Installing a crown on a tooth is one of the prosthetic options used when one or more dental units in a row are lost. Sometimes a dental crown is required even in the absence of a single edentia - for example, if it is necessary to restore the aesthetics of the dentition in the smile area. There are specific indications and contraindications for the procedure, and it is performed in several stages. We will discuss the specifics of the process of installing dental crowns in detail below.
After reading the material, you can find out how to install a crown on a tooth, what types of structures can be used in the procedure, and whether the process will be painful for the patient. We will also separately consider the specifics of removing a dental crown.
Calculate the cost of treatment by taking a short test in 20 seconds!
Do not delay your treatment, because in this matter time plays against us.
What is a dental crown
A crown is a type of dental prosthesis, non-removable, completely or partially covering the visible part of the tooth. Sometimes it is part of a larger prosthesis, such as a bridge. Crowns are distinguished:
- orthopedic. Replenish the missing part of the tooth crown. These include equatorial, three-quarter (for premolars), half-crowns (protect part of the vertical surface and the cutting edge);
- full clinical. Like a cap, they cover the entire stump of the tooth.
- stump, fenestrated, crowns with a pin are placed when more than 80% of tooth decay occurs, so they are often classified as pin structures.
To ensure that the crown does not interfere with the closure and active movement of the jaw, it is made according to the shape of the tooth, with a tight coverage of the neck without immersing more than 0.2 mm in the gum pocket. “Parts” for this type of fixed prosthetics are cast from metals, alloys, porcelain, and plastic. There are combined dentures, when a material different from the base is used for lining.
An inlay is first installed under the crown. Happens:
- straight (direct), made in the mouth, used when the tooth has 3 out of 4 walls left. Externally, it is a screw or pin that is inserted into the canal with a filling;
- indirect (indirect), an impression is made, and the inlay is cast from it in the laboratory.
The pin cult inlay is considered more reliable (and expensive); a ceramic inlay is placed under ceramic dentures.
Dental crown
Crown restoration process
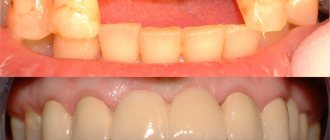
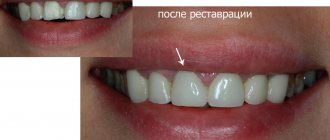
Prosthetic structures, like healthy teeth, require proper hygienic care and periodic restoration. The period of use and the need for restoration work on the crown are determined in accordance with the properties of the material used. For example, defects may occur on the surface of metal-ceramic and ceramic prostheses. If you want to find the best option in terms of reliability and duration of use, you should give preference to zirconium material. As for the need for restoration of the crown, it is carried out when cracks, chips appear and the shade of the prosthesis changes.
In what cases is a crown placed on a tooth?
Purpose of artificial crowns:
- replenish lost tooth tissue;
- restore its damaged surfaces.
They are made when it is impossible to restore a tooth by filling or placing inlays, i.e. it has already been destroyed by 60% - 80%. Protective “caps” are used for certain diseases of the jaw, oral cavity, and soft tissues. For example, with arthrosis of the TMJ, a prosthesis is indicated to protect teeth from abrasion (wear) while restoring the size of the jaw opening.
Crowns are also retaining elements that secure bridges or removable dentures; they can level the surface of incorrectly positioned teeth with congenital defects of hard tissues (hypoplasie). Quite often, dentures are used to cover stained, discolored teeth due to caries and teeth with or without dead pulp.
Indications for tooth replacement with artificial crowns:
- Pathology of hard tissue, spreading over an area of 50 to 80%: caries;
- wedge-shaped defects (for example, a part broke off as a result of injury);
- pathological abrasion, for example, due to pathological clenching of the jaw (bruxism);
- hypoplasia (congenital anomaly, partial or complete absence of enamel);
- fluorosis (softening of hard tissues due to excess fluoride);
- erosion (destruction of enamel and dentin).
