Types of occlusion Indications for orthopedic treatment In case of deep bite In case of open bite In case of cross bite In case of small defects Implantation
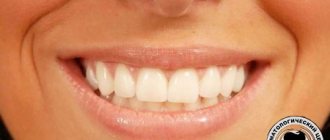
The position of teeth with closed jaws in dentistry is called occlusion. Unfortunately, not every one of us can boast of perfectly straight teeth. Most people experience malocclusion. Most often, they are small and few people notice them, but there are situations when the malocclusion is pronounced and causes a lot of inconvenience. In these cases, it is customary to install braces. What to do if for some reason it is impossible to install braces? Dentistry has developed methods for correcting malocclusion using prosthetics, but doctors warn that they can only be used in specific clinical cases, strictly according to indications.
Types of bite
All babies are born with a malocclusion. Their lower jaw is moved back. Thanks to active sucking, it gradually moves forward. When bottle-feeding, you need to take this point into account and not give children a nipple with a large hole so that they train their muscles, ensuring their load.
By age 14
A permanent (adult) bite is formed, all milk teeth are replaced by permanent ones, the number of teeth reaches the physiological norm (28-32).
By this time, it becomes clear what type of bite has formed:
- Normal
It is also called physiological. A normal bite has variations: the lower teeth slightly overlap the upper teeth, the teeth meet rather than overlap, and some may be tilted forward. The main definition is that all teeth are closed, there is contact between them, the lateral teeth are closed without gaps.
- Deep
The upper teeth cover the lower ones by more than a third. Contact is broken. This pathology is called traumatic because it leads to injuries to the mucous membrane, abrasion of teeth, and disruption of the temporomandibular joint.
- Open
A gap remains between the teeth, resulting in food not being chewed completely. The defect affects the process of swallowing and even breathing. The mucous membranes dry out, saliva does not wash away plaque in time, hence frequent caries and other diseases of the oral cavity.
- Distal
The gap is formed as a result of the fact that the upper jaw is strongly pushed forward. Accompanied by dysfunctions of breathing, swallowing, and chewing. Pain in the joints often occurs.
- Mesial
With this defect, the lower jaw moves forward. With this pathology, two extremes can be observed: crowding of teeth or gaps between teeth (trema and diastema). When there is crowding, tartar accumulates very quickly and if it is not cleaned off in time, periodontal diseases (gingivitis, periodontitis) occur.
- Cross
The teeth overlap each other. Such a defect is difficult to treat and forces one to resort to surgical methods. Leads to facial deformation, disruption of the TMJ, and permanent injuries to the mucous membrane.
Treatment Options
In such a situation, there may be several options for solving the problem, among which are surgical intervention and orthopedic treatment of microstomia. The choice of a specific method directly depends on the individual characteristics of the clinical picture, including the age of the patient, the severity of the pathology and its pathogenesis.
Before proceeding directly to surgery or prosthetics, the doctor must remove plaque and deposits and fill carious cavities, if any. Next, he moves on to the chosen treatment tactics.
Surgical intervention
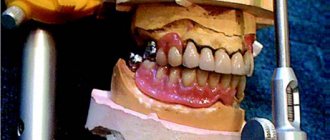
This method of treating microstomia is more often prescribed to patients in whom the narrowing of the oral opening occurred as a result of a severe purulent course of the pathological process or burns. The operation is usually carried out according to the following scheme:
- the doctor administers anesthesia to numb the selected area,
- makes small incisions every 1 - 2 cm, depending on the distance - this is how he restores the level of the mouth,
- forms a piece of skin in the form of a loop and places it behind the cheek, and also forms the tissue above and below,
- the inner part is turned out and attached to the cut areas,
- the stitched part is placed on the formed wounds to form the lip.
The photo shows surgical treatment of the pathology.
However, this method has its contraindications. Thus, surgical intervention is not resorted to in cases where dense scars are the result of a long course of a serious illness. Also, when choosing this option, be sure to take into account the patient’s age, current state of health, tolerance to anesthesia and other factors1.
“A mother I know and her daughter’s little son received severe burns to his face. That’s exactly the diagnosis he was given, microstomia. I had never even heard of this before, but it turns out that sometimes children are born with such a problem. When the boy recovered a little, he underwent surgery. It's gotten much better, thank God. And it’s a pity, of course, it was a child, you wouldn’t wish it on your enemy...”
Ludmila79, from correspondence on the forum www.32top.ru
The operation is not performed for leukemia, tuberculous lupus, as well as for some systemic connective tissue diseases. After surgery, the patient remains in the hospital for about 4 days.
