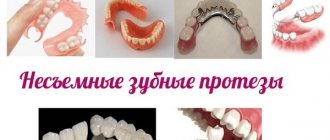
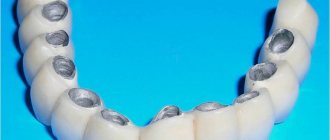
What are fixed dental bridges?
This is a prosthesis that restores lost teeth. It is a structure (bridge) of three or more teeth. The bridge is installed based on the patient’s outermost natural teeth. That is, in essence, this is a bridge thrown between the supporting teeth. In this case, the supporting teeth must be prepared (ground). This design allows you to quickly recreate a missing tooth or several teeth.
We would like to point out that a more modern, functional and aesthetic method of dental restoration is implants. If possible, it is better to place an implant in place of the missing tooth. And then - cover the implant with a crown.
How many teeth can be restored with a bridge?
A bridge is indicated for partial loss of teeth. If one or two teeth are missing, three at most. To restore the loss of 4 or more teeth, other options are needed.
Could there be bridges supported by implants?
They can. Bridges are indicated for implant-supported prosthetics. An implant-supported (implant-supported) design is preferable to a bridge supported by your teeth.
For example, a patient is missing 4 teeth in a row. You can do this: install 3 implants and attach a bridge of 4 teeth to them. This will be an acceptable option in terms of price/quality ratio.
Dental bridge: general characteristics
With the help of prosthetics, a number of visual and functional dental problems are solved. The name for the installation was not chosen by chance, because the principle of the device is reminiscent of engineering structures. Artificial crowns are held on a base, and adjacent intact incisors, canines and molars act as supporting elements.
The choice of the appropriate type of construction depends not only on the financial capabilities and personal preferences of the patient, but also on his medical history. That is why a full restoration is impossible without a thorough diagnosis, medical examination and adjustment of the finished system, created from casts, to the required parameters.
Types of Dental Bridges
Modern dental clinics offer many options for restoring lost units using prosthetic bridges. They differ according to different criteria:
- by manufacturing method - solid cast, adhesive, stamped, pressed, combined;
- by material - metal, metal-ceramic, ceramic, plastic, zirconium dioxide and aluminum oxide;
- according to the method of fastening - locking, adhesive, on healthy teeth, on implants.
There is also a classification according to purpose. For example, artificial prostheses are restorative, splinting, temporary and permanent.
Manufacturing technology
The main selection criterion is the amount of time spent on creating a design according to the individual standards of a particular patient. There are 3 main groups:
- Solid cast. Ideally adjacent to hard and soft tissues, airtight. In this way it is possible to reproduce the natural shape with high precision. They are strong and durable. The disadvantages include the need to grind healthy teeth, as well as the use of high-precision casting and the high cost of production.
- Adhesive. Modeling takes place directly in the oral cavity. This is a gentle alternative to the previous method when only one element is missing. There is no need to grind the adjacent crowns; the plates are glued to them using a special cement composition.
- Stamped. An outdated option that most doctors refuse because the product weighs a lot and often leads to injury to the supports.
Material for production
The type of raw materials from which products are made determines their durability, practicality and care. Modern clinics offer many options to suit every taste and budget. Types of bridges and their features (photos are presented in the article):
- Metal. They were actively used decades ago, cast from precious metals, gold and silver. They are distinguished by high strength and affordable price. However, this type has a significant drawback: the dentition looks unattractive. Damage to the supporting elements is also possible.
- Metal-ceramic. The base consists of an alloy, which is complemented by ceramic inserts. This option is considered ideal with an optimal ratio of cost and high quality. The color is matched to the shade of the enamel.
- Ceramic. There is no all-metal cast frame. These teeth look quite natural, but do not tolerate strong mechanical stress due to their fragility. You need to be very careful when wearing it.
- Plastic. They are used primarily as temporary substitutes for permanent products while they are being manufactured in the laboratory. They are produced very quickly, do not cause allergic reactions, weigh little, look attractive, but do not last long.