Color selection
Based on the color of neighboring teeth, antagonists and characteristics: shade, brightness, intensity, the required tone for the future crown is selected. It will be uneven, like a natural one. The neck has one undertone, the cutting edge has a slightly different one. By mixing different numbers of colors of ceramic powder, the technician achieves the desired result.
The Vita scale is used in dental practice
, where red, brown, yellow, gray lead the groups, and the tones of each of them are indicated by numbers. 1 - the lightest tone and then darker in increasing order.
Lighting in the office is no less important when determining the color of future artificial teeth. All these points are always taken into account by experienced specialists.
Contraindications for installation
The main contraindication to the use of a fixed prosthesis is considered to be poor oral hygiene. Over time, plaque may form around the “cap,” which damages the periodontium and intensifies caries. Therefore, first, teeth are cleaned, damaged teeth are removed, carious cavities are filled, and foci of inflammation are treated. Only then can the crown be installed.
Temporary contraindications also include:
- age up to 16-18 years (individually, they look to see if the jaw continues to grow and the roots of the teeth continue to form);
- severe health condition (heart attack, ischemia, hypertensive crisis).
Absolute contraindications:
- Completely healthy teeth (intact), when they do not serve as support for devices or dentures.
- Pathological tooth mobility of the 3rd degree (mobility with an inclination, the tooth can rotate 360 degrees).
- Incurable infection in the periodontal area.
What the patient needs to understand before root removal
You need to assess the health risks, you need to talk to the attending surgeon, find out about his experience. Quite often, tooth root removal is carried out, unfortunately, with the following negative consequences:
- gums are torn
- fractured bony vestibular plate
Sometimes when visiting such patients, you get the feeling that the tooth was not removed, but knocked out with something. There were cases when a patient’s extraction began in some clinic, and there, in the middle of the patient’s appointment, the doctor announced that he was unable to remove it, and the patients came to us in this form to remove the root of a tooth that was already in the extraction stage.
When removing the roots of wisdom teeth, you may face risks such as jaw fracture. One of the common risks of removing the roots of 3 molars is damage to the mandibular nerve
, leading to cuts and numbness in areas of the jaw. There is a risk of damaging the artery on the lingual side.
If, when a tooth is removed, a root or part of it is left behind, what should you do?
According to Russian treatment standards, the tooth root cannot be left during extraction. That is, if the patient was left with a root or part of it during removal, then this is considered a poorly performed surgical procedure.
In European countries there are doctors who agree that if there is no inflammation on the tooth and if the root part is not infected, and removal of the root leads to trauma, then only the cortical part of the root is removed, and the other part remains in the bone.
If the patient is left with a part of the root that is infected, then this is a problem. A cyst may develop and inflammation may develop. If the apical part was not infected, then everything heals and does not bring any trouble to the patient.
Tooth root without crown part
Can a tooth root without a crown cause inflammation in the gums or bone? Of course it can. There is a canal at the root of the tooth; if this canal is infected, then the problem will develop into a negative prognosis.
Inflammation, suppuration, periostitis, osteomyelitis - diseases can develop due to an infected tooth root. And the source of infection at the root must be removed; if it is impossible to remove the infection and preserve the root, then it must be removed.
Which crown is better to put?
Based on the materials used, the following types of crowns are distinguished.
Sitall
Crowns made of glass-crystalline materials are biologically inert, i.e. do not cause adverse clinical manifestations. Dentures resist the chewing load well, are quite elastic, and have increased resistance to the corrosive effects of aggressive agents. The main disadvantage is fragility. Recommended for allergy sufferers and chronically ill people (due to the consumption of a large number of medications, they should avoid anything that can provoke an allergy or cause a rejection reaction).
Porcelain (ceramics)
Standard porcelain “caps” are made with a stably fixed or separate metal pin (the second option is more convenient). A more expensive option is custom-made prostheses based on a platinum matrix. After 2 annealings, a stage of shape correction between them, the individual characteristics of the teeth (cracks, stains) are imitated on the surface. Then they are tinted with majolica glazes, securing with another annealing. Then the “cap” will look natural.
