Only a few months pass after the baby is born when teething begins. They are still milky, but almost until school they will help the child eat right. However, even a baby’s weak teeth often become a headache for parents. They quite often begin to break down, causing physical pain to the child and interfering with digestion. In the future, the situation may worsen, since the problem will quickly affect young molars.
Why does a child have bad baby teeth and how can you try to help your baby cope with the problem?
How does childhood dental caries occur?
According to statistics, caries in children under three years of age occurs in 90% of cases, that is, 9 out of 10 children have dental caries. This term refers to the pathological, slow process of destruction of hard tooth tissue under the influence of unfavorable factors.
In this article
- How does childhood dental caries occur?
- The main causes of dental caries in children 1 year of age
- Features of bottle caries
- A one-year-old child has caries - what to do?
- How will caries be treated for a one-year-old child?
- How is deep caries treated for young children?
- How to prevent caries in one-year-old children: preventive measures
The oral cavity is home to many microorganisms, including cariogenic bacteria. They can ferment sugars into acids that are destructive to dental tissue. When the number of these bacteria in the mouth increases sharply, they produce large amounts of acid, which causes dental caries in the child.
Why should caries in primary teeth be treated?
It is a mistake to think that baby teeth do not require treatment. Tooth decay is a disease caused by the growth of bacteria in the mouth. It weakens the immune system, and this leads to frequent illnesses in the child.
Tooth irritation from food forces the child to spare the affected side when chewing, which can disrupt the bite for life.
Consequences of refusing treatment:
- Maintaining a focus of chronic infection. From the oral cavity, bacteria can spread to the ENT organs, the digestive tract, the lungs and even lead to sepsis.
- Violation of the formation of permanent teeth. Unrecognized deep caries has a negative effect on the rudiments of permanent teeth. As a result, they grow up weakened or already affected by caries.
- Violation of the integrity of the dentition. In the absence of timely treatment, children quickly develop pulpitis. Such teeth are removed, the integrity of the dentition is damaged, and the bite changes.
The main causes of dental caries in children 1 year of age
The main cause of tooth decay is exposure of teeth to acid produced by bacteria. At the same time, a number of reasons contribute to the increase in the number of pathogenic microorganisms in the oral cavity and the negative impact of these bacteria on teeth.
- Lack of proper care.
Many parents do not consider it necessary to brush their one-year-old child's teeth. Some are convinced that daily hygiene should begin only after all baby teeth have erupted. Others are afraid to injure the baby’s tender gums with a brush. Still others are sure that caries cannot damage teeth in one year, because the child eats only “baby” foods. Dentists say that dental caries in children can develop at any age. Regular and high-quality timely brushing of teeth is one of the most important conditions for maintaining dental health. It is necessary to start brushing with the appearance of the first tooth, that is, long before the child turns one year old.
- Long-term bottle feeding.
The teeth of a child who eats formula from a bottle for a long time are susceptible to developing so-called bottle caries. Its development begins with the upper front incisors. As a rule, it is localized in the cervical and contact areas.
- Infection from parents.
Cariogenic bacteria can enter the mouth of a one-year-old child from an adult. This happens when kissing on the lips or when a mother licks a pacifier and gives it to her baby. To reduce the risk of pathogen transmission, it is important for mom and all family members to monitor their dental and oral health.
- Congenital problems.
A predisposition to the development of caries may be associated with a violation of the correct formation of teeth during the prenatal period, a lack of minerals and vitamins, and diseases that a woman suffered during pregnancy.
- Abuse of sweets.
The most common cause of dental caries in children is an excess of sweet candies, juices, and foods high in fast carbohydrates in the diet, which are a breeding ground for cariogenic bacteria. Children under one year old are not recommended to consume sugar at all, but many parents ignore this advice from doctors and begin to give store-bought juices, sweets, and ice cream from 8-9 months. Improper eating behavior increases the risk of dental caries in a child several times.
- Lack or excess of fluoride.
Fluoride is an essential element that affects dental health. A lack of this component, as well as its excess, can cause dental problems, including caries in children.
How to prepare your child for treatment
It's no secret that children are afraid of dentists, and without reason. Today, dental procedures are performed quickly and painlessly. You just need to prepare your baby for treatment so that he doesn’t worry. Find a good specialist. Some doctors turn the treatment process into an interesting game and thereby distract the child from terrible thoughts.
Practice your visit to the dentist at home. Soft toys can also act as “patients”. Tell your child that both mom and dad go to the dentist. Choose a time to visit the clinic when your baby is alert and cheerful. Make up a story about how a doctor saves teeth from monsters. Never scare children with hospitals or doctors when they misbehave.
