Treatment of herpes in the mouth
Can herpes be in the mouth?
Maybe! Herpes in the mouth requires the same responsible approach and competent treatment as other diseases of the oral cavity. Despite the fact that the infection is often mild and goes away naturally, there are still risks of serious complications, and the possibility of infecting other people remains. Many factors influence the degree of development of the pathology and the presence of possible dangers for the patient. Complete diagnosis and comprehensive treatment can completely stop the manifestations of the infection, although complete elimination of the virus is considered impossible. Herpes, a viral disease known to many as a “cold sore,” is often perceived as a minor problem that does not require treatment. It is characterized by the appearance of a moderately painful blistering rash, but not many people know that this disease is not limited to appearing only on the lips , but can also develop on the oral mucosa . The disease is often accompanied by weakness, general malaise and severe itching, and in some cases can cause complications. During the active phase of the virus, a patient can easily infect others with it through household items, close contact or by airborne droplets.
Types of herpes virus infections
More than 100 representatives of the herpetic family of viruses are known. However, most often a person is affected by 8 of them. Let us consider in detail the features and symptoms of the most common infections.
Herpes simplex virus types 1 and 2
The herpes virus type 1 causes blistering rashes on the mucous membranes of the lips and nose. As a rule, infection occurs in childhood. By the age of 5-7 years, more than 50% of children are carriers of the infection. Infection often occurs from sick parents: through kisses, household items.
The incubation period lasts from 2 days to 2 weeks. In addition to the characteristic rashes, the infection may be accompanied by elevated body temperature and enlarged local lymph nodes. After damaging the mucous membranes, the virus reaches the trigeminal nerve, where it can remain latent for a long time.
Herpes simplex virus type 2, or genital herpes, is primarily transmitted through sexual contact. In Russia, the average is 20% among the adult population. In European countries, the incidence rate is even higher. The risk group includes people who have promiscuous sex. Most infections occur during puberty, at the beginning of active sexual life.
Symptoms of the virus include:
- blistering rashes on the genitals;
- enlargement of regional lymph nodes;
- painful urination;
- itching in the groin area;
- elevated body temperature.
The disease can occur with frequent relapses (6-12 times a year or more).
Herpes virus type 3
This virus can cause two diseases: chickenpox and herpes zoster. As a rule, chickenpox occurs in childhood and is accompanied by characteristic symptoms:
- vesicular rash that lasts about 10 days;
- high body temperature, fever;
- headache;
- itching of the skin;
- symptoms of body intoxication.
Chickenpox in adults occurs rarely and can occur in a more severe form: with damage to the eyes and nervous system. In such a situation, a person requires urgent hospitalization. After the disease, the virus remains in the body for life, remaining latent in the nerve ganglia.
Vaccination is the most effective way to prevent the disease in children and adults who did not have chickenpox in childhood and were not vaccinated against it. Vaccination is given to children from one year of age. The immunobiological drug is administered twice with an interval of 6 weeks. Vaccination is also carried out as an emergency measure in the first three days after a person comes into contact with a patient with chickenpox.
Typically, herpes zoster occurs in people over 65 years of age. The disease is severe and is accompanied by severe symptoms:
- severe pain;
- sleep disturbance;
- high temperature;
- vesicular rashes that appear along the nerve endings.
The disease has a rather difficult rehabilitation period. Even after the rash disappears, a person may remain sore for a long time in those areas that were affected by the infection. In all civilized countries of the world, elderly people are vaccinated to prevent herpes zoster.
Epstein–Barr virus
Herpes virus type 4 or Epstein-Barr virus affects the human body in a complex manner, provoking various and sometimes unrelated pathologies. The virus can cause infectious mononucleosis, lymphoma, hepatitis, affect the nervous and immune systems, and the hematopoietic apparatus.
In the human population, infection with the Epstein-Barr virus reaches 75% or higher. Children over two years of age and adults under 30 years of age are at risk. Children under one year of age rarely get sick due to passive immunity received from the mother.
The symptoms of the disease are many-sided and can have various manifestations: from mild discomfort to severe health problems. The most common symptoms of the disease are:
- high temperature, fever;
- sore throat, muscles;
- enlarged lymph nodes, liver, spleen;
- the appearance of rashes, peeling, inflammation, bruising on the skin;
- photophobia;
- nausea.
