Author of the article: Goldstein Maria Anatolyevna
Doctor-expert
Specialization: Dentist-therapist
Total work experience: since 2008
Reading time: 7-8 minutes
- Direct restoration
If the aesthetic properties of teeth are lost, a person experiences certain discomfort. The quality of life deteriorates if uneven or unsightly teeth prevent you from smiling broadly or if the enamel is too yellow, chips and cracks lead to complexes. Modern dentistry allows us to solve these problems by offering various types and methods of restoration, which is an alternative to full prosthetics.
What you need to know about dental restoration?
If restoration of the anatomical shape of teeth, their aesthetic properties and almost full functionality is required, then a number of procedures will be required to achieve the desired effect. Dental restoration is a set of dental measures to restore and correct shape and color. The materials used make it possible to imitate natural fabrics as accurately as possible, guaranteeing the aesthetics of the result.
Formally, restoration is essentially similar to filling, for example, some of the materials used and a number of stages. At the same time, it is impossible to compare the results, since aesthetic restoration manipulations guarantee a flawless smile.
Advantages
The advantages of artistic dental restoration are:
- Relatively quickly obtaining the desired result
. The restored tooth is visually no different from the rest in the row. The emphasis of the procedure is on maximum aesthetics. - Durability
. The materials and work performed are guaranteed for up to 10-15 years. - Durability
. As a result of restoration, the functionality of the tooth is restored - it is as strong as the rest. After the procedure, there is no need to make adjustments or additionally visit the dentist. - Easy to care for
. It is enough to follow the rules of basic oral hygiene and not to use abrasive pastes and hard brushes. - Resistance to aggressive environments
. The materials used for restoration are highly resistant to most food dyes. They are less resistant only to the effects of tobacco smoke (during active smoking) and red wine.
In addition, the advantages include a minimized risk of recurrence of caries and other diseases that led to partial destruction of the tooth and the need for its restoration.
Disadvantages and nuances
It makes sense to talk about the disadvantages, which are more nuances and features. These include:
- The need for careful treatment.
No matter how durable the result of the restoration is, there is still a risk that the restored part may break. To avoid this, you need to be careful with your teeth and not chew hard objects (for example, nuts, crackers, nails, wire, thread, etc.). - Chewing function not fully restored
. Artistic restoration of teeth is a procedure that is aimed at restoring aesthetic properties. Chewing function, however, is not fully restored. Please note that in some cases, instead of restoration, it is better to use the service of full prosthetics. - Relatively high cost of the procedure
. This nuance is natural in comparison with filling. Restoration requires extensive experience from the doctor and competent selection of materials (including color).
It is worth noting one more nuance - when restoring using the indirect method, you will not get the result after the first visit to the dentist. In addition, there is a need for regular visits to the doctor for fitting and adjustment of dental structures.
You might be interested in:
Dental restoration
Dental treatment
Veneers
Free consultation
Our specialists will conduct a free consultation and select the best treatment option for you.
Sign up now! Online registration
+7 (495) 649-41-19
Content
1 What methods of dental restoration exist?
2 Stages of dental restoration
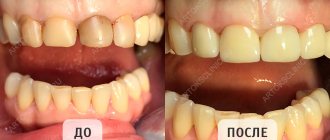
3 Dental restoration before and after photos
4 What influences the price of tooth restoration? 4.1 Complete crown correction
4.2 If half a tooth needs to be restored
4.3 Restoration of a chipped cutting edge of a front tooth
5 What are the disadvantages of artistic dental restoration?
6 Alternative to composite restoration
7 Prices for dental restoration
Types and stages of dental restoration
Today, dental clinics are ready to offer two methods of dental restoration, these are:
- Straight
. To achieve the desired result, self-curing filling materials (photopolymers) are used. This type of restoration is called aesthetic. The work is carried out by a dentist-therapist. - Indirect
. At its core, the method is similar to prosthetics, since veneers are used to achieve the result. The work is carried out by an orthopedic dentist.
Restoration is an individual approach for each individual case. Therefore, the choice of the optimally suitable method can only be made by a dental specialist.