Porcelain crowns
The main disadvantages of porcelain fixed dentures:
- fragility;
- poor marginal fit;
- abrade the surface of antagonist teeth.
They are chosen by people who have high aesthetic requirements for the oral cavity (show business). Ceramic dentures are also used for those who cannot undergo restoration with a composite. If the occlusal load is distributed unevenly, the dentist will suggest a different material.
Metal
More than 500 alloys are used in dentistry, but most metal fixed dentures are made of chromium-nickel or silver-palladium alloy, as well as 900 gold with the addition of copper, silver, and platinum as a ligature.
Metal “caps” are resistant to alkali and acid (in small concentrations), have high wear resistance, are moderately elastic, and are relatively biologically indifferent. The fashion for the “gold tooth” is back. Metal prostheses are durable products that do not require special attention. The retention time of the properties of a metal crown depends on the alloy.
Zirconium dioxide
These are the most popular of all fixed types of prostheses. Zirconium oxide (or dioxide, in the formula there are 2 oxygen molecules per molecule of zirconium) is chosen by public figures. The process of making a “cap” is labor-intensive, using computer modeling, so the product is expensive. This is a category of elite prosthetics.
The crown is durable, its color and transparency are very similar to a real tooth. In terms of all the characteristics of medical implants (bioinertness, resistance to acid-base influence, elasticity) it is one of the best.
There are 2 types of crowns:
- with the application of ceramics, when metal is used as a base;
- without porcelain, then the desired shade is manually applied to it.
Advantages of zirconium fixed prostheses:
- Making fairly thin crowns with minimal grinding (this way the teeth remain alive).
- Accuracy of fit (computer modeling is used).
- The service life of crowns is from 10 to 20 years.
- High aesthetics. In terms of transparency and structure, they best match natural teeth.
- Strength. They are made for both front and chewing teeth.
- Biocompatibility.
- High precision in the manufacture of crowns allows you to achieve the tightest possible fit, avoiding the inflammatory process and the development of caries.
Metal ceramics
This is a good alternative to porcelain crowns, since metal-ceramic prostheses are characterized by:
- increased strength;
- better fit at the edges.
Metal ceramics
A metal alloy is used for the base, and a ceramic mass is applied to it. The best base is gold, in which case the base is thin, freeing up more space for ceramics. The metal will not show through the porcelain - this makes your smile look more natural. But there is a nuance: it is highly undesirable to install several fixed dentures (or a base with ceramics) made of different metals. For installation, deep preparation is used only on the vestibular surface (this is the side of the tooth turned towards the lips and cheeks) to mask the frame of the prosthesis.
Contraindications to installing metal-ceramic crowns on teeth:
- Teeth with thin crowns, when there is a risk of pulp damage.
- Deep blocking or wearing away bite.
- Pathological abrasion of tooth tissues.
- Parafunctions of the masticatory muscles, in which there is high muscle excitability, bruxism, and lateral displacement of the jaw.
Please note: it is better to avoid metal-ceramic crowns if you have marginal periodontal diseases, because Patients regularly experience functional overload of teeth, which leads to exacerbation of inflammation and deepening of the destruction process.
Metal-plastic
The second name for “caps” is combined, because Composed of plastic, composite, porcelain. These are temporary “caps” since the service life usually does not exceed 3 years. Plastic deteriorates over time under the influence of acids and alkalis, and can be colored with natural food dyes (wine). Summary: not bad, as a temporary option (there are situations, for example, injury, accident, but tomorrow you need to speak, be at negotiations).
Plastic
With good aesthetic properties, a plastic fixed prosthesis is inferior to its analogues in strength. It is not used to restore thin or flat incisors, with a deep or receding bite, pathological abrasion of teeth, or some dentition defects. This type of crown should not be placed on people with allergies.
