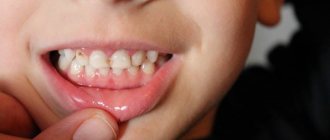
Enamel is one of the hardest tissues in the human body. It is continuously exposed to a wide variety of loads: thermal (hot/cold food), chemical and mechanical. Moreover, it is attacked by cariogenic microorganisms. The enamel of baby teeth has a porous structure, it is less dense and durable. After 3 years, children begin to show signs of physiological wear and tear. Destruction of enamel can be a consequence of caries, trauma (chips), development of erosion, enamel hypoplasia and a number of other pathologies. Treatment tactics are selected individually based on the results of the examination. It depends on age, type of bite (temporary or permanent), as well as the individual characteristics of the patient.
Causes
Caries in the age category up to 5-10 years develops for various reasons:
- Improper hygiene – pathogenic bacteria accumulate in the oral cavity, which multiply and lead to damage to the enamel.
- A large amount of sweets in the diet – sugar remains on the teeth and promotes the growth of bacteria.
- Early use of antibiotics - some medications change the color of the enamel.
- Poor absorption of calcium by the body.
- Heredity.
- Dysbacteriosis.
- Chronic diseases.
- Insufficiently formed enamel.
- Improper diet - deficiency of vitamins, minerals, fats leads to darkening of teeth due to specific plaque.
Causes of the problem
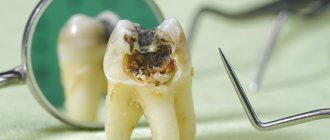
Enamel is the hardest tissue in the body, which is continuously exposed to mechanical, thermal and chemical stress. There are many reasons for its destruction and they can all be divided into two groups: carious and non-carious.
Carious causes
Most often, it is caries that destroys teeth, and in children this happens very quickly - in a few months, snow-white milk teeth can turn into black “stumps”. Bottle caries is a problem in the first years of life, when the use of a bottle with formula or sweet liquids at night creates a favorable atmosphere for an increase in the number of bacteria, leading to the development of caries and destruction of tooth enamel.
Non-carious causes
Often teeth are destroyed due to a lack of minerals in the enamel: calcium, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium, which enter the body with food.
The main non-carious reasons why baby teeth crumble:
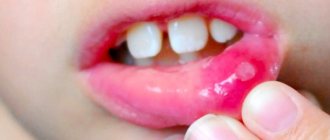
Enamel hypoplasia is a serious problem in which the enamel layer on a tooth may be completely or partially absent due to abnormal processes that are formed during the formation of the rudiments of teeth. The reason is a difficult pregnancy, stress, bad habits and a lack of vitamins in the body of the expectant mother.
Visually, enamel hypoplasia looks like grooves on the enamel, through which dentin shines through. Such teeth are not protected and are more susceptible to physical and chemical stress.
Fluorosis is a disease that develops due to excess fluoride in the body. The child's teeth are covered with bright white spots. This problem is caused by drinking water with high levels of fluoride content.
Non-carious lesions also include:
- poor nutrition (lack of important substances);
- lack of fat-soluble vitamins;
- high levels of phytic acid;
- excessive sugar consumption;
- excess fluoride in the body;
- enamel defects or absence;
- heredity;
- taking antibiotics during the mother's pregnancy;
- poor oral hygiene;
- the habit of chewing on everything - pencils, pens, toys, nuts, candies;
- problems of intrauterine development;
- low quality of drinking water;
- jaw injuries resulting from a fall.
To protect children's teeth from further damage, it is necessary:
- make sure that there are no cracks on them, which become “gates” for caries-forming bacteria (cracks usually occur as a result of injuries);
- maintain oral hygiene, which will prevent the formation of plaque (the child should brush his teeth twice a day with age-appropriate toothpaste);
- supplement the menu with protein products that help strengthen enamel, as well as seasonal vegetables and fruits;
- if this is not possible, select a vitamin-mineral complex with the help of a pediatrician.
Treatment methods for enamel hypoplasia in children
If white spots on teeth are invisible to others, they are usually not removed. But the enamel, severely affected by the disease, ceases to protect the tooth tissue, resulting in complications - increased wear of teeth, destruction of dentin up to the loss of teeth, and the appearance of malocclusions. To prevent this, timely therapy is necessary.
