From this article you will learn:
- Why is it necessary to perform a gingivectomy?
- Indications for gingivectomy
- Contraindications to gingivectomy
- Methods of performing gingivectomy
- Rehabilitation after gingivectomy
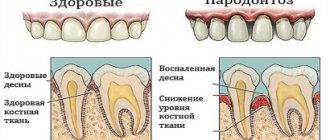
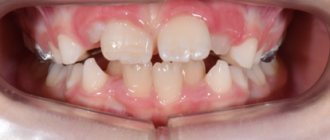
Plaque and food debris often accumulate in the necks of teeth and in the spaces between teeth. These irritants cause inflammation of the gums - gingivitis and periodontitis. Gingivectomy is used to treat periodontal inflammation with irreversible changes, when the pathological process cannot be eliminated by professional hygiene and gentle curettage of periodontal pockets alone.
If the edge of the gum has changed, gingivectomy will help eliminate the affected tissue and stimulate the regeneration of the mucous membrane so that it tightly covers the teeth again, does not bleed, and returns to normal as much as possible.
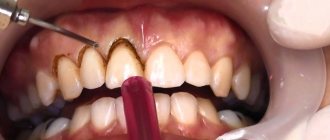
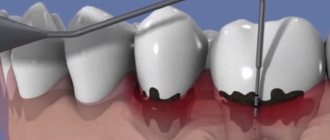
Gingivectomy is an operation performed by a highly qualified dental surgeon or periodontist. It consists of excision, removal of the edge of the gum. At the same time, a sufficient amount of tissue remains for regeneration. The mucous membrane heals quickly, tightly surrounding the teeth. In this way, deep periodontal pockets and gum growths (as with hypertrophic gingivitis) can be removed.
What it is?
Gingivectomy is a rather complex surgical intervention, during which the inflamed edge of the periodontium (gum) is excised and thus the periodontal pockets, which serve as a place for the accumulation of pathogenic microbes and bacteria, are removed and cleaned. The operation can be performed on one tooth or cover several units. Also, correction of the gum edge can be carried out for aesthetic purposes, when the height of the teeth visually increases and the smile becomes more attractive.
Gingivectomy: indications
Appropriate dental procedures are performed for the following pathologies:
- Advanced form of periodontitis.
- Destruction of gingival tissue.
- Formation of periodontal pockets.
- Gingivitis, stomatitis, periodontitis in mild and moderate form.
- Loose connection of soft tissues to the elements of the masticatory system.
Indications for gingivectomy may include the need for endodontic treatment. The procedure can also be performed for aesthetic purposes, such as correcting overhanging gum tissue and increasing tooth height.
In all these cases, surgical intervention is required, without which bone tissue damage, infection of other areas, loosening of dentition elements and their loss may occur.
When does it become necessary?
Improper or insufficient oral care can cause periodontitis, an inflammatory process of the supporting apparatus of the teeth, one of the most insidious dental diseases, leading to very sad consequences. Pieces of food left in the mouth and mineralized dental deposits almost always cause inflammation in the gums. During surgical intervention, the pockets that form between the tooth and gum and are gradually filled with pathological “contents” are cleaned and the free space is eliminated.
Cleaning the periodontal pockets can also be done using traditional methods, but this is not always effective. Even if everything is cleaned, the gap between the gum and tooth will again gradually fill with food debris and dental plaque, which will lead to the same problems in the future. Only excision of the affected area with its further restoration and regeneration will guarantee complete adherence of the tooth to the gum and prevent the inflammatory process from penetrating into the deeper tissues of the tooth or into its roots. And of course, if periodontitis is very advanced, then such radical measures simply cannot be avoided, because infection from the oral cavity can penetrate further into the body and cause various diseases from tonsillitis and cystitis, to rheumatoid arthritis and adnexitis.
In our clinic you can get a free dental consultation!
Cost of treatment
The final price of the operation is influenced by many factors: procedure technique, area of the operated area, type of anesthesia. If anesthesia or sedation is used, the cost will increase.
When using laser equipment, the price will be higher than when using a scalpel. However, the risk of complications is significantly reduced, and gum health will be restored faster.
