Although orthopedics as a science was formed not so long ago, people have been practicing dental prosthetics since ancient times. Animal bones, semi-precious stones, hard wood - everything that ancient doctors did not use as prosthetic material. But the methods of fastening were quite monotonous - using gold, less often silver, wire.
What are dentures made of now? The composition for prosthetics is selected for a specific clinical case, taking into account the patient’s wishes, indications and contraindications.
Content
- Composite
- Ceramics. Metal ceramics
- Ceramic dentures
- Metal alloys
- Plastic
Modern materials for prosthetics help facilitate this process. Today, dentures are high quality structures that are barely distinguishable from real teeth and are comfortable to wear. They are made from various materials.
Modern prostheses:
- High quality;
- Wearable, with a long service life;
- Aesthetic;
- Ensuring the full functioning of the dental system.
Each of the materials from which dentures are made has its own characteristics.
This group includes:
- Ceramics;
- Metal ceramics;
- Plastic;
- Composites;
- Metal alloys.
The choice of the optimal option is carried out taking into account many factors.
PROMOTION
All-on-4 prosthetics turnkey!
120,000 rub.
What are dentures?
These are unique structures used in dentistry that replace a person’s own teeth. They come in two types: removable and non-removable. The name “removable” speaks for itself: such dentures are removed from the mouth to clean and remove food debris. This is quite convenient, but at the same time, this property can also be considered a disadvantage, because for some, the need to clean the prosthesis every day can be tedious. Therefore, many people resort to permanent dentures. These include:
- Veneers are used mostly to correct aesthetic imperfections of teeth.
- Crowns placed on a tooth to prevent further decay.
- Bridges are several interconnected crowns that are installed when two or more teeth are missing.
Teeth perform a number of very important tasks. In addition to the obvious chewing function, without which people would not be able to chew food as necessary for its normal digestion and smooth functioning of the digestive system, they perform an aesthetic function. A person feels much more confident in communicating with others, having healthy teeth and a beautiful, attractive smile. Therefore, if you have any problems with your teeth, you should not delay treatment. Properly selected dentures can help restore an attractive smile.
What should we do to find a prosthesis that would fully meet our requirements and be comfortable and safe? First of all, you need to know what materials quality products are made from.
Composite
The composite is durable and has a long service life. Its only drawback is the high price. But if you need a prosthesis for life, it makes sense to resolve the issue in favor of this composition. Composite is a polymer with many additives that provide exceptional strength and make artificial teeth look like real teeth.
Prosthetics are carried out according to the following algorithm:
- A polymer composition is applied to the prepared area in layers, giving it the shape of a lost tooth;
- Each layer is dried with a special lamp.
As a result of this build-up, the tooth becomes stronger and regains its lost shape. The doctor may use a pin to strengthen the structure. The pin is installed into the remains of the tooth or directly into the root canal.
Preparation for prosthetics
Before proceeding with the manufacture and installation of dentures, it is necessary to carry out thorough preliminary preparation. If during the initial examination the doctor reveals diseases of the teeth, gums or other problems with the oral cavity, then you will need to undergo a mandatory course of therapeutic treatment. Also, regardless of the planned type of dentures, you should have your teeth professionally cleaned. If a patient requires microprosthetics using lumineers or veneers to improve their appearance, they will need to undergo whitening procedures in addition to cleaning. The presence of malocclusion and lack of space for implantation may require a course of orthodontic treatment.
Ceramics. Metal ceramics
Ceramics for many years was considered the main material for prosthetics, despite the lack of high strength. This delicate material deteriorated over time, and prosthetics had to be started all over again. Modern ceramic and metal-ceramic prostheses have changed - they are reliable and strong.
The advantage of the material is lightness. Teeth made from it are almost not felt in the mouth. Aesthetic indicators are the best. Ceramics are used for both molars and front teeth.
When performed professionally, prosthetic structures are durable, their shade, translucency and shape are indistinguishable from natural teeth. The manufacturing process does not require much time and lengthy preparation. Treatment is carried out relatively quickly. Ceramics are suitable for patients prone to allergic reactions.