Fixed dentures are made in 2-3 layers on an interpenetrating polymer mesh. They are recommended for prosthetics for children, during the correction of dentoalveolar anomalies, during periods of primary and mixed dentition.
Temporary crowns made of plastic
Prices at Doctor Zhuravlev Clinic
| Plastic crown (temporary) | PC. | 1000 rub. |
| Solid crown | PC. | 3600 rub. |
| Metal-ceramic crown | PC. | 6000 rub. |
| Metal-ceramic crown on an implant | PC. | 15,000 rub. |
| Zirconium oxide crown for implant | PC. | 16,000 rub. |
| Crown based on zirconium oxide | PC. | 13000 rub. |
| Endocrown | PC. | 12000 rub. |
| Pressed ceramic crown | PC. | 14,000 rub. |
| Stump tab | PC. | 3600 rub. |
How to install crowns on a tooth - all stages
Let's look at the stages of installing a crown on a tooth in more detail.
Diagnostics
Before making a fixed denture, a clinical evaluation of the tooth is performed. Using a dental mirror, tweezers and a probe, the doctor:
- determines the degree of crown destruction, the severity of the equator:
- records the presence of seals;
- determines the relationship of the prosthetic tooth with adjacent teeth and antagonist teeth;
- studies the condition of the periodontium and the degree of tooth mobility.
To exclude contraindications (neoplasms, inflammatory processes), the dentist may also refer the patient for an x-ray.
Preparing for installation
The tooth under the denture should be as healthy as possible, i.e. cleared of plaque, caries, sealed if necessary, and the inflammatory process is eliminated. In this case, the dentist may recommend removing the nerve, but the tooth without the nerve dries out under the prosthesis and becomes less durable. Underneath it, even with perfectly filled canals, 1 in 10 (statistics from The American Dental Association (ADA)) develops an infection in the periodontium. Over time, pain will appear in this place, the “cap” will begin to dangle, and secondary caries will develop underneath it.
Remember: the doctor must do a cold test on the nerve (usually a cold stream of water is used for this). The nerve is removed if the pain does not go away after a few seconds.
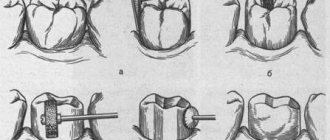
After removing the nerve and filling the canals, everything unnecessary is removed from the tooth (pin, fillings, caries). The thin walls are shortened, forming a platform for the inlay, and the edges of the treatment are smoothed so that they do not scratch the tongue or cheek when the inlay is installed. When turning, the tooth is given the shape of a cylinder, and the cavity inside is oval-shaped - this increases the reliability of fixation of the inlay.
Grinding a tooth for a crown
Taking an impression, choosing a color
To obtain an impression use:
- standard impression trays with perforations to hold the impression material in the tray;
- impression materials (for example, Algmat).
The taken impression is called a “negative”. When it is cast with hard plaster, they will receive a “positive” - an exact model of the teeth.
An inlay pin is placed in the prepared tooth, then an imprint is taken using silicone mass (always together with adjacent teeth). Another impression is made of the entire jaw and antagonist teeth. Quality criterion: the impression must accurately reproduce the position of prepared and unprepared teeth, the relative position and distance between them, as well as the position of soft tissues.
The average production time for an inlay is a week. Before cementing the inlay, the pins are cut to the same level as it. They try the inlay on the tooth, check the tightness of the fit, and then cement it. It is clear that this is not construction cement, especially not a cement mortar with sand. This is a special glass ionomer cement for dentistry.
After 20-25 minutes, the excess is removed, a retraction thread is laid around the perimeter of the tooth to slightly move the edge of the gum. Then in the future the “cap” will not hang over the gum. Then the tooth is polished and smoothed again so that the fit of the fixed prosthesis is as tight as possible and the remainder of the tooth is not destroyed. A silicone impression is then taken to create the crown.