- Made from zirconium dioxide. All-ceramic combined dental bridges on this basis are among the most modern. They absorb all the advantages of their predecessors: light weight, reliability, aesthetic appeal, hypoallergenicity, long service life.
- Made from aluminum oxide. They are not widespread enough because they have an exorbitant price. In terms of durability, strength, beauty and other characteristics, they have proven themselves exclusively on the positive side.
Mounting type
The structures are attached in different ways, the most common in dentistry:
- Consolidation on healthy units. The product consists of crowns with holes intended for teeth and bridges that connect them. For strength, the elements are made solid. When choosing this type, preliminary grinding and depulping will be required. Dentists are resorting to the latter procedure less and less; modern technologies make it possible in some cases to skip this stage.
- On implants. When choosing this method, intact incisors, canines and molars remain intact. They will not be ground or depulped. However, the cost of treatment increases significantly.
- Adhesive method. The bridge is not put on supports, but is attached to the rear surface using special composite compounds.
- Lock fastening. This is a removable bridge, which, if necessary, can be detached and returned to its place. Grinding of the abutment crowns is also not carried out.
Which bridge material to choose
Metal prostheses are a thing of the past; they have been replaced by progressive designs made from modern materials. Anyone can put a bridge on their teeth, taking into account price and functionality. I suggest installing bridges with segments from 3 to 5 teeth
(now we are not talking about total prosthetics during implantation):
Metal-ceramic bridges
Solid versions will be made by specialists in the laboratory using an impression, taking into account all anatomical features. Layers of ceramics are applied to the crowns by hand and baked at high temperatures. Such bridges are durable and belong to an affordable price category. They are often chosen for molar prosthetics and are suitable for installation on implants. Price – from 17,900 rubles. for 1 tooth.
Ceramic dental bridges
The advantage is rapid production using CEREC technology, indistinguishable from natural ones. Ideal for installation on teeth that fall within the smile zone. But in terms of strength they are close to natural teeth and require careful handling. They are performed on teeth (from 16,900 rubles per tooth) or on implants (from 24,900 rubles per tooth).
Zirconium bridges
Durable, suitable for installation on molars or anterior teeth. For the beauty zone, it is advisable to cover the base with ceramics for complete visual resemblance to real enamel. The CEREC manufacturing process allows defects to be eliminated quickly. Mounted on implants only. Cost from 24,900 rub. per tooth
Plastic temporary bridges
Only temporary structures are produced from plastic (RUB 9,900 per tooth). Temporary bridges are also needed for immediate loading when restoring the dentition using the “All on 4 (6)” protocols.
Indications and contraindications for installation
The procedure is indicated when a person is missing one molar or 1-4 front incisors and canines. In this case, intact teeth should remain on the sides, which will subsequently act as supporting elements and withstand the greatest pressure when chewing food. Also, this cannot be avoided when the previous design has become unusable.
Despite all the advantages of orthopedic intervention, there is a list of cases when it is contraindicated:
- absence of more than 4 crowns;
- bruxism (involuntary grinding of the jaws, which is most often observed at night);
- malocclusion (before prosthetics you will have to undergo long-term orthodontic treatment);
- acute form of periodontitis or severe periodontal disease;
- pathological abrasion of the enamel layer;
- diseases of the skeletal system (for example, osteomyelitis);
- inflammatory processes in the oral cavity;
- poor hygiene preventing installation.
In addition, this also includes general contraindications to surgical intervention. These are problems with blood clotting, allergic reactions to drug components, manufacturing materials, chronic diseases during exacerbation, taking medications that prevent blood clots, and mental disorders.
Advantages of bridges
The positive properties of high-quality and professionally installed bridges include:
- the possibility of restoring the integrity of the dentition with minor defects;
- aesthetic value - a good prosthetic complex is invisible in the mouth while smiling, even if it replaces the front teeth;
- comfort of wearing - discomfort and complications from bridges occur much less frequently than when using structures with the possibility of self-removal;
- quick process of adaptation to operation;
- reliable fixation - the risk of the structure spontaneously falling out is minimal;
- service life - from several years to more than 10 years, depending on the specific type of prosthesis.
