When we are seriously faced with the issue of restoring missing teeth, we have to solve several issues at once:
- choice of prosthetic technique;
- selection of material for the prosthesis.
The range of materials for dental prosthetics is now wide, which is better? Metal, plastic or ceramics, or maybe a combination of them? In this article we will try to highlight all the features of metal-ceramic prostheses, as well as the pros and cons of the increasingly popular prostheses made of metal-free ceramics.
What is cermet?
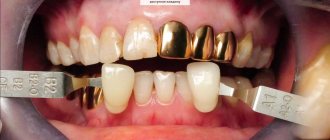
When we say “metal-ceramics,” we most often mean crowns and bridges on a metal frame coated with ceramic. Otherwise, it is an orthopedic base made of metal, repeating the shape of a tooth ground for a crown, which is covered on top with a layer of thin ceramics. Ceramic metal is less likely than other materials to cause allergies. Metal-ceramics are used mainly for dental prosthetics in the chewing region, where preference is given not so much to aesthetic qualities as to reliability and functionality.
Prosthetics with metal-ceramics.
As already noted, metal-ceramics have found their application more in the prosthetics of chewing teeth, where the main thing is strength, not appearance. However, this does not mean that metal ceramics are completely devoid of aesthetics, not at all. The widest range of ceramic coatings allows metal-ceramic crowns to perfectly imitate the shade and structure of natural tooth tissue.
The problem may arise when prosthetics are placed on the front teeth. It is as follows: a dark metal frame can show through a layer of ceramics, that is, the metal simply shines through the translucent coating. Therefore, when replacing anterior teeth, it is most often recommended to use metal-free ceramics or ceramics based on zirconium (zirconium dioxide) - this is, in fact, the same metal ceramics, but the frame material is white metal - zirconium, by the way, is absolutely biocompatible with the human body .
Tooth crowns: which ones are better in price?
The cost of crowns consists of materials, technologies and equipment used, as well as the qualifications of the doctor and the level of the clinic where the treatment is performed.
Types of crowns for teeth and which ones are better in terms of cost
| Type of crown | Price |
| Metal crown | 3,000 rubles |
| Metal-ceramic crown | 7,000 rubles. Metal-ceramics with shoulder mass - on average from 12,000 to 14,000 rubles, but may cost more (depending on the alloy and manufacturing technology) |
| Gold or platinum crown | 15,000 rubles. The upper threshold can reach 40,000 - 50,000 rubles |
| Ceramic crown | 15,000 rubles for standard crowns. Using Empress technology - on average 20,000 - 23,000 rubles |
| Zirconium dioxide crowns | 25,000 rubles |
You can view all prices for dental crowns here.
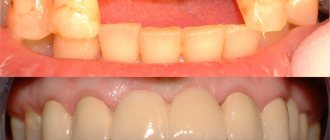
Metal-ceramic prostheses.
What is a metal-ceramic prosthesis upon closer examination? First of all, it is a metal frame covered with a layer of hypoallergenic ceramics. If we compare modern metal-ceramic prostheses with their predecessors made of various composites, we will see the undoubted advantages of metal-ceramics:
- firstly, metal-ceramics reproduces the color and texture of natural tooth tissues quite well;
- secondly, it does not fade, does not absorb dyes and, therefore, does not change color over time;
- thirdly, dental ceramics used in dentures are hypoallergenic and do not cause rejection, except in rare cases;
- and finally, cermets are very durable.
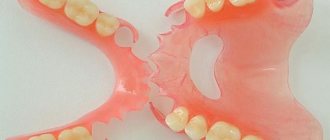
If we are talking about removable dentures made of metal ceramics, then we are talking about a clasp denture. “Bugel” (clasp) means “arc”, and the prosthesis itself is precisely a metal arch with metal-ceramic crowns attached to it. Removable metal-ceramic structures are used when there are contraindications to installing a permanent metal-ceramic prosthesis.
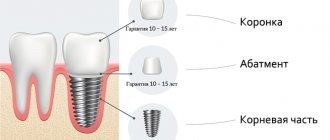
What crowns are best to put on implants?