Temporary composite “caps” are made that will protect the gums until the next visit. They are installed with temporary cement. Now you can choose the color of the future prosthesis.
To do this, they use a “color key”, which contains on average about 15 samples. The sample is compared with the teeth, choosing the color closest to them in daylight, neon and artificial light (!). It is better to meet with a technician for this, because... a real tooth has a color transition from light to dark, more transparent at the edges. Only a technician can correctly determine:
- color;
- tonal ratio (light – dark);
- color intensity (saturated – pale);
- color (yellowish – reddish).
They come to the dental technician without makeup, wearing uniform, gray clothes.
Crown making and fitting
In a modern dental clinic, crowns are made using the best impression materials and computer modeling, so there is no fitting stage. If the clinic is budget (but this does not mean that bad doctors work there), or several prostheses are made, fittings are carried out. To put a “cap”, it is placed on temporary cement and the quality of work is checked.
Making crowns
The process of installing a crown on a tooth
The tooth is cleaned of the remains of temporary cement, a retraction thread is laid so that when the “cap” is installed, moisture does not get on the tooth. They place a crown on the tooth and check the tightness of the edges. They are fixed with cement (the excess is, of course, removed).
The quality of the installation is checked using dental floss: it should pass between the teeth under tension and make a loud click. Then food remains will not remain between the teeth.
How to place crowns on implants
Installing a crown on an implant is slightly different from installing a crown on a tooth; it is recommended for severely damaged teeth. After diagnosis, the dentist prepares the oral cavity for implantation. This is a titanium alloy screw that is screwed into the bone. It has a conical head that imitates a tooth. This is where the “cap” will be put on.
Just like with conventional crowns, the inflammatory process and caries are first treated. Then an implant is installed into the bone or tooth root (an anesthetic injection is given first), which will take root in 5-6 months.
Please note: as the healing time decreases, the risk of implant failure increases.
Next begins the stage of installing gum formers, which are required for uniform growth of soft tissue around the implants, taking into account future crowns. Impressions for dentures are removed after 2 weeks. First, using a dental key, the formers are removed and transfers are installed, which will remain in the impression and become the basis for attaching the implants.
An impression is taken using silicone impression material, as when installing conventional crowns. Then a plaster model is cast. While the crowns are being made, the cone is again covered with a former. The role of the gasket when installing the prosthesis on the implant is performed by the abutment. It is screwed on with a screw, and the head is isolated with a temporary filling before installing the “cap”. The crown itself is secured using glass ionomer cement. Read more about different types of implantation here.
Requirements for the surviving part
Unfortunately, fixing the prosthesis to the tooth root is not always possible. To do this, the latter must satisfy a number of requirements:
- have strong walls and be long enough;
- not be affected by caries;
- be well passable (otherwise it will not be possible to seal it);
- have walls of the required thickness to hold the inserted pin and withstand the pressure exerted during chewing food;
- do not have inflammatory changes in the upper part.
If the root is very curved, it is very small in size, it will not be possible to use it during prosthetics. The situation is similar if there are fistulas in the gums that do not go away even after filling.
What to do after installing a crown on a tooth
The time during which you cannot eat after a crown is installed depends on the type of cement. In addition, anesthesia is still in effect, and you can accidentally injure yourself. It is better to refrain from eating for 2-3 hours.
It is not recommended to load the side where the crown was installed - chew on the opposite side. Drinks and food with coloring pigments (red wine, berries, seasonings) should be kept to a minimum. It is recommended to avoid:
- sudden temperature changes (for example, drinking ice cream with coffee);
- solid food (bones, cartilage, nuts);
- sticky foods (taffy, some oriental sweets).
Hygiene requirements are standard: cleaning the mouth in the morning and evening. Superfloss, dental brush, and irrigator are recommended for bridges.
Pros and cons of crowns
All medical procedures have both pros and cons. Before you decide to install crowns, you should compare the pros and cons.