Advantages and disadvantages of dental bridges
Advantages of bridges in prosthetic dentistry:
- There is no need to wait for the installed structure to take root. That is, there is no need for osseointegration, which can last up to six months. It turns out that the adaptation process lasts quite quickly (up to 12 hours).
- This is the most economical option for restoring rows when individual units are lost than implantation.
- Modern technologies make it possible to obtain aesthetically attractive artificial teeth with full functioning. Hidden elements (fastenings, etc.) are not visible to others, so no one will even notice the medical intervention.
- The procedure has virtually no contraindications. A bridge is also placed in cases where implantation of an implant is not possible.
- Normal diction is maintained.
Weak sides:
- It is necessary to grind down the adjacent crowns remaining in the mouth. Very often, dentists resort to depulpation (removal of the nerve, cleaning and cementing of the canals).
- The normal load on the jaw bone is not fully restored. When a person chews food, the supports are loaded; the central part is practically not involved in this. As a result, the risk of bone tissue atrophy increases.
Results and discussion
In all modeling options, it is clear that the maximum stress occurs around the implant located closer to the cantilever element and on the surface of the abutment of this implant. The table shows the dependence of the maximum stresses on the surface of the bone on the load exerted on the structure with a cantilever element with a length of 4, 10, 12 mm.
Dependence of stresses in the bone tissue around implants on the magnitude of the load and the length of the cantilever element of a fixed prosthesis
The influence of the length of the console is as follows: the minimum stresses at a chewing pressure of 60 N in the presence of a console of 10 and 12 mm increase to 2.8 and 3.9 MPa, while with a console of 4 mm they do not exceed 1.6 MPa; the maximum stresses appear at a chewing pressure of 350 N and are 8.7 MPa with a console of 10 mm and 12.3 MPa - 12 mm, while with a console of 4 mm the stresses do not exceed 6 MPa. When the length of the cantilever element increases to 14 mm or more, stresses arise up to 20 MPa in the bone and up to 200 MPa in the implants, which indicates the possibility of their destruction.
When modeling the length of the cantilever part of the prosthesis of 10 mm, but with the application of different values of masticatory pressure (60N vertical and 24N horizontal; 350N vertical and 104N horizontal), stresses in the bone tissue were obtained in excess of 23 MPa, even with sufficient sizes of supporting implants (diameter 3.5 mm and length 9 mm for the one located closer to the cantilever element; diameter 5 mm and length 14 mm for the one located further from the cantilever element). At such stresses, destruction of bone tissue is possible, since, according to the literature, peak loads during the chewing process can exceed the loads applied to the models in this study, and the strength limits of cortical bone are 45 MPa (cancellous bone 15 MPa), with a safety margin within 50 %. Thus, for this orthopedic design, implants with a diameter of 4.5-5 mm and a console length of no more than 12 mm are recommended.
According to a number of authors, it has been established that studies carried out by the finite element method allow one to draw conclusions about the general patterns of load distribution, but cannot calculate the clinical individual structure, therefore it should be borne in mind that accurate data on the parameters of the stress-strain state of bone tissue are purely individual for each patient [17].
Installation of a dental bridge: stages of the procedure
The process of manufacturing and installing the structure is simple and does not require additional actions aimed at violating the integrity of soft tissues, suturing, etc. The adaptation period is easy and painless. Despite its simplicity, the doctor and patient will have to go through several successive steps before the lost units are completely restored. On average, 3 visits to the dental office will be required.
Stage 0: sanitation of the oral cavity before the procedure
If during the initial examination the specialist suggested installing a bridge, he should carefully examine the oral cavity. One of the main conditions for prescribing treatment is the absence of carious lesions, inflammatory processes and other dental disorders.
The duration of this period depends on the condition of hard and soft tissues. If a person regularly visits the clinic for preventive purposes, it is likely that a routine cleaning will be required without applying filling material. If there are advanced diseases, they must be treated, and only then can you contact an orthopedist.
Stage 1: preparation of abutment teeth and production of a bridge.