It is characteristic that the use of antibiotics does not affect the duration of fever.
Herpes virus type 5
Cytomegalovirus infection, caused by herpes virus type 5, occurs in both children and adults. It can occur as a mononucleosis, with high fever, intoxication, purulent sore throat, and damage to the salivary glands. In addition, the infection may be asymptomatic.
There are also congenital forms of the disease, which often lead to the development of hearing loss, microcephaly in the child, cause enlargement of the liver and spleen, and hematological disorders.
Herpes viruses type 6 and 7
The range of diseases caused by these viruses is diverse. Often infections occur in the form of a sudden exanthema. Hepatitis virus type 6 can provoke chronic fatigue syndrome and infectious mononucleosis. It is believed that a consequence of viruses can be a lymphoproliferative process (the formation of tumors of the lymphatic system).
As a rule, sudden exanthema affects children under two years of age. The disease occurs with high fever and intoxication of the body. Febrile convulsions may occur and a rash appears, which goes away on its own after a few days.
Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is accompanied by rapid fatigue and decreased performance. Patients are concerned about low-grade fever, enlarged lymph nodes, and the appearance of catarrhal manifestations in the pharynx.
Symptoms of herpes on the oral mucosa
Symptoms of herpes are individual, have varying degrees of manifestation, and can occur in different parts of the oral cavity. For most cases, there are a number of signs that indicate the occurrence of herpes:
- Regular headache;
- Fever;
- A person gets tired quickly;
- Discomfort when eating and drinking;
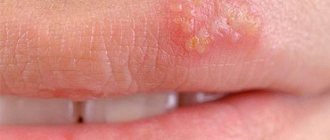
- The appearance of water bubbles filled with transparent white or yellowish exudate, up to 3 mm in diameter;
- The appearance of ulcers at the site of burst blisters;
- Inflammation of the soft tissues of the oral cavity, redness, itching, burning, swelling of the lesion.
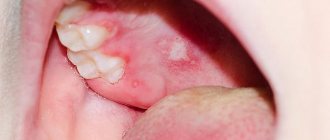
According to clinical studies, blisters in the mouth can form in different areas: on the palate, on the inside of the cheeks, on the tongue, on the gums, on the tonsils.
Choosing tablets for herpes -
Herpes treatment in adults: drugs in tablets
- Acyclovir,
- Valaciclovir,
- Famciclovir.
Below we will compare the effectiveness of these antiviral tablets against the herpes simplex virus. It should be noted that Acyclovir tablets are approved for use from 0 years of age, and the drugs “Valacyclovir” and “Famciclovir” - only from 12 years of age. All these drugs are available only with a doctor's prescription.
Acyclovir in tablets of 200 and 400 mg –
Tablet acyclovir has the same disadvantages as creams: low tropism for the virus (i.e., acyclovir molecules do not find viral particles well); in patients with poor immunity + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in 10-27% of cases the herpes virus may be resistant to acyclovir; plus low oral bioavailability. Pros: no age-related contraindications, affordable price, fairly few side effects.
We recommend choosing the original drug with acyclovir - Zovirax 200 mg tablets (instructions for use, see PDF). Moreover, its cost is not much higher than that of Russian generics.
Examples of drugs with acyclovir -
Acyclovir tablets certainly work, especially when it comes to patients with good immunity and rare relapses of herpes. If you have a weakened immune system, if you have taken acyclovir too often in the past, if you decide to start taking the drug more than 24-48 hours after the onset of herpetic rashes, acyclovir will not be particularly effective. In this case, it is better for you to immediately start taking the drug Famciclovir, which works better even at later dates of initiation of therapy, as well as in patients with immunodeficiency conditions.
The regimen of use - if you look at the official instructions, the standard regimen for adults and children over 2 years old - is to take acyclovir 200 mg 5 times a day (for 5 days). A single dosage of 400 mg is recommended in the official instructions - either only for severe herpes infection, or in patients with weakened immune systems. However, most clinical studies (source) show that a dosage of 200 mg has virtually no effect on either the duration of symptoms or the healing time of herpes.
