necessary, wiped down. Depulpation is a procedure for removing the neurovascular bundle from a tooth. Why is this necessary before installing a bridge? During tooth rotation, overheating of the pulp is possible, causing the development of pulpitis. In this regard, the pulp is sometimes pre-squeezed.
- Receiving a fingerprint (scanning).
In our clinic, ground down teeth are scanned instead of taking impressions. The 3Shape trios scanner scans everything in the mouth, individual teeth and bridge spaces. The workflow becomes more efficient and comfortable for patients. It makes it easy to take full-color 3D impressions for subsequent creation of prosthetics. When the bridge is ready, the patient is asked to try it on.
- Fitting
If during fitting no manufacturing inaccuracies are found: it fits tightly, fits well over the bite and the patient likes the appearance of the prosthesis, the bridge in the oral cavity is installed with special dental cement. After this, the doctor conducts a detailed consultation and gives recommendations on how to properly care for the oral cavity and the product.
Ceramic fixed bridge: features
As you know, a ceramic bridge is considered the most expensive: its price is determined by the use of a material characterized by ideal aesthetic qualities and increased strength. We are talking about zirconium dioxide.
At the same time, in the process of creating these structures, a milling machine with modern software is used. However, not the entire bridge is milled, but only the base, made of zirconium dioxide, which is subsequently lined with porcelain. Thanks to this technology, the aesthetic parameters of the structure are significantly improved.
Due to the extreme strength indicators (more than 900 MPa), a metal-free prosthesis can have any length, which is not possible when using other types of ceramics. The following is an algorithm for producing such bridges.
So, the process of manufacturing a metal-free structure includes the following steps:
- Initially, the doctor prepares the supporting crowns, which involves removing the nerves and further preparation in order to ensure the most precise fit of the prosthesis;
- Next, the product is reproduced in three-dimensional format, during which special software and the resulting scan of the jaw are used;
- The frame of the product is produced;
- After this, the frame made on the basis of a three-dimensional model is fired, which makes it possible to obtain the necessary characteristics of wear resistance and strength;
- Ceramic mass is applied to the base layer by layer;
- The structure is being painted.
Since zirconium material has the same light transmittance as natural enamel, bridges made from it perfectly recreate the lost units in the frontal zone.
In addition, ceramic products are distinguished by a tight fit to the supporting crowns, which prevents the penetration of infection under them. The ability to maintain a natural shine for a long time is also one of the “advantages” of metal-free dentures.
Some "cons" of zirconium bridges
When using ceramic bridges for prosthetics, the following disadvantages may occur:
- Overpriced;
- High risk of chipping. Despite the fact that zirconium material has extreme strength, the outer porcelain layer is quite fragile and there is an increased likelihood of chipping. According to statistics, such defects occur in approximately 10% of patients within 6 years from the date of installation of ceramic products;
- Some aesthetic inconsistency. If ordinary zirconium blocks are used, they have a milky tint and do not provide the translucency inherent in natural crowns. However, nowadays you can find more expensive and natural-looking zirconium material that allows you to achieve ideal aesthetics, for example, Katana® UTML (Japan) and Prettau® Anterior (Germany).
Caring for bridges
When replacing teeth with bridges, dentists recommend the following measures:
- Daily hygiene morning and evening. You need to use a brush and paste. After each meal, rinse your mouth with clean water or mouthwash and use dental floss (floss).
- Hard-to-reach places and interdental spaces are cleaned with wide movements, without pressing on the crowns.
- It is important to exclude hard nuts, seeds and other foods that can cause chips and cracks.
- For the first time after installation, you should not drink coffee and tea, red wine, or freshly squeezed juice.
- At least once every six months, visit the dental clinic for preventive examinations and undergo professional cleaning.
- All structures have a certain duration. It depends on the material used and manufacturing technology. This period ranges from 5 to 15 years. Sooner or later the product will need to be replaced, otherwise it may simply break and fall off.
Basic rules of care
Careful care of the prosthesis is a guarantee of its long-term operation. At the same time, it is important to pay attention to hygiene: it is necessary to clean the bridge, as well as the places where it adjoins the supporting dental units, at least 1-2 times a day. This will avoid the accumulation of food debris in this area and the development of infectious processes.
Experts recommend using gentle products that do not contain solid particles to eliminate the possibility of damage to the prosthesis. Also an important condition for the durability of the product is regular visits to a specialist for preventive purposes.
What material to choose a bridge from?
Metal-ceramic bridges
The next stage of construction is metal-ceramic bridges. This type of “bridge” has made it possible to significantly expand the scope of application of bridges in solid castings by covering them with ceramics. The statement “cover them with ceramics” is not entirely true, since this design of the prosthesis implies not only an all-metal coating, but also a modification of the design, due to which the metal-ceramic bridge consists of a metal frame and a ceramic coating. This led to its advantages and disadvantages.
Advantages:
- Significant improvement in aesthetic performance compared to permanent bridges
- Expanding the scope of application, which implies the possibility of using such a design when restoring defects in the anterior group of teeth
- The almost complete correspondence of this type of prosthesis to the natural appearance of the teeth allows the patient to quickly psychologically adapt to them, which largely restores the level of quality of life.
Flaws:
- The absence of a chemical bond between the metal structure and the ceramic veneer suggests the possibility of the ceramic cracking
- The presence of metal in the oral cavity can cause allergic reactions, galvanic effects and negative effects of metal on dental tissue and staining.
The aesthetics of metal-ceramic prostheses is relative. Compared to solid bridges, the design of the prosthesis is much wider, however, the passage of metal through ceramic masses and designs with a “garland” do not allow comparing the aesthetic qualities of such a prosthesis with an all-ceramic one.