When the dentist is sure that all units are completely healthy, a support is selected. The elements are ground, depulped, and the roots are filled.
Impressions are taken from the finished fastenings. They are sent to the dental laboratory.
While the permanent product is being manufactured, the patient will have to wear a temporary one with a plastic base. This may take 1-2 weeks depending on the workload of the institution and the complexity of the technological processes.
When there are not enough natural teeth, or they are of too poor quality, they cannot be cured and properly prepared for the procedure, implantation is indicated. Typically two anchor points are implanted.
Stage 2: installation of a fixed prosthesis
At the last visit to the dental clinic, the plastic structure is dismantled, and in its place is installed one made in the laboratory using impressions. The orthopedist checks how tightly the material adheres to the surfaces. There should be no obstruction to the closure of the jaws and no visible color differences, otherwise the artificial areas will be noticeable.
A full fitting, fitting and fixation is carried out. For greater reliability, special cement is applied.
If the client feels discomfort, prosthetics are not performed. The system is dismantled and returned to the laboratory for adjustment. If there are no unpleasant sensations, the treatment is completed.
Adaptation occurs even while wearing plastic. This means that the patient will be able to easily return to their normal lifestyle within a few hours. The doctor gives recommendations on the use and care of the product, prescribes routine examinations and provides other important information.
Types of prostheses based on the principle of fixation
The bridge is fixed in the mouth in different ways. If there are teeth to which it can be attached, they are pre-treated. The supporting elements of the prosthesis are made for specifically prepared teeth - for healthy supporting teeth, fixation is used on half-crowns or on inlays. In case of severe destruction of the crown of supporting teeth, pins are used, and in the absence of such teeth, implants are used.
Important! The method of fixing the prosthesis in the mouth is determined by the doctor, taking into account the clinical picture and the condition of the patient’s dental system. If it is possible to choose a fixation method, our specialists discuss all options with the patient, giving him the right to choose.
Dentures on crowns and inlays
When crowns are used as a supporting element, the “native” crowns of abutment teeth are completely replaced. This method is suitable for patients whose teeth are quite damaged. If the teeth are in good condition, half-crowns are used - that is, structures that replace only part (½-⅓) of your own dental crown.
An even more optimal option for fixation is the use of inlays: in this case, there is no radical grinding of the teeth - the doctor forms a stepped depression on the chewing surface, into which the inlay (fixing element) is placed. Our specialists prefer, whenever possible, to use methods with minimal destruction of supporting teeth
Pin prostheses
When the outer part of the supporting teeth is completely destroyed, but their teeth are relatively intact, the optimal option for fixing the bridge in the mouth is pins. A pin is a rod-shaped structure inserted into the tooth canal. It can be made of metal, glass or carbon fiber. The purpose of the pin is to strengthen the tooth roots. Subsequently, the prosthesis is attached to the pin, and the attached part is also made in the form of a tooth crown. This allows you to achieve such an aesthetic effect that the prosthesis is indistinguishable from natural teeth.
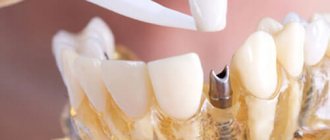
Bridges on implants
An alternative to post dentures are dental bridges placed on implants. These structures are used in the complete absence of supporting teeth. with marginal defects of the dentition. This type has a significant advantage - with their help you can use prosthetics for defects of almost any extent. Other advantages include the strength and durability of such prostheses.
A relative disadvantage of this type of prosthesis is the significantly longer preparatory stage, but the final result outweighs this disadvantage. The cost of bridges on implants is certainly higher compared to other types, but their quality and service life differ for the better.
Cantilever prostheses
Bridges with a cantilever type of fastening are a kind of exception among the entire group: cantilever prostheses are attached only on one side - this creates a “single-support” bridge. This type of prosthesis is suitable for prosthetics of the anterior teeth (incisors and canines), since they bear minimal chewing load. Occasionally, they are used to replace the first premolar; for this purpose, the support is installed on the second premolar and first molars.