Procedures for the treatment of enamel hypopalsia in children:
Effective prevention of caries
What else can be done if a child has bad baby teeth? Engage in prevention. It is very important to teach your baby to rinse his mouth after every meal in order to remove sources of bacteria from the oral cavity as often as possible. A child should brush their teeth under the supervision of an adult, and even better if mom or dad does this for a while.
It would be a good idea to remove candies, toffees and other sweets from the diet, and instead introduce your baby to cottage cheese, hard cheese, fish, sour cream, and eggs. The child should spend enough time in the air and get his portion of sunlight - a source of vitamin D. All this together will help protect the teeth from further destruction.
How to strengthen enamel at home?
To protect the enamel from damage, it is recommended to follow a balanced diet (the diet should contain foods containing calcium - fermented milk products, almonds, hazelnuts, beans, peas, meat, hard cheeses, oatmeal and barley), and take vitamins with calcium.
Special toothpastes (for example, Vivax Dent, Elmex, ApaCare, Lacalut) and gels (ROCS, Amazing White Minerals) are also indicated.
Do not forget that the result of treatment depends on the professionalism of the dentist. On our website you can find a list of clinics that successfully treat this disease.
Is it worth treating baby teeth?
It is much more important to decide where and how to treat caries than to torment yourself with the question of why a child has bad baby teeth. Dentists are convinced that treatment of baby teeth is mandatory, and here’s why:
- the roots of the lateral milk teeth are spaced widely and cover the rudiments of permanent teeth, therefore, with pulpitis or periodontitis, the rudiment of the molar tooth may die;
- a carious cavity is a source of infection, in which any manipulation is prohibited (for example, ordinary caries can cause a ban on planned or unscheduled surgery if it is suddenly needed);
- It is impossible to correct a bite in the mouth with untreated teeth.
If this problem has affected you, do not panic: make an appointment with a good pediatric dentist and ask him all the questions that interest you. The main thing is to keep the situation under control!
What is tooth enamel hypoplasia
Tooth enamel hypoplasia is a specific disease in which the formation and development of enamel due to metabolic disorders does not occur as it should be. As a result of metabolic disorders, the body does not receive all the necessary beneficial microelements, and this contributes to the fact that the enamel becomes vulnerable and very thin. Because of this, the tooth can break even with a slight load.
In addition, hypoplasia indicates serious disorders of protein metabolism and metabolism, so it can not only be called an independent disease, but also a serious sign that the child has certain health problems.
If children's teeth are crumbling...
Teeth change color and become extremely sensitive to hot and cold: as soon as children have permanent teeth, many already suffer from so-called molar hypomineralization (MIH).
This is a special form of disruption of the formation of tooth enamel. First of all, this disease affects the chewing teeth. But incisors can also suffer from this disease.
A lack of minerals makes teeth porous. Teeth affected by MIH have fewer minerals present than are present in healthy teeth. First of all, they have a lower concentration of calcium and phosphates. As a result, teeth become porous, and this, in turn, leads to very rapid development of caries.
When affected molars erupt in schoolchildren, molar hypomineralization is now diagnosed quite simply. But just a few years ago the situation was completely different, since this form of diagnosis simply did not exist yet.
The picture of the disease has only recently been described. It was not until 2001 that this phenomenon was brought together under the term Molar Incisor Hypomineralization (MIH), that is, “mineral deficiency in the molars and incisors.”
This approach has significantly improved the diagnosis of children's and adolescent teeth. After all, before this, it was very difficult for the dentist to determine whether the tooth was porous even before the onset of the disease or whether it was a matter of ordinary caries.
Every tenth child has problems with the formation of tooth enamel. Doctors say that the problem of MIH affects ten percent of children, and in five percent it manifests itself in a severe form, accompanied by significantly increased sensitivity and loss of substance.
In adults, it is much more difficult to assess the extent of molar hypomineralization. Even if they had manifestations of MIH, the teeth affected by this disease in most cases have already undergone treatment and restoration, for which reason an appropriate diagnosis is no longer possible.
