Microdental dentures are a modern, effective method for eliminating tooth defects.
Modern dentistry offers several methods and systems of microprosthetics that allow you to restore the shape and function of a missing or damaged tooth. Microdental prosthetics - what is it? This method of orthopedic dentistry is prosthetics with minimal intervention in the tissues of healthy supporting teeth. Often this approach is the “golden mean” between conventional filling and direct dental prosthetics. It includes features of both methods and may well be an alternative to traditional filling.
Microprosthetics does not imply grinding existing healthy teeth, therefore it makes it possible to quickly and efficiently restore a tooth, returning its functions and aesthetics if the tooth defects are minor.
Advantages of microprosthetics
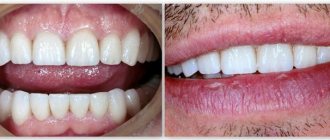
Onlays and inlays are similar in appearance to the fillings familiar to most patients. However, these microprostheses have comparative advantages - high accuracy of fit according to a previously taken dental impression, high aesthetic and functional characteristics. Thus, the ceramic material used allows you to effectively restore a tooth that will be indistinguishable in appearance from your own teeth - this applies to shape, shade, and the degree of transparency of the enamel.
Microprosthetics is a very effective method of restoring a damaged tooth; it has especially proven itself when it is necessary to restore the front teeth.
Indications for microprosthetics
There are several indications for microprosthetics:
- pathological abrasion of teeth;
- destruction of the crown - as a result of caries, trauma, which is especially in demand in cases where it is impossible to classically restore the crown with filling materials;
- complete destruction of the crown, saving only the tooth root - in this case, pins can be used to fix an artificial crown;
- missing tooth - the choice of prosthetic method in this case depends on the structure of the jaw, which tooth is missing and what caused its removal/loss;
- chips, cracks in enamel, darkening or inability to whiten yellow enamel - these indications apply to the installation of veneers.
Contraindications to microprosthetics
- poor oral hygiene;
- bruxism;
- multiple caries, damage to a large number of teeth;
- shallow cavity depth (for inlays);
- inability to provide conditions for prosthetics - absolute dryness of the tooth surface or cavity.
The need to use a particular method of microprosthetics is determined by the doctor individually, taking into account the characteristics of the dental system, the condition of the oral cavity, and the wishes of the patient.
Types of microprosthetics
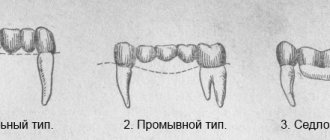
This method of eliminating tooth or dentition defects consists of several types of prosthetics:
Adhesive
. Microprosthetics of a missing tooth are often performed using this method. In this case, the artificial tooth is fixed in place of the removed or fallen tooth with the help of supporting teeth - the use of inlays and onlays is assumed. Grinding of teeth is not implied here at all or is carried out in gentle ways. The advantage of this type in comparison with classical prosthetics is the preservation of most of the tissues of healthy teeth.
This method is indicated in cases where there is an allergic reaction to metal elements of dentures. It is worth noting that it can also be used as a temporary measure.
The artificial tooth can rest on inlays installed in adjacent teeth. If they have old fillings, the doctor simply replaces them with newly made inlays. If there are no old fillings in the teeth, the doctor creates a cavity in it, into which the inlay is installed. The artificial tooth subsequently rests on it. Creating a cavity does not imply removing the pulp - the tooth remains “alive”. The amount of tissue removed is insignificant, in contrast to classical turning. The procedure eliminates the loss of your own tissues completely if the tooth has already been filled in advance - only the material is replaced.
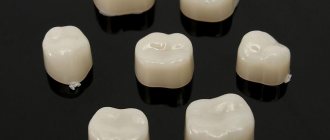
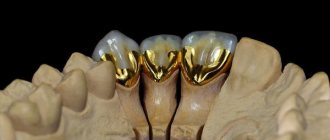
Inlays and overlays
. These microprostheses are manufactured in a dental laboratory using ceramic compounds. Tooth restoration is carried out in a similar way to a filling - pre-fabricated elements are installed in the tooth cavity using filling materials, as a rule, we are talking about liquid light-curing composites. The advantages of this type of microprosthetics are the precision of fitting the prosthesis to the individual parameters of the tooth cavity, the full correspondence of their properties (in terms of functionality and aesthetics) to the tooth’s own hard tissues. The inlay is a filling made in advance in the laboratory from durable and aesthetic material. The onlay is a relatively larger microprosthesis. The main indication for their use is the need to restore the shape and function of the chewing part of the teeth.
Veneers.
This type of microprosthetics is designed to hide tooth defects - chips, cracks, diastemas (gaps between teeth), slight curvature, scratches. Veneers can also be used if the shade of tooth enamel is unsatisfactory. Of course, they are more often used for the front teeth - noticeable when talking and smiling, their main function is to give aesthetics to the teeth.