Check your child's teeth every few months. Get him used to brushing them twice a day. Buy a special children's brush with soft bristles. To make it more interesting for him to take care of his teeth, you can choose a brush stylized as a cartoon character. Similar hygiene products are available in our online store.
Features of bottle caries
Bottle caries in a child under 1 year of age is one of the most common types of carious lesions in primary teeth. It occurs when young children are bottle-fed before bed. As a result, food remains in the oral cavity, which bacteria actively process while the child sleeps.
There is a myth that bottle caries cannot occur if the child is fed natural products - milk, kefir, juice without sugar. But cariogenic bacteria feed not only on artificial, but also on “natural” sugars - lactose, fructose, so the “naturalness” of children’s products does not reduce the risk of developing bottle caries.
Use of anesthesia for children during dental treatment
In some cases, during dental treatment in children, it becomes necessary to use general anesthesia.
Indications
There are the following indications for the use of anesthesia in pediatric dentistry:
- the need to perform a large volume of dental procedures, treating more than 5 teeth at the same time;
- the child has certain neurological and mental diseases, such as epilepsy, Down syndrome, cerebral palsy;
- allergic reactions to local anesthetics;
- ineffectiveness of local anesthesia;
- impossibility of establishing contact between the doctor and the child necessary to perform dental procedures.
How will caries be treated for a one-year-old child?
For young patients, the most gentle, gentle treatment is usually selected. In modern clinics, when treating young children, doctors try to ensure that the appointment time does not exceed 30 minutes.
If anesthesia is necessary, application is mainly used; in rare cases, an anesthetic injection is given. For babies under one year of age, it is preferable to treat caries using non-invasive methods, without drilling. But such therapy is justified and effective only if caries is detected early at the spot stage.
The most popular methods of treating caries in children.
- Remineralization.
Remineralizing therapy at the carious stain stage helps restore the mineral composition of the enamel, restore its strength and prevent the destruction of dental tissues. The essence of the method is that gels and pastes containing phosphorus, calcium and other components beneficial to dental health are applied to the surface of the enamel. Remineralization can be carried out both in a dental clinic and at home, using products recommended by the doctor. Home treatment is preferable for one-year-old children, because the mother or another family member will treat the teeth, and the baby will feel comfortable.
- Silvering.
Today this technique is considered outdated, although in some clinics it is still used to treat caries in children under three years of age. The essence of the method is that the enamel is coated with a 30% solution of silver nitrate, which neutralizes the activity of bacteria and stops the process of tooth decay. Among the main disadvantages of the method is a decrease in the aesthetics of the smile, because after silvering, white teeth turn black.
- Ozone therapy.
A modern non-contact method of caries treatment that is suitable for children of any age. It is based on the antibacterial effect of ozone, which neutralizes carious lesions at an early stage and disinfects the tooth. Usually ozone therapy is combined with remineralization. First, the affected area is cleaned with ozone, and then the enamel is coated with strengthening compounds.
Which treatment method to choose for a particular child is determined by the dentist after the first appointment.
How to help your child
The main question is, if a child has bad baby teeth, what should parents do? There are some ways to improve a bad situation. These include the following rules:
- reduce carbohydrate intake if possible;
- do not lick the pacifier or sugar it, especially before bedtime;
- From an early age, accustom your child to brushing his teeth;
- if artificial feeding, use only adaptive formulas after consulting a pediatrician;
- wipe teeth with a swab after feeding;
- Rinse your mouth after every meal as soon as your child is able to do so.
But there is also a main factor that will help cope with bad baby teeth. Of course, this is a visit to the pediatric dentist. The sooner the doctor diagnoses and treats carious teeth, the more likely it is that the baby will grow up healthy and strong. After all, the functioning of the entire child’s body depends on proper digestion. Since dangerous bacteria accumulate in carious cavities, complete tooth destruction cannot be prevented except with the help of an experienced dentist.
How is deep caries treated for young children?
If a one-year-old child is diagnosed with deep caries, it cannot be treated like a superficial one, without drilling. In this case, the teeth are filled with photopolymer composite or glass ionomer cement. To ensure that the baby sits still or as calm as possible during treatment, sedation or general anesthesia is used. Unfortunately, any anesthesia has a number of side effects, so it is better not to start caries and treat it in the early stages, when you can do without preparation and filling.
