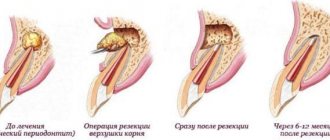
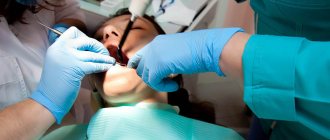
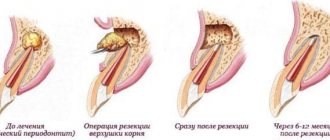
First of all, we note that the price for treating pulpitis of a three-canal tooth really depends on the number of these very root canals in it, and here the general rule is this: the more there are, the more expensive the treatment procedure usually costs. And not only more expensive, but, in addition, with a large number of roots, a number of nuances of endodontic procedures often arise, which we will talk about in more detail later.
On a note
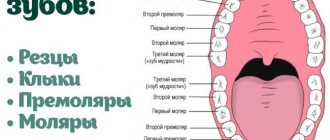
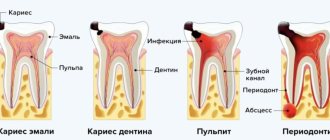
Pulpitis is a disease in which inflammation of the so-called dental “nerve” (pulp) occurs. Large molars (molars) most often have three canals, each of which contains a neurovascular bundle. When an inflammatory process occurs in the pulp, it swells and is compressed, as a result of which a person can feel severe pain.
Pulpitis requires mandatory treatment: you should not expect that everything will somehow resolve and the pain will go away on its own, as sometimes happens in the case of pain during caries. The pain may indeed disappear when the “nerve” completely dies, but then it will begin to decompose right inside the tooth, and without appropriate treatment this will not lead to anything good.
Treatment of pulpitis of a three-canal tooth, in contrast to a single-canal one, is often technically more difficult, so in order to carry out high-quality work, the doctor has to spend more effort and time, and also actively apply the achievements of modern dentistry.
Today, in most clinics, three-channel pulpitis is almost always treated by extirpation - removing the nerve from all canals and filling them at the final stage of intracanal treatment.
This is interesting
In the upper wisdom teeth there are the most unpredictable variations in the number and location of roots and canals. As a rule, doctors are faced with one-, two- and three-canal eighth teeth, but there have also been cases of 4 and even 5-root teeth with up to 8 full canals!
Three-channel pulpitis in most dental clinics is treated in two visits. For these purposes, the so-called vital extirpation technique is well suited, when, under local anesthesia, the pulp is removed from all three canals and they are filled, followed by the placement of temporary filling material on the tooth. And on the second visit, the permanent filling is successfully installed.
Let's now see how this happens in practice.
First visit:
- tooth pain relief;
- preparation of carious softened tissues with a turbine tip, removal of necrotic and pigmented dentin;
- washing with antiseptics;
- opening good access to the mouths of three canals;
- expansion of mouths;
- rubber dam application;
- extirpation (extraction) of pulp from all three canals using pulp extractors;
- passing the canals with files, measuring their length, expanding with K-files, H-files, machine instruments with constant irrigation (washing) of the canal system with sodium hypochlorite solution;
- the use of EDTA preparations for poorly traversed canals;
- drying of canals, control measurement of their lengths;
- filling the canals using the method of cold lateral condensation of gutta-percha pins with paste or using the Termafil system for obturation;
- placement of a temporary filling or temporary restoration of a tooth;
- control image (x-ray).
Second visit:
- reprocessing of the tooth;
- placement of a permanent filling made from a light-curing composite or other imported material (an example is shown in the photo below).
Sometimes pulpitis of a three-rooted tooth is treated in three visits or even more. This depends on the chosen technique, the doctor’s tactics, the level of his professional skills and sometimes on the difficulties that arise during intracanal treatment.
If it is impossible to immediately remove the pulp from the canals, the dentist places a devitalizing drug on the opened pulp chamber in order to “kill the nerve” for the next appointment. Accordingly, this increases the treatment of three-channel pulpitis by one visit.
In Soviet times, even single-channel pulpitis was treated with “arsenic” for a period of 24 hours. This practice is no longer acceptable at the current level of development of dentistry. Treatment of pulpitis of a single-canal tooth, as well as a double-canal one, is almost always carried out in one visit (with rare exceptions).
Large molars (mainly the lower ones), due to the structural features of the jaw and the location of the nerves that determine the sensitivity of the tooth, sometimes may not be “frozen” to such an extent that the nerve can be removed immediately, that is, pain sensitivity remains. Therefore, the way out of this situation is the preliminary use of pulp-killing pastes (popularly they are still called “arsenic,” although modern preparations have not contained arsenic for a long time).
It is also useful to read: Symptoms of pulpitis: what is important to know in case of severe tooth pain
On a note
In a number of clinics, treatment of pulpitis is always carried out in one visit, regardless of the number of canals: they are filled, and a permanent filling is immediately installed on the tooth. Studies have shown that this practice often leads to long-term negative consequences, since the material introduced into the canals must first harden. In construction, work does not begin until the foundation hardens, as the consequences can be disastrous - and the situation is the same here. That is why it is recommended to treat pulpitis in at least two visits.
