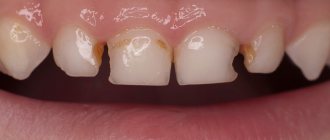
The term “ dead tooth ” is used in dentistry to refer to a tooth whose pulp has been removed or has lost its vitality.
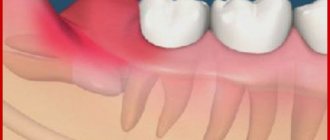
The pulp is loose connective tissue with a huge number of lymphatic, blood vessels and nerves. It is this neurovascular bundle, located in the so-called pulp chamber, that provides nutrition to the tooth, perceives various irritations, stimulates regenerative processes and acts as a biological barrier that prevents pathogenic microscopic organisms from entering the carious cavity into the periodontium.
A tooth with dead pulp quickly becomes brittle, darkens and loses its ability to regenerate.
What is a “dead” tooth?
This is what dentists call a tooth without nerve endings that no longer receives blood. Consequently, the tooth stops receiving nutrients and its work stops, the tooth dies. The disruption of blood supply is explained by damage to the pulp, the area where blood vessels and nerve endings gather into a single bundle. If the vessels and nerves do not function, then the nutrients no longer support the life of the tooth.
Method of treatment
The use of analgesics numbs the pain, but when a dead tooth appears, a trip to the dentist is inevitable. Doctors will take therapeutic measures:
- remove the remains of decomposed pulp;
- root canals are filled with gutta-percha;
- restore the front part of the tooth with a filling or crown
Restoration of the coronal part is carried out using a filling, or a filling on a pin, in case of a large volume of lost tooth tissue. If the filling is ineffective, the doctor will install a crown or inlay.
The indication for pulp removal is its extensive inflammation, which threatens decomposition processes and further development of infection.
Is it possible to cure such a tooth?
You can cure, but you cannot resurrect. The dentist will remove all affected tissues, nerves, root canals, expand them, clean them and treat them with an antiseptic, and then seal them hermetically so that infection does not enter from outside. The crown, if more than half of it is preserved, will be restored with a filling. For more severe lesions, an artificial crown will be installed. However, in case of extensive inflammation, the tooth can be removed and replaced with a prosthesis - an implant.
A “dead” tooth must be shown to a doctor, otherwise there is a risk of complications from the infection, which will develop into gumboil, osteomyelitis. A cured tooth can perform its function fully, but it can withstand the load worse, so its service life is significantly lower than that of “living” teeth.
Removing the pulp of the affected tooth
Pulp removal is a complex dental procedure that requires a highly qualified doctor.
Stage 1 – local anesthesia or general anesthesia
At the first stage of treatment, local anesthesia is administered in the area of the affected tooth. In exceptional cases, the patient may require general anesthesia. The use of anesthetics allows one to avoid preliminary killing of the nerve with arsenic.
Stage 2 – x-ray
At the next stage, the doctor conducts an X-ray examination to determine the length of the root canals.
Stage 3 – pulp removal and tooth filling
All video presentations
After reviewing the x-rays, the dentist:
- gently removes pulp,
- cleans, rinses with antiseptic preparations and fills root canals,
- and then restores the natural anatomical shape of the tooth.
If all procedures are carried out competently, and the patient carefully and impeccably observes personal hygiene, then the service life of a pulpless tooth can reach several decades.
Severe toothache is a consequence of unprofessional dentists
Evidence that the dental operation was performed incorrectly is a sharp toothache accompanied by an increase in temperature. If depulpation is of poor quality, the patient may need repeated surgery. At the same time, aching, mild pain after removal of the dental nerve is considered normal.
What can lead to the need to remove a “dead” tooth:
- damage to the tooth root by caries;
- the occurrence of longitudinal fractures and root cracks (below the gum level);
- the presence of a cyst or granuloma on the root of the tooth, inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth, the treatment of which is not possible.
