What kind of pathology is this
Herpetic gingivitis is an inflammatory lesion of the gums caused by the introduction of a herpes viral infection into their mucosa. This infection is considered highly contagious and can be contracted anywhere, on the street and in public places. During the cold season, there are more cases of this infection. Its source is a sick person. Often this disease becomes a complication of viral stomatitis.
The virus is transmitted to children in the following ways:
- contact;
- household;
- airborne;
- hematogenous.
The first introduction of the virus into the baby’s body is manifested by gingivitis and stomatitis.
3.Herpes
Herpes on the lips
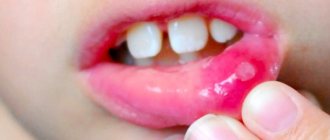
appears due to a virus called herpes simplex virus type 1. Unlike ulcers, herpes is contagious from the moment the herpes blisters rupture until complete recovery. Primary infection often occurs during childhood and can be confused with cold or flu symptoms. Once a person becomes infected with the herpes virus, the virus remains in the body and lies dormant most of the time. But during stress, colds, injuries, hormonal changes, under the influence of sunlight, the virus is activated and herpes appears on the lips.
Herpes tends to appear in the same place. And in addition to infecting other people, the herpes virus can spread to other parts of the infected person's body - the eyes and genitals.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Causes
Often a child gets sick for the first time during teething. It prevents you from brushing the area where the tooth is erupting. As a result, infection accumulates in this place and inflammation of the gum tissue occurs, which gradually spreads. It is aggravated by frequent allergic reactions to introduced complementary foods.
In older children, pathology is provoked by the following reasons:
- mechanical microtraumas - damage to gum tissue occurs when brushing teeth with hard brushes or hard food when biting it;
- the introduction of herpes is provoked by other viral or infectious lesions of the oral cavity;
- the presence of polyps in the nasal cavity and breathing problems contribute to the penetration of an infectious agent into the gum tissue;
- an incorrect bite in a child leads to constant trauma to the mucous membrane and the development of inflammation;
- lack of nutrients, vitamins and microelements in the baby’s diet reduces local immunity;
- the manifestation of a viral infection is provoked by burns in the mouth;
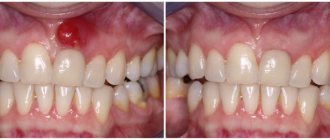
- Dental diseases (caries, pulpitis) contribute to the development of the virus in the gum tissue, weakening local immunity.
The infection spreads to other tissues quite quickly, and isolated gum damage spreads to periodontal structures.
How Covid-19 manifests itself in the mouth
COVID-19 leaves the body of an infected person in several ways: breathing, sneezing, talking, coughing, singing. All pathways involve the oral cavity. Therefore, when taking a coronavirus test, a swab is taken from the mouth and respiratory tract. Saliva is one of the main sources of transmission of the new coronavirus infection.
Remember, to protect yourself and your loved ones from coronavirus infection, you must wear medical masks and maintain social distance.
Coronavirus with complications in the oral cavity occurs in 45% of patients, complaints: dry mouth, rash on the mucous membrane, loss of taste, ulcers. However, complications of the virus may appear 12 days after the onset of the main symptoms and during the rehabilitation period. An oral infection from COVID-19 can also be asymptomatic, which complicates the treatment of the patient and the identification of the cause of complications in the oral cavity. Complications are associated with the poor state of the oral microflora, periodontal disease and other dental diseases, the treatment of which the patient postponed until later. From all this it follows that the connection between lack of oral care and the disease of the new coronavirus infection is close and it is always necessary to monitor your health.
Symptoms
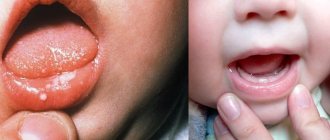
Signs of herpes gingivitis in a child do not appear immediately after infection. Its latent period lasts up to eight days. The disease begins abruptly. At first, the baby becomes capricious, lethargic and restless. He sleeps poorly, refuses to eat, and complains of pain in his mouth.
After some time, the following manifestations of the disease appear:
- high temperature up to 39 degrees;
- increased salivation;
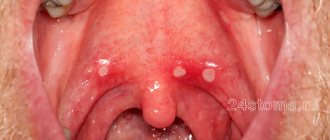
- gums become swollen and red;
- intergingival papillae increase;
- the oral mucosa is swollen;
- the tongue swells and becomes covered with a white coating;
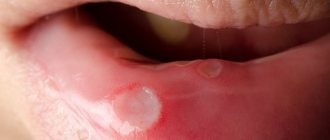
- blistering rashes on the mucous membranes and skin around the mouth;
- nearby lymph nodes enlarge;
- headache;
- bad breath;
- general malaise;
- burning.
In place of the blisters, when they burst, ulcers appear that do not heal for a long time. All other manifestations disappear within a week, but they persist for up to fourteen days.
How is viral stomatitis treated?
Often, treatment of viral stomatitis is based on local exposure to damaged areas of the mucous membrane and skin. Ulcers and erosions are treated with an antiseptic and painkillers, the dentist prescribes applications (application of the drug) with anti-inflammatory and wound-healing compounds. To strengthen the immune system, the patient is prescribed medications based on echinacea and vitamins.
It is also important to follow a diet during therapy. All products consumed must be neutral in taste, pureed, and not hot.
You cannot self-medicate: without the help of a doctor, the disease can develop into a chronic form.