Veneers are thin ceramic shells that are bonded to the outside of teeth. They are widely used in cases where other aesthetic dentistry procedures do not bring the desired result. Installation involves grinding off the top layer of enamel.
Lumineers
- a type of microprosthesis with an even smaller thickness (less than 0.3 mm). Their installation involves grinding down a smaller amount of tooth enamel, and in some cases this procedure can be avoided altogether.
Butterfly
. This design is installed mainly in adolescence, during the formation of permanent teeth. It is an element made of nylon; it serves as a microprosthesis for one or two teeth. Installation does not imply grinding of adjacent teeth.
Classification by installation method is not the only one. Microprostheses are also divided into types according to other characteristics: the method of transmitting the chewing load, the typography of the row defect, the material and manufacturing technology.
Microprostheses: types and frequency of production
The article provides a systematization of the types of microprostheses, indications and advantages of their use.
Key words: dental inlays and onlays, pins, removable dentures.
Currently, a significant portion of patients pay great attention to the aesthetic appearance of their teeth. To achieve the desired aesthetics, it is possible to manufacture microprostheses, i.e., minimally invasive structures with minimal preparation of hard dental tissues.
The article [2] presents a classification of microprostheses, which is based on the method of their inclusion and coverage of dental tissues.
Today, microprostheses are represented by the following varieties: non-removable: onlays (veneers, lumineers); tabs; dentures on pins and removable: immediate dentures.
When choosing the design of a microprosthesis, it is necessary to be guided by the following parameters: the location and area of the damaged or destroyed part of the tooth, the route of insertion of the microprosthesis, contact points with the antagonist tooth and neighboring teeth [3]. Let us consider the types of microprostheses, their characteristics, indications and advantages of use in more detail.
- Onlays (veneers) are a microprosthesis made of porcelain, light-curing material or plastic, covering the vestibular, both proximal (mainly to contact points) surfaces, if necessary, the cutting edge of the tooth, restoring the anatomical shape and color of mainly the anterior group of teeth in order to restore aesthetics. To ensure adequate support of the veneers and the thickness of the veneering materials, it is recommended to use an anatomical zirconia framework design [5].
Indications: change in color (color) of the crown part of the tooth, in particular due to pulp devitalization; chipping of the corner of the tooth crown, if the defect occupies more than 1/3 of the tooth crown; dental dystopia; non-carious lesions of teeth (fluorosis, hypoplasia, etc.); anomalies in the shape, size and position of the tooth crown; diastema and trema; inadequate previous dental treatment (large discolored fillings, failed large fillings).
Advantages: accurately imitates the properties of the surface layer of the tooth - enamel; protects enamel from physical influences; stain resistance; compatibility with dental tissues, oral cavity and body; strength and durability; elimination of unsightly gaps between teeth and other defects with minimal grinding of the tooth enamel of the damaged crown part.
- Onlays (Lumineers) are ultra-thin (about 0.2 millimeters) onlays made of ceramic reinforced with leucite crystals, which are fixed on the outside of the teeth and serve to restore the aesthetics of the dentition.
Indications: the need for prosthetics without grinding teeth; restoration of only a group of 8–10 teeth; increased sensitivity of teeth; longer service life requirements; predisposition to enamel wear.
Advantages: during development and manufacturing, 3D modeling is used to recreate the patient’s jaw model, which allows increasing the accuracy of their positioning on the teeth; no tooth grinding required; protect not only the front, but also the cutting surface of the tooth; durability and color constancy throughout the entire service life (service life of 20 years or more).
- Inlays are special fillings that differ from light fillings in their strength and longer service life.
Indications: to correct the color and shape of partially destroyed teeth - those areas that are located inside the tooth.
Advantages: complete imitation of the anatomy of a natural tooth; minimizing the recurrence of caries due to the constant volume of ceramics, good marginal fit and lack of shrinkage of the material; less load on the prepared tooth walls; biological compatibility with hard dental tissues [1].
Pin-based dentures - special fiberglass rods are inserted into root canals that are cleared of infection or untouched. The cavity is filled and the main surface is built up over the pin, which becomes the future tooth.
Indications: the presence of only 2 crown walls in anterior teeth and premolars; 2 crown walls less than 3 mm high in molars; to improve retention of restorations and distribute occlusal load; indicated for loss of more than 50% of tooth tissue; for patients with impaired fixation of an artificial crown with partial or complete destruction of the hard tissues of the coronal part of a natural tooth [4].
Advantages: Possibility of installing a prosthesis for a damaged tooth without grinding the teeth on both sides of the crown being installed.
Immediate dentures (butterflies ) are a removable microprosthesis for one or two teeth, which is an artificial tooth placed on a base that imitates gums or enamel. It is inserted into the place of the lost tooth and, thanks to the base, is held on the adjacent teeth.