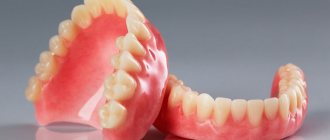
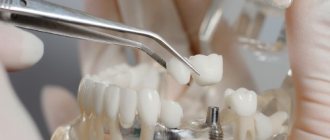
Orthopedic solution – prosthetics
This method also has its contraindications. For example, prosthetics for microstomia are not performed if the patient has a pronounced loss of elasticity of the skin around the mouth, or if growths appear on the face due to burns or physical trauma. However, this option most often becomes a salvation for advanced cases.
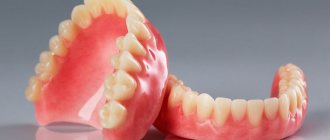
First, impressions of the patient's jaws are taken. Usually they have to be removed in parts and then connected to each other to get a single solid frame. The prosthesis can be integral or dismountable. The second option is used in cases where it is not possible to place the entire orthopedic system in the mouth. The design can consist of 2-3 parts, which are fastened together directly in the oral cavity, and for this purpose special tubes or pins are used. Another option is a folding fixation prosthesis. It includes two parts that are connected by a front element.
For this pathology, folding dentures are used
Prosthetics for deep bite
The task of the orthopedist in this case is to eliminate damage to the mucous membranes, recreate occlusion (touching of teeth when closing), evenly distribute the chewing load and restore the height of the lower part of the face.
To do this, the occlusal surfaces of the teeth are leveled by grinding away the hard tissues. If a large number of units are missing, partial removable dentures with occlusal overlays are used. If the teeth are intact, the bite is corrected with crowns.
Methods for correcting open bite
The teeth that prevent the jaw from closing are ground down. After a little grinding, the surface is polished and calcium and fluorine preparations are used for remineralization. When grinding off a significant thickness, the tooth is covered with a crown.
Teeth that lack height are augmented with crowns. In cases of insufficient height of the front teeth, veneers can be used. If all teeth are intact, then the main goal is to create occlusal contact. If a part is missing, then the task becomes more difficult. It is necessary to restore the dentition and occlusion at the same time. For this purpose, bridges and removable dentures (clasps) are used.
Symptoms you can't ignore
A person who does not have specialized education may note such symptoms as:
- inability to eat and bite;
- external changes on the face, features become rougher;
- the mouth becomes smaller.
During examination, the doctor may note:
- changes in the teeth and jaw system;
- narrow mouth opening.
Symptoms of microstomia in the photo:
Prosthetics for crossbite
Intervention is possible only with the skeletal form of the anomaly, if the patient has refused other types of help. In a preserved dentition, crowns are installed on the lateral teeth. If there is a large overlap, the natural crown (the part of the tooth that is visible) is shortened, cutting off the excess. If there are missing teeth, bridges are used.
If the teeth are slightly tilted, preparation is limited. For large deviations, tabs are used, changing their axis relative to the axis of the root. Such dentures are used for malocclusion if the deviation does not exceed 15 degrees. A crown is placed on top of the stump with an inlay.
Preventive measures
Unfortunately, there are no specific rules for preventing microstomia. In general, experts voice some general recommendations in this regard:
- take a responsible approach to the issue of pregnancy planning, carefully monitor your health while carrying a child, prevent severe illnesses, be less nervous and lead a healthy lifestyle,
- be more careful when bending and when working with potentially dangerous equipment, behave prudently when engaging in traumatic sports or completely abandon them,
- If you observe obvious changes in the oral cavity, immediately contact a specialist, without delaying your trip to the dentist.
The cause of the problem may be severe pathology during gestation. After
prosthetics, the patient must carefully monitor the integrity of the installed structure, maintain oral hygiene and regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations. Since microstomia often becomes a complication of serious injuries, burns and systemic pathologies, it is worth taking as a basis an important rule - any changes in the body should always be a good reason to see a doctor. Any disease must be treated in a timely manner to prevent its severe course and the development of such unpleasant consequences.
1Beitinger V.F. World trends in microsurgery, 2005.
Minor defects
If there are anomalies in the size and shape of the front teeth, the position can be corrected without the intervention of an orthodontist. Veneers and crowns change the shape, close diastemas (gaps between the front teeth), tremata (gaps between other teeth), and visually increase the size of the teeth. Increasing the height of the bite has a positive effect: the lower jaw that has moved back returns, this reduces the load on the temporomandibular joint. The pain and clicking go away. Facial proportions are restored and posture is straightened.
Etiology
Microstomia can be:
- congenital (rare disease associated with intrauterine development disorders);
- acquired (occurs due to various circumstances).
Causes of acquired microstomia:
- mechanical injuries to areas near the oral fissure;
- unsuccessful plastic surgery;
- surgical removal of tumors on the face;
- treatment of osteomyelitis;
- burns, skin lesions;
- systemic scleroderma.
Microstomia prevents the mouth from fully opening, causes significant discomfort when eating, and sometimes there is a violation of speech functions.