To protect children's teeth from further damage, it is necessary:
- make sure that there are no cracks on them, which become “gates” for caries-forming bacteria (cracks usually occur as a result of injuries);
- maintain oral hygiene, which will prevent the formation of plaque (the child should brush his teeth twice a day with age-appropriate toothpaste);
- supplement the menu with protein products that help strengthen enamel, as well as seasonal vegetables and fruits;
- if this is not possible, select a vitamin-mineral complex with the help of a pediatrician.
How to prevent caries in one-year-old children: preventive measures
Simple preventive measures will help prevent the development of this pathology, which can lead to the loss of several baby teeth at once:
- Clean your baby's teeth and gums with a special fingertip immediately after eating.
- Do not bottle feed a 1 year old child.
- Dentists note that bottle caries can also develop in one-year-old breastfed children. What's more, breast milk contains more sugar than formula, so prolonged breastfeeding can be damaging to children's teeth.
- Brush your teeth immediately after teething. First, use a soft toothbrush with fluoride-free toothpaste; after two years, you can use baby toothpaste with fluoride.
- Brush your child's teeth or supervise this process until he is at least eight years old.
- Don’t give sweet drinks, it’s better to teach them to drink plain water and unsweetened tea.
- Do not feed your baby at night. At night, the production of saliva, which has a bactericidal effect and fights germs, decreases. If necessary, you can give your child clean water to drink at night.
- Do not share a spoon with your child or put his pacifier in his mouth to avoid the transmission of cariogenic bacteria.
- Check your teeth regularly. If you notice white spots on them, lines on the tooth enamel near the gums, be sure to contact your dentist.
- Visit your dentist regularly, even if there are no stains on your teeth.
Follow all preventive measures, and you can prevent caries in children under one year old and maintain oral health.
“Black teeth in very young children” and other problems. Competently about caring for children's teeth
Shakovets Natalya Vyacheslavovna, head. Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Belarusian State Medical University, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor. Natalya Vyacheslavovna Shakovets answered 18 questions from mothers . Department of Pediatric Dentistry, Belarusian State Medical University, Doctor of Medical Sciences, Professor.
1. At what age does teething usually begin, and what difficulties may arise?
– On average, teething in children begins at 6-8 months with the central lower and then upper incisors. It ends at the age of 20-30 months (that is, at 2.5 years the child usually has all his temporary teeth). The deadline for teething is 3 years; if it is exceeded, you should consult a doctor for advice.
Teeth in the gums can be detected by touch, or in some cases - by x-ray, which is undesirable due to age. It also happens that a child is born with teeth, then he is examined and a decision is made to remove them if they interfere with feeding.
If eruption is delayed, do not panic: as a rule, early eruption is worse, since in this case the mineralization of the teeth is lower and the risk of caries is higher.
2. How can you alleviate the condition of teething?
– Usually it does not cause serious problems, except when molars erupt at the age of 12 to 16 months: they are large, difficult to erupt, and a hematoma may even appear on the gum. Sometimes this is accompanied by pain, anxiety, runny nose (no more than three days) or a fever above 38 degrees. In such cases, chilled teethers provide relief. Today, experts do not recommend using gels with lidocaine, or no more than twice a day and in small quantities. You can use homeopathic remedies - it is safe and quite effective.
3. How to properly care for your child’s teeth?
– Dental care should begin from the moment the child’s first tooth appears. It is imperative to brush your teeth: the lower ones can be done first with a silicone fingertip, but it rather massages the gums irritated by the teething process than cleans them. It is already necessary to brush the upper incisors with a children's toothbrush in accordance with the age markings. According to modern research, you should use a fluoride-containing paste: the amount per cleaning is about the size of a grain of rice. There is no need to rinse your mouth with this amount of toothpaste - rinsing, by the way, negates the effect of the toothpaste (even parents should remember that after brushing your teeth, you only need to rinse your mouth once, forcefully releasing water through clenched teeth, so that the effect of the components included in the paste is preserved). This type of cleaning is the most effective prevention of caries.
Even in the absence of dental problems, it is worth visiting a dentist at the age of 1 year so that the doctor can assess the development of the organs of the maxillofacial area, identify risk factors and make recommendations.