It is advisable to reduce home treatment of viral stomatitis in adults and children only to procedures that will speed up the healing process of lesions. The doctor will recommend rinsing with decoctions of herbs and oak bark.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis of herpes gingivitis is quite easy for a child to make, since the disease has characteristic clinical manifestations. The diagnosis is made by the dentist based on an examination of the baby’s oral cavity and data on the course of the disease. Characteristic formations on the mucous membrane and manifestations of inflammation in the mouth clearly indicate that this is a specific lesion. To clarify the nature of the lesion, the doctor prescribes general blood and urine tests. If the disease is severe, it is necessary to clearly identify the type of pathogen. In this case, specific laboratory research methods are used.
These include:
- virological study;
- polymerase chain reaction;
- immunofluorescence method;
- HSV test for the determination of immunospot G-specific glycoprotein;
- serological test with immunoglobulin M.
These methods determine with a high degree of accuracy the type of pathogen in the blood and discharge from ulcers. But they are very expensive and labor-intensive, so they are used quite rarely.
What to do to avoid oral complications
If you have been diagnosed with coronavirus infection and are experiencing complications in the oral cavity, contact your doctor to get permission to visit the dentist. When making an appointment with a dentist, be sure to tell them: you are or have been sick with Covid-19. The dentistry of the ElitDental M clinic will help alleviate the symptoms of the disease in the oral cavity and provide comprehensive treatment. We are located at:
- Rostov-on-Don, st. Zhdanova 3. Make an appointment by phone, +7(863) 544-63-54.
- Rostov-on-Don, Mironova street 6. Make an appointment by phone.
Opening hours: Monday – Friday from 9.00 to 20.00. Saturday from 10.00 to 17.00. Sunday is a day off.
Treatment
Treatment of mild forms of herpetic gingivitis in children is carried out on an outpatient basis under the supervision of a physician. In severe cases of the disease, the patient is hospitalized in a hospital. The patient is prescribed a diet with a predominance of pureed food that does not irritate the oral mucosa. It shouldn't be hot. There is no need to give your child solid food to prevent additional injury to the gums.
For mild forms, local treatment is used.
The following drugs are used:
- antiviral agents (Acicovir, Ganciclovir) - destroy the DNA of the virus, use ointment to lubricate the gums up to five times a day for two weeks;
- local anesthetic gels and ointments (Lidochlor gel, Kamistad) - they anesthetize, disinfect, have an anti-inflammatory effect, are used three times a day, two weeks;
- local antiseptics (Iodinol, Miramistin, Hexoral) - these agents rinse the mouth every four hours, two weeks;
- reparative preparations (Solcoseryl-gel, Methyluracil ointment) - applying ointments to ulcers promotes their epithelization and rapid healing, applied three times a day for two weeks.
Herbal infusions (chamomile, rose hips, calendula, sage, St. John's wort, licorice) are widely used for rinsing when gums are damaged.
In severe cases, the baby is prescribed oral medications.
The following drugs are prescribed:
- antiviral drugs (Famciclovir, Acyclovir, Zovirax) - taken according to the regimen prescribed by the doctor, the drug must be taken to the end, otherwise there will be a relapse;
- antihistamines (Suprastin, Tavegil, Citrine) - reduce swelling of gum tissue and reduce pain;
- antipyretics (Panadol, Nurofen) are used to reduce high fever.
Parents should monitor the baby’s oral hygiene; during illness, it is carried out especially carefully. To prevent gum injury, it is recommended to use toothbrushes with soft bristles. It is necessary to treat toys and objects that the baby uses with antiseptics.
Preventive actions
It is almost impossible to prevent infection with herpes; in practice, 9 out of 10 school-age children are infected with the infection, but not all have a clear clinical picture.
Prevention of the disease is aimed at preventing repeated episodes of herpes. The main reason for the exacerbation of the pathology is a weakened immune system, so all preventive measures will be aimed at maintaining the body’s defenses.
Prevention of pathology can be specific and nonspecific. Non-specific activities include:
- rejection of bad habits;
- frequent exposure to fresh air;
- timely dental treatment;
- limiting the consumption of allergenic products (chocolate, confectionery, semi-finished products);
- regular observation by a specialist for somatic problems;
- visits to the dentist to remove tartar and plaque.
Repeated manifestations of herpes occur in a mild form in both adults and children. In case of relapse of the disease, which does not manifest itself with significant symptoms, you should not take immunomodulators, since the body itself is able to cope with the activated pathogen.
Types of stomatitis
Depending on the nature of the disease and its clinical manifestations, experts divide catarrhal, catarrhal-hemorrhagic, as well as bullous, erosive, ulcerative-necrotic and allergic stomatitis.
The latter, in turn, is divided into the following types:
- medicinal;
- contact, for example, as an allergy to dentures, braces, plates;
- catarrhal;
- catarrhal-hemorrhagic;
- ulcerative-necrotic;
- erosive.
From the point of view of etiology and pathogenesis, allergic stomatitis includes medication, contact (including dentures), toxic-allergic, autoimmune dermatostomatitis, chronic recurrent aphthous stomatitis and other forms.
Depending on the speed of development of the reaction, doctors distinguish immediate and delayed types of allergic stomatitis. In the first case, angioedema is observed, and in the delayed type, the reaction to a particular irritant usually appears a few days after contact with the allergen.
In rare cases, allergic stomatitis develops while wearing dentures. Sometimes a reaction occurs even after 5–10 years of wearing them, after a long asymptomatic period.
Ask a Question