Indications: replacement of a lost tooth until permanent prosthetics are performed.
Advantages: ideal for teenagers.
Thus, the listed types of microprostheses are most often used in dental orthopedics to restore the aesthetics of the dentition and the chewing function of the tooth.
Literature:
- Ivanova V.I., Makarova E.S., Nikonorov M.K., Udaltsova E.V. Clinical cases showing the advantages of restorations with ceramic inlays over composite fillings // Problems of Dentistry. - 2021. - T.15. - No. 1. - P.104–108.
- Kozitsyna S. I., Gritsay I. G., Makarova A. N., Kirienko A. Yu., Dmitrieva N. G. What are veneers and ultraneers? // Institute of Dentistry. 2011. - No. 3(52) - P.42–45.
- Sizov A. A. Restoration of the chewing group of teeth with microprostheses made of lithium disilicate // Healthcare of the Far East. –2018. - No. 1(75). — P.32–35.
- Faychuk N. V. The use of metal-free pins in the daily practice of a dentist: a collection of materials from the Republican Scientific and Practical Conference with international participation / Under the general editorship of S. A. Naumovich. — Publisher: “Integralpolygraph”, 2021. — pp. 445–452
- Tomohide Kondo, Futoshi Komine, Junichi Honda, Hiroki Takata, Yuta Moriya Effect of veneering materials on fracture loads of implant-supported zirconia molar fixed dental prostheses //Journal of Prosthodontic Research, Volume 63, Issue 2, April 2021, Pages 140–144
Stages of microprosthetics
The microprosthetics procedure involves two main stages:
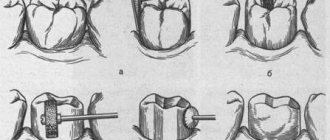
- The doctor treats the decaying tooth - removes tissue softened by caries, prepares the tooth for further prosthetics, and places a temporary filling in the tooth cavity. This stage also involves the creation of a tooth impression, from which a microprosthesis will subsequently be made in a dental laboratory. This allows you to take into account individual parameters and create a design that exactly fits the tooth cavity.
- The specialist installs the finished inlay/onlay into the tooth cavity or on its surface, ensuring reliable fixation using adhesive materials (composite cements). This allows the cavity to be filled hermetically and ensures reliable installation.
Design of dental microprostheses
In our dentistry in Saratov “Flart” you can install removable dental microprostheses.
One or more artificial teeth on a base made of acrylic or nylon are attached to adjacent teeth using a gentle method - using “wings” - clasps that tightly cover the bases of adjacent teeth, without causing harm to them, but perfectly fixing the prosthesis itself.
For such an interesting structure, removable microprostheses are called “butterflies”. They are easy to take off, easy to put on, and easy to care for.
Service life of microprostheses
The peculiarities of microprosthetics are that each element designed to replace a defect is manufactured in a dental laboratory - under special conditions that cannot be reproduced in the patient’s oral cavity. This makes it possible to achieve maximum polymerization, lightness, strength, and reduce the likelihood of tissue damage - this greatly affects the service life of microprostheses. Thus, the average service life of a microprosthesis on fiberglass is at least 5 years, inlays - 10-12, veneers - more than 20 years. These periods may vary depending on individual characteristics and compliance with the rules of care for microprosthetic teeth.
Advantages of dental microprostheses
In addition to ease of care and ease of manufacture, butterfly dental implants have many other advantages:
- Low price compared to, for example, bridges and implants;
- There is no need to injure neighboring intact and beautiful teeth, as when installing bridges;
- Long service life, especially with proper care (depending on the type of prosthesis);
- The ability to supplement the all-plastic design with metal clasps - grippers in the event that the plastic cannot cope with fixing the prosthesis in its place.
Care of microprostheses
It is necessary to brush teeth with inlays or veneers in the usual way, but it is better to avoid toothpastes with abrasives. After installing veneers, you will have to forget about teeth whitening procedures, but this is unlikely to be necessary - after all, these microprostheses are designed to improve the aesthetics of teeth.
It is very important to forget about a number of bad habits (such as biting your nails) - especially when it comes to installing veneers or lumineers. Otherwise, mechanical loads can lead to damage to microprostheses, and they will have to be replaced with new ones.
The use of dental floss and, if possible, an irrigator is advisable; the dentist will definitely explain the specifics of using these products to maintain hygiene.
When are removable microprostheses placed?
- Constantly worn in the absence of one or more teeth in order to avoid deformation of the dentition and to normalize chewing and digestion;
- As a temporary measure in the period before preparing for dental implantation (for example, when the hole is healing after tooth extraction);
- Wearing a microprosthesis if there are contraindications for the installation of permanent structures (for example, if it is impossible to carry out implantation or unwillingness to install bridges).