There are several rules that patients can follow to prolong the life of their teeth:
- cover the tooth with a ceramic inlay or crown;
- visit the dentist once every 6 months for a check-up, hygienic cleaning and, if necessary, a control X-ray of the tooth;
- do not chew hard food (nuts, seeds, crackers, etc.);
- Avoid temperature changes when eating (for example, hot coffee with cold ice cream).
As we see, a patient can do a lot for his health. But in order for the tooth to last longer, it is much more important to choose a specialized clinic that uses modern technologies, high-quality equipment and materials. An experienced and knowledgeable doctor will ensure the vital activity of a pulpless tooth for a long time.
Reasons why the pulp dies
There are many reasons why pulp dies. Most often, it is removed when pulpitis has already developed, the nerve is inflamed, it no longer brings any benefit, but is only a cause of torment (this situation leads to the development of severe pain) and a source of infection. It is important to understand that an attempt to endure the pain from pulpitis, when a person uses various painkillers that relieve discomfort, but do not stop the destructive process, can also destroy a tooth.
Also on the list of reasons why pulp dies is injury. For example, if a person hit his jaw hard, and after that did not visit a doctor, leaving everything as it was. Against the background of such a situation, pain often persists for some time, and then gradually subside, while the tooth inside dies.
A tricky problem. What you need to know about toothbrushes and how to choose them? More details
What causes a tooth to die?
Trauma or damage to a tooth is one of the possible causes of tooth death. For example, putting something dangerous in your mouth that can cause the death of your tooth. The tooth can die quickly, over a few days, or slowly, over a period of months or years.
A tooth can also die as a result of poor oral hygiene. This can lead to cavities which, if left untreated, can slowly destroy your tooth. Cavities start with the enamel, which is the outer protective layer of your tooth. If left untreated, they can slowly eat away at the enamel and eventually reach the pulp. This leads to contamination of the cellulose, which separates the blood from the pulp and eventually causes it to die. You will likely experience severe pain as the decay reaches the cellulose.
A dead tooth can be identified during a routine dental examination, which includes an x-ray. You should always see your doctor after any tooth injury or if you have signs of a dying tooth. This way, your dentist can begin treating the tooth as soon .
External difference
Doctors note that a tooth devoid of pulp can often be recognized by external signs. For example, immediately after living tissue has been removed from it, it may acquire a grayish tint, which will become darker over time. In addition, such a tooth stops reacting to cold and hot. One of the disadvantages is the fact that, even if such a tooth is damaged by caries, a person may not feel the destructive processes in a timely manner, since due to the lack of nerve endings he simply will not feel pain. Such a tooth, in addition, over time begins to gradually deteriorate and crumble.
Teeth guarantee. Why is it important to read a contract in dentistry? More details
Why is a tooth without pulp considered dead?
The main thing that changes in the condition of the tooth after depulpation is that the trophism (nutrition) of the hard tissues is lost, the tooth becomes very fragile and reacts sharply to external factors.
The absence of nerve endings affects the protective function of the tooth: in the absence of a pain reaction, a person can damage the tooth by biting something hard on it and not notice it. The pulp ceases to protect the tooth from microbes, as a result of which it becomes more susceptible to caries.
As you can see, a pulpless tooth requires additional care, as it is more vulnerable than healthy ones.
For chronic and acute inflammatory processes
In most cases, tooth extraction is accompanied by acute or chronic periodontitis, inflammation of the gum tissue, or even the formation of purulent foci. If such a process covers a large area of tissue and is accompanied by high temperature, the formation of fistulas and edema, then most likely the attending physician will prescribe enhanced antibacterial therapy to slightly reduce the severity of inflammation. And only after this will surgery be performed in the oral cavity. On the other hand, there may be a need for immediate surgical intervention if the surgeon considers such intervention urgent. There can be many criteria for this choice, and only an experienced doctor can make an adequate decision.
What is atraumatic tooth root removal?