Technology and methods of prosthetics
Innovative technologies are also coming to dental orthopedics. The emergence of new materials and techniques allows for high-quality diagnostics (computed tomography, 3D modeling of future structures, etc.). From the initial examination to the stage of installation of dental prostheses, the orthopedic dentist has the opportunity to use the latest achievements of science. Today it has become possible in practice to manufacture high-precision durable orthopedic structures made of ceramics using milling machines using 3D models.
For all types of dental prosthetics, laboratory stages are mandatory, although today the use of innovative materials and technologies makes it possible to install dental prosthetics in one visit to an orthopedist. In this situation, the construction is manufactured on a special machine.
Metal alloys
As a rule, it is a compound of chromium, nickel and cobalt. The advantage of such materials is their increased resistance to mechanical stress.
Disadvantage: high allergenicity. In patients prone to allergic manifestations, adverse reactions occur frequently.
The preferred material is an alloy of platinum, palladium and gold. The prosthesis from it will be:
- Expensive, but safe and durable.
- Be comfortable and give a feeling of naturalness;
- With a ceramic coating, it will completely match the appearance of natural teeth.
Titanium is a popular and most modern solution in prosthetics.
Titanium prostheses:
- Durable;
- Safe;
- Lungs.
The only drawback is the lack of full compliance with aesthetic requirements. Titanium crowns are placed on the far molars. Here they are not visible to others, but they perform their task flawlessly.
Zirconium oxide remains the traditional choice:
- Lasting;
- Stable;
- Biologically compatible and safe;
- Meeting high aesthetic requirements;
- The color matches the natural enamel of the teeth.
Thanks to laser processing, artificial teeth made of zirconium dioxide completely match the natural shape of the tooth being restored.
What is the best material for prosthetics?
As you can see, the choice of modern materials for dentures is quite large. It is impossible to say definitively which material is better, since each is suitable for a specific purpose. For installing crowns on the front teeth, the best materials for dentures are ceramics, and for molars, metal-ceramics or zirconium oxide are more suitable. A specialist will help you choose which denture material is right for you.
Another important question is what is the compatibility of dentures made of different materials with oral tissues? According to medical research, the most biocompatible bases for artificial teeth are ceramics and zirconium dioxide. Such crowns never cause allergies, this is another big advantage.
Metal crowns
These crowns can be called the best for prosthetics of chewing teeth only in terms of price: it will be the lowest, and then only if the crown is made of an alloy of ordinary metals. If the crown is made of gold, its price will be equal to the cost of products made of ceramics and zirconium.
Metal crowns are durable and this quality can also be attributed to the advantages of this option, but there are still more disadvantages to prosthetics with metal crowns. Patients are often allergic to metal crowns; they can cause a galvanic effect, in which a person constantly feels the taste of metal in the mouth. To install metal crowns, you have to remove a fairly large amount of tissue from the tooth being ground, and this is bad, because the more a tooth is ground, the more fragile it becomes.
Installation of metal crowns can cause increased abrasion of antagonist teeth and, of course, metal crowns have poor aesthetics. Such a prosthesis is always clearly visible in the mouth. Aesthetics is not a determining factor when it comes to prosthetics for back teeth, but if you want the crown on a chewing tooth to not stand out from the background of other teeth, it is better to initially consider options for crowns made from other materials. Since metal crowns have much more disadvantages than advantages, we cannot call them the best, and we do not offer them to patients of our dental clinic in Moscow - “Aesthetica”.
Acrylic plastics
For decades, the primacy among structural materials has been held by polymeric (i.e., consisting of a large number of repeating units) derivatives of acrylic and methacrylic acids. They received their unique privileged position due to low toxicity, cost and ease of use: the transition from a fluid to a solid state does not require additional heating (cold polymerization polymers), which makes their use in clinical conditions possible.
Like any material, they are not without negative properties.
Among the disadvantages are:
- Surface microporosity (can cause plaque formation and discoloration);
- The presence of residual monomer - unreacted component - regardless of the manufacturing method;
- Volumetric and linear shrinkage - a decrease in size after curing due to the formation of bonds and ordering of the structure;
- Sufficient rigidity, which lengthens the period of adaptation (accustomation) to prostheses, and for some patients makes it impossible to use them without additional modification.