However, it is important to note that replacing the cobalt-chromium alloy more commonly used in metal frames with noble high-gold alloys provides superior aesthetics.
The natural color of gold, which shines through the ceramic masses, allows you to recreate the natural color of your teeth. Together with the advantages of metal-ceramic prostheses and the absence of the disadvantages of all-ceramic bridges, this design occupies a leading position in terms of aesthetics and functionality.
All-ceramic bridges
All-ceramic bridges have firmly established themselves as one of the most aesthetically pleasing and functional designs. This explains that manufacturing companies often improve methods for making just such prostheses. Computer modeling and milling are increasingly being introduced into everyday dental practice. The development of these technologies makes it possible to increasingly reduce the time required to build bridges, right down to visiting the dentist.
Methods of layering ceramic masses with restoration of the smallest dental structures make it possible to create prostheses that are as close as possible to natural teeth. Thanks to the strength characteristics of modern ceramic materials, metal-free bridges have excellent functional characteristics, but this also has a downside.
While metal-ceramic implants have a certain degree of flexibility, all-ceramic implants have a much lower elastic modulus. For this reason, loads that lead to chipping of ceramics in metal-ceramic structures can lead to rupture of metal-free “bridges” with the need for their complete replacement, and ceramic fragments can be repaired in a clinical setting.
And yet, despite this drawback, all-ceramic bridge designs are the most progressive and will be the vector for the development of materials and production technologies.
Adhesive bridges
An alternative to the work of a prosthodontist is increasingly offering adhesive bridges, which can also be made by appointment with a dentist, if he has sufficient skills. Adhesive bridges are made of composite materials using fiberglass tape, similar to the construction of a bridge, or using conventional orthodontic wire.
This combination allows dentures to be made directly in the patient’s mouth in one visit with minimal preparation of the supporting teeth, which significantly reduces the financial component of the problem.
However, the functional qualities of such prostheses are not always satisfactory, and the aesthetic qualities of composite materials often cannot compete with ceramic materials due to the impeccable polishing and natural shine of the latter. But with the correct choice of such a treatment method for the restoration of short-length defects in the dentition in the lateral areas extending beyond the aesthetic zone, in areas with less functional load, this design of bridge prostheses turns out to be extremely logical and convenient: the dentures have a long service life, providing patients with a beautiful appearance view.
What are the features of adhesive bridges?
An adhesive bridge has a more gentle method of attachment to the supporting crowns. When using this design, there is no need for total preparation of the natural units necessary for its fixation.
Below we describe cases in which it is better to use an adhesive bridge:
- Minor defects in dental units located in the chewing and frontal zones;
- In the presence of inflammatory processes in the area of periodontal tissue;
- If standard methods of restoring teeth are unacceptable, due to a particular disease in the patient;
- Ideal for people who have had a heart attack;
- Patients who prefer a gentle method of prosthetics.
To fix the above bridge, only one visit to a specialist is required. If the bridge structure is planned to be made in a laboratory, you will have to visit the doctor again.
3 methods of fixing an adhesive prosthesis:
1. Using a composite adhesive
In this case, the specialist glues strips of fiberglass or plastic to the inner surface of the teeth. The main purpose of these elastic plates is to connect artificial crowns with natural ones. This method is not used for units located in the chewing zone;
2. Beam technique
To do this, small recesses are made in the supporting crowns, into which a special wire beam is subsequently attached. In this case, the priority option would be for the patient to have dental units with impressive fillings, which makes it possible to obtain ready-made recesses for the beam. But this method has one significant “minus” - an increased likelihood of pulpitis in the abutment crowns.
3. Splinting method
This method is based on the use of a special tape made of fiberglass material, for fixation of which the dentist drills a small cavity in the support units.
The advantages of such designs include:
- Possibility of instant removal of the bridge from the oral cavity if necessary;
- Good aesthetics, since the prosthesis does not contain any metal components;
- There is no need to remove the nerve;
- Easily repairable in case of fracture;
- It is possible to maintain some mobility of the supporting units, which is achieved due to the presence of an elastic composite material.
When can you build a bridge?
It is important to correctly draw up a prosthetic plan and ensure the stability of the supporting teeth.
Movable units or those affected by caries cannot serve as the basis for the structure. An upper or lower bridge is installed on natural teeth. When asked by patients: “Is it possible to install a bridge structure on an implant on one side and a tooth on the other?” there can only be a negative answer. A real, living dental unit has some mobility, and the implant is fixed rigidly, motionless, as in the following photo:
The bridge will loosen the implanted artificial root and place an inadequate load on the natural tooth. Plus, the service life of the implant is long, often lifelong. Real units are more vulnerable. The supports can be either two real teeth or a pair of implants.
If a tooth has been removed, but the crowns and roots of the units located next to the gap are strong enough, then a bridge is one of the rational and inexpensive methods of prosthetics.
Classification
Solid-cast bridge structures are prostheses made without the use of connecting techniques, which eliminates breakage at the soldering site, errors in the manufacture of the device and guarantees the presence of a base from the only material chosen by the patient.
Most often, the design is made of gold, silver-paldium or cobalt-chrome alloy. The latter are often coated with gold plating or ceramics to improve aesthetics.
Bridge stamped and soldered
This method is considered the oldest and has been used since Soviet times. Made from a thin-walled sleeve shell. This occurs during the process of compressing a plaster copy of the tooth. At the joints they are soldered, which ensures a continuous connecting structure.
Disadvantages can be considered:
- the impossibility of creating an exact shape due to a loose fit,
- using this type of prosthetics, there is a high probability that caries will form in the future and this will lead to tooth loss,
- the walls turn out to be thin and, as a result, quickly wear off, which leads to destruction and breakage.
- Patients experience bleeding from the gums and an unpleasant metallic taste due to metal oxidation.