Adhesive bridges
This is a type of denture that is “glued” to the supporting teeth using composite compounds. In dentistry, Academy Dent, fixation of such prostheses is carried out using light-curing polymers. The advantage of adhesive dentures is that their installation either does not require preliminary preparation of the supporting teeth, or this preparation is minimal. Therefore, the adhesive prosthesis is installed in one clinic visit.
Advantages of adhesive dentures:
- hardly noticeable from the outside;
- easy to replace;
- the supporting teeth are not pulpless;
- the elasticity of the composite support does not interfere with micromovements of the supporting teeth;
- easy to repair.
Unfortunately, they are applicable for replacing only one tooth.
Recommendations after installation
Artificial structures also need to be properly maintained. If hygiene rules are not followed, this will significantly reduce the life of the product, and the patient will again have to use the services of an orthopedist.
Dentists recommend the following measures when performing dental prosthetics with bridges:
- Daily cleaning in the morning and evening. You must use a brush and paste. After each meal, you need to rinse your mouth with clean water or mouthwash, and use floss (dental floss).
- Hard-to-reach areas and interdental spaces are cleaned using sweeping movements without pressing on the crowns.
- It is important to exclude hard nuts, seeds and other foods from your diet that can cause chips and cracks.
- During the first time after installation, you should not drink coffee and tea, red wine, or freshly squeezed juice.
- You should visit the dental clinic for preventive examinations at least once every six months and undergo professional cleaning.
All structures have a certain service life. It depends on the material used and manufacturing technique. This period varies from 5 to 15 years. Sooner or later the product will have to be replaced, otherwise it may simply break and fall out.
The device is dismantled prematurely with the following problems:
- loosening;
- broken crowns;
- chipping of small fragments, appearance of microcracks;
- inflammation of soft tissues, bleeding gums;
- washing out the cement composition on which the system rests.
Only a specialist can safely remove the prosthesis; you cannot do it yourself at home. If you follow all the rules listed above, your smile will remain dazzling for a long time, and replacement will not be needed soon.
Ceramic dentures
Ceramic bridges can be classified as cast, as they are produced by casting ceramic mass into molds with further milling (turning). Zirconium dioxide prostheses are considered one of the most modern - they are maximally biocompatible and have excellent aesthetic properties. These advantages are overshadowed only by the high requirements for their manufacturing technology, but this problem is solved through the active use of computer technology. The color of the material is also selected on the computer.
The high accuracy of fitting of permanent ceramic bridges, including those made of zirconium dioxide, is due to the use of CAD/CAM technology - specialized computer software with a programmable manufacturing process. This technology is actively used in our clinic and has already proven itself to be very positive.
The advantage of ceramic bridges is that they can be used to replace defects that cannot be replaced by other prostheses. For example, 4 missing incisors or 2 small molars can be replaced with ceramic dentures. A relative disadvantage is their slightly lower strength compared to metal-ceramics.
This is interesting! Ceramic dentures are very resistant to all types of loads - static and dynamic, but they can crack from a strong point blow, so you should not click your teeth while trying to crack a nut or open a beer bottle.
Combined dentures
This group includes metal-plastic (metal with plastic lining) and metal-ceramic structures. For many years, the combination of plastic as a facing material and a metal frame has made it possible to carry out effective, visually beautiful prosthetics, especially for anterior teeth. However, with the advent of ceramics, the popularity of metal-plastic structures for dental prosthetics is waning.
The basis for a metal-ceramic bridge is a metal frame onto which ceramics are applied. The frame provides maximum rigidity and strength, and with the help of special processing of the ceramic part, the dentures are given an excellent appearance. At AcademyDent, preference is given to metal-ceramic bridges; the clinic’s specialists have all the necessary skills for their manufacture and installation.
How much does it cost to build a bridge?
The price for dental bridge crowns is determined by the cost category of the impressions, the design itself, installation and fitting services. There are the cheapest options available to most patients, but they will be significantly inferior to the more expensive ones in terms of operational and other characteristics.