The causes of MIH should probably be sought in pregnancy. It has not yet been possible to determine where MIH originates from. Doctors admit that they can only guess about the causes of this disease. For example, problems during pregnancy are considered, which could theoretically have a negative impact on dental development.
In addition, events that occur in early childhood, such as high fever infections, antibiotic use and respiratory diseases, as well as dioxin in breast milk, are also suspected. It is possible that the cause of MIH is a combination of several different factors.
Doctors use different methods to treat molar hypomineralization. If MIH is detected in the early stages, the teeth are usually “sealed,” meaning they are coated with a special compound. In more complex cases, fillers and even crowns are used.
Treatment: special dental care, in some cases – removal. In some severe cases of violations of the formation of tooth enamel, the decision remains with the doctors: does a particular tooth have the prospect of long-term preservation? But if a tooth still has to be removed, it should be taken into account that the issue of filling the vacated space must be resolved as soon as possible, since in this case, due to the increased load, neighboring teeth will also suffer.
And you should remember: if children suffer from problems with the formation of tooth enamel, they should brush their teeth only with soft toothbrushes, using fluoride-containing toothpastes.
Why is it better to go to the Aesculapius clinic?
Cooperating with our dentistry is profitable and comfortable. We work with each client on an individual basis and always adapt to the customer's needs. Filling of baby teeth in children in our clinic is performed using the most modern equipment and tools. By contacting us, you get a number of advantages:
- high quality standards;
- responsible approach to work;
- treatment by experienced specialists;
- no queues;
- favorable prices.
You should only trust trusted professionals to fill the root canals of your child’s primary teeth. Only such specialists work in our clinic. During its existence, Esculapius dentistry has already helped hundreds of clients. Filling baby teeth for children in our clinic is safe and reliable. Absolutely all customers are satisfied. Our medical center also installs braces for children and adolescents. Experienced orthodontists have reliable and modern systems for forming a correct bite.
All you need to do to receive quality dental services is make an appointment. Getting to our clinic is very easy. We are located next to the Kyiv metro station, but there are also Studencheskaya and Kutuzovskaya nearby.
Types and compositions of popular fillings for baby teeth
The most popular in pediatric dentistry:
- Chemically cured fillings made of glass ionomer cement. The material contains fluoride ions, which are responsible for the remineralization of tooth enamel and prevent the proliferation of pathogenic bacteria. Positive characteristics include non-toxicity, biocompatibility, low shrinkage, and good fixation on different surfaces. The filling composition performs well when working with chewing teeth. It is often used under a crown for children's prosthetics. There is only one serious drawback: it takes about a day for the filling to dry completely.
- Metal fillings based on silver amalgam. When hardened, the compounds look rather unaesthetic, so they are used when filling distant teeth. Fillings are famous for their durability. Due to their pronounced antibacterial properties, secondary caries does not form underneath them.
- “Light” photopolymer fillings. The light-curing composite is plastic and easy to use - it allows you to recreate the surface of the tooth down to the smallest detail. This is the best material for restoring incisors, but is also suitable for treating other teeth. The polymer hardens quickly under the influence of a special lamp, but is very sensitive to moisture. Protection from saliva is provided by a rubber dam, a special rubber insulator placed around the teeth being restored.
- Colored compomer fillings. The material is a symbiosis of a hybrid composite and glass ionomer cement, which guarantees double advantages and improved properties. It is convenient to control the colored filling based on the degree of wear - changes in the shade indicate the need to visit a doctor.
All fillings, with the exception of colored fillings, are used equally successfully in both pediatric and adult dentistry, which inevitably leads to the question: is it possible to give children adult fillings?
Degrees of tooth abrasion
- Stage I – the enamel of the cutting edges of the child’s incisors and canines and the upper part of the chewing cusps and molars is erased, the dentin is partially affected.
- Stage II – severe abrasion of the chewing tubercles with exposure of dentin tissue.
- Stage III – the height of the tooth crown is reduced to 2/3 of the normal size during wear.
- Stage IV – abrasion of the tooth to the level of the neck. The crown of the tooth is almost completely erased.