4. Can the food a child eats affect the condition of his teeth?
– The child’s nutrition has a direct impact on teething and their condition. Food must be balanced in the content of essential nutrients, calcium and phosphates, vitamin D. Nutrition has a dual effect - endogenous (supply of substances necessary for the construction of enamel before eruption) and exogenous - external influence after eruption. During the period of endogenous formation, the balance of proteins, fats and carbohydrates (nutrition of a pregnant woman and a child in the first years of life) is very important, and in the second - the regime of sugar intake. With their frequent occurrence, the enamel cannot withstand acid attacks, and its destruction occurs. Parents should remember that food at an early age should not be sweet and sticky, which is why children should not often give, for example, corn sticks or dried fruits: their remains stick to the enamel and can cause caries. Therefore, after such a treat, you need to thoroughly brush your teeth or eat something hard, for example, an apple or a piece of cheese. In general, experts recommend giving any sweets to children only during meals.
5. Some children already have black, broken teeth at an early age - what is the reason for this?
– As for teeth “spoiled” at an early age, this disease was first described in 1932 under the name “black teeth in very young children.” Then this disease was called differently: “bottle caries”, “early age caries”. These terms refer to multiple dental caries. The reason is night feeding of a child over 12 months of age with sugar-containing products, including “regular compote”. This is due to the fact that at night there is no natural cleaning of the teeth in the oral cavity and practically no saliva is released. The upper teeth are especially vulnerable. Sugars accumulate on them and pathogenic microflora develop. At first, the damage to the enamel looks like white stripes on the gum at the base of the tooth, but within a few weeks they begin to darken, and subsequently the crowns break off along the line of circular caries: a characteristic picture is formed - dark “stumps” of teeth. To prevent the problem, from 9 months it is worth accustoming the child to a cup and spoon, and not giving anything but water at night.
6. Does the so-called “geographic language” pose any threat to the child?
– As a rule, such a symptom as a “geographical” tongue (alternating depressions and thickenings on the surface of the tongue - author's note) goes away with age and nothing other than sensitivity to sour or salty foods bothers the owner.
7. What can parents do to prevent caries in their child?
– This is already listed: the absence of sweets in the diet until 3 years of age and a small amount thereafter, the use of fluoride-containing toothpaste from the moment the first tooth erupts, the abolition of night feedings after 12 months. For the same purpose, you can coat children's teeth with fluoride varnish: this is the only highly concentrated product recommended for children under 6 years of age, since it “sticks” firmly to the enamel and is not swallowed. In temporary teeth in the presence of carious cavities, fillings must be placed - this protects against subsequent damage and destruction of permanent teeth. Sealing is also useful - this is the application of a protective coating that prevents the accumulation of food in the recesses of the teeth; the procedure is performed from 1.5 years. The first permanent teeth to erupt are usually the 6th teeth (first permanent molars). They are located far in the oral cavity, parents do not notice their eruption and pay insufficient attention to their cleansing. Therefore, these teeth are very susceptible to caries in the first two years after eruption. A preventive procedure such as sealing can protect them. And from the age of 6, children are recommended to use adult toothpaste.
8. Is prosthetics performed on children?
– Dental prosthetics in children, as a rule, are not carried out until the final formation of the bite. If a tooth is lost, a space-preserving structure can be installed.
9. What should parents pay attention to after all their baby teeth appear?
– Since the crowns of permanent teeth are wider than baby teeth, from the age of 4-5 years gaps should appear between the teeth - this indicates the correct growth of the jaws and their readiness for the eruption of permanent teeth. Parents should also pay attention to the chewing surface of the teeth: if the tubercles of the crowns are sharp and not smoothed, the chewing function is insufficient, which may lead to problems with the formation of the bite; in this case, it is recommended to consult a specialist. Recently, a fairly common occurrence is the absence of the rudiments of permanent teeth in a child, especially the 5th and 7th teeth. If suspected, a panoramic x-ray is recommended, based on the results of which a decision is made, including prosthetics in the future or removal of a damaged tooth.
10. When should a baby tooth be removed by a specialist?
– A child’s teeth can be easily removed at home in the event of a physiological change, if they have already lost their roots and are “held on by a thread.” In some cases, you need to urgently consult a doctor, for example, if there is an inflammatory process: periodontitis, periostitis and others - in children they progress very quickly.
11. When and why is the bridle trimmed?
– There are three frenulums in the oral cavity: the tongue, the upper and lower lips. Plastic surgery of the frenulum of the upper lip can be done at the age of 8-9 years, and the need for surgery is determined by the dentist depending on its condition, place of attachment, and weaving into the palatine suture. The frenulum of the lower lip rarely causes problems. The frenulum of the tongue can be “cut” already in the maternity hospital if it interferes with the sucking function. But more often the question of surgery is decided at the age of 3-4 years, when a violation of sound pronunciation becomes obvious. Here, the question of the advisability of plastic surgery is decided jointly by a speech therapist and a dental surgeon.