When studying the question of which crowns are best placed on implants, one should remember the classic procedure for installing dentures. If it is necessary to recreate the missing units in the frontal region, experts give preference to the aesthetic component. The best dental crowns in this situation will be made from zirconium material or ceramic.
If you need to fix crowns on your chewing teeth, and you don’t know which ones are better, any experienced dentist will give clear advice - in this area it is advisable to install prosthetic devices made of metal ceramics, zirconium material or e.max glass ceramics. It should also be taken into account that adapters in dental structures, in the event of subsequent use of the above prostheses, must be obtained from materials that are unable to be seen through the ceramic layer.
Many patients are interested in which crowns are better, ceramic or zirconium, to be fixed to implants? According to leading experts, the most advantageous options include devices made from the innovative material E-max or zirconium dioxide.
Additionally, when evaluating whether metal-ceramic or zirconia crowns are better, it is important to consider the need for zirconia adapters. This will prevent the body from becoming allergic to metal, as well as obtain the desired aesthetic result.
Advantages and disadvantages of metal ceramics.
Patients who decide to have metal-ceramic prosthetics often ask themselves and their doctor the question: can metal-ceramics cause harm?
If the prosthesis is made by professionals from high-quality certified materials in a laboratory in compliance with relevant standards, then the danger of such prosthetics is minimal and practically eliminated. The materials that are used in the manufacture of metal-ceramic crowns are themselves non-toxic, but, nevertheless, they can behave differently in the oral cavity. For example, nickel in frames made of chromium-nickel alloys can cause an allergic reaction. And structures made from base metals can oxidize over time due to a reaction with saliva.
In general terms, the advantages of metal-ceramic prostheses include their durability and strength, while the disadvantages are the need for deeper treatment of the tissues of a living tooth, as well as exposure of the frame when the gums recede and the metal base is visible through the ceramic (the exception is zirconium crowns).
Strength:
Today, metal-ceramic structures are installed mainly on teeth exposed to significant chewing load, although until quite recently they were used everywhere. Metal-free ceramic crowns, on the contrary, did not enjoy increased popularity due to the fragility of their design, and therefore were mainly used to restore front teeth.
But with the advent of zirconium dioxide frames in dentistry, the situation has changed dramatically. An increasing number of both dentists and patients are inclined to use these new materials for prosthetics of both chewing and frontal teeth.
The ultra-strength of cermets also has a downside. Damage occurs to the teeth in contact with the metal-ceramic prosthesis, which can lead to their premature and excessive wear. Whereas the hardness coefficient of ceramic prostheses based on zirconium dioxide is very close to the hardness coefficient of real teeth, therefore, when in contact with a prosthesis made of metal-free ceramics, the opposing teeth are not injured from the impact load.
Allergy:
Allergies in the design of a metal-ceramic prosthesis are caused not by ceramics, which are hypoallergenic, but by the metals used in the frame. Symptoms of an allergy to metal ceramics may include:
- burning sensation in the gums or tongue;
- metallic taste in the mouth;
- swelling and swelling at the site of contact with the crown.
If you experience any of these phenomena after installing a metal-ceramic crown, contact your dentist immediately. If you are allergic to metal-ceramics, there is a way out - this is replacing the metal-ceramic crown with an all-ceramic metal-free orthopedic structure.
Color:
Dental ceramics allow you to choose any color that perfectly matches the natural color of the patient’s teeth. The shade is carefully selected by the dental technician using a special Vita scale.
A metal-ceramic crown will not change color over time and will not fade because it does not absorb pigment at all, unlike composite materials from which fillings are made. For all the above reasons, metal ceramics do not require special bleaching.
Durability:
The main misconception of happy owners of metal-ceramic prostheses is ignoring the service life of such a structure. All patients are confident that it is enough to install a metal-ceramic crown once and for all, and it will serve for the rest of their lives. Let us immediately refute this false statement; it is not true! No matter how regrettable it may be, the service life of any metal-ceramic prosthesis is limited on average from 5 to 12 years.
The key to the longevity of the prosthesis is its high-quality production using individually and precisely made casts, as well as the patient’s compliance with all recommendations for its care when wearing it.