Dental surgeons at our clinic use modern equipment. We use safe drugs for sedation or anesthesia. Prices are discussed with the patient before treatment begins.
Our doctors
18 years of experience
Baghdasaryan
Armen Evgenievich
Chief physician, dentist-orthopedist-therapist
Graduated from VSMA named after. N.N. Burdenko. Internship on the basis of MGMSU named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “General Dentistry”.
Clinical residency at the Moscow State Medical University named after. A.E. Evdokimov in “Orthopedics”.
More about the doctor...
5 years experience
Sadina
Ekaterina Vladislavovna
Dental therapist, surgeon
Penza State University Medical Institute, specialty “Dentistry”.
In 2021, she underwent professional retraining in the specialty “Therapeutic Dentistry” at the Moscow State Medical and Dental University named after A.I. Evdokimov.
More about the doctor...
8 years of experience
Arzumanov
Andranik Arkadievich
Dentist-orthodontist
Graduated from Moscow State Medical University. Internship - Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics.
Residency at Moscow State Medical University at the Department of Orthodontics and Children's Prosthetics. Member of the Professional Society of Orthodontists of Russia since 2010.
More about the doctor...
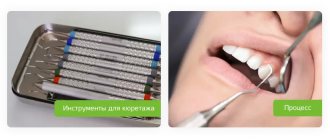
Stages of the procedure
- Professional oral hygiene. The doctor removes soft and hard plaque manually or using an ultrasonic device. Mechanical manual cleaning uses special dental instruments, brushes and professional pastes.
- Anesthesia. Local anesthesia is usually used. An anesthetic drug is selected for each patient. If a person does not know whether he has an allergy, then a test is performed on him - an injection is given in the forearm. If the patient is prone to allergic reactions, then he is referred for testing.
- Measuring the depth of periodontal pockets with a special instrument.
- Incision of the gums with a laser or scalpel.
- Removal of dental plaque.
- Excision of excess gum tissue.
- Treatment of the intervention area with an antiseptic drug.
- Stop bleeding (if necessary).
- Applying a sterile dressing.
Existing indications for surgery
This surgical intervention becomes possible only if there are certain indications for gingivectomy, expressed in the following pathological changes:
- Hyperplasia of the gum margin (fibromatosis, periodontitis, hypertrophic gingivitis);
- Elongated natural tooth crown;
- Deformation and overhanging gums;
- Proliferation of the interdental papilla;
- Formation of periodontal pockets of pathological depth;
- For cosmetic and aesthetic purposes.
Despite the fact that this is a minor surgical intervention, it is not performed without special reasons. The purpose of the operation is justified if the problem cannot be solved with the help of drug treatment, or the depth of the periodontal pocket does not allow the use of the closed curettage technique.
Gingivectomy - price in dentistry
A mandatory preliminary consultation with a specialist will determine how necessary gingivectomy is in general and which method is optimal in this particular case. Without serious indications, gingivectomy will not be performed.
The price for gingivectomy ranges from 300 rubles to 2,000 rubles for treating the area around one tooth.
Also, many clinics provide services to eliminate the consequences of poorly performed gingivectomy. Some institutions provide video and photographic materials of the gingivectomy operation to introduce the patient to the procedure.
Possible contraindications
There are also a number of restrictions that prevent this operation on the gums. Absolute contraindications include tuberculosis, cancer, weakened immunity, heart, liver or kidney disease, high sugar levels, poor blood clotting, subacute bacterial endocarditis.
Local contraindications include the presence of inflammation affecting the bone tissue of the tooth, implants in the joints, a frenulum or mucous cord at the site of the intended incision, a significant depth of intraosseous pockets (more than 5 mm), and a too narrow area of the gum.
What complications can occur after gingivectomy?
According to the observations of our dentists, complications develop quite rarely after gingivectomy. However, negative consequences can occur if the dentist is not aware of the patient's chronic immune system conditions. Periodontal disease and periodontitis are diseases that occur most often in patients with weakened immune systems. Gingivectomy can also cause complications in chronic connective tissue and cardiovascular diseases. This is explained by the fact that pathogenic bacteria can get into postoperative wounds. If the dentist has as much information as possible about the health status of his patient, he will be able to minimize the risk of such complications.