12. Should anything be done if problems with a child’s bite are detected?
– The first problems with bite can be noticed after the eruption of all temporary teeth at the age of 3-3.5 years. Correction can be carried out in the form of myogymnastics, which is most effective at the age of 4-7 years, or with the help of removable appliances during the period of temporary and mixed dentition. At this age, it is important to pay attention to the correct functions: nasal breathing, active bilateral chewing, correct swallowing, pronunciation of all sounds, the habit of keeping lips closed, formation of posture, absence of bad habits. After all permanent teeth have erupted, fixed appliances are used. If the bite is not corrected in time, not only aesthetic problems may arise, but also problems with chewing, sound pronunciation, headaches, problems with periodontium and the temporomandibular joint. Subsequently, some professions may be contraindicated (for example, military personnel, pilot, diver).
13. At what age is it recommended to install braces on a child, if such a need arises?
– Braces are an orthodontic device that is indicated for use from the age of 12, that is, after the completion of the formation of a permanent dentition. Usually the whole process takes about two years, the cost can reach 2-3 thousand dollars in equivalent (the minimum price for the service in Bobruisk is approximately 1,600 rubles for both jaws - author's note).
14. Can children use an electric toothbrush, mouthwash and floss?
– Electric brushes can be used without fear or risk; they are recommended, first of all, for children who refuse to brush their teeth or cannot withstand the required duration of brushing. Some models of electric brushes have applications for mobile devices. This rotating brush helps adapt the child to dental procedures in the form of professional cleaning. Parents should brush their children's teeth at least until the child learns to tie his shoelaces. And then control this process for up to 12 years. Dental floss can be used from 3 years of age to prevent proximal caries (on the lateral surfaces of the teeth). It is more convenient to use flossets for this purpose - special holder devices. Mouthwash can be used when there is no risk of ingestion - from 6 years of age and older.
15. How should parents act in emergency cases if their child has a very bad toothache?
– In emergency cases with a toothache, a child will be seen in 24-hour dental offices, but with a very young child, if possible, it is better to go to hospitals where there is a dental department. Parents of the baby should not feed and water him in advance in case of need for treatment under general anesthesia.
16. How should children with allergies prepare for a visit to the dentist?
– Parents of allergy sufferers should contact the dentist in a timely manner and not delay the visit until emergency intervention. You can do an allergy test first, although lidocaine, for example, is now rarely used.
17. What should parents do if their child is often bothered by stomatitis?
– Stomatitis can be of different nature – herpetic, aphthous, contact, candidiasis, etc. Only your doctor can determine the exact cause and prescribe treatment in each specific case.
18. What are your recommendations on how to make sure that a child is not afraid of the dentist?
– I recommend visiting a specialist regularly, and not just in case of an advanced problem. A healthy and calm child will more easily accept manipulations, which are also painless. It is worth getting to know the doctor in advance and finding out how the doctor communicates with young patients: a friendly relationship will serve as the key to a child’s long-term and positive attitude towards the dentist.
Treatment of caries in adolescents
Caries in the first and second stages can be eliminated by remineralization, during which the enamel is saturated with calcium and fluoride. The doctor applies a solution containing these microelements in large quantities to it, due to which its structure is restored. At home, the patient is recommended to use special pastes and gels that strengthen the enamel. Teenagers can use the same hygiene products as adults: ROCS “Active Calcium”, Stomysens® Desensitizing Repairing Treatment 4, Vivax “Remineralization”, etc. If caries has penetrated into the dentin, filling is required, which is carried out according to the standard algorithm:
- pain relief with an injection;
- cleaning the carious cavity from dead tissue;
- disinfection of the tooth surface;
- applying a protective pad;
- filling the cavity with filling material;
- grinding a hardened filling.
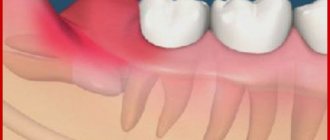
Treatment may be more difficult if the caries is located under the gum. In such cases, it has to be cut, and after the operation, self-absorbing sutures must be placed on it. Also among the frequent complications of caries is pulpitis. When it develops, the nerve is partially or completely removed.
If possible, the doctor tries to preserve both the tooth and part of the pulp so that it remains “alive”, otherwise it will darken. If pulpitis and caries have developed on the incisors or canines that fall into the smile area, a darkened tooth will ruin it aesthetically. In adolescence, this is dangerous because it can affect the child’s self-esteem.