Symptoms
- pain syndrome
. A typical sign of acute inflammation is spontaneous pain, intensifying at night, which spreads to the temporal/occipital area, cheekbones, and ear. It occurs unexpectedly and does not depend on the influence of external stimuli. The attack can be long with short intervals, short with long intermissions. As the infection spreads, unpleasant sensations appear during palpation and percussion of the tooth. The chronic disease is characterized by an asymptomatic course, in 10-15% of cases there is a weak reaction to solid/hot foods; - bad breath
; - the presence of tooth deformations
- enamel cracks, caries; - Body temperature
and enlarged regional lymph nodes are rarely recorded.
Acute inflammation is accompanied by hyperemia and swelling of the connective tissue, which occurs against the background of deep caries. The development of hyperemia is manifested by moderate paroxysmal pain that passes after 1-2 minutes. During diagnosis, a depression filled with softened dentin is revealed; the patient experiences unpleasant sensations when probing its bottom.
Causes of pulpitis
- caries.
Pathogenic microflora actively multiply, releasing toxins; - dentist mistakes.
The defects are filled with low-quality material, microorganisms contribute to the destruction of the organ. When drying, due to excessive use of air, a dentin burn may occur (aseptic inflammation that develops without bacteria); - the presence of a chronic source of infection
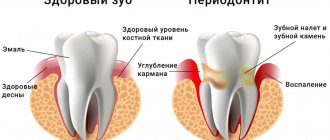
- sinusitis/tonsillitis; - with periodontitis,
the infection penetrates from deep periodontal pockets, provoking the development of retrograde pulpitis; - injuries
- bruise, broken parts of the crown, chipped enamel, fracture; - increased organ wear
due to osteoporosis and diabetes.
Classification
- Acute (focal, diffuse).
Characterized by changes in the horn area, outside the coronal part. Discomfort occurs under the influence of external irritants. Timely initiation of therapy guarantees a 100% positive result. This phase lasts about 2 days, progressing to the diffuse stage - the roots and coronal segment are affected. Characterized by paroxysmal pain that occurs without the influence of internal/external factors; - Chronic (hypertrophic, purulent, gangrenous, fibrous).
The disease becomes permanent, the intensity of the pain syndrome decreases. The fibrous appearance does not produce pronounced symptoms; a diagnostic examination by a dentist reveals a depression extending to the chamber. Against the background of constant hypertrophic inflammation, it connects with the chamber, a process appears - a polyp, occupying all the free space. The patient experiences pain while eating, and blood may ooze from the organ. Serious consequences in the form of gangrenous pulpitis of permanent units develop due to putrefactive decay. At this stage, putrid breath appears, prolonged aching pain from irritants, which intensifies after eating hot food. In the retrograde form, periodontal pockets are diagnosed, which occupy a large part of the root. The source of infection is located in this place. Inflammatory processes begin to cover the root segment, gradually moving to the coronal segment.
Prevention
Prevention is required in combination; this includes not only the patient’s independent actions at home, but also professional measures. The clinic offers the following services:
- regular preventive examinations;
- monitoring the condition of the oral cavity, timely treatment of dental diseases;
- office cleaning of tartar and plaque;
- professional selection of hygiene products.
At home, the patient should do the following:
- daily cleaning using special pastes and brushes of the hardness specified by the doctor (at least twice a day);
- using an irrigator and dental floss to remove food debris from the interdental spaces;
- rinsing your mouth after eating.
Modern techniques
- Gutta-percha lateral condensation method.
In clinics in the West, this option is used to treat roots for acute and chronic pulpitis in approximately 80% of cases. The bottom line is that the canal, after removing the tissue and mechanical processing with special instruments, is filled with thin flexible gutta-percha pins in combination with a special hardening paste. Gutta-percha is the dried sap of the gutta-percha tree, growing in Brazil and Malaysia. It has an antiseptic effect, working in the canal similar to a sealant. All drugs used are non-toxic and non-irritating. A positive result is possible only with strict adherence to technology. It is important that the filling paste does not extend beyond the root tip. If the doctor says that nothing bad happened and it will resolve over time, this is not true. Some substances irritate the periodontium, which can lead to complications in the jaw; - Thermafil system.
The roots are processed with a special apex locator device, which controls the approach to the apex and prevents damage. Flexible nickel-titanium instruments allow you to restore even curved canals, giving them the correct conical configuration. Then one gutta-percha pin of the required thickness, heated in a special oven, is placed into the canals. Pros: accuracy, reliability, low time consumption. With the help of equipment, treatment of pulpitis of a three-canal tooth (premolar) takes only 30 minutes, while manual treatment can take more than one hour, which is difficult for the patient. The only negative is the high cost; - Resorcinol-formalin.
This conservative technique in dentistry was invented almost 100 years ago and is considered obsolete. Is it possible to help patients who have already been treated with the resorcinol-formalin method? It is much more difficult to cure a resorcinol-formalin tooth. The complexity arises, since in 70% of cases there are complications in the form of chronic periodontitis, cysts, granulomas. The question of the possibility of re-treatment of the affected canals and elimination of dangerous complications is decided individually, after a thorough diagnosis.