Advantages
The advantages of using this method of prosthetics are much greater than the disadvantages. The advantages of installing crowns include:
- preventing the destruction of pulpless teeth;
- preservation of a living tooth even with partial destruction;
- restoration of the ability to chew food normally;
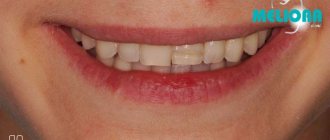
- restoration of an aesthetic appearance while smiling;
- prevention of diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, which can be caused by insufficient chewing of food;
- restoration of the ability to speak clearly.
Due to the large number of advantages, the procedure has become so popular among patients.
Flaws
The procedure for installing crowns has its disadvantages. Flaws:
- the need to grind healthy parts of the tooth;
- limited period of wearing a prosthesis;
- inability to carry out the procedure with a damaged root;
- the need for regular visits to the dentist for monitoring.
The disadvantages of the procedure are offset by its advantages. Therefore, crowns remain the most popular way to restore the integrity of the dentition.
Does it hurt to put a crown on a tooth?
The presence of a pain symptom during installation of a crown on a tooth depends on the tooth:
- on the pulpless one the pain is not felt. However, if you ask for additional anesthesia, they will give it;
- on “living” teeth, with the root preserved, there is an unpleasant sensation, pain is felt during grinding. Anesthesia solves the problem, but it is advisable to do a test to avoid an allergic reaction.
When installing dental crowns, when a temporary prosthesis is installed, the edge of the gum may be damaged and discomfort may be felt, but this is a normal process - no medications are required. If there is increased nervous excitability, the pain threshold is low - you can take sedatives and painkillers (be sure to discuss this issue with your dentist!).
Cases in which crown removal is necessary
The need to remove the crown may be due to the following reasons:
- The tooth was poorly prepared for installation of the prosthesis. Statistics show that 60% of cases of dental canal filling are carried out with errors. This serves as a prerequisite for the development of inflammation, and tooth treatment leads to the need to remove the structure.
- Error during construction. If the product distorts the bite, does not fit tightly around the neck, or causes physical or aesthetic problems, it is removed.
- Planned replacement. At the end of its service life (usually 10-15 years), the prosthesis is replaced.
- Damage to the structure, the appearance of cracks or holes on it from washed cement, requires urgent replacement of the product.
- The occurrence of complications.
Possible complications after the procedure
Complications are rare after crown placement, but complications do occur. Most often this is a medical error or lack of professionalism. Therefore, the best prevention of complications is choosing a clinic with an excellent reputation. In addition, there are several diseases that do not depend on the doctor. They can be caused by medications, gastrointestinal diseases, and injuries.
Complications after crown installation
Prosthetic stomatitis (allergy)
Stomatitis, the cause of which is dentures, happens:
- allergic, this is a contact allergic inflammation, which often occurs after repeated prosthetics;
- toxic (occurs more often than allergic).
Prosthetic allergic stomatitis is a reaction to metal compounds and plastic. The more metal (a large number of bridges, crowns), the more likely an allergy. Moreover, this type can develop both immediately after installation and after 5-15 years of wearing crowns. Patients with gastrointestinal diseases and endocrine disorders are at risk. Typical complaints are swelling of the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and larynx, sometimes it is difficult to breathe, the tongue swells and does not fit in the mouth, but there are no ulcers familiar to ordinary stomatitis.
If a metal, metal-ceramic or metal-plastic crown is installed, a burning sensation of the tongue, drooling, and dry mouth are noted. If you are allergic to acrylates, granular bright red foci of inflammation appear on the mucous membrane of the palate, matching the shape and size of the prosthesis. In addition, skin reactions are noted - eczema, urticaria, dermatitis.
With toxic prosthetic stomatitis, the mucous membrane is damaged, and there is massive destruction of the epithelium of kidney, liver, intestinal cells, red blood cells, and nerve cells. Most often, poisoning is caused by stainless steel; if the crown (whole or base) is made of gold or a silver-palladium alloy, the disease occurs much less frequently.