Studies have shown that only 400 mg (respectively, 5 times a day, for 5 days) is an effective single dose. In children under 2 years of age, the dosage is reduced by exactly 2 times - from the adult dosage. In case of severe herpes infection, taking the drug can be extended to 7-10 days. By the way, abroad, at the moment, acyclovir is practically not used for chronic recurrent herpes, giving preference to valacyclovir and famciclovir.
Valacyclovir (Valtrex) tablets –
We have already said above that tableted acyclovir has poor bioavailability, i.e. only about 10-20% of its amount is absorbed in the intestine, which makes it difficult to achieve high concentrations of acyclovir in tissues. This problem is solved by Valacyclovir, which has a bioavailability of 50%. Valaciclovir is a precursor to acyclovir (i.e., it is converted to acyclovir once it enters the bloodstream). Taking tablets with valacyclovir allows you to create a concentration of acyclovir in tissues that can be achieved with traditional acyclovir - only through intravenous infusions of the latter.
The drug Valtrex is the original drug of Valaciclovir (we recommend this drug), but there are also a large number of cheaper generics. The cost of the original drug “Valtrex” (UK) is from 1350 rubles for 10 tablets. 500 mg each. There is a good Bulgarian generic “Valvir” - it costs from 750 rubles for a package of 10 tablets. 500 mg each. The cost of the Russian “Valacyclovir-Akos” will be from 450 rubles (for a package of 10 tablets of 500 mg).
Regimen: There is a short 1-day treatment regimen. Clinical studies have shown that taking high dosages of the drug for 1 day was the most effective for the treatment of herpes on the lips and facial skin, as well as herpetic stomatitis. In this case, the dosage regimen is 2000 mg 2 times a day, with an interval of 12 hours (1 day in total). But it should be noted that such a short regimen will be effective only if treatment begins no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic eruptions appear, and also in patients with satisfactory or good immunity.
If more than 12 hours have passed since the appearance of the rash, and also if you have a weakened immune system, it is optimal to use the standard treatment regimen of 500 mg 2 times a day for 3-5 days (for severe herpes infection - up to 10 days). When choosing a drug, keep in mind that if your herpes virus is resistant to acyclovir, taking valacyclovir will also be ineffective.
Famciclovir tablets (Favirox, Famvir) –
Famciclovir products are the most modern and effective tablets for herpes. Above we told you about the cream “Fenistil-pencivir” (based on penciclovir), which is used on the skin of the face and the red border of the lips. So, drugs with famciclovir are tablet analogues of penciclovir. Most often in pharmacies you can find drugs with famciclovir - under the trade names “Favirox” or “Famvir”.
The advantage of famciclovir drugs like Favirox is their rapid antiviral effect due to maximum bioavailability (for famciclovir it is about 74%, for example, for valacyclovir it is only 54%, and for acyclovir only 10-20%). Therefore, a package of three 500 mg tablets is enough for a short 1-day course of therapy to relieve the manifestations of herpes on the lip. Read more about this application scheme below.
→ Favirox instructions for use (view PDF)
Regimen for using famciclovir - there is a short 1-day treatment regimen: either take 1500 mg once, or 750 mg 2 times a day (with a 12-hour interval between doses) - our experience suggests that the second option is still better. This 1-day regimen is effective only if you start taking the drug before 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears, and also if the patient’s immunity is normal. In case of weakened immunity, and/or if treatment is started later than 12 hours from the moment of the appearance of herpetic eruptions, the standard dosage regimen should be used.
The standard regimen according to the instructions is 250 mg 2 times a day for 5 days (however, in severe cases of herpes infection, dosage can be extended to 7-10 days). Here I would like to add that numerous clinical studies show the weak effectiveness of this standard regimen - especially in patients with poor immune system conditions. Studies have shown that the effectiveness of therapy increases significantly when famciclovir is prescribed in higher dosages. In patients with good immunity, a more effective regimen will be 500 mg 2 times a day (for 5 days). In immunocompromised patients - 500 mg 3 times a day (for 7 days).
Important: once again we draw your attention to the fact that short 1-day treatment regimens for herpes in adults (herpes on the lips and skin around the mouth, on the face) work well only if the following conditions are met. Firstly, only if you start taking medications no later than 12 hours from the moment the herpetic rash appears. Secondly, if you have a satisfactory or good immune system. If treatment is started later than 12 hours from the onset of the rash, as well as in patients with weakened immune systems, short 1-day courses of therapy are usually ineffective. Here we already need a standard regimen of administration.