Dental clinics provide a guarantee for metal-ceramics for a period of one to three years, taking into account the frame material and the clinic’s policy. According to the warranty terms, the crown must maintain its integrity and not be subject to destruction under mechanical influence for a certain period specified in the warranty. The crown may last the stated time, however, remember that the most “popular” reason for the crown to fall out is not its damage, but secondary caries that has developed under the crown. To avoid this situation, do not neglect regular preventive examinations and do not delay replacing worn-out orthopedic structures with new ones.
Ceramic metal, like any other material, has a service life, after which the product made from it wears out and becomes unusable, as it cannot fully perform its functions. Ignoring the service life of metal-ceramic dentures can lead to tooth loss!
Which crown is better for a chewing tooth?
On the one hand, the answer to the question of which crowns are best to place on chewing teeth is obvious. Molars are tireless workers who bear almost the entire chewing load, so they need to be restored with very strong and reliable crowns. The issue of functionality really comes first, but you shouldn’t focus only on it. Despite the fact that molars are not so noticeable when smiling, it is simply criminal not to worry about aesthetics in this day and age. In addition, the choice of crown is also important from the point of view of the compatibility of its material with soft tissues.
Which crown is best for chewing teeth?
- Metal crowns.
These are reliable and cheap crowns with a good margin of safety: the likelihood of breakage and chipping is minimal. On the other hand, aesthetics with them will be at zero level. Another problem is individual intolerance to materials. - · Crowns made of gold-platinum alloy.
They are not cheap (see the course on precious metals), but they are quite reliable, non-toxic and safe for soft tissues. The amount you will pay for the precious alloy is quite comparable to the cost of a ceramic crown, which is much more similar to a natural tooth. However, it’s up to you to decide in this case. - Metal-ceramic crowns.
The most popular option for dental restoration. The choice in favor of metal-ceramics is really justified, since these are the crowns that have the optimal price-quality ratio. However, this product has its drawbacks. Firstly, metal-ceramics are less durable compared to classic metal crowns and are more susceptible to chipping. Secondly, the contact edge of the crown is not covered with ceramic, so a blue stripe appears at the junction of the crown and gum, which is bad from an aesthetic point of view. This problem is partly solvable (see crowns for front teeth), but the money spent in this case is not always justified. - Ceramic crowns.
It all depends on the type of crown. Classic ceramic crowns are not recommended for installation on chewing teeth due to the high risk of breakage and chipping, but today specialists have managed to significantly increase the strength of the material and improve manufacturing technology. Modern Emax glass-ceramic crowns allow for prosthetics in any part of the jaw. Their only drawback is their relatively high price. - Zirconium dioxide crowns.
Very strong, very durable, comparable in cost to ceramic ones. Monolithic zirconium crowns are more often used for prosthetics of chewing teeth, since porcelain veneer increases the possibility of chipping.
Metal ceramics VS Ceramics.
If you have indications for prosthetics with a “bridge” or crowns, it is logical that you will begin to ask the question “What is better to install: metal-ceramics or ceramics?”
So, how are they different? Metal-based ceramics and metal-free ceramics will differ in their aesthetic properties, functionality and, of course, price. Of course, a metal-ceramic prosthesis is durable, incomparable to the strength of an all-ceramic one, but it is not always appropriate for prosthetics in the smile area. In this regard, if we are talking about the restoration of the frontal dentition, then in all respects prostheses made of metal-free ceramics win. Therefore, metal-free crowns for the front teeth certainly have superior aesthetic properties.
However, prices for all-ceramic dentures are higher. Therefore, if you want to restore teeth in the chewing section, affordable metal-ceramics will be very acceptable there - it has the necessary strength, and aesthetic defects are unlikely to be visible in the lateral sections.
Preparation for prosthetics and its stages
Whether it is metal-ceramics or metal-plastic, the general technology of prosthetics with these materials is practically the same.