This complication appears 1-7 days after installation. Characteristic symptoms of toxic denture stomatitis:
- burning tongue;
- drooling (hypersalivation);
- unpleasant feelings in the tongue, such as tingling, rawness (glossalgia);
- nervous disorders;
- gastrointestinal disorders.
Caries on supporting teeth
The ground teeth under the crown, if the nerve is removed, dry out over time. As soon as the seal is broken, bacteria and food particles penetrate under the denture and caries develops. That is why, even if part of the tooth and the root remain, it is better to build up the support than to remove the tooth along with the nerve.
Jaw trauma and hard food lead to a violation of the integrity of the crown and further development of caries underneath it. Development is promoted by poor oral care.
Galvanic syndrome
Saliva is a complex electrolyte, and the oral cavity is an electrochemical system in which:
- saliva (liquid phase), saturated with oxygen and carbon dioxide, acts as an electrolyte;
- teeth, dentures (solid phase) act as electrodes.
If there are metallic inclusions in the oral cavity that are not covered with ceramics (insulator), the potential of the electrode system increases sharply. There is a feeling of acidity and burning in the mouth. With a galvanic symptom, the functioning of the nervous system is disrupted, which leads to a general deterioration in the patient’s condition.
Which material to choose?
Thanks to new developments, in modern dentistry there are several types of materials from which crowns are made. Let's consider the main ones:
- Metal ones are classic dentures that have been used for many years. Most often they are made of gold. The advantages of such products are strength, reliability and durability. They do not oxidize, have an abrasion coefficient almost like that of natural enamel, and do not damage opposing teeth. The main disadvantage is minimal aesthetics, which is why they are placed on invisible areas of the jaw.
- Metal-ceramic, combining the advantages of metal and ceramics. They have durability, strength and high aesthetic values. They cost less than all-ceramic ones. The disadvantage of these prostheses is the mandatory preparation of a large amount of living tissue before their installation, as well as the possibility of abrasion of the enamel on the opposite dental organs. A strip of black metal near the gum may also be visible if its edge is lowered or the product was not made accurately.
- Crowns that have the most aesthetic appearance are made from ceramic or porcelain. They are as similar as possible to natural teeth and retain their properties for a long time. However, ceramics are significantly fragile and cannot always withstand the load of chewing. For this reason, ceramic products are often placed on the front teeth. The main disadvantage of these crowns is their high price.
When should crowns be removed?
Crowns are removed if:
- they are worn out (stains appeared on metal ones, cracks and chips appeared on ceramics);
- loose fit;
- caries develops under the crown, especially deep ones.
The most common, simple, fast method is sawing, which is carried out with a special drill. The crown is not sawn completely: notches are made, then the crown is expanded from below and removed. If the tooth is not pulpless, this operation may be painful. The disadvantage is that the crown is damaged and cannot be restored.
To remove crowns, if they are installed on phosphate cement (or analogues), crown removers (for example, a Kopp apparatus) are also used. They are accompanied by removable hooks of various sizes, which are used to act on the edge of the prosthesis, displacing the crown, and then removed. The crown will remain intact, but will be scratched.
The Coronaflex device destroys cement using a shock wave. The crown remains intact under this influence and is reused. The most expensive method, the device is used mainly for “caps” made of zirconium dioxide.
Another method (not suitable for all materials): crumbling cement under the crown with ultrasound. A thin rod is inserted under the prosthesis, which vibrates and destroys the fastening.
If the crown comes off a tooth...
This also does not mean that the tooth will have to be removed. After all, even crowns with a zirconium frame, an expensive and high-quality material, can fall out. Parting with it is an unaffordable luxury if you have the opportunity to install it again. By the way, if the crown falls out on its own, this is a guarantee that it will not be sawed. Whatever materials are used to make crowns, it is almost always possible to re-attach them to the tooth, only with new cement. The main thing is not to lose the crown and bring it to the doctor.