What instruments does the surgeon use to achieve atraumaticity? For atraumatic removal, special instruments are used - thin, neat and elastic elevators that can minimally invasively penetrate and expand the periodontal tissue that connects the tooth root directly to the jaw. Using special instruments, the periodontal ligaments are cut so that the root can be removed as carefully as possible, in its “pure form.”
The vestibular plate that surrounds the bone is very thin. And we work with her carefully when removing teeth. It may also be necessary to saw the root of the tooth so that it can be removed in pieces. Sawing can be carried out with oscillating ultrasonic attachments - ultrasonic knives. Cutting the root of a tooth can be done quite effectively with a high-quality thin surgical dental bur, which has a certain length.
After cutting the root, the medial wall of the root is first removed, and then the vestibular wall of the root is removed. This allows for maximum preservation of surrounding tissue.
Then, after such removal, you can preserve the tooth socket or place an implant so that the bone is preserved as much as possible. Preservation of the tooth socket is carried out if there are no conditions for installing an implant at once, or if the patient undergoes delayed implantation.
If the roots of wisdom teeth are removed, the socket is not preserved; it is enough to remove them as atraumatically as possible. Let's talk about this in a little more detail.
Features of root removal of decayed wisdom teeth
Are there any difficulties when removing the roots of wisdom teeth? Removing the roots of wisdom teeth requires that the surgeon has sufficient experience. Often the roots of these third molars (wisdom teeth) are located close to the mandibular canal. Often the roots of molars are adjacent to the upper or lateral wall of the mandibular canal. The configuration of wisdom tooth roots is extremely diverse and sometimes extremely difficult to remove:
Therefore, when removing the roots of wisdom teeth, it is imperative that the patient undergo a CT scan. And the surgeon, as I said, needs to have some experience in surgical training in order to avoid the risks of removing the roots of such teeth and carry out the manipulation as efficiently as possible.
Like any root teeth, the roots of wisdom teeth are removed by cutting them along the roots. Wisdom teeth do not have problems because they are close to the angle of the lower jaw and there are strong cortical plates there. When I talked about thin vestibular walls, this comparison refers to the aesthetic zone of the smile, to the frontal group of teeth, including the premolars:
.
Tooth crack - symptoms and treatment
A tooth crack (fracture) is a non-carious violation of its integrity. It can affect both the enamel and the deeper layer of the tooth - dentin. Such defects are diagnosed during examination in more than 90% of patients [13]. In most cases, they are superficial, do not cause concern and do not require treatment. But sometimes deep cracks occur, which can lead to tooth loss [1].
Most often, cracks in teeth appear in patients over 35-40 years old. This is due to a decrease in enamel strength due to the loss of calcium and fluoride ions, as well as carious lesions requiring root canal treatment.
In patients 15-34 years old, fractures are more common on filled and carious teeth, while in patients over 35 years old, enamel damage is found in most cases on intact (healthy) teeth. On average, the enamel of intact teeth is damaged 3 times more often than filled ones [2].
Cracks can occur on teeth affected by caries, appear after contact with dental instruments, improper treatment, or for other reasons (for example, injuries).
The following factors contribute to the formation of fractures::
- mechanical damage;
- solid food;
- sudden changes in temperature;
- abuse of bleaching agents;
- dental procedures;
- shrinkage of filling materials;
- some malocclusions;
- bruxism;
- frequent consumption of carbonated drinks;
- hereditary enamel defects;
- disturbances in the exchange of calcium and fluoride in the body.
Deep fractures may appear as a result of falls, bruises of the maxillofacial area, sports injuries and road traffic accidents. Enamel and dentin cannot withstand heavy mechanical load, as a result their integrity is compromised. Such damage is usually noticeable immediately and requires immediate dental care. With a strong impact, a complete fracture of the tooth crown may occur.
Sudden temperature changes on the surface of the teeth, consumption of sour and carbonated drinks have a detrimental effect on the enamel. Like any substance, it expands at high temperatures and contracts at low temperatures. When these processes follow one after another, the bonds between the crystals that make up the enamel are disrupted. Acidic substances soften the surface of the tooth and make the enamel less durable. First, microcracks appear in it, which are visible only during a dental examination using additional lighting sources. Over time, the defects become visible to the naked eye, become deeper and change color.