Preparatory activities include
professional visual examination and control x-ray to ensure there are no foci of inflammation. If there are any, they must be eliminated therapeutically;- if there are previously sealed canals, monitor their condition; if necessary, damaged seals are removed and new ones are installed;
- tooth depulpation procedure - nerves are removed followed by canal filling. When installing a prosthesis on a front tooth, this is mandatory; in the case of a multi-rooted tooth, the decision is made by the dentist based on the individual characteristics of the patient and the condition of the tooth. This need is caused by the high probability of pulp destruction with accompanying unpleasant symptoms, which will entail removal of the prosthesis and additional treatment. Therefore, this moment is extremely important;
- in case of carious tooth damage, therapeutic treatment is carried out until the process is completely eliminated;
- if the tooth is destroyed by less than 50%, then a pin is installed in the root canal. Next, the tooth crown is restored using filling materials;
- complete or critical destruction of the coronal part of the tooth requires the installation of a stump inlay.
Stages of prosthetics
- circular grinding of the tooth to the thickness of the walls of the crown, thus forming a stump;
- the color of the future prosthesis is selected using a special scale;
- a measuring impression is taken, on the basis of which the dental technician creates a metal-ceramic or metal-plastic prosthesis;
- the patient is temporarily (7-10 days) fitted with a special plastic crown. This is done to protect the ground tooth and eliminate the patient’s psychological discomfort, because a ground tooth looks unaesthetic;
- direct installation of the finished prosthesis, including fitting and, if necessary, adjustment.
Metal ceramics VS Metal.
All-metal crowns compare favorably with metal-ceramics in price and are not inferior in structural strength. But there are a few “buts”:
- metal can imitate a natural tooth only in terms of anatomical shape (the “iron teeth” effect);
- metal teeth destroy the teeth they come into contact with, increasing their
Pros and cons of metal ceramics
Advantages:
- They are visually pleasing, can be matched to the color of your teeth, and have the same visual properties as natural teeth.
- Durability. They are extremely durable dental materials that easily withstand the stress of chewing and years of wear and tear. Thus, they can last for several years.
- Minimal grinding.
Flaws:
- Some patients have individual intolerance to metals.
- The ceramic part sometimes peels off from the metal structure.
Are you interested in a metal-ceramic crown? The price is clarified in the corresponding section of our website, by phone or directly at the dentist’s appointment.
Metal ceramics VS Zirconium dioxide.
frame of metal-ceramic crowns
crown frame based on zirconium dioxide
We have already explained the differences between metal ceramics and ceramics based on zirconium dioxide. In principle, zirconium is the same metal, which is favorably distinguished by its aesthetic properties (white color) and absolute biocompatibility, but is less favorably distinguished by its price. When choosing a material for dental prosthetics in the smile area, it would be logical to give preference to crowns on a zirconium frame. When restoring chewing teeth, it will be cheaper to install metal ceramics. If the patient has metal intolerance, the solution would be to install a prosthesis on a zirconium frame.
Which ones are better to choose?
Clinics offer many options for crowns. One of the differences between them is the material used. It is on this parameter that the quality, cost, indications for the use of a particular crown and, of course, aesthetics largely depend. Another very important nuance that also affects the quality parameters is the manufacturing technology of the product.
Types of crowns
- Metal crowns.
They are considered hopelessly outdated. They can be made from various alloys (cobalt-chromium, nickel-chromium). Among the disadvantages are the not very aesthetic appearance, the risk of an allergic reaction to the metal. - Crowns made of precious metals.
As a rule, these are solid prostheses made of gold-platinum alloy. They allow you to achieve the necessary strength and maintain biocompatibility. However, crowns are not made entirely from this alloy. It is used as a frame for metal-ceramic crowns and is covered with ceramics on top. - Metal-ceramic crowns.
The most common products that consist of a metal frame and ceramic cladding. First, the frame is cast, then a layer of ceramic is applied, which can be manufactured using computer modeling. - All-ceramic crowns.
Metal-free ceramic crowns. Due to its biological inertness, this material is considered one of the safest for soft tissues. Manufactured using firing technology (on a refractory model or platinum foil); ceramic pressing method (surface painting technique or layering technique); on a milling machine using CAD/CAM computer modeling. - Zirconium dioxide crowns.
They are manufactured using computer modeling using special milling equipment. There are two types of zirconium dioxide crowns: monolithic (entirely made of zirconium dioxide without veneering) and combined (porcelain mass is applied to a zirconium dioxide frame). The presence of a frame allows you to hide darkened teeth, as well as existing metal inlays and pins. This gives the prosthesis more aesthetics.