How much does it cost to install a crown on a tooth?
The final cost of prosthetics depends on the crown material, treatment plan, associated costs (radiovisiograph image, impression, anesthesia, etc.).
| Type of crown | Price for 1 tooth, rub. |
| Metal | From 4500 |
| Metal ceramics | From 9000 |
| Zirconium dioxide | From 17500 |
| Plastic | From 2000 |
| Metal-plastic | From2500 |
| Sitall | From 14000 |
| Ceramics | From 13000 |
Manufacturing
Crowns are made using prepared plaster models. Metal, metal-ceramics and ceramics can be used as the manufactured material.
Manufacturing is quite labor-intensive and time-consuming, so while the dental technician is working on their creation, the patient is put on temporary plastic products. This way, the aesthetic appearance of the ground teeth is restored, and they are protected from external influences and infection. These dentures, in addition to protecting teeth, also allow them to be fully used when chewing.
Installation of the stump tab
Before prosthetics with stump inlays, it is necessary to remove the nerve and carry out endodontic treatment of the canals in order to eliminate their inflammation and seal them properly. After this, the tooth is prepared for an inlay, the canals are unfilled to 1/3 or 2/3 of their length, they are made wider and given a conical shape, and then procedures typical for the direct or indirect method of manufacturing a microprosthesis are carried out.
Stages of installing the stump tab
- All teeth are disinfected with alcohol and dried.
- The stump tab is degreased and covered with cement along with the pins.
- The holes in the channels are filled with a solution, and a microprosthesis is installed in them.
- For final fixation of the stump tab, the doctor applies strong pressure on it.
After this, all that remains is to take impressions from the stump insert installed in the tooth to make a crown from the material chosen by the patient.
Making a core inlay for a crown
For the manufacture of stump pin inlays, direct and indirect methods are used. The direct method of manufacturing a stump insert has the following steps.
- After preliminary treatment of the tooth canals and its preparation for the stump inlay, the cavity is treated with Vaseline.
- The plastic, heated to a viscous state, is poured into a syringe and squeezed into the cavity through a wide needle to form an inlay.
- The pin is processed with the same material and inserted into the canal.
- After the plastic structure has hardened, the finished model of the inlay is removed from the cavity and sent to a dental laboratory for the manufacture of a microprosthesis from the material chosen by the patient.
The indirect method includes the following stages of manufacturing a stump inlay:
- After preliminary preparation of the tooth and canals, the doctor takes an impression and transfers it to the dental laboratory.
- The technician casts a plaster model and creates a prototype of the inlay from wax.
- Based on the wax sample, a metal stump inlay is made.
If we talk about stump inlays made of zirconium or ceramics, then CAD/CAM technologies are used for their production, which involve computer modeling of a microprosthesis, transferring the model to a milling machine and subsequent “cutting out” of the inlay from the workpiece.
But how to place a tooth if there is no root?
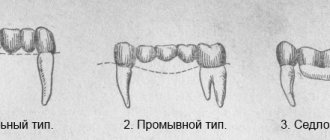
The main goals of prosthetics are to return the patient to the ability to chew food normally, restore the aesthetics of a smile, and prevent further tooth decay due to chewing overload. Here are 3 main ways to insert a tooth:
- removable prosthetics
- making a prosthesis from nylon, acrylic, silicone, Acry Free material; - bridge prosthetics
- the classic technique involves grinding two adjacent teeth with a defect, which will be used as supports for a prosthesis that replaces a lost tooth. It is also possible to install a bridge on implants; - installation of an implant
followed by loading with a crown.
Sometimes patients ask if it is possible to grow a tooth in any way without a prosthesis? Alas, no - if a tooth is removed or lost along with the root, then there is literally nothing to build up. The methods of tooth extension, which we also talked about, are effective only in cases where there is a root and some volume of the crown has survived.