On average, a budget bridge can be installed for 3 thousand rubles. Zirconium and metal-ceramic elements will cost 20 thousand or more, especially if implantation was performed.
The main factors on which the final installation cost depends
What affects the cost of orthopedic intervention:
- Material of manufacture. Plastic can be purchased several times cheaper than metal or ceramics. The last option with a zirconium dioxide frame is the most expensive.
- Application of implants. They can significantly increase the number of zeros on a check.
- Number of elements to install.
- Clinic location. Treatment in Moscow is much more expensive than in the regions.
- Pricing policy of a dental institution. This is due to market conditions, competitiveness, status and reputation of dentists.
Prosthetics allows you to restore lost teeth in a short time and without large material costs. When installing the structure, certain conditions must be met, and the patient must go through several successive stages. Unfortunately, despite the obvious advantages, bridges are not without their negative aspects. In addition, there are contraindications when it is not possible to restore the aesthetic appeal of a smile without harm to health in this way.
Examples of work “Before” and “After”
Partial restoration of teeth on both jaws
Case: partial absence of teeth on both jaws.
Prosthetics of chewing teeth with zirconium dioxide crowns
Case: destruction of the posterior teeth on the upper and lower jaw.
Complete prosthetics of the upper and lower jaws
Case: absence of teeth in the upper jaw (completely), absence of an orthopedic structure in the lower jaw on existing implants (installed in the USA two years earlier) Work: production of a complete removable denture in the upper jaw as a temporary structure until the installation of one-stage implants with subsequent prosthetics.
Combined prosthetics and dental implantation (June 2012)
Case: a large number of teeth are destroyed, partial adentia, chewing function is impaired due to the absence of almost all chewing teeth Work: a detailed diagnosis of the condition of the teeth and bone tissue, studies of the tension of the masticatory muscles, the position of the articular head in the temporomandibular joint were carried out.
How to care for a bridge
The presence of artificial teeth does not relieve a person from the obligation to maintain oral hygiene. On the contrary, a foreign structure in the mouth imposes a number of other, not particularly burdensome, hygienic requirements. Careful care can significantly extend the life of any prosthesis.
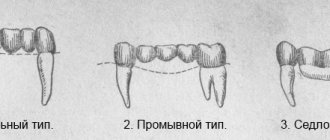
The special design makes maintenance easier. The intermediate part is performed either tangentially or flushing. In the first case, there is a small gap between the middle part of the product and the gum mucosa, from which food debris can be easily washed out. Bridges that replace lateral teeth are made with rinsing. In the second case, the front edge of the bridge touches the gum tissue, but a small space is left in the back, which is also quite easy to clean.
Our specialists give patients the following care recommendations:
- carry out daily routine brushing of teeth in the usual way (including in the presence of removable dentures);
- After hygienic cleaning, constantly use mouth rinse;
- hard-to-reach areas near the gums are cleaned with smooth sweeping movements;
- the interdental spaces, including those near the supporting teeth, are cleaned with floss;
- You should not chew seeds, nuts, or bite hard foods;
- Visit your dentist every six months for a preventive examination.
A bridge can serve its owner for many years, but sometimes it requires replacement. That is why you should not neglect the supervision of a dentist. Improper care or expiration of the recommended service life can cause structural failure, which sometimes leads to unpleasant consequences that can be avoided by promptly contacting the Academy Dent clinic. We do not offer “consumer goods” for pennies - we produce high-quality products at an adequate cost!
The concept of a composite structure
A prosthesis for replacing several teeth of a standard type for installation with existing inclination of adjacent teeth is not used. It will not be possible to eliminate the non-parallel position of the supporting teeth by grinding. It becomes possible to touch not only the dentin, but also to open the pulp channels.
The problem can be solved with composite bridge systems that have articulation. This connection allows you to install the prosthesis on non-parallel units of the dentition. These types of structures are made from dental metal.
It contains a similar version of the intermediate part, which looks like an occlusal pad over the place of lost teeth. Also in the bridge-like composite overlays there are fastenings of various types. There are also components of the mechanism connecting the parts of the bridge.