There are also temporary crowns that are placed while the permanent structure is being manufactured, but we cannot talk about them as a full-fledged orthopedic structure.
Each of these types of crowns has variations within its category (type of alloy, material features, production method). The overall quality indicator consists of many nuances that must be taken into account when choosing a product. Below is a table with the main parameters that determine the quality of the crown. Two plus signs or two minus signs indicate a characteristic feature of the crown in a particular indicator.
Quality table
| Product | Strength | Aesthetics | Durability |
| Metal crown | + | – – | +/– |
| Golden crown | + | – | + |
| Metal-ceramic crown | +/– | +/– | +/– |
| Ceramic crown | + (depending on the type of crown) | ++ | + |
| Zirconium dioxide crown | + | + | ++ |
All types of crowns are capable of restoring the functionality of a tooth, but the appropriateness of choosing one or another product largely depends on the specific clinical case.
How to install metal ceramics?
Installation of metal ceramics occurs in several stages. First, the patient needs to undergo a general examination, diagnostics and dental treatment, if necessary.
After this, the teeth are prepared for a crown: the enamel is ground down, the nerve is removed (if the condition of the supporting teeth is good, the doctor can leave them alive).
Impressions are taken from the ground teeth, from which individual orthopedic structures are made in the laboratory. Thus, the production and installation of metal-ceramic prostheses takes on average about two weeks.
Keep in mind that grinding for an all-ceramic crown is more gentle, this is due to the thickness of the crown itself (a ceramic crown is thinner). Usually the tooth is not ground down completely; a ledge is formed at the border with the gum, which does not allow the metal frame to come into contact with the gum and, thus, reduces the risks of developing allergies, tissue irritation, bleeding gums and swelling.
How to properly care for metal-ceramic dentures?
There is nothing supernatural in caring for metal-ceramic structures. It is necessary to brush your teeth morning and evening. No special brushes or cleaning equipment are required. A regular toothbrush will work fine. The main thing is not how to clean it, but how! Pay attention to the movements when cleaning: they should be sweeping, that is, directed from the gums to the edge. If, however, we talk about any specific devices recommended for cleaning metal-ceramic dentures, use dental floss and an irrigator.
If you have the feeling that a tooth or teeth under metal-ceramics hurt or ache, consult a doctor immediately, as pain may be a symptom of secondary caries that has developed under the crown.
In some cases, restoration of a metal-ceramic orthopedic structure may be required. For example, if metal ceramics break off right in the mouth. If the metal frame is not exposed, then most likely the chip is minor and can be restored using composite materials in the oral cavity. Unfortunately, if the frame of the prosthesis is exposed, then reconstruction is impossible. Most likely, you will need to remove the damaged metal-ceramic prosthesis and install a new one in its place. Remember about the service life of metal-ceramics; replacing them in a timely manner will help avoid problems and save the tooth.
What problems may arise after prosthetics?
Possible problems after metal-ceramic prosthetics include the possibility of darkening of the gum edge. This may appear immediately after the crowns are installed or several weeks later.
The cause of the defect is associated with a metal frame protruding through the mucous membrane. The visibility of such a flaw directly depends on the person’s smile. If your gums are visible when you smile, then the darkening of the gum edge will be noticeable to others.
If the installation was carried out by an unqualified dentist or low-quality materials were used during manufacturing, there is a possibility that chips and cracks will appear on the structure after a few weeks. Other possible problems include:
- galvanic syndrome (metallic taste);
- the appearance of inflammation of the gum tissue under the structure (due to improper oral care and penetration of food debris and pathogens under the crown);
- pain and discomfort (feelings of the presence of a foreign body). This problem can arise if the anatomical features of the oral cavity were not taken into account when making crowns. For example, if the structure is too high, the tooth begins to experience increased loads;
- development of carious lesions (the probability is high if the crown is not closely adjacent to the gum);
- increased sensitivity. If the molar or premolar located under the crown has not been pulped, then there is a high risk of increased sensitivity to heat and cold.
One of the disadvantages of metal ceramics is the blueness of the gums.