If 1 – 2 teeth of a child are worn out, then this is local abrasion; if several teeth or the entire dentition are affected, then this is generalized abrasion.
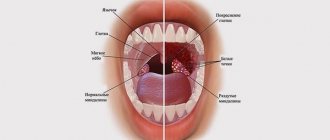
Symptoms of tooth erosion in children
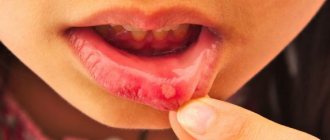
The severity of symptoms largely depends on the degree of destruction and activity of the process. With a shallow lesion, tissue changes are invisible; a specific yellowish coloration is visualized only in the dentist’s office after drying the surface and/or treating it with iodine.
As the process spreads, round or oval lesions resembling a bowl begin to appear on the surface of the teeth. Initially they are whitish in color, but as they approach dentin they acquire a yellowish or light brown tint.
Subjective complaints arise in the active phase of the process with moderate or deep damage. The child pays attention to the increased sensitivity of the teeth to hot, cold, sour foods, and discomfort when brushing the teeth.
What to do if your child's teeth are worn out
Treatment for tooth wear is developed individually. At the appointment, the pediatric dentist analyzes the causes of the pathology, determines the stage of erasure, the nature of the disease and the characteristics of the development of the child’s body.
Classification and stages of development of tooth enamel erosion in children
Depending on the depth of the lesion, three degrees of the disease are distinguished:
- initial: only the top layer is affected;
- medium: the pathological process involves the entire enamel;
- deep: destruction affects the upper layer of dentin.
The activity of the process allows us to distinguish two clinical stages of erosion development. In the active stage, relatively rapid destruction occurs: defects spread over the surface and become deeper. The enamel takes on a matte appearance, and in severe cases changes color to yellowish. In the stable phase, the teeth are not externally changed, there are no obvious symptoms, but when examined under a microscope, the lesion is clearly visible.
Features of filling
Our dentists use a variety of treatment options, starting from a very young age. Doctors use treatment approaches that do not cause mental trauma to children.
Installing fillings on milk bone tissue is practically no different from filling adults.
What materials are used
- Amalgam.
- Glass ionomer cement.
- Composites (combined filling).
Advantages of breast filling
- Filled baby teeth look aesthetically pleasing and are visually indistinguishable from natural ones.
- After filling, baby teeth are reliably protected from pathogenic infection; it will not penetrate into the bone tissue.
- Thanks to modern filling materials, even large cavities of destruction can be restored.
Colored fillings
This modern method of breast bone tissue restoration was developed specifically for the treatment of children. The fear and tears of children in front of dentists are replaced by interest when doctors offer children to get such fillings. All kids love bright, beautiful fillings and teeth painted in all the colors of the rainbow. They can choose their own color.
In addition, funny fillings have one advantage - they release fluoride ions, which prevents the development of secondary caries in the future.
The advantages of colored material include:
- eight spectacular, brilliant and bright colors that will not leave any child indifferent;
- fillings are perfectly polished;
- prevention of caries;
- the material is strong, so you won’t need to worry before replacing baby teeth with permanent ones;
- anti-allergenic and safe for children.
Causes of the disease
To successfully treat a disease, you need to know what causes it. The following main reasons for its development can be identified:
- chronic somatic pathology in children
- disruption of metabolic processes as a result of an imbalance of mineral and protein metabolism
- acute infectious diseases
- toxic dyspepsia
- brain disorders that began between 6 and 12 months of age
Types of enamel hypoplasia
The location of the lesion depends on its severity and the age of the child. This process is irreversible.
In dental practice, there are two main types of hypoplasia - local and systemic.
With local hypoplasia, one or two teeth are predominantly affected. In this case, only permanent teeth are affected - it never occurs on milk teeth.
The reasons why local hypoplasia occurs are as follows:
- infection of the permanent tooth germ
- tooth injury
- chronic course of periodontitis of a baby tooth
Externally, local hypoplasia looks like a yellowish or white stain on the enamel, and the enamel of the dental crown may be absent either partially or completely.