Cracks often occur in people with deep fissures - natural grooves on the surface of their chewing teeth. This anatomical feature makes teeth less resistant to heavy loads.
If you do not follow the filling technology, then over time the material used will shrink, which will lead to displacement of the walls of the treated carious cavity. Sometimes this can compromise the integrity of the tooth, especially if the walls of the carious cavity are very thin [3].
Often cracks occur during preparation of root canals before filling, installation of a pin and root tab. If over-preparation occurs, the dentin becomes thinner and a vertical root crack occurs. The integrity of the tooth can also be compromised if the diameter of the pin is incorrectly selected, excessive pressure during its installation, or compaction of gutta-percha (filling material) [4].
Stuck root
The most common complication of tooth extraction can be a stuck, broken off root. If the root tip remains in the tissue, then the dentist has to use the entire arsenal of tools to get to the fragment: sometimes the tissue is drilled out or a section of the alveolus is removed to get to the desired depth. When hard tissues are crushed, this process can take quite a long time, since the dentist faces the difficult task of removing absolutely all the scattered fragments. In some cases this may take several hours.
Should I remove the decayed tooth or treat it?
With the development of modern dentistry, many people look differently at the process of dental treatment, but there are still frequent cases when a person does not go for dental treatment solely out of fear, remembering the negative personal experience of dental treatment 20-30 years ago.
And there are situations in life, everyone has their own and they are all understandable, when it is not possible to do dental treatment in a timely manner. And the inflammatory process from caries develops into deeper damage to the tooth tissue. Often the situation reaches the point where a badly damaged tooth remains in the mouth. And at this moment a person is often inclined to think that the destructive process has already gone so far that he sees no other solution to the problem other than contacting a professional dentistry center and removing the affected tooth.
We advise you not to draw independent conclusions on this matter.
What should be done in this situation?
- Make an appointment with your dentist. Moreover, you need to make an appointment not with a surgeon, but with a dental therapist and an orthopedic dentist, only the two of them decide on the possibility or impossibility of saving the tooth.
- The specialist will definitely do a computed tomography scan in the area of this tooth or suggest, if necessary, an orthopantomogram.
- Based on the examination and modern X-ray diagnostic methods, the doctor will tell you whether it is possible to cure and restore this tooth, and explain all possible restoration options.
There are often ambiguous situations when none of the doctors can guarantee with one hundred percent certainty that the tooth can be saved. A lot depends on the body’s ability to cope with inflammatory processes. When you are offered a probable chance that the tooth will be saved or that your body will not cope and the tooth will still have to be removed, despite the money invested and the time spent, the choice will always be yours. How ready are you?
There are cases when doctors give rather pessimistic forecasts for saving a tooth, but the patient is ready to try treatment, the body reacts very favorably, the cyst goes away and the tooth serves well for many years. And it happens the other way around: the forecasts are very promising, but during the treatment process some kind of failure may occur in the body and for a long time no positive dynamics are observed, or even vice versa, the affected area progresses.
In what cases do teeth definitely need to be removed:
- The crown part of the tooth has chipped deep under the gum; such a tooth can no longer be restored.
- The x-ray shows that there is resorption of bone tissue between the roots of the tooth; treatment of such a tooth is pointless, because the inflammatory process has already begun to destroy the bone and in order to stop this process of inflammation, there is only one way out - tooth extraction.
- There are large cystic formations at the apex of the root(s).
- If the jaw is severely injured, it may be necessary to remove the tooth(s).
- If a tooth is fractured (if it occurs longitudinally, its restoration becomes impossible)
- When there is severe tooth mobility.
- Eighth teeth (“wisdom teeth”), also known as third molars. They usually grow in the wrong position, put pressure on the dentition, cause crowding and put strong pressure on the adjacent seventh teeth.