Important : if more than 12 hours have passed since the first rash appeared (and even more so if more than 24 or 48 hours), it is better to opt for famciclovir, because the latter works better at later dates of initiation of therapy for herpetic infection.
Stages of development of herpes in the oral cavity
The disease develops sequentially, including passing through several distinct stages:
- At first, the patient may experience drowsiness, malaise, and tingling or itching of the mucous membrane. Sometimes body temperature rises slightly;
- Next comes redness and swelling of the lesion, minor pain occurs due to the appearance of herpes on the tongue or lip;
- Blisters appear in the oral cavity, filled with transparent contents. During this period, the patient is most contagious, blood counts change;
- The blisters become cloudy and open, and yellowish, shallow, painful ulcers form in their place;
- A hard, fragmented crust forms on the ulcers, damage to which causes bleeding. After a few days, the crusts disappear.
In the best case, the disease resolves naturally within two weeks and without treatment. All wounds heal quickly and without scars.
But there are also complications that lead to infection of internal organs. Suppuration occurs at the site of the wounds, the temperature rises to 40 C. Inflammation of the lymph nodes in the jaw and neck may begin.
Herpes: photo
The herpes simplex virus is clinically manifested by the formation of a group of crowded blisters located on an inflamed base (skin or mucous membrane). The bubbles are first filled with transparent contents, which quickly become cloudy. If you have herpes, treatment must be started before the herpetic vesicles open. Otherwise, not only the ointment for herpes, but also the best tablets for herpes will no longer allow any noticeable acceleration of healing.
What does herpes look like?
Important: the appearance of herpetic rashes is almost always preceded by the appearance of itching or burning in this area, or a feeling of tissue swelling. It is very important to teach the patient to “catch” these first symptoms, because if you start treatment for herpes already at this stage (during the prodromal period of the disease), the number and size of the herpetic blisters that subsequently form will be significantly smaller. And besides, the healing of erosions will occur much faster.
In rare cases, early initiation of therapy can even prevent the appearance of herpetic blisters (for example, when using combination drugs containing “5% acyclovir + 1% hydrocortisone”). Faster healing can also be achieved if treatment for herpes is started in the first 12 hours - from the moment the first herpetic blisters appear. You must understand that the later treatment begins, the lower its effectiveness will be. After opening the vesicles, treatment with antiviral ointments and tablets will no longer affect the healing rate, although it will still be indicated for patients with severe herpes.
Causes of oral herpes infection
Herpes that affects the oral cavity develops when infected with the herpes simplex virus type 1, which not only provokes the appearance of a blistering rash, but can also cause complications in 10% of cases. The second type of herpes virus (genital) also causes a rash in the mouth, but does not cause serious disruption to the body and differs in its mode of transmission (through sexual contact).
Most often, primary infection with a herpes virus occurs in childhood, after which it is introduced into the genome and remains in an inactive form for life.
The main routes of infection with a viral agent are close conversation, skin-to-skin contact, kissing, and the use of shared hygiene products or utensils. However, the entry of viral particles into the body does not guarantee that the disease will develop, since the immune system can suppress the action of the pathogen. In this case, situations that worsen the overall health of the body, on the contrary, provoke a clear manifestation of infection:
- surgical interventions;
- emotional and physical stress;
- lack of sleep, overwork;
- colds;
- chronic pathologies;
- long-term use of antibiotics;
- periods of menstruation, pregnancy or lactation;
- vitamin deficiencies;
- AIDS;
- abuse of nicotine or alcohol;
- the appearance of microtraumas from excessive exposure to the sun or frost.
Herpes virus type 8
Herpes virus type 8 can cause Kaposi's sarcoma and Castleman's disease. Kaposi's sarcoma is a serious pathology that is accompanied by the appearance of malignant skin tumors. It is quite difficult, especially with immune deficiency. May be complicated by inflammation of the mucous membrane of the palate and lymph nodes.
Castleman's disease is a rare disease in which fever, enlargement of the liver and spleen, anemia, and a sharp decrease in body weight are observed.