Why do they trust us?
Our dentistry uses modern scientific methods in dental treatment. Over 16 years of impeccable work, we have helped more than 20,000 patients to promptly cure oral diseases, maintain healthy gums and a beautiful smile.
We have our own diagnostic room with modern digital equipment and a dental laboratory. You will receive all the necessary examinations, treatment and prosthetics in one place.
The clinic employs successful specialists with highly professional experience in dentistry. Doctors annually take special courses, improve their qualifications, and participate in international symposiums.
We see the following specialists:
- dentist-therapist;
- orthopedic dentist;
- orthodontist;
- dental surgeon;
- periodontist;
- pediatric dentist;
- Dental Technician;
- radiologist.
Diagnosis of pulpitis
The disease is diagnosed after consultation, analysis of the patient’s complaints and a dental examination and x-ray examination of the problem tooth. During an instrumental examination, carious lesions, a painful reaction to thermal stimuli, and softened dentin are detected. Percussion is painless. To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor prescribes additional medical tests. Using a special apparatus, the electrical excitability of the pulp and the degree of its damage are determined. An X-ray is required to identify a diseased tooth and determine the depth of periodontal damage.
Performing pain relief
It is impossible to treat pulpitis without anesthesia. Therefore, the doctor will certainly perform a blockade of nerve endings to make the patient feel better and the doctor to work more conveniently. The lower chewing teeth in the back of the mouth are the most difficult to respond to painkillers. Here the dentist will have to show the art of administering mandibular anesthesia. In most cases, some of the painful sensations will remain during the treatment of distant teeth; this is determined by the anatomy of the nerves located in these teeth.
Stages and methods of treatment of dental pulpitis
There are two traditional approaches
: removal of inflamed tissue and preservation. The choice of technique is determined by the course and stage of the disease:
Biological method
. This method is recommended for use at the initial stage of development of the inflammatory process in a vital tooth; it allows maintaining the viable state of the pulp.
Indications
:
- acute focal form;
- fracture of the coronal part of the unit due to injury, unplanned exposure of the intact pulp during dental procedures;
- fibrous form of pathology of chronic genesis;
- low intensity of caries;
- no allergies to medications used;
- young age;
- no history of concomitant diseases, ARVI during therapy.
Under anesthetic anesthesia, the dentist prepares the cavity with a drill, applies medications with anti-allergic, anti-inflammatory, therapeutic, restorative effects to the dentin layer, and places a temporary filling. In the absence of significant complications for tooth restoration, a permanent filling is placed.
Surgical intervention
. An effective method of treating advanced tooth pulpitis involves partial/radical removal of the pulp. The peculiarity of the procedure is that it is carried out after necrosis of the nerve by applying a mixture containing arsenic or under local anesthesia. After removing the softened tissues and opening the mixture, the cavity is closed for 48 hours, at the next visit the root segment is extirpated, medicated and the canals are filled with filling material. To fill them, pins, pastes, and cements are used. To assess the quality of the operation, visiographic and radiographic methods are used.
Mechanical processing of channels
It is performed with special devices: K-files, cone-shaped with spiral-shaped cutting edges. By turning the instrument inside the canal, the doctor expands the walls for the subsequent introduction of obturation material.
The world's leading dentists adhere to the position: it is not so important how the canal is filled, what is much more important is how well it is prepared. During the preparation process, it will be necessary to expand the channel cavity to a certain depth, which will result in the formation of chips. In addition, the canal is washed to remove living and dead bacterial biomass, pulp residues, etc.
Prices for the treatment of acute and chronic dental pulpitis
To find out the cost of treating pulpitis, sign up for a consultation at Dr. Razumenko’s clinic by calling: 8 (495) 380-01-38.
| Code no. | NAME OF PROCEDURES | Unit of measurement | Cost, rub. |
| Mechanical processing of channels | |||
| 401 | Mechanical treatment of the canal with hand tools | 1 500,00 | |
| 402 | Mechanical canal processing (Profail, pro-taper) | 2 000,00 | |
| 404 | Filling with temporary (therapeutic) material | 1 000,00 | |
| 405 | Canal filling using lateral condensation method | 1 500,00 |
* The prices indicated on the website are not a public offer. The exact cost can only be determined by visiting a doctor.
Prices for treatment in Moscow full price list
Share on social media networks:
Article Expert:
Ustinova Elena Fedorovna
Doctor of the highest category. Root canal treatment (complex, repeated retreatment), microprosthetics with ceramic restorations.
Work experience 15 years
Reviews
Kamila
Very good place and professional doctors. Respectful, attentive attitude towards patients. They are able to treat very well, even complex cases. Many thanks for your professionalism, patience and high personal qualities.Igor
Not long ago I came to treat three-channel pulpitis. From experience in other dentistry, I know that anything can happen. I was very worried about how everything would happen this time. I want to say that the treatment went just fine. I fully felt the professionalism of the doctors. I am very pleased with my visit to this dentistry!
We recommend that you read
Tooth nerve removal
Treatment of anterior teeth
Dental filling
Canal filling