- Almost always, a tooth is removed that was previously subjected to canal treatment and during the previous treatment a perforation of the root canal occurred.
- A chronic inflammatory process has already formed in the bone tissue, which cannot be treated.
- Sometimes, during orthodontic treatment, when the jaw has already formed, there is a lot of crowding of the teeth, and there is not enough room for the teeth to move to form a correct bite. The teeth that need to be removed in this case are determined by the orthodontist after diagnosis and calculations.
When you need qualified advice and help from a dentist, come to us for a consultation. You will receive answers to absolutely all questions regarding the health of your teeth. Regardless of how long you have not sought treatment from a dentist and what condition your teeth are in, you will not see reproachful glances, but will receive high-quality treatment from our doctors. As a rule, we always select a time for consultation when all the necessary specialists can spare time for a conversation with you.
Even severely damaged teeth often have a chance of recovery; consult a doctor. And it’s better to come late than completely late or never.
What happens to such a tooth?
“Of course, such a tooth ceases to receive the microelements it needs, its resistance to bacteria is impaired, and over time it becomes fragile. But at the same time, it is worth understanding that such processes do not occur at lightning speed, but proceed very slowly, and such a tooth can remain in the oral cavity for many years,” notes Ilya Antonov.
Of course, certain rules of hygiene will help to preserve even a dead tooth: regular and correct brushing of teeth, the use of additional oral care products on the recommendation of a doctor, as well as preventive examinations according to the approved rules of dental medical examination.
An alternative to implantation is autotransplantation of wisdom teeth
Don't rush to remove your wisdom teeth. Firstly
, there must be clear indicators for their removal.
Secondly
, you don’t need to follow fashion, trends and delete eights just because “a girlfriend or friend deleted them and it’s cool.” There are a number of moments in life when wisdom teeth come to our aid.
It is not for nothing that nature has created a number of organs that duplicate each other in our body, for example, we have two lungs, two kidneys, which in case of problems with one lung/kidney come to our aid. Also with wisdom teeth: if a person (for some reason) has problems with the chewing group of teeth, for example, caries has destroyed the sixth or seventh tooth, then eights can come to the rescue. How so? After all, wisdom teeth are not involved in the chewing process. Yes, you are right here. But a wisdom tooth can serve as a donor, and it can be transplanted into place of a tooth with destroyed roots. Fantastic? No, advanced technologies in dentistry. This is called autotransplantation.
In the following video we show in detail the dental transplant surgery. The roots of two sixths of the patient's teeth had just been destroyed, and they were replaced by the patient's own wisdom teeth. And, by the way, this patient at the end of the video gives a detailed review after 1 year after the operation. Look, this is useful:
How long does a tooth live without pulp?
This period varies greatly. In some patients, the tooth is destroyed within a year, and in others it can last for another ten years. What's the difference? Here are the factors that affect the condition of the tooth after depulpation:
- the degree of initial destruction of the crown of the tooth;
- pulp removal technique, quality of root canal filling;
- the method by which the tooth was restored after removal of the nerve (filling/inlay/crown);
- caring for the tooth after treatment, performing the necessary hygiene procedures.
After the tooth is depulped, treatment procedures are required that will improve its vitality. First of all, this is filling. Empty root canals are filled with special material. Complete and high-quality removal of the entire pulp, as well as hermetically filling the canals with filling material over the entire length, reduces the risk of inflammation of the tissues surrounding the tooth and the appearance of a cyst.
Depending on the degree of tooth decay and the specific clinical situation, the doctor may suggest restoring the tooth with either a filling, a ceramic inlay, or an artificial crown. An inlay and a crown are the optimal methods for restoring “dead” teeth, because they cover the tooth from above and fit hermetically to the tooth, thereby reducing the contact of the internal environment of the tooth with bacteria in the oral cavity, moisture and air, and protecting the tooth from chips and cracks. In addition, it is comfortable for the patient and has an aesthetic appearance.