Direct restoration
This procedure is indicated for damage to the front teeth and is carried out in six main stages:
- Preparation
. Consists of the following mandatory dental activities:- hygienic teeth cleaning (polishing paste and nylon brushes are used for these purposes);
- choosing the color of the filling material (the doctor uses a special color scale so that the tooth being restored is no different from the rest in the row);
- anesthesia (anesthesia is administered to relieve possible discomfort during the procedure).
- Preparation
. For example, it may be necessary to drill out caries or simply bring a damaged tooth into a form convenient for further restoration. At this stage, modern specialists use the most gentle technologies to preserve as much healthy tissue as possible. - Insulation from moisture
. Photopolymers used for restoration deteriorate their properties when in contact with saliva or wet breath. That is why it is very important to prevent their contact, for example, by using a rubber dam. - Fixing the pins
. This stage is carried out if there is a need to fix the pins in the tooth canals. If there is no such need, the specialist proceeds immediately to the fifth stage. - Rough modeling
. Using layer-by-layer application of photopolymers, primary (rough) modeling is carried out - the size, shape and relief are reproduced. - Final modeling
. This is the stage where the final restoration work is carried out using grinding and polishing.
This type of restoration is also called composite. As a result of a correctly performed procedure, the restored tooth is identical to its neighboring natural counterparts in shape and color (if the dentist takes into account all anatomical features) and the patient does not feel any discomfort or the presence of anything foreign in the mouth when closing the jaw and touching it with the tongue.
Indirect restoration
The procedure involves covering the entire front part of the tooth with a veneer. In this case, the veneer cannot be considered a crown, since it only covers 1-2 sides and not completely. Using this technique, you can achieve an even more aesthetic result than using photopolymer fillings.
Indirect restoration is carried out in five main stages:
- Definition of color
. This is necessary so that the veneer does not visually differ from the rest of the teeth in the row. Since ceramics is used as a material, at the manufacturing stage it can be given any shade and it is very important, at the first stage, to determine which one. - Preparation (turning)
. Only the front part is subject to grinding, where the veneer will be installed. As a rule, the enamel is ground down to a thickness of 0.5-1.5 mm (depending on the thickness of the lining) so that the veneer does not stand out and is flush with the rest of the dentition. - Taking impressions.
This requires that the overlays be made taking into account all individual anatomical features. - Installation of temporary protection
. To protect prepared and ground teeth from the negative effects of aggressive environments in the oral cavity, temporary veneers are installed for the patient. They will remain there until the permanent ones are ready. - Installation of permanent veneers
. Veneers made from impressions are installed with a special glue.
It is worth noting that indirect restoration has a number of contraindications, for example, this restoration method is not recommended for those who have a habit of biting their nails, opening bottles with their teeth, etc.
Methods of tooth restoration in modern dentistry
Dental restoration methods in modern dental clinics make it possible to completely recreate the shape, color, shine, transparency and light refraction of dental tissue.
I would like to proudly note that teeth restored at the Interdent dental clinic are considered healthy even by dentists from other clinics. What teeth are subject to restoration and what methods of restoration exist? To begin with, it should be noted that teeth that are subject to restoration often require endodontic treatment. Removing inflamed dead pulp residues from the canals, then making a high-quality filling. Without professional root canal treatment, there is no point in proceeding with the actual restoration. The remains of dead tissue, “immured” in the roots or under the roots, will sooner or later make themselves felt by pain or swelling of the gums. Very rarely, a tooth is destroyed in such a way that it needs to be restored with living pulp. In such cases, after a thorough diagnosis, the doctor restores the tooth, keeping it alive. The restoration itself can be single-stage or multi-stage.
Indications for the procedure
The main indications for restoration include the following:
- Correction of aesthetic defects. It is an improvement in the appearance of teeth damaged by caries or having defects in hard tissues. As part of this, dentists offer: Correction of enamel color. Moreover, restoration allows you to even out the color of not only a living tooth (using veneers on the vestibular surface), but also a dead tooth (using an indirect restoration method with the production of composite veneers or crowns).
- Correction of tooth shape and size. The main advantage of modern dentistry in solving this problem is the ability to obtain results in one visit to the clinic, especially if the issue concerns a minor diastema or other purely aesthetic defects. If the case is complex or advanced, experts offer alternative correction methods, for example, using inlays or crowns.