The indications for the use of these structures are the broadest:
Indications for the use of crowns
- Defects of the natural crown are more than half its size;
- Increased (inappropriate for age) abrasion of teeth; correction of jaw relationship (bite);
- Deep wedge-shaped defects are areas of triangular-shaped loss of hard tissue in the neck of the tooth (near the gums), weakening it and increasing the risk of complete breakage during chewing;
- Congenital anomaly of tooth shape (for example, underdevelopment or complete absence of enamel) or acquired (for example, after injury);
- Some congenital or acquired pronounced color changes that cannot be eliminated by bleaching (discolorities) are the consequences of injuries, medications used or materials for filling root canals;
- Tilting and/or protrusion of a tooth or a group of them when the patient refuses orthodontic treatment (orthopedic “movement”);
- Combining - splinting - teeth when they are mobile (the crowns are not made separately, but as a single block and are fixed at the same time);
- The need to improve the shape and protection of the tooth during removable prosthetics (creating pronounced convex contours that will hold the fixing elements and, along with them, the prosthesis itself);
- The presence of aesthetically unsatisfactory crowns (all-metal, combined with chips of the facing material or a gray-blue border, visible at the gingival margin when it decreases or thins).
Despite the variety of clinical situations in which the use of these structures is justified, the general rule is prosthetics in the early stages.
Disadvantages of nylon thermoplastics
- Uneven (point) distribution of chewing pressure due to the flexibility of the prosthesis and softening during use;
- Severe uneven atrophy of the alveolar ridge (this worsens the fixation of existing and subsequently manufactured prostheses);
- Absorb liquid and dyes (it is recommended to limit the consumption of strong tea, coffee, sour and hot foods);
- Impossibility of relocation and repair;
- Fairly high cost ;
- Difficulty in complete cleaning at home.
Therefore, their main purpose should be temporary prosthetics (from several weeks to two to three years). The period of adaptation to prostheses, of course, is strictly individual, but on average it is 5–10 days.
How are they attached?
Several fixation methods are used for dentures.
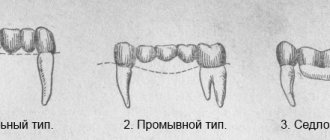
On the closing valve. It is often called a “suction cup”; it is an element of the base, the basis of the structure, which in shape must exactly match the gum. When the denture is placed and bitten, air escapes from the gap between it and the mucous membrane. When completely sealed, a sealed space is formed, and the base is held as if on a suction cup. For more reliable fixation of a complete denture with a closing valve, special gels can be used.
On clasps. This fastening is used for conditionally removable, partial structures; they are mainly made of acrylic. Fixation is performed using metal hooks that are placed on the remaining teeth. Usually these are the incisors in the smile area, and therefore the clasps can be visible. Fixation is reliable, without the risk of displacement or accidental loss, the chewing load is distributed better than when using a locking valve.
On elastic clasps. They are used for structures made of nylon, made of plastic, pink in color, and invisible. Fastening is almost the same as when using metal hooks, but elastic clasps are more convenient, less damaging to the mucous membranes, and easier to get used to.
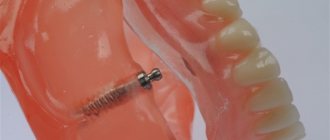
On attachments. These are composite micro-locks that can be used if the patient has preserved at least part of the dentition. One of the attachment elements is built into the base, the other is fixed to the supporting tooth and covered with a crown. The fixation is reliable, durable, the entire structure is protected from displacement, and transfers the chewing load well. Attachments are used with clasp dentures (having a metal base).
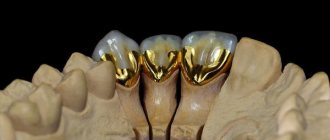
Metal-ceramic crowns: can they be called the best for prosthetics of chewing teeth?
In some materials on the Internet you can see that metal ceramics are advertised as the best material for crowns of chewing teeth. Is it really? Let's try to figure this issue out together, but first we will briefly tell you what metal-ceramic crowns are.
A metal-ceramic crown has a metal base, which is covered with layers of ceramic mass on top. The metal frame ensures the strength of the crown, the ceramic coating provides aesthetics, and some doctors seriously recommend them to their patients as the best option for installation on chewing teeth. In fact, this is not the case; metal-ceramic crowns cannot be called the best for restoring chewing teeth for a number of reasons.