Diagnosis and treatment of herpes infection
It is better to start treatment of herpes in the mouth at earlier stages of development to reduce the risk of complications and reduce the likelihood of infecting other people. In order to identify the disease, specialists carry out diagnostic measures:
- collect anamnesis;
- conduct an examination, determine the location of the rash and its nature;
- take a smear to identify the herpes virus and determine its type;
- laboratory tests are prescribed.
Modern methods for identifying the pathogen are a patient’s blood test to detect antibodies to the pathogen and a PCR study of tissues aimed at searching for the DNA of the viral particle. Differential diagnosis is of great importance, since herpetic infection must be distinguished from other similar diseases: stomatitis (not herpetic), tonsillitis, etc.
How to treat herpes on the lip, tongue or gum? Herpes therapy is based on an integrated approach that combines:
- The use of local antiviral agents to stop the process of reproduction and spread of the pathogen;
- Prescribing antiviral medications for internal use (usually indicated for those whose symptoms occur frequently and acutely, or who are immunosuppressed);
- The use of antiseptic drugs for treating blisters and ulcers, rinsing;
- Use of topical anesthetic gels;
- Prescribing non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs to alleviate general well-being;
- Strengthening the immune system by taking vitamins and immunomodulators.
To eliminate symptoms, advanced technologies such as laser radiation are also used. The technique allows you to quickly and painlessly destroy viral particles without harming mucosal cells and effectively healing damaged tissue. In most cases, several short procedures are sufficient for complete disappearance of symptoms in 2-4 days.
Choosing an ointment for herpes -
If you have herpes, treatment in adults and children is most often carried out with one of the external agents containing 5% Acyclovir (an antiviral agent effective against the herpes virus). Preparations based on acyclovir: Acyclovir cream 5% (Russia), Acyclovir ointment 5% (Russia), Acyclovir-Hexal cream (Germany), Acyclovir-Sandoz cream (Switzerland), as well as original drugs with acyclovir - a line of branded products Zovirax (UK).
Zovirax cream: the original drug of acyclovir
Herpes cream or ointment with acyclovir should be applied to the lesion and the skin around it at least 5 times a day (but better every 2 hours while you are awake). The duration of therapy is usually 5 days, but in case of severe herpetic lesions, the duration of use can be increased to 7-10 days. It should be noted that the cream form is more preferable to the ointment, because from the ointment substance, the active substances penetrate the skin much worse.
It is worth paying attention to the composition, for example, the effective concentration of acyclovir is exactly 5% (although in pharmacies you can also find products with a 3% concentration). In addition, the composition should preferably contain propylene glycol and/or cetomacrogol, which increase the penetration of acyclovir molecules through the surface layers of the skin. This is important because Acyclovir itself penetrates quite poorly through the epidermis of the skin and the resulting crusts.
For women, it may be important to be able to apply cosmetics on top of the absorbed cream. In this case, you should choose a cream that contains dimethicone (silicone). Today, dimethicone in combination with propylene glycol and cetomacrogol is found in the following products - Zovirax cream, Zovirax Active-Duo cream, Acyclovir-Sandoz cream.
The best remedy for herpes with acyclovir is
Today, the best drug for external use against herpes is Zovirax Duo-Active cream, which contains a combination of 5% acyclovir and 1% hydrocortisone. Acyclovir blocks the multiplication of the virus, and hydrocortisone reduces inflammation and swelling. Moreover, if the use of the cream begins even before the appearance of herpetic blisters, then hydrocortisone sometimes makes it possible to prevent their formation altogether. But if bubbles do form, their number and size will be smaller, which in itself will significantly speed up healing.
Disadvantages of acyclovir-based drugs - acyclovir is an outdated drug, but in principle it works well for most patients (with some exceptions). For example, in patients with good immunity, resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir occurs on average in only 3% of cases, which is quite small. However, the problem is in patients with weakened immune systems + frequent courses of acyclovir use in the past - in such groups of patients, resistance to acyclovir can be observed in 10 to 27% of cases.
In addition, acyclovir molecules have a very low tropism for the herpes virus, which means that acyclovir usually simply does not find a certain percentage of viral particles in cells (for example, drugs based on penciclovir / famciclovir have a much higher tropism in the virus). In addition, acyclovir molecules tend to penetrate poorly through the skin, as well as through the resulting crusts (to the site of virus reproduction). In order to somehow reduce this problem, some manufacturers add propylene glycol and cetomacrogol to external products containing acyclovir.
