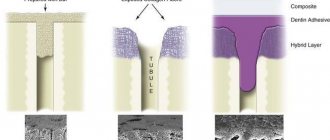
Silicate cement
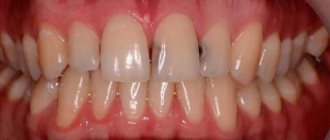
Silicate cements are used mainly as materials for restoring tooth structure, which is removed during the preparation of a carious cavity, in particular for filling cavities of III, V anterior teeth and class II in premolars.
Like zinc phosphate cements, silicate cements are prepared by mixing a powder with a liquid containing phosphoric acid. The mixture hardens relatively quickly, forming a transparent substance that is similar to dental porcelain.
Powder. Silicate cement powders are a finely ground ceramic composition. They are essentially acid-soluble glasses.
The powders generally consist of silica, aluminum dioxide, potassium oxide, sodium fluoride, calcium fluoride, cryolite, or a combination of fluorides. It has been established that only a narrow range of compositions containing calcium oxide, silicon dioxide and aluminum dioxide, when sintered, form a glass that, after crushing and mixing with a cement liquid, hardens within a suitable time. The reaction occurs precisely due to these components.
The powder components are sintered together at a temperature of about 1400°C. Fluoride compounds melt at a lower temperature than other ingredients and promote better sintering. Some substances are known in ceramics as fluxes, for example beryllium oxide, sodium carbonate, etc. However, the best cements are formed using fluorides.
The hardening time of cement depends on the ratio of silicon: aluminum: calcium. Along with this, the inclusion of large amounts of aluminum and calcium reduces the hardening time of cement. Most often, the ratio of silicon to the aluminum-calcium combination ranges from 1.02 to 1.44. Most powders contain calcium or aluminum phosphate fluxes. These phosphates reduce the hardening time of cement, but they can affect other properties.
The powder of domestic silicate cement silicin-2 is a finely ground glass obtained by melting a charge consisting of quartz, alumina, cryolite, fluorspar and other components. The melting of the charge is carried out in fireclay or quartz crucibles in a gas-plasma furnace at a temperature of 1370-1450°C, followed by rapid cooling of the melt in cold water. The resulting granulate is ground in 200-liter open-circuit ball mills to a residue on a control sieve with a particle size of 60 μm not exceeding 0.5%. Silicate cement powder is available in seven shades: from light yellow to yellow-gray.
Liquid. The composition of silicate cement fluids does not differ significantly from zinc phosphate cement fluids, except that zinc and magnesium phosphates are used in most cases as buffering agents in silicate cement fluid in combination with the commonly used aluminum phosphate.
In addition, silicate cement fluids generally contain more water than zinc phosphate cement fluids. It is possible that the combination of aluminum and zinc as modifiers helps prevent precipitation during standing liquid. When two modifiers are combined, a saturation point of the incorporated metals is likely to be reached.
Cement powder often contains traces of arsenic, which makes it difficult to remove this impurity from the remaining ingredients. Arsenic is not harmful if the amount is less than 1 part per 500,000 parts of powder. This determined amount is one of the requirements of the international standard.
A small amount of glass fiber is used in the powder of some foreign products (Austria, France).
Clinical significance of fluoride. Most manufactured silicate cement powders contain up to 15% fluorides. The effect of fluoride on the final properties of the filling is unclear, but the clinical significance of fluoride is extremely important. It is known that secondary caries develops less often around silicate fillings than around other filling materials. Although silicate cement has many disadvantages, it is significantly superior to all other filling materials in terms of anti-caries resistance. This protective mechanism is associated with the presence of fluoride in cement. Silicate-cement filling is quite soluble in oral fluid, while a certain amount of fluoride is gradually washed out of the filling and acts as a bactericidal and anti-enzyme agent, and also significantly increases the resistance of the adjacent enamel. However, by the end of the 5th day, only approximately 14 ppm of fluoride is released from the cement, and this amount continues to decrease over time. It is doubtful that such a small concentration of fluoride can have an inhibitory effect. It has been found that some bacteria are inhibited only in the first 24 or 48 hours, and this is probably due to the presence of phosphoric acid.
Silicophosphate fillings
Dental Services
Silicophosphate fillings
The discovery of silicophosphate powders at one time became a breakthrough in dental practice. True, this was a long time ago, however, this type of filling is still widely used today. In essence, silicophosphate cements are a modification of phosphate compounds using aluminosilicate glass. The latter additive provided fillings, which in professional dentistry are designated by the abbreviation SFC, with higher aesthetics than phosphates and higher strength than silicates.
Composition and application of silicophosphate cements
The consistency of fillings based on zinc oxide enriched with silicate glass is a dough-like mass.
Prepare within 4 minutes. They harden in 5–7 minutes, but this process can be slowed down so that the dentist has time to distribute the material well throughout the tooth tissues. The shares of the main components (silicate and phosphate cements) in the formula of silicophosphate materials can be distributed differently. The composition may contain up to 90% silicates and up to 40% phosphates (the second part is leveled based on the standard maximum of 100%).
The scope of application of silicophosphate fillings is quite wide. They are often recommended for treatment on a limited budget:
- carious area located on the posterior (non-vestibular) side, when fillings are required on the front part of the dentition;
- small cavities of (pre)molars;
- filling teeth that are planned to be subsequently replaced with prosthetics (silicophosphate cements are also used to secure crowns).