Types of operations
The depth of periodontal pockets, their distribution in the oral cavity and the degree of complexity of the existing problem directly affect the choice of a specific technique for future surgery:
- Partial or gentle Minimal surgical intervention affecting a very small volume of tissue (up to 2-3 mm), pockets are cleaned using an open curettage method. Suitable for minor pathological changes and in the case of aesthetic dentistry procedures in the front row of teeth;
- Simple Classic method of wave-shaped excision of the gums along with the periosteum. To open access to the desired area of the gum, incisions are supposed to be made both from the inside and from the outside. Next, cleaning and curettage are carried out, a bandage is applied for 48 hours;
- Radical The most complex operation affecting not only the gums, but also the tissue of the alveolar area of the jaw. The gum edge, epithelial cords, granulation tissue and affected areas of bone are removed. Then the alveolar arches are aligned and a bandage is applied to the wound.
In addition to these methods, there are more than 15 techniques used for the treatment and excision of periodontal pockets. The most famous of them are named after the dentists who developed them, these are the Gubman technique and the Krekshina technique (the main differences are the minimization of aesthetic damage, the incision is made strictly parallel to the edge of the gum with an indentation of 2-3 mm, several teeth fall into the operating area at once).
The surgical intervention, which usually lasts no more than 30-40 minutes, can be performed in a classic way using a conventional surgical scalpel, but laser gingivectomy is a more advanced and completely bloodless method in modern dentistry. In this case, the impact on the tissue is minimal, the edges of the wound are completely sterile, which avoids infection in the oral cavity and prevents the occurrence of various postoperative complications. In addition, it is absolutely safe, it is not so painful, and the recovery period lasts much less.
Follow these guidelines after surgery
- Temporarily eliminate the consumption of solid foods, including fresh vegetables.
- Consume foods when they are warmed to room temperature.
- It is not recommended to drink hot or cold drinks.
- Until tissue restoration is complete, alcoholic drinks should be completely excluded from the diet.
- It is also not recommended to smoke until the rehabilitation period is complete.
- Minimize chewing loads on the healing area.
The recovery period for each individual case is different, primarily depending on the food used in the diet. Therefore, during the rehabilitation stage, doctors recommend consuming exclusively soft foods that cannot harm the gums. You also need to brush your teeth very carefully so as not to damage the sutures.
Postoperative period
If the surgical intervention is successful, the recovery period will not be long. It is enough to follow the recommendations of your treating dentist and ensure proper oral care and no complications will arise. Be sure to follow these instructions:
- While the wound is healing, give up alcohol and smoking;
- The food should not be too cold or too hot, ideally warm;
- You should avoid products that can cause injury to your gums;
- Limit chewing loads;
- Maintain careful oral hygiene to avoid the occurrence of suppuration or infection. A soft toothbrush will gently and carefully clean your teeth and will not irritate your gums.
Gingivectomy will solve problems even with a very advanced form of periodontitis, restore healthy appearance to teeth and gums, cleanse gum pockets of pus and bacteria, and make your smile confident and attractive. Remember: healthy and beautiful teeth definitely “live” only in equally healthy gums.
How to get rid of a gum pocket
To get rid of the gum pocket, a surgical operation is performed - gingivectomy. It is possible with moderate severity of periodontitis, when cleaning the periodontal pocket from tartar, plaque and food debris, as well as medications no longer help. This can be explained by the fact that the gums, after removing stone and food debris, cannot immediately fit tightly to the body of the tooth. A person continues to consume food, and it again ends up in the gum pocket, rots and causes re-inflammation. To prevent this from happening, the edge of the gum must be trimmed a little, removing the gum pocket.
Get a gingivectomy at Dr. Granov's clinic!
Our dentists will carry out the necessary manipulations to get rid of the gum pocket, preventing more serious diseases!
Leave your phone number. The clinic administrator will call you back.
By leaving a request on the site, you consent to the processing of personal data
Make an appointment
Initial consultation with a dentist
400 rubles