Alternative external remedies for herpes -
First of all, this is the Fenistil-Pentivir cream, which contains the antiviral component Penciclovir. Compared to acyclovir, penciclovir is several times more effective (including due to the significantly greater tropism of penciclovir for the herpes virus, and due to better penetration into cells affected by the virus). It should also be noted that the resistance of the herpes virus to penciclovir is extremely low - it is no more than 0.2%.
The drug is applied to the lesion every 2 hours (8 times a day), but the course of use is usually only 4 days. Such a short course is due to the fact that after the last application of the cream, the clinically active concentration of penciclovir will remain in the cells for about 2 more days (i.e., the therapeutic effect after a 4-day course will last about 6 days). Clinical studies have also found that repeated outbreaks of herpes occur less frequently when using Fenistil-pencivir than when using other drugs. However, in recent months this drug has disappeared from Russian pharmacies, most likely due to the re-registration procedure.
We have already said above that patients with weakened immune systems often develop resistance of the herpes virus to acyclovir. What should such patients do? International recommendations in this case speak of the need to use courses of famciclovir in tablets - these are drugs such as Favirox or Famvir. Tablet preparations based on valacyclovir (if resistance to acyclovir is suspected) does not make sense to use, because valacyclovir is a precursor to acyclovir. The latter means that if there is resistance to acyclovir, there will be resistance to valacyclovir.
Cream Devirs for herpes –
Maybe there are some other topical products that would be effective against herpes and do not contain acyclovir? In pharmacies you can find such a prescription drug - Devirs cream (manufactured by Vertex, Russia), containing the antiviral component ribavirin. According to the instructions, this drug can be used in patients over 18 years of age - for genital herpes, for the treatment of labial herpes, herpes localized on the face and body.
Unfortunately, there are very few clinical studies on the effectiveness of local ribavirin-based products, and all of them, in our opinion, have a rather weak degree of evidence. Getting acquainted with the studies, we noticed that this drug was very rarely used in studies in the form of monotherapy (usually it was combined with either oral ribavirin or oral acyclovir), which already indicates the rather weak effectiveness of the cream. Therefore, our editors cannot recommend this drug for widespread use, especially for the treatment of herpes lips and small lesions on the face. But the drug may well be used as part of complex therapy, for example, for genital herpes.
Stomatitis: how to overcome the “language barrier”?
Stomatitis on the tongue is just one of the manifestations of this “popular” disease. There are a huge number of reasons for its appearance, as well as ways to treat it.
There are several types of stomatitis, when it manifests itself specifically on the tongue: glossitis, viral stomatitis, vesicular stomatitis, enteroviral vesicular stomatitis, catarrhal stomatitis, fungal stomatitis, etc.
In general, stomatitis on the tongue is most common. Its notable feature is small ulcers, from which the patient suffers greatly. If inflammation is observed only on the tongue, and, for example, there are no signs of stomatitis on the palate, cheek or gum, then this disease is called glossitis.
Eppstein-Barr virus
The Epstein-Barr virus predisposes to premature termination of pregnancy, fetal malnutrition, and in newborn children it causes damage to the nervous system, visual organs, recurrent chroniosepsis, hepatopathy and respiratory distress syndrome. However, this virus provokes the listed pathologies only under certain conditions, under which it becomes dangerous during pregnancy. It is very bad if a pregnant woman has not previously encountered the Eppstein-Barr virus, which is why she does not have antibodies to this virus in her body. If there was contact, and antibodies were detected after treatment, then this is a good sign, because in this case there is nothing to be afraid of. This serves as evidence that if a woman’s body becomes infected again, she will cope with this dangerous disease on her own. This means that a pregnant woman will not have to take medications that are heavy and quite dangerous for the development of the fetus.
How does the virus become infected?
The virus can be infected in different ways: airborne droplets, contact (through shared towels, cutlery, through kissing), sexual intercourse, self-expression (when the virus from ulcers enters healthy mucous membranes and infects them). You can become infected through a blood transfusion and a child can receive the virus from the mother in utero. The incubation period (from the moment of contact until the first signs appear) is 2-14 days. A person becomes contagious as soon as sores appear on the lip, and is contagious to others until the scabs fall off .
Photo: One of the most common ways of transmitting herpes is contact.