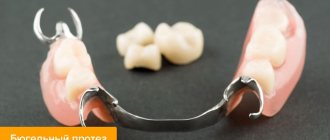
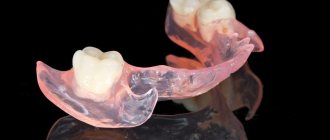
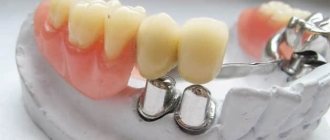
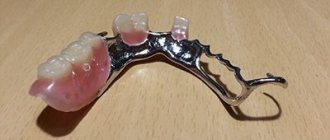
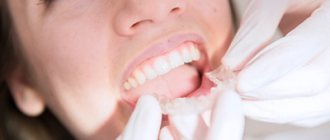
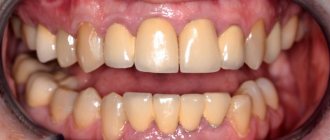
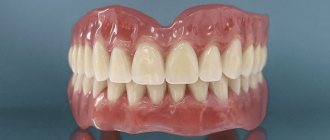
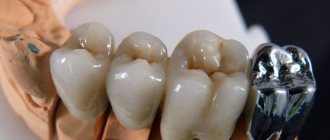
Clasp prosthetics is a popular method of restoring the dentition, which uses removable dentures with clasps (hooks) and attachments (locks).
Designs with clasps are at least half the price, but they are durable, strong and reliable, and do not require special care. They are also considered a budget alternative to implants and a reliable analogue of bridges and plate prostheses.
Features of clasp dentures on hooks
The structure consists of the following elements:
- arc (in German – bugel);
- artificial teeth (attached to an arch);
- base (gum simulator);
- clasps (hooks that secure the prosthesis to the supporting teeth).
If for conventional plastic prostheses fixation was provided by a massive and thick base, then clasps are also responsible for reliable fastening of clasp structures. Therefore, the base is made thin, with reduced volume.
This design is much more convenient: the anterior part of the palate on the upper jaw is not covered by the base plastic and this does not affect diction or taste sensations. On the lower jaw, a miniature base gives freedom to the tongue and reduces the risk of the structure falling out due to its movements.
Indications for installation
In dentistry, clasp prosthetics are recommended in cases where it is not possible to make dentures on implants (contraindications, financial issue), or a person is afraid to install fixed dentures. Then there is a solution - the clasp system. But only if there are two supporting teeth.
The clasp can perform a splinting function. In case of periodontal disease and loose jaw teeth, the orthodontist will prescribe it to fix and prevent mobility of the elements of the row.
Contraindications for installation:
- bruxism;
- metal allergy;
- absence of supporting teeth or they are low;
- bite pathology (deep occlusion);
- short bridle;
- inflammatory processes on the gums and in the oral cavity;
- shallow sky;
- mental illness.
Work examples
How often do you visit the dentist?
Advantages and disadvantages
Advantages:
- strength (structures with a metal arc are much stronger than plate ones);
- durability (they last up to 10 years, and plate ones need to be changed every 2-3 years);
- no need to grind the supporting teeth (unlike a bridge, which is fixed only to the processed teeth);
- ease of wearing (due to the thin and non-volume base);
- relatively low cost (cheaper than implants and ceramic bridges);
- assistance in the treatment of periodontal disease (splinting structures hold teeth with pathological mobility).
Minuses:
- low aesthetics (clasps are visible when you smile);
- long addiction (due to the base on the sky, addiction takes a couple of weeks);
- the pressure of the clasps on the tooth enamel (with strong chewing loads, the enamel can be damaged).
To avoid these disadvantages, many choose clasp dentures with locks.
Expert opinion
Roman Borisovich Alekperov
orthopedic dentist
Experience: 24 years
Advantages of clasps over attachments. When there is a need to restore the dentition, and the dental defects are scattered, the patient does not have enough financial resources, I recommend installing clasp dentures with clasps. You quickly get used to them, their production does not require much time, the chewing load is distributed on the teeth, and not on the gums, as is the case with lamellar ones. Yes, the aesthetics are insufficient because of the visible hooks, but you have teeth, you can eat, drink, and live a normal life.
Types of clasp dentures with clasp fixation
According to the design and purpose of the structure, two types of prostheses are distinguished - conventional and splinting.
Conventional clasp dentures with clasps
They are recommended in cases where it is not possible to place implants and there are still teeth in the mouth that can be used as a support for a prosthesis. The design allows you to eliminate such dental defects as:
- absence of three or more teeth in a row (front, side, on one side of the jaw and/or on different ones);
- terminal defects of the dentition (when the last teeth are missing).