- Correction of the position of the tooth(s) in the row. The use of composite materials can provide immediate results when a single “movement” of individual teeth is required. If the problem is not purely aesthetic, then planned orthodontic treatment will be required.
In general, aesthetic restoration of teeth is an opportunity to correct minor cracks and chips, even out unsatisfactory enamel color, correct slight curvatures of the dentition (arising, for example, as a result of periodontitis), and get rid of the consequences of interdental, cervical and deep caries.
Types of damage and their complexity
All mechanical injuries can be divided into:
1. Dislocations are a fairly complex injury, which is characterized by the displacement of one tooth relative to the others.
2. Fractures are severe types of injuries. These include: cracks in the coronal part, chipped enamel, and root fractures. The method of treating and eliminating the problem depends on the specific case.
3. Bruises are the mildest type of all injuries. It is characterized by minor tissue damage, without displacement.
The main causes of damage are:
- caries;
— thinning of tooth enamel due to problems (diseases) in the human body, and as a consequence deformation of the tooth shape;
- large and sudden load on the front part of the jaw;
- direct blow or careless handling.
Contraindications
Aesthetic dental restoration is not only an excellent result and an excellent alternative to prosthetics, but also a restoration technique that is not suitable for everyone. Like most other dental procedures, restoration has absolute and relative contraindications.
Absolute contraindications include the following:
- The patient has a pacemaker installed
. The use of a device such as a photopolymerizer for composite restoration can cause a disturbance in the pulse frequency of the pacemaker. This is a huge risk to the health and life of the patient, as it can lead to cardiac arrest. - Allergy to composite materials
. It is extremely rare, but if the patient has an allergic reaction to adhesive systems or photopolymer materials, then it is worth choosing other methods of solving aesthetic problems rather than restoration. - Inability to isolate the tooth from moisture
. Some patients experience a psychosomatic reaction that does not allow the installation of a dental dam in the oral cavity. In these cases, restoration with composite materials with a quality guarantee is simply impossible.
So far, no other absolute contraindications to restoration have been found. This means that if you do not have the listed points, it is worth studying the relative contraindications in order to understand whether this recovery method is suitable for you or not.
Relative contraindications include:
- Teeth wear due to incorrect (straight) bite
. In this case, restoration should be postponed until the occlusion correction is completed. - Bruxism
. Strong compression of the jaws can cause premature destruction of the composite materials used in restoration. Therefore, in case of involuntary teeth grinding, it is recommended to use not restoration, but more reliable restoration methods, for example, installing crowns or other orthopedic structures. - No chewing teeth
. If they are absent in the lateral parts of the oral cavity, restoration of the anterior teeth is contraindicated. The fact is that in this case, the entire chewing load will be redistributed to the front teeth, which will lead to premature wear and destruction of the restored parts. - Significant destruction of hard tissue
. If, at the time of contacting the dentist, the tooth is destroyed by a third or more, the restoration cannot guarantee the reliability of the structure. In this case, it is worth using alternative methods to solve the problem.
In addition, restoration by direct and indirect methods is contraindicated for those patients who do not observe regular and mandatory oral hygiene. For such people, it is better to get metal or ceramic crowns rather than using composite fillings.
Restoration with veneers
A veneer is a ceramic or composite “facet” that is attached to the front (front) surface of the tooth with special light-curing cement. Veneers are used to restore mainly the front group of teeth, the color and shape of which are of particular importance. In order to restore a tooth with a veneer, only the front and slightly cutting surfaces of the tooth are ground down within the enamel layer by only 0.5 mm. Naturally, for this purpose the tooth does not need to be depulped (removing the nerve), unless there are other indications.
Then impressions are taken of the ground tooth or group of teeth, the color is determined, and a ceramic or composite “onlay” is made in the laboratory.
Veneer, unlike filling material, does not change color over time and does not lose its shine. Moreover, a veneer, unlike a one-step tooth restoration, has a clearer marginal fit to the gingival tissue, which is important for the prevention of periodontal diseases.
Read also
Why do teeth crumble?
Tooth decay in general, and crumbling in particular, is not an aesthetic problem.
How to restore and strengthen tooth enamel
Enamel is the outer shell of the tooth, which bears the heaviest load (chewing). She is the first to take on the “blows” of active substances contained in food and drinks.