Advantages of SFC
When compared with earlier solutions - fillings based on phosphates and silicates - then silicophosphate materials have a number of advantages:
- they are very easy to use;
- provide sufficient strength at the level of durable temporary fillings;
- more aesthetic than phosphates;
- less irritating to the pulp than silicate fillings;
- silicophosphate cements are less susceptible to being washed out by saliva than phosphate and silicate analogues;
- Due to the release of fluoride, silicophosphate cements prevent secondary carious lesions;
- This is an inexpensive treatment option.
Features of dental cement
In dentistry for fixing inlays, pin teeth, metal-ceramic, plastic and porcelain dentures, crowns and bridges, filling teeth to be covered with crowns, linings for other filling materials, etc. special dental cement
, which includes certain substances. When such specialized cement hardens, a stone-like solid mass is formed, which preserves the teeth.
General characteristics of the material
Dental cement
It contains powder and liquid, when mixed, a paste-like mass is formed.
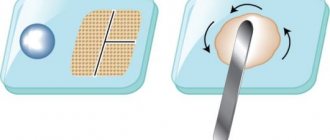
Dental glass is used to mix dental cement .
An accompanying attribute is dental glass for mixing cement, available without a hole, with 1, 2, 3 holes
During the hardening process, the mass begins to harden and becomes like stone. Hardening occurs as a result of the components entering into a chemical reaction.
The main indicators that high-quality dental cement
, the following:
- mixing time;
- work time;
- curing time.
Mixing time refers to the period of time recommended for preparing the solution. Typically this figure is 90 seconds , and it is not recommended to exceed it.
The time during which the doctor must have time to apply the mixture to the tooth and model the filling is called working time. Each manufacturer of dental cement has its own characteristics, but the average varies from 4 to 10 minutes .
The period allotted for hardening of the cement mass also varies among manufacturers. Sometimes it can take a week for the ingredients to react and cause hardening. An important role in the setting of the material is played by the temperature and mixing proportions of dental cement.
with liquid.
12. Silicate phosphate cements. Compound. Principle of use and scope of application in dentistry.
Silica phosphate cements are a combination of zinc phosphate and silicate cement.
In terms of physical and chemical properties, it occupies an intermediate position between them. Silicate cement 95-60%, phosphate cement 5-40%.
1) mechanical strength; 2) less fragility than silicate cements; 3) better adhesion than silicate cements; 4) plasticity; 5) availability, low cost; 6) radiopacity; 7) coefficient of thermal expansion is close to dental tissues.
Negative: 1) discrepancy with the color of the tooth tissue;
2) toxicity (used with a gasket);
3) solubility and instability to saliva.
Technique for mixing silica phosphate cement
It is produced in the same way as for silicate cement, with the only difference that it is necessary to apply a little force to overcome the viscosity of the cement paste. In addition, it is necessary to add smaller portions of the powder so that the ingredients fully react with each other. The hardened mass of silico-phosphate cement is mainly a conglomerate of silicic acid gel and a crystalline mass of the hardening products of phosphate cement.
Due to this, silica phosphate cements are radiopaque.
Indications for use
• filling cavities of classes I, II, V premolars and molars (in the absence of more
modern materials or the presence of contraindications to their use);
• filling of temporary teeth in children.
Silico-phosphate cements are introduced into the cavity in several portions with careful
condensation. Previously, a gasket made of
The group of silico-phosphate cements includes:
• Silicap (Vivadent, Liechtenstein) in capsules;
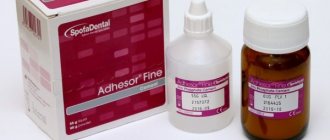
• Infantid (Spofa Dental, Czech Republic);
• Lumikolor Cement (GC, Japan);
• Posterit Cement (GC, Japan)
Great Encyclopedia of Oil and Gas
In addition to minerals, silicate cement contains a glassy mass, which is a eutectic melt from which minerals did not have time to separate due to the rapid cooling of the cement clinker. Glass consists mainly of uncrystalized ferrites, aluminates, dicalcium silicate, alkali compounds, and part of the magnesium oxide contained in the clinker. [31]
In addition to minerals, silicate cement contains a glassy mass, which is a eutectic melt from which minerals did not have time to separate due to the rapid cooling of the cement clinker. Glass consists mainly of non-crystallized ferrites, aluminates, dicalcium silicate, alkali compounds, and part of the magnesium oxide contained in the clinker. [32]
A porcelain spoon of silicate cement is poured into a test tube and distilled water is poured to half. Shake the contents of the tube vigorously for 2 - 3 minutes, then filter off the precipitate. [33]
Portland oil well cement is a type of silicate cement. This is a product consisting of a mixture of crushed materials of a given mineralized composition. The main part of Portland cement is clinker, which is obtained by firing a special mixture of limestone and clay (marl) until the components included in its composition are sintered (temperature approximately 1450 C). [34]
Portland cement cement is a type of silicate cement and consists of a mixture of crushed materials of a given mineralized composition. [35]
The maximum contraction value for most pure silicate cements is 8 - 9 ml per 100 g of cement. [36]
Compound
Any dental cement consists of a special liquid substance and powder. After mixing, the substances change from a liquid form to a solid state, similar to construction cement.
Now clinics use different types of cements, differing in their characteristics and performance indicators. The choice in favor of one composition or another is made based on the specifics of the work being performed and the requirements for the final result. To process the substance, the dentist uses spatulas and a dental mirror, which allows him to examine the base being formed from different sides.