Conventional clasp prosthesis
Splinting clasp dentures on hooks
They differ from ordinary ones in that in their design they have special retainers (processes on the arch) for supporting teeth. Used to restore dentition in patients suffering from:
- pathological mobility of teeth (the prosthesis fixes loose teeth and protects them from excessive chewing load);
- malocclusion (the design holds the teeth in the correct position, thereby correcting abnormal jaw closure);
- increased abrasion of the upper teeth (the prosthesis covers the chewing surface of worn-out teeth, making them higher and protecting them from further abrasion).
Splinting clasp prosthesis
Depending on the materials, there are 2 types of clasp dentures:
- Prostheses containing metal. The arc and clasps (and sometimes the base frame) of such structures are made of chromium-cobalt or gold-platinum alloy.
- Metal-free structures. The so-called Quadrotti prostheses (Quattro Ti) with nylon clasps and a base made of a mixture of nylon and hypoallergenic plastic.
Contraindications
The installation of structures is contraindicated in the following cases:
- The presence of less than 4 healthy teeth in the jaw;
- Complete edentia;
- Low level of hygienic care;
- Allergic reaction to the materials used;
- Periodontal disease in stage 3;
- Severe bone atrophy;
- Pregnancy and lactation period;
- Acute viral, bacterial diseases;
- Exacerbation of chronic pathologies of the body;
- Mental disorders;
- Serious diseases that cast doubt on the success of treatment (oncology, tuberculosis, diabetes, AIDS, etc.)
Manufacturing stages and installation
Prosthetics with clasp dentures with clasps includes two main stages - clinical and laboratory. From the moment you contact the clinic until the restoration of the dentition, the following stages occur:
- Examination. The doctor draws up a prosthetic plan, makes a conclusion about the state of oral health and, if necessary, sends the patient for treatment of caries and/or periodontal disease.
- Taking an impression of both jaws.
- Making a prosthesis in the laboratory. Structures with metal elements are made by casting methods, while plastic ones are produced under exposure to high temperatures.
- Trying on the finished design. If necessary, correction is carried out.
- Installation of the prosthesis.
On average, the clinical and laboratory stages of prosthetics take one week.
Stages of prosthetics
During the first visit, the dentist assesses the general condition of the patient’s oral cavity and prepares the teeth for prosthetics. The supporting units are ground to fit the crowns (later clasps will be attached to them).
The aesthetic properties of clasp prostheses leave much to be desired: when smiling, during a conversation, metal hooks become noticeable to others
After this, the specialist takes a picture of the patient’s jaw and determines the shade of the future artificial teeth using a scale. Temporary crowns are placed on the prepared units. Next, clasp structures and crowns are made in the laboratory, and when ready, the latter are fixed to the teeth. The dentist tries on the frame of the prosthesis, this is followed by finalizing the product in the laboratory and handing over the removable structure to the patient.
How to care for a prosthesis?
Clasp dentures with clasps should be cleaned at least twice a day, or better yet, after each meal. Hygienic measures include:
- rinsing the structure under running water after eating;
- daily disinfection (soaking in solutions of disinfectant tablets Corega, Lacalut, Efferdent, President, Dentipur, Dontodent, etc.);
- professional cleaning (performed by a dentist to remove hard deposits).
cleaning with a brush and low-abrasive paste at least twice a day;
To maintain the original appearance of the prosthesis, you should not abuse smoking, coffee and tea, which cause artificial teeth to change color and become covered with plaque.
It is advisable not to remove the prosthesis at night and to remain in it constantly. Once every six months you need to visit the dentist to reline the structure (correction to evenly distribute the chewing load).
The result of prosthetics depends not only on the quality of the prosthesis, but also on the qualifications and skill of the orthopedic dentist. Our website provides an up-to-date list of clinics that effectively restore dentition using clasp structures.
Types and structure of clasps
Clasp fasteners can be retaining (settle under load, transfer pressure to the oral mucosa), support (evenly distribute pressure under load during clenching, unclenching teeth, talking, eating on the supporting teeth and gums), support-retaining. The latest (combined) types of hooks have a complex design:
- body (fixed element located in the upper part of the tooth);
- shoulders (adjacent in front and behind to the supporting units);
- occlusal overlay (a protective barrier that prevents the clasp from immersing in soft tissue and transfers the load to the supporting teeth);
- process (connects the hook to the base of the prosthesis).
Classification of clasps:
- round, flat, ribbon, semicircular (in shape);
- single-, double-armed, double-armed, single-linked, ring-shaped (according to the girth of the tooth);
- holding, supporting, supporting-holding (by function);
- cast and bent (according to technology and materials of manufacture).