Systemic hypoplasia, unlike the local form, immediately affects all teeth. It occurs for the following reasons:
- during the intrauterine development of the baby, when the expectant mother has suffered serious illnesses (rubella, toxoplasmosis, etc.) or when she has metabolic disorders.
- as a result of a woman taking certain medications during pregnancy or a child in the first year of his life (for example, tetracyclines);
- if the baby has a malnutrition or has a serious pathology
If a child has been diagnosed with systemic enamel hypoplasia, he must be registered at the dispensary.
Several types of systemic hypoplasia can be distinguished. It depends on the type of dental damage and their shape.
Fournier's teeth - with this type of disease, the central incisors on the upper jaw take the shape of a screwdriver or butterfly;- Hutchinson's teeth - the shape of the teeth is almost the same as with Fournier's teeth, but only on their cutting edge you can see a semicircular notch that is not covered with enamel.
- Pflueger's teeth - with this type of hypoplasia, the first large molars are affected. They have underdeveloped cusps, and the size of the crown at the neck of the tooth is much larger than at its cutting edge.
- “Tetracycline” teeth - this type of hypoplasia is formed if a woman used tetracycline antibiotics during pregnancy or they were given to the baby herself. The teeth have a yellowish tint, their enamel is underdeveloped. If a child is given tetracycline or its analogues after 6 months, the permanent teeth that form during this period will also become stained.
In modern dentistry, there are 3 main forms of enamel hypoplasia:
- Discoloration of the enamel is the mildest form, in which yellowish or white spots of the same size are formed on the enamel, their boundaries are sharply defined. Such spots do not react to various irritants, do not hurt, do not cause discomfort, and are not stained with dyes (unlike carious lesions).
- Underdevelopment of enamel is a more severe form of the disease. It is characterized by the appearance of small depressions on the surface of the enamel - dots, waves or grooves, but its surface remains smooth and dense.
- Aplasia is the most severe form, in which tooth enamel is completely absent. Fortunately, it is very rare. With aplasia, there is no enamel at all in a certain area of the tooth crown. In most cases, a child experiences pain from chemical, thermal or mechanical stimuli.
For clarity, you can see what enamel hypoplasia looks like in the photo.
Symptoms of hypoplasia
Enamel hypoplasia is manifested by the following symptoms:
- The appearance of yellowish or white spots, pinpoint depressions or grooves on the smooth surface of tooth enamel.
- The presence of lesions on the crown of the tooth with an absolute absence of enamel.
- The teeth take on a bizarre shape, which is due to the absence of enamel on almost their entire surface.
Prevention
The main thing that needs to be done to prevent the disease is to eat rationally and nutritiously for the woman who is carrying a child, as well as for the baby in the first years of life. At this time, taking medications is strictly contraindicated, especially for tetracycline antibiotics. It is also necessary to prevent the possibility of developing systemic diseases, as they contribute to metabolic disorders, which can result in hypoplasia.
Treatment of dental enamel hypoplasia
Unfortunately, today this pathology is irreversible, and there are no drugs that could eliminate its symptoms. Therefore, treatment of enamel hypoplasia is only symptomatic. It involves the reconstruction of tooth enamel. In that case, there are only small foci of local hypoplasia, there is nothing to worry about, because there is no pain syndrome. If deep erosions and stains occur on the enamel, it is necessary to fill the tooth with composite materials. If the enamel is partially or completely missing, the dentist may perform orthopedic treatment and place a crown on the tooth.
Forms of the disease
It is worth highlighting several forms:
- The color of the enamel of those teeth that were affected changes. This form is considered the easiest, because here the size of the spots is the same, and their boundaries are clearly defined. A child or an adult does not feel any discomfort, there is no pain, and there is no reaction of the teeth to irritants of a thermal or mechanical nature. Also, such stains will not take on the color of the dye;
- the enamel has not fully developed. This form of hypoplasia is already more severe. Grooves, waves, and dots appear here. If you look closely at the surface of the teeth, you can see depressions and grooves of small or medium size. The enamel in them is smooth and dense;
- enamel is completely absent. This form of the disease is also called aplasia, but it is much less common. In some part of the tooth crown there is no enamel at all. A person experiences pain and has difficulty reacting to stimuli of thermal, chemical, and mechanical types.