The main advantage of clasp structures is the ability to remove them at night and provide rest to the oral mucosa and supporting teeth. Hooks on clasp dentures must meet a number of requirements: securely fix the structure, distribute the chewing load along the axis of the teeth and oral mucosa. Clasps should not affect teeth at rest; in case of periodontitis, they also have a fixing function.
Classification
Clasp structures refer to a removable or conditionally removable method of prosthetics. They are divided by type of material and type of fastening. The base of the prosthesis, the arch, is made of three types of material:
- Made from medical alloy (cobalt, chromium).
- Noble metals (gold-platinum).
- Plastics.
It is obvious that metal-free clasp dentures are less durable, wear out quickly and break under load. However, it is an inexpensive alternative for patients with high sensitivities and metal allergies.
A more durable option is made from an alloy of gold and platinum. Also suitable for patients with allergies, but costs several times more.
How much does a clasp prosthesis cost?
The price of lower jaw prosthetics using a clasp design depends on the following factors:
- base and frame material;
- the number of teeth that need to be restored with a prosthesis;
- material for dental crowns.
The average price of a clasp prosthesis is from 32,000 rubles. The price, as a rule, already includes payment for the prosthesis itself, treatment planning, installation of the system, and check-ups with the dentist.
Clasp dentures are an inexpensive and accessible way to restore a smile with a long service life (more than 10 years).
How clasps are made
The structures in question are made in a dental laboratory, and first you need to choose one from all the varieties. Most often, such fixing elements are made from base metals. Any type of hook is bent with pliers, tongs or round nose pliers - it is given its original shape. Then the metal element is “implanted” into the base and the prosthesis is given to the patient to try on and, if necessary, the product is adjusted.
Important! Thorough polishing of the metal in the element that is adjacent directly to the tooth is required: the material should not injure the enamel or serve as a place for plaque accumulation. But the process, on the contrary, is covered with small notches, which ensure its reliable fixation with the acrylic base.
Clasps are an integral part of a removable denture, which has an extensive classification. The choice of a specific model is made by the dentist, because it is important to take into account not only the financial capabilities of the patient, but also the condition of the supporting teeth, gums and alveolar process.
Telescopic fixation system
This fastening system is the most complex and modern. In this case, telescopic crowns are made of two parts in contact with each other. One part of the crown (lower, non-removable) is installed in the supporting teeth, and the other (upper, removable) is firmly fixed to the metal plate of the clasp.
When fastening, the upper part of the telescopic crowns fits tightly onto their lower part. Shrinkage of the fastening when installing a removable structure ensures reliability and strength of fixation. And although this type of fastening is not cheap, it serves reliably for a long time and only needs minor correction.
Unfortunately, for Russia this type of fastening is still new and is used infrequently. To work with these types of clasp fastenings, you need a highly qualified orthodontist. But in America and Europe, telescopic mounts are already common and familiar.
Design
The standard design of a clasp includes three elements: a shoulder, a body and a process.
The shoulder is a special part that provides coverage of the dental crown, and is located between the gum line and the middle part. A prerequisite is a tight fit to the tooth surface in all areas, the identity of the anatomical structure and the strength of the element. The supporting part of the shoulder is two-thirds of its length, and is placed above the boundary line, eliminating lateral displacement of the prosthetic structure, and maintaining the basic rigidity parameters. The retaining element, which makes up the remaining third of the length, is located below the boundary line and fixes the prosthesis in a given position.
The process is a part used when using the method of rigidly connecting the clasp to the base of the system, which is placed under artificial crowns. In such designs, the connecting link is the body of the clasp, which is a spring element located on the chewing surface of the unit.
Models of the support-retaining type are characterized by the absence of a process, which is replaced by an occlusal pad and an anchor part.
Care Tips
Any orthopedic structure will last longer if it is properly cared for. General recommendations for clasp dentures are simple:
- Clean your dentures regularly and thoroughly with a toothbrush.
- Rinse the structure after eating food.
- Periodically remove and soak the product in a special solution. Each structure has its own frequency at which the structure can be removed so as not to damage it. The doctor tells the patient about the peculiarities of care after installing the clasp prosthesis.
To avoid damaging the surface of the crowns, it is not recommended to use whitening pastes or too hard toothbrushes. It is also important to visit the dentist 1-2 times a year for preventive procedures.
Prices
| Service | Price |
| Consultation + treatment plan | |
| Clasp prosthesis | 47 700 ₽ |
| Quadrotti | from 57,100 ₽ |
| Splinting | 52 150 ₽ |
Expert of the article you are reading: Natalich Boris Anatolyevich Chief physician, CMN, doctor of the highest category, orthopedist, surgeon, implantologist, leading specialist of the NovaDent network
37 years
Clinical experience
Otradnoe
st. Khachaturyan, 7
+7 +7
Free consultation with this specialist